OpenGL学习--07--模型加载(obj)
1.tutorial07.cpp
// Include standard headers
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <vector> // Include GLEW
#include <GL/glew.h> // Include GLFW
#include <glfw3.h>
GLFWwindow* window; // Include GLM
#include <glm/glm.hpp>
#include <glm/gtc/matrix_transform.hpp>
using namespace glm; #include <common/shader.hpp>
#include <common/texture.hpp>
#include <common/controls.hpp>
#include <common/objloader.hpp> int main( void )
{
// Initialise GLFW
if( !glfwInit() )
{
fprintf( stderr, "Failed to initialize GLFW\n" );
getchar();
return -1;
} glfwWindowHint(GLFW_SAMPLES, 4);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MAJOR, 3);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MINOR, 3);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_FORWARD_COMPAT, GL_TRUE); // To make MacOS happy; should not be needed
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_PROFILE, GLFW_OPENGL_CORE_PROFILE); // Open a window and create its OpenGL context
window = glfwCreateWindow( 1024, 768, "Tutorial 07 - Model Loading", NULL, NULL);
if( window == NULL ){
fprintf( stderr, "Failed to open GLFW window. If you have an Intel GPU, they are not 3.3 compatible. Try the 2.1 version of the tutorials.\n" );
getchar();
glfwTerminate();
return -1;
}
glfwMakeContextCurrent(window); // Initialize GLEW
glewExperimental = true; // Needed for core profile
if (glewInit() != GLEW_OK) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to initialize GLEW\n");
getchar();
glfwTerminate();
return -1;
} // Ensure we can capture the escape key being pressed below
glfwSetInputMode(window, GLFW_STICKY_KEYS, GL_TRUE);
// Hide the mouse and enable unlimited mouvement
glfwSetInputMode(window, GLFW_CURSOR, GLFW_CURSOR_DISABLED); // Set the mouse at the center of the screen
glfwPollEvents();
glfwSetCursorPos(window, 1024/2, 768/2); // Dark blue background
glClearColor(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.4f, 0.0f); // Enable depth test
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);
// Accept fragment if it closer to the camera than the former one
glDepthFunc(GL_LESS); // Cull triangles which normal is not towards the camera
glEnable(GL_CULL_FACE); GLuint VertexArrayID;
glGenVertexArrays(1, &VertexArrayID);
glBindVertexArray(VertexArrayID); // Create and compile our GLSL program from the shaders
GLuint programID = LoadShaders( "TransformVertexShader.vertexshader", "TextureFragmentShader.fragmentshader" ); // Get a handle for our "MVP" uniform
GLuint MatrixID = glGetUniformLocation(programID, "MVP"); // Load the texture
GLuint Texture = loadDDS("uvmap.DDS"); // Get a handle for our "myTextureSampler" uniform
GLuint TextureID = glGetUniformLocation(programID, "myTextureSampler"); // Read our .obj file
std::vector<glm::vec3> vertices;
std::vector<glm::vec2> uvs;
std::vector<glm::vec3> normals; // Won't be used at the moment.
bool res = loadOBJ("cube.obj", vertices, uvs, normals); // Load it into a VBO GLuint vertexbuffer;
glGenBuffers(1, &vertexbuffer);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vertexbuffer);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vertices.size() * sizeof(glm::vec3), &vertices[0], GL_STATIC_DRAW); GLuint uvbuffer;
glGenBuffers(1, &uvbuffer);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, uvbuffer);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, uvs.size() * sizeof(glm::vec2), &uvs[0], GL_STATIC_DRAW); do{ // Clear the screen
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); // Use our shader
glUseProgram(programID); // Compute the MVP matrix from keyboard and mouse input
computeMatricesFromInputs();
glm::mat4 ProjectionMatrix = getProjectionMatrix();
glm::mat4 ViewMatrix = getViewMatrix();
glm::mat4 ModelMatrix = glm::mat4(1.0);
glm::mat4 MVP = ProjectionMatrix * ViewMatrix * ModelMatrix; // Send our transformation to the currently bound shader,
// in the "MVP" uniform
glUniformMatrix4fv(MatrixID, 1, GL_FALSE, &MVP[0][0]); // Bind our texture in Texture Unit 0
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, Texture);
// Set our "myTextureSampler" sampler to user Texture Unit 0
glUniform1i(TextureID, 0); // 1rst attribute buffer : vertices
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vertexbuffer);
glVertexAttribPointer(
0, // attribute
3, // size
GL_FLOAT, // type
GL_FALSE, // normalized?
