Spring IOC小记
1. What
IOC (Inversion Of Control,控制反转)与DI(Dependency Injecion,依赖注入)
用于对象间解耦,如在以前若对象A依赖B则需要在A中负责B的创建初始化等工作,现在有了IOC容器(如Spring的)专门负责对象的创建等生命周期的管理,A中只要声明一个B对象就可使用而不再需要负责初始化B(@Autowired等)。“反转”体现在A获得依赖对象B的过程由之前的主动行为变成了被动行为,即获得依赖对象的过程“反转了”。
IOC主要通过DI(Dependency Injection,依赖注入)实现,而DI在实现上主要是通过反射完成的,通过反射动态创建对象。
依赖注入的方式:
构造器注入
setter注入
注解注入:@Autowired、@Resource等用于引用对象的注入,@Value用于基本类型的的注入
循环依赖问题可以通过setter延迟注入解决:循环依赖使得实例化Bean时因对彼此的依赖满足不了,从而实例化失败;通过延迟注入使得注入时Bean已经创建了,从而可注入成功。
IOC与DI的区别:
IOC表示对象的创建等生命周期由特定容器如Spring容器管理。"instantiating objects (beans)"
DI表示对象所依赖的其他“合作者”(其他对象)由容器负责注入到当前对象中。可能是创建对象时注入,也可能是用到依赖的对象时注入。"wiring up of collaborators (or dependencies)"
2. Spring IOC过程分析
三部分组成:
类定义:定义普通的POJO。
元数据定义:关于所要创建的Bean的一些元数据信息。定义方式有三种:xml、java注解、java代码。
创建和关联Bean:Spring容器将根据元数据信息及POJO创建出一系列Bean,并进行管理。
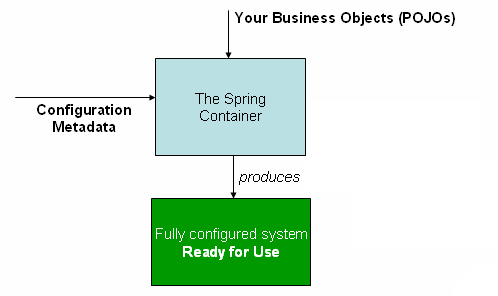
主要过程:
定位Bean元数据:可在classpath、filesystem、network等位置;Bean可通过XML(beans、bean元素等)、注解(Congifuration、Bean注解等)、Java代码三种方式定
加载Bean元数据:读入后创建成BeanDefinition
注册:根据BeanDefinition创建Bean对象并注册到IOC容器(即ApplicationContext)。注意并不是一定都立马创建实例,未被用到的会延迟到等被使用时再创建。
依赖注入:对Bean中依赖其他Bean实例的属性赋值(AbstractAutoWireCapableBeanFactory.populateBean)
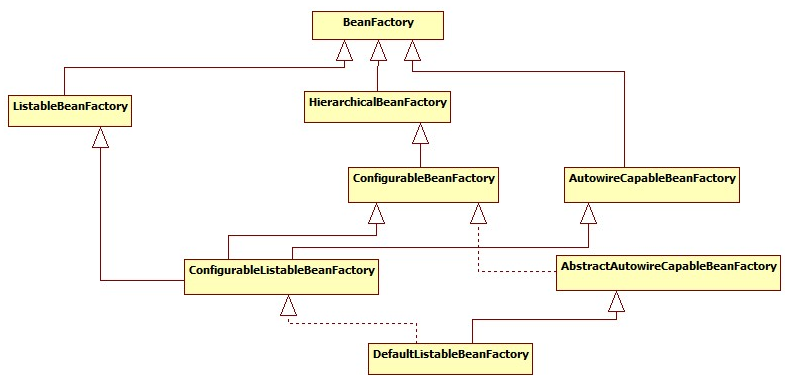
Spring IOC容器、Context、BeanFactory可以理解为同一个东西:Context和BeanFactory为对容器概念的实现,只不过前者为读容器内容,而后者可以读写容器内容。
BeanFactory体系:
Bean体系:Spring中Bean对象用BeanDefinition描述
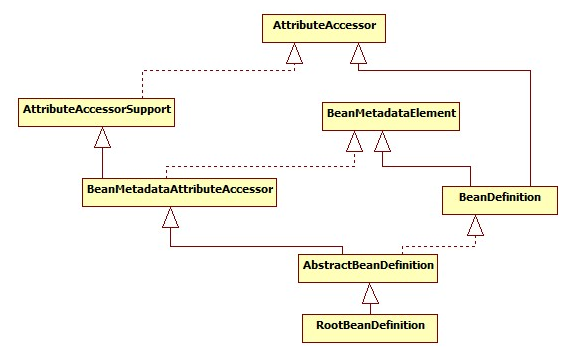
BeanDefinition包含如下信息:
A package-qualified class name: typically, the actual implementation class of the bean being defined.
Bean behavioral configuration elements, which state how the bean should behave in the container (scope, lifecycle callbacks, and so forth).
References to other beans that are needed for the bean to do its work. These references are also called collaborators or dependencies.
Other configuration settings to set in the newly created object — for example, the size limit of the pool or the number of connections to use in a bean that manages a connection pool.
