[Javascript] Getter and Setter Abstractions
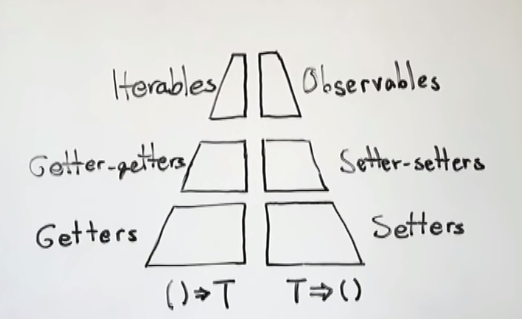
JavaScript provides primitive types and means of processing those. However, those are not enough. Real data must somehow come into the program and data must somehow leave the program, for it to become useful to us. In this talk, we will see how two abstractions are essential for data flow and to build up other abstractions, such as Iterator, Iterable, Observable, Scheduling, and others. Talk
Getter as abstractions:
const ten = ; // Abstractions
// Laziness
const getTen = () => { console.log("hi"); // hook for side effects // Implementation flexibility
return + ;
// return 2 * 5;
// return 10
}
Benefits:
- First of all: 'getTen' if you don't call the function, the calcuation inside the fucntion never run.
- You can do any side effects inside function.
- Implmentation flexibility, you can do different ways to aecieve the same effects.
Think about this code:
function add(getX, getY) {
const x = getX();
const y = getY();
return x + y;
}
'getX' and 'getY' are abstract. What we are doing now is adding two abstract number in concrete world. What if we add in abstract world?
function add(getX, getY) {
return () => { // put code into a get getter function
const x = getX();
const y = getY();
return x + y;
}
}
Now the function are complete lazy, lazyniess is a good thing, when you have some lzay you use getter can make things concrete.
function add(getX, getY) {
return () => {
const x = getX();
const y = getY();
return x + y;
}
}
const getTen = () => ;
const getY = Math.random;
const getSum = add(getTen, getY); // so far no calcuation happens
Lazy initialization and lazy iteration:
let i = ;
const array = [,,,];
function getArrayItem() {
// lazy iteration
return array[i++];
} console.log(getArrayItem());
console.log(getArrayItem());
console.log(getArrayItem());
console.log(getArrayItem());
console.log(getArrayItem()); // undefined
This is a concrete example, we call the fucntion mutiplue time and loop though the array.
And we also see that after call result as 'undefined', if we want to loop the array again from zero idnex, we have to do:
let i = ;
const array = [,,,];
function getArrayItem() {
// lazy iteration
return array[i++];
} console.log(getArrayItem());
console.log(getArrayItem());
console.log(getArrayItem());
console.log(getArrayItem()); i = ;
console.log(getArrayItem());
console.log(getArrayItem());
console.log(getArrayItem());
console.log(getArrayItem());
We call
i = ;
Of course this is not good at all, we leak the information.
The way to improve it is by using getter & lazyniess:
function getGetArrayItem() {
// lazy initialization
let i = ;
const array = [,,,];
return function() {
// lazy iteration
return array[i++];
}
}
let getArrayItem = getGetArrayItem();
console.log(getArrayItem());
console.log(getArrayItem());
console.log(getArrayItem());
console.log(getArrayItem());
getArrayItem = getGetArrayItem();
console.log(getArrayItem());
console.log(getArrayItem());
console.log(getArrayItem());
console.log(getArrayItem());
getter-getter: Abstract List:
Think about the following example:
function range(left, right) {
return () => {
// lazy initialization
let x = left;
return () => {
// lazy iteration
if (x > right) {
return undefined;
}
return x++;
}
}
}
const getGet = range( , );
const get = getGet();
console.log(get()); //
console.log(get());
console.log(get());
console.log(get());
console.log(get()); //
console.log(get()); // undefined
console.log(get());
console.log(get());
It prints out the range of nuber, which we defined, we can notice after the right limit of the number, it just print out undefined.
One way to solve the undefined problem is using for loop:
function range(left, right) {
return () => {
// lazy initialization
let x = left;
return () => {
// lazy iteration
if (x > right) {
return undefined;
}
return x++;
}
}
}
const getGet = range( , );
for(let get = getGet(), x = get(); x !== undefined; x = get()) {
console.log(x) // 10 ... 14
}
The good thing about this code is that no matter how large the range it is, the menory size is always 1. Every time you call the fucntion, it pull one value from the abstract getter function every time. It makes CPU and memory efficient.
Completion markers:
function range(left, right) {
return () => {
// lazy initialization
let x = left;
return () => {
// lazy iteration
if (x > right) {
return {done: true};
}
return {done: false, value: x++};
}
}
}
const getGet = range(, );
for(let get = getGet(), res = get(); !res.done; res = get()) {
console.log(res.value) // 10 ... 14
}
We added {done: true | false} as a complete marker.