0, // stride
(void*)0 // array buffer offset
); // 2nd attribute buffer : UVs
glEnableVertexAttribArray(1);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, uvbuffer);
glVertexAttribPointer(
1, // attribute
2, // size
GL_FLOAT, // type
GL_FALSE, // normalized?
0, // stride
(void*)0 // array buffer offset
); // Draw the triangle !
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, vertices.size() ); glDisableVertexAttribArray(0);
glDisableVertexAttribArray(1); // Swap buffers
glfwSwapBuffers(window);
glfwPollEvents(); } // Check if the ESC key was pressed or the window was closed
while( glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_ESCAPE ) != GLFW_PRESS &&
glfwWindowShouldClose(window) == 0 ); // Cleanup VBO and shader
glDeleteBuffers(1, &vertexbuffer);
glDeleteBuffers(1, &uvbuffer);
glDeleteProgram(programID);
glDeleteTextures(1, &TextureID);
glDeleteVertexArrays(1, &VertexArrayID); // Close OpenGL window and terminate GLFW
glfwTerminate(); return 0;
}
2. common/objloader.cpp
#include <vector>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string>
#include <cstring> #include <glm/glm.hpp> #include "objloader.hpp" // Very, VERY simple OBJ loader.
// Here is a short list of features a real function would provide :
// - Binary files. Reading a model should be just a few memcpy's away, not parsing a file at runtime. In short : OBJ is not very great.
// - Animations & bones (includes bones weights)
// - Multiple UVs
// - All attributes should be optional, not "forced"
// - More stable. Change a line in the OBJ file and it crashes.
// - More secure. Change another line and you can inject code.
// - Loading from memory, stream, etc bool loadOBJ(
const char * path,
std::vector<glm::vec3> & out_vertices,
std::vector<glm::vec2> & out_uvs,
std::vector<glm::vec3> & out_normals
){
printf("Loading OBJ file %s...\n", path); std::vector<unsigned int> vertexIndices, uvIndices, normalIndices;
std::vector<glm::vec3> temp_vertices;
std::vector<glm::vec2> temp_uvs;
std::vector<glm::vec3> temp_normals; FILE * file = fopen(path, "r");
if( file == NULL ){
printf("Impossible to open the file ! Are you in the right path ? See Tutorial 1 for details\n");
getchar();
return false;
} while( 1 ){ char lineHeader[128];
// read the first word of the line
int res = fscanf(file, "%s", lineHeader);
if (res == EOF)
break; // EOF = End Of File. Quit the loop. // else : parse lineHeader if ( strcmp( lineHeader, "v" ) == 0 ){
glm::vec3 vertex;
fscanf(file, "%f %f %f\n", &vertex.x, &vertex.y, &vertex.z );
temp_vertices.push_back(vertex);
}else if ( strcmp( lineHeader, "vt" ) == 0 ){
glm::vec2 uv;
fscanf(file, "%f %f\n", &uv.x, &uv.y );
uv.y = -uv.y; // Invert V coordinate since we will only use DDS texture, which are inverted. Remove if you want to use TGA or BMP loaders.
temp_uvs.push_back(uv);
}else if ( strcmp( lineHeader, "vn" ) == 0 ){
glm::vec3 normal;
fscanf(file, "%f %f %f\n", &normal.x, &normal.y, &normal.z );
temp_normals.push_back(normal);
}else if ( strcmp( lineHeader, "f" ) == 0 ){
std::string vertex1, vertex2, vertex3;
unsigned int vertexIndex[3], uvIndex[3], normalIndex[3];
int matches = fscanf(file, "%d/%d/%d %d/%d/%d %d/%d/%d\n", &vertexIndex[0], &uvIndex[0], &normalIndex[0], &vertexIndex[1], &uvIndex[1], &normalIndex[1], &vertexIndex[2], &uvIndex[2], &normalIndex[2] );
if (matches != 9){
printf("File can't be read by our simple parser :-( Try exporting with other options\n");
return false;
}
vertexIndices.push_back(vertexIndex[0]);
vertexIndices.push_back(vertexIndex[1]);
vertexIndices.push_back(vertexIndex[2]);
uvIndices .push_back(uvIndex[0]);
uvIndices .push_back(uvIndex[1]);
uvIndices .push_back(uvIndex[2]);
normalIndices.push_back(normalIndex[0]);
normalIndices.push_back(normalIndex[1]);
normalIndices.push_back(normalIndex[2]);
}else{
// Probably a comment, eat up the rest of the line
char stupidBuffer[1000];
fgets(stupidBuffer, 1000, file);
} } // For each vertex of each triangle
for( unsigned int i=0; i<vertexIndices.size(); i++ ){ // Get the indices of its attributes
