C++运算符重载 模板友元 new delete ++ = +=
今天的重载是基于C++ 类模板的,如果需要非类模板的重载的朋友可以把类模板拿掉,同样可以参考,谢谢。
一、类模板中的友元重载
本人喜好类声明与类成员实现分开写的代码风格,如若您喜欢将类成员函数的实现写在类声明中,那么可以跳过该部分。
请看下面这段代码:
头文件:
#pragma once
template<typename T>
class CLA
{
T m_value;
public:
CLA(const T&);
friend CLA operator+(const CLA&, const CLA&);
};
template<typename T>
CLA<T>::CLA(const T& a)
:m_value(a)
{ } template<typename T>
CLA<T> operator+(const CLA<T>& lhs, const CLA<T>& rhs)
{
return CLA<T>(lhs.m_value + rhs.m_value);
}
源文件:(已包含上述的头文件)
int main()
{
CLA<int> a{ }, b{ }, c{ };
a + b;
return ;
}
我们去执行上述代码的时候,编译器就会报错:一个无法解析的外部指令。
当然,将实现放入声明中是可以的,但是为了维护类的书写风格,我们还是希望有一种方法可以去维护这个风格。
那么我们可以将类中友元函数的声明写成如下形式:
friend CLA operator+<T>(const CLA&, const CLA&);
原因很简单,类模板具有抽象性,而刚刚那个友元函数就是普通的函数,不具有模板的抽象性。
即使参数为CLA<T> ... 还是一样,它代表的只不过是一个参数的类型,函数本身依旧是一个普通的 函数。
而上述的形式更像一个函数模板,将函数的模板实参同步于类模板的参数,这样就可以作为类模板的友元了。
二、各种运算符重载
这部分我们将会说到 + - * / 关系运算符 赋值 自增自减 以及new delete 的重载。
首先,几个简单的 + - * / 友元以及非友元重载形式
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
using namespace std; template<typename T>
class CLA
{
T m_value;
public:
CLA():m_value(){}
CLA(const T&);
CLA(const CLA&);
//友元形式
friend CLA operator+<T>(const CLA&, const CLA&); //同类型
friend CLA operator+<T>(const CLA&, const T); //不同类型
friend CLA operator-<T>(const CLA&, const CLA&); //同类型
friend CLA operator-<T>(const CLA&, const T); //不同类型
//非友元形式
CLA operator*(const CLA&); //同类型
CLA operator*(const T); //不同类型
CLA operator/(const CLA&); //同类型
CLA operator/(const T); //不同类型
};
template<typename T>
CLA<T>::CLA(const T& a)
:m_value(a)
{ }
template<typename T>
CLA<T> operator+(const CLA<T>& lhs, const CLA<T>& rhs)
{
return CLA<T>(lhs.m_value + rhs.m_value);
}
template<typename T>
CLA<T> operator+(const CLA<T>& lhs, const T rhs)
{
return CLA<T>(lhs.m_value + rhs);
}
template<typename T>
CLA<T>::CLA(const CLA<T>& rhs)
: m_value(rhs.m_value)
{ } template<typename T>
CLA<T> operator-(const CLA<T>& lhs, const CLA<T>& rhs)
{
return CLA<T>(lhs.m_value - rhs.m_value);
}
template<typename T>
CLA<T> operator-(const CLA<T>& lhs, const T rhs)
{
return CLA<T>(lhs.m_value - rhs);
}
template<typename T>
CLA<T> CLA<T>::operator*(const CLA<T>& rhs)
{
return CLA<T>(m_value * rhs.m_value);
}
template<typename T>
CLA<T> CLA<T>::operator*(const T rhs)
{
return CLA<T>(m_value * rhs);
}
template<typename T>
CLA<T> CLA<T>::operator/(const CLA<T>& rhs)
{
if (rhs.m_value)
return CLA<T>(m_value / rhs.m_value);
else
cout << "非法除法!" << endl;
return CLA<T>();
}