Convert to Symbol.iterator:
function range(left, right) {
return {
[Symbol.iterator]: () => {
// lazy initialization
let x = left;
return {
next: () => {
// lazy iteration
if (x > right) {
return {done: true};
}
return {done: false, value: x++};
}
}
}
}
}
Javascript notice that when you are using [Symbol.iterator] and have 'next' inside, then it provides you a nice syntax to loop over the iterator and get the value of out it.
for(let x of range(, )) {
console.log(x) // 10 ... 14
}
We might have done this:
function range(left, right) {
return {
[Symbol.iterator]: () => {
// lazy initialization
let x = left;
return {
next: () => {
// lazy iteration
if (x > right) {
return {done: true};
}
return {done: false, value: x++};
}
}
}
}
}
for(let x of range(,)) {
if(x % === ) {
console.log(x)
}
}
We using 'if' inside 'for' loop, well it is nothing wrong, but we can do better. Because range() is abstract function, we don't need to pull all the value done to the concrete world to do the filtering, we can also do the filtering in abstract function.
const filter = pred => iterations => {
let z = [];
for (let x of iterations) {
if(pred(x)) z.push(x);
}
return z;
};
function range(left, right) {
return {
[Symbol.iterator]: () => {
// lazy initialization
let x = left;
return {
next: () => {
// lazy iteration
if (x > right) {
return {done: true};
}
return {done: false, value: x++};
}
}
}
}
}
for(let x of filter(x => x % === )(range(,))) {
console.log(x)
}
Setter-setter abstraction:
You can think of "setter-setter" is callback:
const setSetTen = (setTen) => {
setTen()
}
setSetTen(console.log) //
The benifits of doing setter-setter is
- Async
- Inversion of control
const setSetTen = (setTen) => {
setTimeout(() => {
//Async
setTen()
}, )
}
setSetTen(console.log) //
Setter-setter to Observable:

[Javascript] Getter and Setter Abstractions的更多相关文章
- JavaScript getter and setter All In One
JavaScript getter and setter All In One getter & setter JavaScript Object Accessors JavaScript A ...
- JavaScript getter和setter
对象的属性是由属性名name,值key,和其他特性(可读写性 writable,可枚举性enumerable,可配置性configurable)组成的.从ES5开发,提供了getter和setter ...
- javascript的getter和setter(转)
显然这是一个无关IE(高级IE除外)的话题,尽管如此,有兴趣的同学还是一起来认识一下ECMAScript5标准中getter和setter的实现.在一个对象中,操作其中的属性或方法,通常运用最多的就是 ...
- JavaScript中闭包实现的私有属性的getter()和setter()方法
注意: 以下的输出都在浏览器的控制台中 <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8&quo ...
- javascript中的function命名空間與模擬getter、setter
function的命名空間 在javascript中,function也可以擁有自己的命名空間例如以下這段程式碼: 12345678 function () { return 'I am A';} A ...
- javascript权威指南笔记--javascript语言核心(五)--getter和setter属性
getter和setter属性: var p = { x:1.0, y:1.0, get r(){ return Math.sqrt(this.x*this.x + this.y * this.y); ...
- javascript中的getter和setter
在ECMAScript 5中,属性值可以用一个或两个方法代替,这两个方法就是getter和setter var man = { name : 'lidg', weibo : '@lidg', get ...
- 基于 getter 和 setter 撸一个简易的MVVM
Angular 和 Vue 在对Angular的学习中,了解到AngularJS 的两个主要缺点: 对于每一次界面时间,Ajax 或者 timeout,都会进行一个脏检查,而每一次脏检查又会在内部循环 ...
- js中的访问器属性中的getter和setter函数实现数据双向绑定
嗯,之前在读js红宝书的时候,在对象那一章有介绍属性类型.第一种数据类型指的是数据属性,第二种是访问器属性.在初识vue的时候,其双向数据绑定也是基于访问器属性中的getter和setter函数原理来 ...
随机推荐
- Shredding Company(dfs)
http://poj.org/problem?id=1416 题意:将一个数分成几部分,使其分割的各个数的和最大并且小于所给的数. 凌乱了..参考的会神的代码..orz... #include < ...
- 运行Django项目指定IP和端口
默认IP和端口 python manage.py runserver 指定端口: python manage.py runserver 192.168.12.12:8080 此时会报错,我们需要修改配 ...
- java热部署
最近使用java做项目,研究了一下热部署,能够提高工作效率. 需要准备的工具: 1.安装文件http://update.zeroturnaround.com/update-site/ 2.破解 下载破 ...
- Android开放百度地图集成
1.创建应用 获取AK (我理解为Application key) 通过百度账号登录百度地图开放平台,进入API控制台 http://lbsyun.baidu.com/apiconsole/key ...
- DeltaFish 校园物资共享平台 第六次小组会议
DeltaFish 校园物资共享平台 第六次小组会议 记录人:娄雨禛 2018.6.3 任务进度(2018.5.28-2018.6.3) 前端 李鑫:商品详情界面设计.总体配色分析 刘鼎乾:卖家页面初 ...
- dubbo之多注册中心
Dubbo 支持同一服务向多注册中心同时注册,或者不同服务分别注册到不同的注册中心上去,甚至可以同时引用注册在不同注册中心上的同名服务.另外,注册中心是支持自定义扩展的. 多注册中心注册 比如:中文站 ...
- 【JSP】常用跳转方式
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/wanghuan203/article/details/8836326 (1)href超链接标记,属于客户端跳转 (2)使用javascript完成 ...
- [Advanced Algorithm] - Symmetric Difference
题目 创建一个函数,接受两个或多个数组,返回所给数组的 对等差分(symmetric difference) (△ or ⊕)数组. 给出两个集合 (如集合 A = {1, 2, 3}和集合 B = ...
- 小程序viewflex布局的对齐不对的问题
index.wxml: <view class="container"> <view class="nav-container"> &l ...
- HTML 5语义化标签
HTML 5的革新之一:语义化标签一节元素标签. 在HTML 5出来之前,我们用div来表示页面章节,但是这些div都没有实际意义.(即使我们用css样式的id和class形容这块内容的意义).这些标 ...