unsigned int vertexIndex = vertexIndices[i];
unsigned int uvIndex = uvIndices[i];
unsigned int normalIndex = normalIndices[i]; // Get the attributes thanks to the index
glm::vec3 vertex = temp_vertices[ vertexIndex-1 ];
glm::vec2 uv = temp_uvs[ uvIndex-1 ];
glm::vec3 normal = temp_normals[ normalIndex-1 ]; // Put the attributes in buffers
out_vertices.push_back(vertex);
out_uvs .push_back(uv);
out_normals .push_back(normal); } return true;
} #ifdef USE_ASSIMP // don't use this #define, it's only for me (it AssImp fails to compile on your machine, at least all the other tutorials still work) // Include AssImp
#include <assimp/Importer.hpp> // C++ importer interface
#include <assimp/scene.h> // Output data structure
#include <assimp/postprocess.h> // Post processing flags bool loadAssImp(
const char * path,
std::vector<unsigned short> & indices,
std::vector<glm::vec3> & vertices,
std::vector<glm::vec2> & uvs,
std::vector<glm::vec3> & normals
){ Assimp::Importer importer; const aiScene* scene = importer.ReadFile(path, 0/*aiProcess_JoinIdenticalVertices | aiProcess_SortByPType*/);
if( !scene) {
fprintf( stderr, importer.GetErrorString());
getchar();
return false;
}
const aiMesh* mesh = scene->mMeshes[0]; // In this simple example code we always use the 1rst mesh (in OBJ files there is often only one anyway) // Fill vertices positions
vertices.reserve(mesh->mNumVertices);
for(unsigned int i=0; i<mesh->mNumVertices; i++){
aiVector3D pos = mesh->mVertices[i];
vertices.push_back(glm::vec3(pos.x, pos.y, pos.z));
} // Fill vertices texture coordinates
uvs.reserve(mesh->mNumVertices);
for(unsigned int i=0; i<mesh->mNumVertices; i++){
aiVector3D UVW = mesh->mTextureCoords[0][i]; // Assume only 1 set of UV coords; AssImp supports 8 UV sets.
uvs.push_back(glm::vec2(UVW.x, UVW.y));
} // Fill vertices normals
normals.reserve(mesh->mNumVertices);
for(unsigned int i=0; i<mesh->mNumVertices; i++){
aiVector3D n = mesh->mNormals[i];
normals.push_back(glm::vec3(n.x, n.y, n.z));
} // Fill face indices
indices.reserve(3*mesh->mNumFaces);
for (unsigned int i=0; i<mesh->mNumFaces; i++){
// Assume the model has only triangles.
indices.push_back(mesh->mFaces[i].mIndices[0]);
indices.push_back(mesh->mFaces[i].mIndices[1]);
indices.push_back(mesh->mFaces[i].mIndices[2]);
} // The "scene" pointer will be deleted automatically by "importer" } #endif
3.common/objloader.hpp
#ifndef OBJLOADER_H
#define OBJLOADER_H bool loadOBJ(
const char * path,
std::vector<glm::vec3> & out_vertices,
std::vector<glm::vec2> & out_uvs,
std::vector<glm::vec3> & out_normals
); bool loadAssImp(
const char * path,
std::vector<unsigned short> & indices,
std::vector<glm::vec3> & vertices,
std::vector<glm::vec2> & uvs,
std::vector<glm::vec3> & normals
); #endif
4. common/controls.cpp
// Include GLFW
#include <glfw3.h>
extern GLFWwindow* window; // The "extern" keyword here is to access the variable "window" declared in tutorialXXX.cpp. This is a hack to keep the tutorials simple. Please avoid this. // Include GLM
#include <glm/glm.hpp>
#include <glm/gtc/matrix_transform.hpp>
using namespace glm; #include "controls.hpp" glm::mat4 ViewMatrix;
glm::mat4 ProjectionMatrix; glm::mat4 getViewMatrix(){
return ViewMatrix;
}
glm::mat4 getProjectionMatrix(){
return ProjectionMatrix;
} // Initial position : on +Z
glm::vec3 position = glm::vec3( 0, 0, 5 );
// Initial horizontal angle : toward -Z
float horizontalAngle = 3.14f;
// Initial vertical angle : none
float verticalAngle = 0.0f;
// Initial Field of View
float initialFoV = 45.0f; float speed = 3.0f; // 3 units / second
float mouseSpeed = 0.005f; void computeMatricesFromInputs(){ // glfwGetTime is called only once, the first time this function is called
static double lastTime = glfwGetTime(); // Compute time difference between current and last frame
double currentTime = glfwGetTime();
float deltaTime = float(currentTime - lastTime); // Get mouse position
double xpos, ypos;
glfwGetCursorPos(window, &xpos, &ypos); // Reset mouse position for next frame