template<typename T>
CLA<T> CLA<T>::operator/(const T rhs)
{
if (rhs)
return CLA<T>(lhs.m_value / rhs);
else
cout << "非法除法!" << endl;
return CLA<T>();
}
接下来重载输入输出流,而且必须为友元才行
friend istream& operator>> <T>(istream&, CLA&);
friend ostream& operator<< <T>(ostream&, const CLA&);
istream& operator>>(istream& is, CLA<T>& rhs)
{
is >> rhs.m_value;
return is;
}
template<typename T>
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const CLA<T>& rhs)
{
os << rhs.m_value;
return os;
}
输入流重载的第二个参数不能为const,因为在函数体中要对之进行修改
然后,我们用下面的代码来看一下测试结果:
int main()
{
CLA<int> a{ }, b{ }, c{ };
CLA<char> B{ 'b' };
b / a; //相同类型
cout << b*c << endl; //相同类型
cout << B + (char) << endl; //不同类型的
cout << B - (char) << endl; //不同类型的
return 0;
}
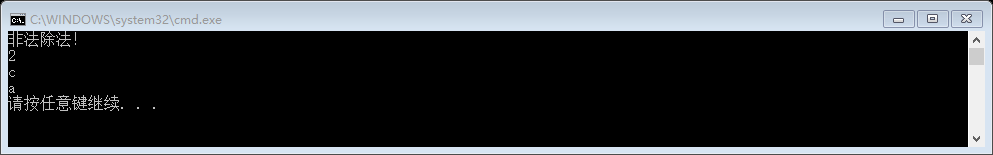
没有问题
接下类重载一些赋值运算符,= += -=
CLA& operator=(const CLA&);
CLA& operator+=(const CLA&);
CLA& operator-=(const CLA&);
CLA<T>& CLA<T>::operator=(const CLA<T>& rhs)
{
if (this != &rhs)
m_value = rhs.m_value;
return *this;
}
template<typename T>
CLA<T>& CLA<T>::operator+=(const CLA<T>& rhs)
{
m_value += rhs.m_value;
return *this;
}
template<typename T>
CLA<T>& CLA<T>::operator-=(const CLA<T>& rhs)
{
m_value -= rhs.m_value;
return *this;
}
赋值号要记得要有判同语句,运算完成后要将*this,也就是操作符的左操作数,返回。
这部分之后进行测试
++重载(--雷同)
CLA& operator++(); //前++
const CLA operator++(int); //后++
CLA<T>& CLA<T>::operator++()
{
++m_value;
return *this;
}
template<typename T>
const CLA<T> CLA<T>::operator++(int) //语法规定,在后++函数的参数中加int以作区分
{
CLA<T> item(m_value);
++m_value;
return item;
}
根据前++和后++的语法规则,前++,将本身的值+1,然后再将其本身返回。如上述操作函数体语句所示。
而后++则是将原值返回,然后本身+1,所以,我们需要借助一个局部变量来保存原值,而且返回之后是不允许改变的,代表一个常量,所以返回值拥有const属性
关系运算符也挺简单的
friend bool operator!= <T>(const CLA&, const CLA&);//友元
bool operator!=(const CLA&); //成员函数
bool operator==(const CLA&);
bool operator<(const CLA&);
bool operator>=(const CLA&);
template<typename T>
bool operator!=(const CLA<T>& lhs, const CLA<T>& rhs)
{
return lhs.m_value != rhs.m_value;
}
bool CLA<T>::operator!=(const CLA<T> & rhs)
{
return this->m_value != rhs.m_value;
}
template<typename T>
bool CLA<T>::operator==(const CLA<T>& rhs)
{
return m_value == rhs.m_value;
}
template<typename T>
bool CLA<T>::operator<(const CLA<T>& rhs)
{
return m_value < rhs.m_value;
}
template<typename T>
bool CLA<T>::operator>=(const CLA<T>& rhs)
{
return m_value > rhs.m_value;
}
我们来测试一下
int main()
{ CLA<int> a{ }, b{ }, c{ };
if (a != b)
cout << "a!=b" << endl;
a++;
if (a == b)
cout << "a==b" << endl; //c++++ //Invalid !!