glfwSetCursorPos(window, 1024/2, 768/2); // Compute new orientation
horizontalAngle += mouseSpeed * float(1024/2 - xpos );
verticalAngle += mouseSpeed * float( 768/2 - ypos ); // Direction : Spherical coordinates to Cartesian coordinates conversion
glm::vec3 direction(
cos(verticalAngle) * sin(horizontalAngle),
sin(verticalAngle),
cos(verticalAngle) * cos(horizontalAngle)
); // Right vector
glm::vec3 right = glm::vec3(
sin(horizontalAngle - 3.14f/2.0f),
0,
cos(horizontalAngle - 3.14f/2.0f)
); // Up vector
glm::vec3 up = glm::cross( right, direction ); // Move forward
if (glfwGetKey( window, GLFW_KEY_UP ) == GLFW_PRESS){
position += direction * deltaTime * speed;
}
// Move backward
if (glfwGetKey( window, GLFW_KEY_DOWN ) == GLFW_PRESS){
position -= direction * deltaTime * speed;
}
// Strafe right
if (glfwGetKey( window, GLFW_KEY_RIGHT ) == GLFW_PRESS){
position += right * deltaTime * speed;
}
// Strafe left
if (glfwGetKey( window, GLFW_KEY_LEFT ) == GLFW_PRESS){
position -= right * deltaTime * speed;
} float FoV = initialFoV;// - 5 * glfwGetMouseWheel(); // Now GLFW 3 requires setting up a callback for this. It's a bit too complicated for this beginner's tutorial, so it's disabled instead. // Projection matrix : 45?Field of View, 4:3 ratio, display range : 0.1 unit <-> 100 units
ProjectionMatrix = glm::perspective(FoV, 4.0f / 3.0f, 0.1f, 100.0f);
// Camera matrix
ViewMatrix = glm::lookAt(
position, // Camera is here
position+direction, // and looks here : at the same position, plus "direction"
up // Head is up (set to 0,-1,0 to look upside-down)
); // For the next frame, the "last time" will be "now"
lastTime = currentTime;
}
5.common/controls.hpp
#ifndef CONTROLS_HPP
#define CONTROLS_HPP void computeMatricesFromInputs();
glm::mat4 getViewMatrix();
glm::mat4 getProjectionMatrix(); #endif
6. common/texture.cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h> #include <GL/glew.h> #include <glfw3.h> GLuint loadBMP_custom(const char * imagepath){ printf("Reading image %s\n", imagepath); // Data read from the header of the BMP file
unsigned char header[54];
unsigned int dataPos;
unsigned int imageSize;
unsigned int width, height;
// Actual RGB data
unsigned char * data; // Open the file
FILE * file = fopen(imagepath,"rb");
if (!file) {printf("%s could not be opened. Are you in the right directory ? Don't forget to read the FAQ !\n", imagepath); getchar(); return 0;} // Read the header, i.e. the 54 first bytes // If less than 54 bytes are read, problem
if ( fread(header, 1, 54, file)!=54 ){
printf("Not a correct BMP file\n");
return 0;
}
// A BMP files always begins with "BM"
if ( header[0]!='B' || header[1]!='M' ){
printf("Not a correct BMP file\n");
return 0;
}
// Make sure this is a 24bpp file
if ( *(int*)&(header[0x1E])!=0 ) {printf("Not a correct BMP file\n"); return 0;}
if ( *(int*)&(header[0x1C])!=24 ) {printf("Not a correct BMP file\n"); return 0;} // Read the information about the image
dataPos = *(int*)&(header[0x0A]);
imageSize = *(int*)&(header[0x22]);
width = *(int*)&(header[0x12]);
height = *(int*)&(header[0x16]); // Some BMP files are misformatted, guess missing information
if (imageSize==0) imageSize=width*height*3; // 3 : one byte for each Red, Green and Blue component
if (dataPos==0) dataPos=54; // The BMP header is done that way // Create a buffer
data = new unsigned char [imageSize]; // Read the actual data from the file into the buffer
fread(data,1,imageSize,file); // Everything is in memory now, the file wan be closed
fclose (file); // Create one OpenGL texture
GLuint textureID;
glGenTextures(1, &textureID); // "Bind" the newly created texture : all future texture functions will modify this texture
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, textureID); // Give the image to OpenGL
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0,GL_RGB, width, height, 0, GL_BGR, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, data); // OpenGL has now copied the data. Free our own version
delete [] data; // Poor filtering, or ...
//glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_NEAREST);
//glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_NEAREST); // ... nice trilinear filtering.
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR_MIPMAP_LINEAR);
glGenerateMipmap(GL_TEXTURE_2D); // Return the ID of the texture we just created
return textureID;
} // Since GLFW 3, glfwLoadTexture2D() has been removed. You have to use another texture loading library,
// or do it yourself (just like loadBMP_custom and loadDDS)
//GLuint loadTGA_glfw(const char * imagepath){
//
// // Create one OpenGL texture
// GLuint textureID;
// glGenTextures(1, &textureID);
//
// // "Bind" the newly created texture : all future texture functions will modify this texture
// glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, textureID);
//
// // Read the file, call glTexImage2D with the right parameters
// glfwLoadTexture2D(imagepath, 0);
//
// // Nice trilinear filtering.
// glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT);
// glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_REPEAT);
// glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
// glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR_MIPMAP_LINEAR);
// glGenerateMipmap(GL_TEXTURE_2D);
//
// // Return the ID of the texture we just created
// return textureID;
//} #define FOURCC_DXT1 0x31545844 // Equivalent to "DXT1" in ASCII
#define FOURCC_DXT3 0x33545844 // Equivalent to "DXT3" in ASCII
#define FOURCC_DXT5 0x35545844 // Equivalent to "DXT5" in ASCII GLuint loadDDS(const char * imagepath){ unsigned char header[124]; FILE *fp; /* try to open the file */
fp = fopen(imagepath, "rb");
if (fp == NULL){
printf("%s could not be opened. Are you in the right directory ? Don't forget to read the FAQ !\n", imagepath); getchar();
return 0;
} /* verify the type of file */
char filecode[4];
fread(filecode, 1, 4, fp);
if (strncmp(filecode, "DDS ", 4) != 0) {
fclose(fp);
return 0;
} /* get the surface desc */
fread(&header, 124, 1, fp); unsigned int height = *(unsigned int*)&(header[8 ]);
unsigned int width = *(unsigned int*)&(header[12]);
unsigned int linearSize = *(unsigned int*)&(header[16]);
unsigned int mipMapCount = *(unsigned int*)&(header[24]);
unsigned int fourCC = *(unsigned int*)&(header[80]); unsigned char * buffer;
unsigned int bufsize;
/* how big is it going to be including all mipmaps? */
bufsize = mipMapCount > 1 ? linearSize * 2 : linearSize;
buffer = (unsigned char*)malloc(bufsize * sizeof(unsigned char));
fread(buffer, 1, bufsize, fp);
/* close the file pointer */
fclose(fp); unsigned int components = (fourCC == FOURCC_DXT1) ? 3 : 4;
unsigned int format;
switch(fourCC)
{
case FOURCC_DXT1:
format = GL_COMPRESSED_RGBA_S3TC_DXT1_EXT;
break;
case FOURCC_DXT3:
format = GL_COMPRESSED_RGBA_S3TC_DXT3_EXT;
break;
case FOURCC_DXT5:
format = GL_COMPRESSED_RGBA_S3TC_DXT5_EXT;
break;
default:
free(buffer);
return 0;
} // Create one OpenGL texture
GLuint textureID;
glGenTextures(1, &textureID); // "Bind" the newly created texture : all future texture functions will modify this texture
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, textureID);
glPixelStorei(GL_UNPACK_ALIGNMENT,1); unsigned int blockSize = (format == GL_COMPRESSED_RGBA_S3TC_DXT1_EXT) ? 8 : 16;
unsigned int offset = 0; /* load the mipmaps */
for (unsigned int level = 0; level < mipMapCount && (width || height); ++level)
{
unsigned int size = ((width+3)/4)*((height+3)/4)*blockSize;
glCompressedTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, level, format, width, height,
0, size, buffer + offset); offset += size;
width /= 2;
height /= 2; // Deal with Non-Power-Of-Two textures. This code is not included in the webpage to reduce clutter.