CLA<int> r = ++++a;
cout << r << endl;
cout << (r += ) << endl;
cout << (r < a) << endl; return ;
}
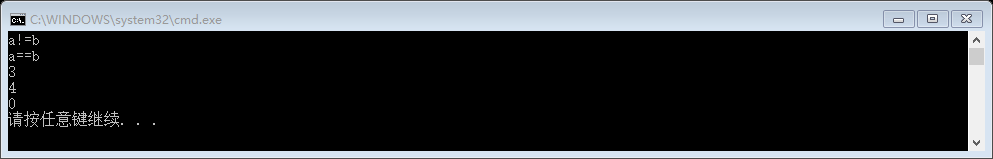
忘了写连续赋值,不过,经测试也是可以的,没问题 。
那么,现在我们来重载 new 和delete 以及new [ ] 和 delete [ ]
void* operator new(size_t size);
void* operator new[](size_t size);
void operator delete(void* p);
void operator delete[](void* p);
这里我们要用到的一个C语言库里面的类型—— size_t,它是unsigned int,sizeof运算符算出来的值就是它喽,在这里作为参数,它会自动计算大小,很方便
那,我们来看一下它的实现:
template<typename T>
void* CLA<T>::operator new(size_t size)
{
cout << size << endl;
cout << "调用了new" << endl;
return malloc(size);
}
template<typename T>
void* CLA<T>::operator new[](size_t size)
{
cout << size << endl;
cout << "调用了new[]" << endl;
return malloc(size);
}
template<typename T>
void CLA<T>::operator delete(void* p)
{
free(p);
cout << "调用了delete函数" << endl;
}
template<typename T>
void CLA<T>::operator delete[](void* p)
{
free(p);
cout << "调用了delete[]函数" << endl;
}
我们写一些对应的输出来帮助我们确定一些信息。
int main()
{
CLA<int>* w = new CLA<int>();
delete w;
CLA<int>* W = new CLA<int>[];
delete[] W;
return ;
}
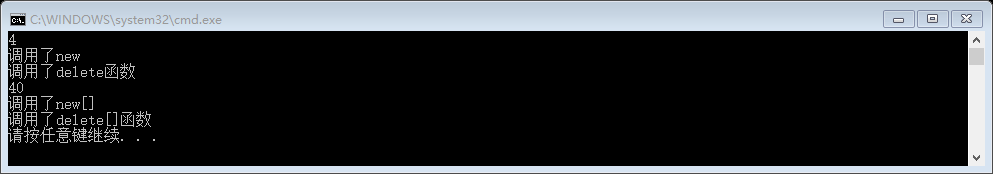
第一个10为创建的对象的值,第二个为开辟的数组的大小
一个int为4个字节,开辟10个大小的内存,为40个字节,没有问题
类模板的运算符重载就到这里了
感谢您的阅读,祝您生活愉快!
C++运算符重载 模板友元 new delete ++ = +=的更多相关文章
- c++入门之—运算符重载和友元函数
运算符重载的意义是:将常见的运算符重载出其他的含义:比如将*重载出指针的含义,将<<与cout联合使用重载出输出的含义,但需要认识到的问题是:运算符的重载:本质仍然是成员函数,即你可以认为 ...
- C++抽象编程·运算符重载与友元函数
运算符重载(Operator overloading) 从我们在几个前篇的类的层次介绍中可以知道,C++可以扩展标准运算符,使其适用于新类型.这种技术称为运算符重载. 例如,字符串类重载+运算符,使其 ...
- CPP_运算符重载及友元
运算符重载 两种重载方法1)成员函数 a + b => a.operator+(b); 一个参数 2)友元函数 a + b => operator+(a, b); 两个参数. friend ...
- C++运算符重载(友元函数方式)
我们知道,C++中的运算符重载有两种形式:①重载为类的成员函数(见C++运算符重载(成员函数方式)),②重载为类的友元函数. 当重载友元函数时,将没有隐含的参数this指针.这样,对双目运算符,友元函 ...