if(width < 1) width = 1;
if(height < 1) height = 1; } free(buffer); return textureID; }
7.common/texture.hpp
#ifndef TEXTURE_HPP
#define TEXTURE_HPP // Load a .BMP file using our custom loader
GLuint loadBMP_custom(const char * imagepath); //// Since GLFW 3, glfwLoadTexture2D() has been removed. You have to use another texture loading library,
//// or do it yourself (just like loadBMP_custom and loadDDS)
//// Load a .TGA file using GLFW's own loader
//GLuint loadTGA_glfw(const char * imagepath); // Load a .DDS file using GLFW's own loader
GLuint loadDDS(const char * imagepath); #endif
8. common/shader.cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std; #include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h> #include <GL/glew.h> #include "shader.hpp" GLuint LoadShaders(const char * vertex_file_path,const char * fragment_file_path){ // Create the shaders
GLuint VertexShaderID = glCreateShader(GL_VERTEX_SHADER);
GLuint FragmentShaderID = glCreateShader(GL_FRAGMENT_SHADER); // Read the Vertex Shader code from the file
std::string VertexShaderCode;
std::ifstream VertexShaderStream(vertex_file_path, std::ios::in);
if(VertexShaderStream.is_open()){
std::string Line = "";
while(getline(VertexShaderStream, Line))
VertexShaderCode += "\n" + Line;
VertexShaderStream.close();
}else{
printf("Impossible to open %s. Are you in the right directory ? Don't forget to read the FAQ !\n", vertex_file_path);
getchar();
return 0;
} // Read the Fragment Shader code from the file
std::string FragmentShaderCode;
std::ifstream FragmentShaderStream(fragment_file_path, std::ios::in);
if(FragmentShaderStream.is_open()){
std::string Line = "";
while(getline(FragmentShaderStream, Line))
FragmentShaderCode += "\n" + Line;
FragmentShaderStream.close();
} GLint Result = GL_FALSE;
int InfoLogLength; // Compile Vertex Shader
printf("Compiling shader : %s\n", vertex_file_path);
char const * VertexSourcePointer = VertexShaderCode.c_str();
glShaderSource(VertexShaderID, 1, &VertexSourcePointer , NULL);
glCompileShader(VertexShaderID); // Check Vertex Shader
glGetShaderiv(VertexShaderID, GL_COMPILE_STATUS, &Result);
glGetShaderiv(VertexShaderID, GL_INFO_LOG_LENGTH, &InfoLogLength);
if ( InfoLogLength > 0 ){
std::vector<char> VertexShaderErrorMessage(InfoLogLength+1);
glGetShaderInfoLog(VertexShaderID, InfoLogLength, NULL, &VertexShaderErrorMessage[0]);
printf("%s\n", &VertexShaderErrorMessage[0]);
} // Compile Fragment Shader
printf("Compiling shader : %s\n", fragment_file_path);
char const * FragmentSourcePointer = FragmentShaderCode.c_str();
glShaderSource(FragmentShaderID, 1, &FragmentSourcePointer , NULL);
glCompileShader(FragmentShaderID); // Check Fragment Shader
glGetShaderiv(FragmentShaderID, GL_COMPILE_STATUS, &Result);
glGetShaderiv(FragmentShaderID, GL_INFO_LOG_LENGTH, &InfoLogLength);
if ( InfoLogLength > 0 ){
std::vector<char> FragmentShaderErrorMessage(InfoLogLength+1);
glGetShaderInfoLog(FragmentShaderID, InfoLogLength, NULL, &FragmentShaderErrorMessage[0]);
printf("%s\n", &FragmentShaderErrorMessage[0]);
} // Link the program
printf("Linking program\n");
GLuint ProgramID = glCreateProgram();
glAttachShader(ProgramID, VertexShaderID);
glAttachShader(ProgramID, FragmentShaderID);
glLinkProgram(ProgramID); // Check the program
glGetProgramiv(ProgramID, GL_LINK_STATUS, &Result);
glGetProgramiv(ProgramID, GL_INFO_LOG_LENGTH, &InfoLogLength);
if ( InfoLogLength > 0 ){
std::vector<char> ProgramErrorMessage(InfoLogLength+1);
glGetProgramInfoLog(ProgramID, InfoLogLength, NULL, &ProgramErrorMessage[0]);
printf("%s\n", &ProgramErrorMessage[0]);
} glDetachShader(ProgramID, VertexShaderID);
glDetachShader(ProgramID, FragmentShaderID); glDeleteShader(VertexShaderID);
glDeleteShader(FragmentShaderID); return ProgramID;
}
9.common/shader.hpp
#ifndef SHADER_HPP
#define SHADER_HPP GLuint LoadShaders(const char * vertex_file_path,const char * fragment_file_path); #endif
10.shaders/TransformVertexShader.vertexshader
#version 330 core // Input vertex data, different for all executions of this shader.
layout(location = 0) in vec3 vertexPosition_modelspace;
layout(location = 1) in vec2 vertexUV; // Output data ; will be interpolated for each fragment.
out vec2 UV; // Values that stay constant for the whole mesh.
uniform mat4 MVP; void main(){ // Output position of the vertex, in clip space : MVP * position
gl_Position = MVP * vec4(vertexPosition_modelspace,1); // UV of the vertex. No special space for this one.