- 运算符重载之new与delete
关于new/delete,援引C++ Primer中的一段话: 某些应用程序对内存分配有特殊的要求,因此我们无法直接将标准的内存管理机制直接应用于这些程序.他们常常需要自定义内存分配的细节,比如使用关 ...
- 我的c++学习(8)运算符重载和友元
运算符的重载,实际是一种特殊的函数重载,必须定义一个函数,并告诉C++编译器,当遇到该运算符时就调用此函数来行使运算符功能.这个函数叫做运算符重载函数(常为类的成员函数). 方法与解释 ◆ 1.定义运 ...
- 从零开始学C++之运算符重载(三):完善String类([]、 +、 += 运算符重载)、>>和<<运算符重载
在前面文章中使用过几次String类的例子,现在多重载几个运算符,更加完善一下,并且重载流类运算符. []运算符重载 +运算符重载 +=运算符重载 <<运算符重载 >>运算符重 ...
- 完善String类([]、 +、 += 运算符重载)、>>和<<运算符重载
在前面文章中使用过几次String类的例子,现在多重载几个运算符,更加完善一下,并且重载流类运算符. []运算符重载 +运算符重载 +=运算符重载 <<运算符重载 >>运算符重 ...
- 新标准C++程序设计读书笔记_运算符重载
形式 返回值类型 operator 运算符(形参表) { …… } 运算符重载 (1)运算符重载的实质是函数重载(2)可以重载为普通函数,也可以重载为成员函数 class Complex { publ ...
随机推荐
- 基于受限玻尔兹曼机(RBM)的协同过滤
受限玻尔兹曼机是一种生成式随机神经网络(generative stochastic neural network), 详细介绍可见我的博文<受限玻尔兹曼机(RBM)简介>, 本文主要介绍R ...
- 20145234黄斐《Java程序设计》第七周
教材学习内容总结 第十二章部分 - Lambda 认识Lambda语法 Lambda去可以重复,符合DRY原则,而且Lambda表达式可读性更好,操作更简单 匿名类型最大的问题就在于其冗余的语法,la ...
- 蓝牙4.0 BLE入门
在BLE协议中有两个角色,一个是周边(Periphery),另外一个是中央(Central).一个中央可以同时连接多个周边,但一个周边某一时刻只能连接一个中央.但是不管periphery还是centr ...
- Celery异步任务队列/周期任务+ RabbitMQ + Django
一.Celery介绍和基本使用 Celery 是一个 基于python开发的分布式异步消息任务队列,通过它可以轻松的实现任务的异步处理, 如果你的业务场景中需要用到异步任务,就可以考虑使用celer ...
- php array转化为utf-8编码以便于转化为json数据
php中转化为json时,字符串或数组编码必须为utf-8编码. 在网上找到了一个方法可以比较简单的转化,在此记录: 利用var_export()和eval()方法var_export():输出或返回 ...
- Linux/Unix系统编程手册 第二章:基本概念
本章预热与后续系统编程有关的概念. 术语“操作系统”通常包含2种含义:一是指完整的软件包,包括管理计算机资源的核心组件,已经附带的标准软件:二是独指管理硬件的内核. 内核具有诸多概功能,包括: 进程管 ...
- Python使用OpenCV实现简单的人脸检测
文章目录: OpenCV安装 安装numpy 安装opencv OpenCV使用 OpenCV测试 效果图: 注意: 图片人脸检测 程序要求: 技术实现思路 注意 本文使用的环境是:Windows+P ...
- AopProxyUtils.getSingletonTarget(Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljava/lang/Object;大坑
这个问题太坑了,试了好多个版本,都是依赖冲突导致的, https://blog.csdn.net/qq_15003505/article/details/78430595 最后找到这一篇博客解决了,就 ...
- shell变量$#,$@,$0,$1,$2的含义
linux中shell变量$#,$@,$0,$1,$2的含义解释: 变量说明: $$ Shell本身的PID(ProcessID) $! Shell最后运行的后台Process的PID $? 最后运行 ...
- replication-manager 搭建
replication-manager 搭建 介绍 replication-manager 主要用于mysql主从结构的监控和主从切换. 安装 vi /etc/yum.repos.d/signal18 ...