UV = vertexUV;
}
11.shaders/TextureFragmentShader.fragmentshader
#version 330 core // Interpolated values from the vertex shaders
in vec2 UV; // Ouput data
out vec3 color; // Values that stay constant for the whole mesh.
uniform sampler2D myTextureSampler; void main(){ // Output color = color of the texture at the specified UV
color = texture( myTextureSampler, UV ).rgb;
}
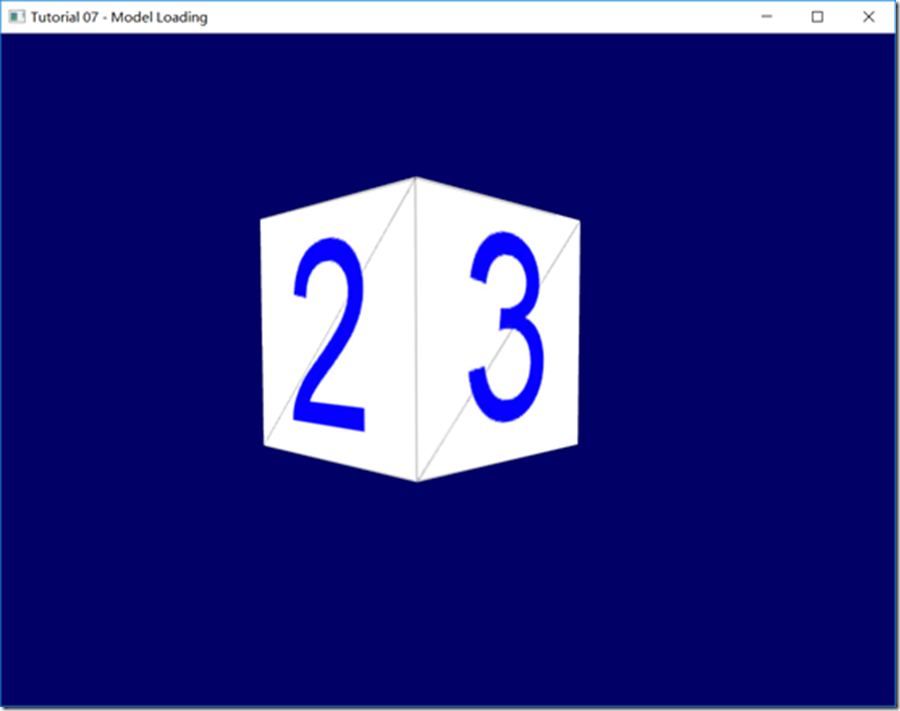
OpenGL学习--07--模型加载(obj)的更多相关文章
- 从零开始openGL——三、模型加载及鼠标交互实现
前言 在上篇文章中,介绍了基本图形的绘制.这篇博客中将介绍模型的加载.绘制以及鼠标交互的实现. 模型加载 模型存储 要实现模型的读取.绘制,我们首先需要知道模型是如何存储在文件中的. 通常模型是由网格 ...
- OpenGL OBJ模型加载.
在我们前面绘制一个屋,我们可以看到,需要每个立方体一个一个的自己来推并且还要处理位置信息.代码量大并且要时间.现在我们通过加载模型文件的方法来生成模型文件,比较流行的3D模型文件有OBJ,FBX,da ...
- openGL加载obj文件+绘制大脑表层+高亮染色
绘制大脑表层并高亮染色的工作是以openGL加载obj文件为基础的,这里是我们用到的原始程序:只能加载一个obj文件的demo. 然而,一个完整的大脑表层是由很多分区组成的,因此我们的程序需要支持两个 ...
- DirectX11 With Windows SDK--19 模型加载:obj格式的读取及使用二进制文件提升读取效率
前言 一个模型通常是由三个部分组成:网格.纹理.材质.在一开始的时候,我们是通过Geometry类来生成简单几何体的网格.但现在我们需要寻找合适的方式去表述一个复杂的网格,而且包含网格的文件类型多种多 ...
- hreeJS加载Obj资源后如何实现内存释放?
问题: 我利用ThreeJS做了一个在同一个场景下动态加载Obj的页面,具体功能是:点击按钮A:加载A模型,点击按钮B:加载B模型...现在的问题是,前面已经加载过的模型,无法实现释放,内存一直在累加 ...
- Wish3D用户必看!模型加载失败原因汇总
上传到Wish3D的模型加载不出来,作品显示页面漆黑一片,是什么原因? 很有可能是操作过程中的小失误,不妨从以下几点检查.还是不行的请加QQ群(Wish3D交流群3):635725654,@Wish3 ...
- 如何使用Three.js加载obj和mtl文件
OBJ和MTL是3D模型的几何模型文件和材料文件. 在最新的three.js版本(r78)中,以前的OBJMTLLoader类已废弃. 现在要加载OBJ和MTL文件,需要结合OBJLoader和MTL ...
- 深入java虚拟机学习 -- 类的加载机制(续)
昨晚写 深入java虚拟机学习 -- 类的加载机制 都到1点半了,由于第二天还要工作,没有将上篇文章中的demo讲解写出来,今天抽时间补上昨晚的例子讲解. 这里我先把昨天的两份代码贴过来,重新看下: ...
- 6_1 持久化模型与再次加载_探讨(1)_三种持久化模型加载方式以及import_meta_graph方式加载持久化模型会存在的变量管理命名混淆的问题
笔者提交到gitHub上的问题描述地址是:https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/issues/20140 三种持久化模型加载方式的一个小结论 加载持久化模型 ...
随机推荐
- WPF一步步开发XMPP IM客户端2:主窗体设计
UI设计方案: 在设计窗体UI之前,先要了解一些主要的接口和帮助类: 对于主窗的左侧列表,容器内的Item必须实现ILeftItem的接口,比如联系人.系统消息.群等,接口包含点击事件 public ...
- centos7搭建kafka集群-第一篇
Kafka初识 1.Kafka使用背景 在我们大量使用分布式数据库.分布式计算集群的时候,是否会遇到这样的一些问题: 我们想分析下用户行为(pageviews),以便我们设计出更好的广告位 我想对用户 ...
- CentOS7搭建FastDFS V5.11分布式文件系统-第三篇
1.测试 前面两篇博文已对FastDFS的安装和配置,做了比较详细的讲解.FastDFS的基础模块都搭好了,现在开始测试下载. 1.1 配置客户端 同样的,需要修改客户端的配置文件: /etc/fdf ...
- 一步一步教你使用 LSMW 批量处理数据
保存退出 输入完后,保存退出
- sass安装及使用
在Mac系统下,Ruby一般已内置在其中,如果您不能确认是否已安装,或者说你不知道你的Ruby使用的版本,你可以打开你的命令工具: $ ruby -v 安装sass 在大多数情况和大部分人群中,还是喜 ...
- Spring Security构建Rest服务-0102-Spring Social开发第三方登录之qq登录
图一 基于SpringSocial实现qq登录,要走一个OAuth流程,拿到服务提供商qq返回的用户信息. 由上篇介绍的可知,用户信息被封装在了Connection里,所以最终要拿到Connectio ...
- 《垃圾回收的算法与实现》——GC标记-压缩算法
基本算法 Mark-Compact与Mark-Sweep的第一阶段均为标记活跃对象,第二阶段则不同,压缩算法则是将活跃对象逻辑上移到一起. Lisp2算法 对象头中增加forwarding指针,其用法 ...
- C/C++内存管理详解
内存管理是C++最令人切齿痛恨的问题,也是C++最有争议的问题,C++高手从中获得了更好的性能,更大的自由,C++菜鸟的收获则是一遍一遍的检查代码和对C++的痛恨,但内存管理在C++中无处不在,内存泄 ...
- Linux-(kill,wc,killall,ln,cal,date)
kill命令 1.命令格式: kill [参数] [进程号] 2.命令功能: 发送指定的信号到相应进程.不指定型号将发送SIGTERM(15)终止指定进程.如果仍无法终止该程序可用“-KILL” 参数 ...
- C/C++中的常量到底存在了什么地方
一般来说,基本类型(整型.字符型等)常量会在编译阶段被编译成立即数,占的是代码段的内存.(代码段是只读的,而且不允程序员获取代码段的地址,所以在c++中,尽量不为const分配数据段的内存,但是一旦取 ...