BeanDefinition解析器:
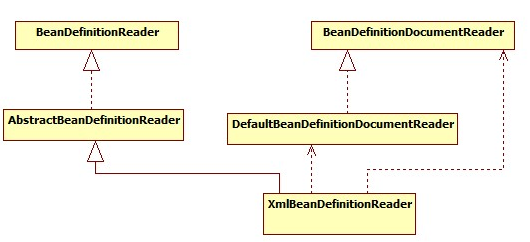
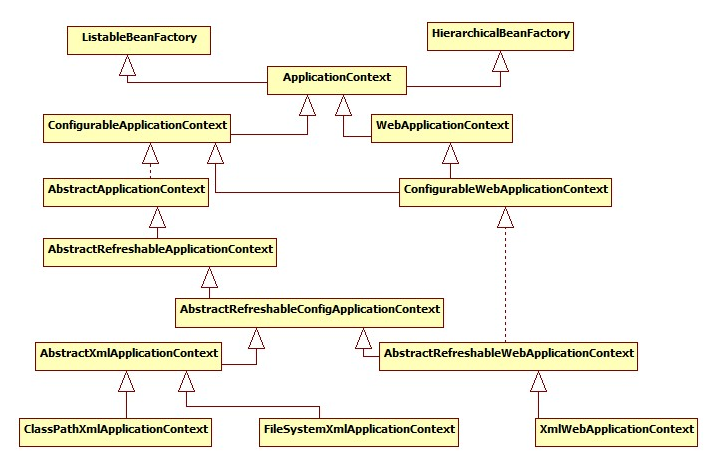
IOC容器体系:
3. Spring Core(IOC Container)doc阅记
官方文档链接:https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/current/spring-framework-reference/core.html
目录:

3.1 Customizing the Nature of a Bean
顺序:
bean Instantiate
BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization
bean Initialize
BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization
@PostConstruct
InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet
@Bean[initMethod]
bean destroy
@PreDestroy
DisposableBean.destroy
@Bean[destroyMethod]
3.1.1 LifeCycle Callback - Bean initialization/destroy callback
定义某个Bean创建完和销毁前的操作,三种方式:
在Bean内通过注解指定方法:@PostConstruct、@PreDestroy
Bean实现特定接口:InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet、DisposableBean.destroy
通过@Bean属性指定方法:initMethod、destroyMethod
The Spring container guarantees that a configured initialization callback is called immediately after a bean is supplied with all dependencies. Thus, the initialization callback is called on the raw bean reference, which means that AOP interceptors and so forth are not yet applied to the bean. A target bean is fully created first and then an AOP proxy (for example) with its interceptor chain is applied.
示例:
@Configuration
class CustomBeanLifecycle { @Bean(initMethod = "myInit", destroyMethod = "myDestroy")
public AdminModel getAdminModel() {
return new AdminModel();
} // The Spring container guarantees that a configured initialization callback is
// called immediately after a bean is supplied with all dependencies. Thus, the
// initialization callback is called on the raw bean reference, which means that
// AOP interceptors and so forth are not yet applied to the bean.
public static class AdminModel implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
//
public void myInit() {
System.err.println(this + " @Bean[initMethod]");
} public void myDestroy() {
System.err.println(this + " @Bean[destroyMethod]");
} //
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.err.println(this + " InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet");
} @Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.err.println(this + " DisposableBean.destroy");
} //
@PostConstruct
public void p1() {
System.err.println(this + " PostConstruct1");
} @PostConstruct
public void p2() {
System.err.println(this + " PostConstruct2");
} @PreDestroy
public void d1() {
System.err.println(this + " @PreDestroy1");
} @PreDestroy
public void d2() {
System.err.println(this + " @PreDestroy2");
}
}
} //启动时输出:
com.marchon.learn.store.config.CustomBeanLifecycle$AdminModel@264f18fe PostConstruct1
com.marchon.learn.store.config.CustomBeanLifecycle$AdminModel@264f18fe PostConstruct2
com.marchon.learn.store.config.CustomBeanLifecycle$AdminModel@264f18fe InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet
com.marchon.learn.store.config.CustomBeanLifecycle$AdminModel@264f18fe @Bean[initMethod] //kill 9时输出
com.marchon.learn.store.config.CustomBeanLifecycle$AdminModel@264f18fe @PreDestroy1
com.marchon.learn.store.config.CustomBeanLifecycle$AdminModel@264f18fe @PreDestroy2
com.marchon.learn.store.config.CustomBeanLifecycle$AdminModel@264f18fe DisposableBean.destroy
com.marchon.learn.store.config.CustomBeanLifecycle$AdminModel@264f18fe @Bean[destroyMethod]
Initialization and Destroy callbacks
当三种方式都存在时,为按上述所列三种方式的优先级;优先级高的initaialization callback、destroy callback先执行。如上述示例创建和销毁时的输出分别如下:
//启动时输出:
com.marchon.learn.store.config.CustomBeanLifecycle$AdminModel@264f18fe PostConstruct1
com.marchon.learn.store.config.CustomBeanLifecycle$AdminModel@264f18fe PostConstruct2
com.marchon.learn.store.config.CustomBeanLifecycle$AdminModel@264f18fe InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet
com.marchon.learn.store.config.CustomBeanLifecycle$AdminModel@264f18fe @Bean[initMethod]
//kill 9时输出
com.marchon.learn.store.config.CustomBeanLifecycle$AdminModel@264f18fe @PreDestroy1
com.marchon.learn.store.config.CustomBeanLifecycle$AdminModel@264f18fe @PreDestroy2
com.marchon.learn.store.config.CustomBeanLifecycle$AdminModel@264f18fe DisposableBean.destroy
com.marchon.learn.store.config.CustomBeanLifecycle$AdminModel@264f18fe @Bean[destroyMethod]
当三种方式指定的initaialization callback方法名有重时,重名方法只会执行一次;destroy callback同理。
3.1.2 LifeCycle Callback - ApplicationContext start/shutdown callback
详情参阅该文档。
3.1.3 LifeCycle Callback - BeanPostProcessor callback
用于指定在Bean initialization前后做的动作(已经instantiate但尚未initailize),可见其比前面介绍的callback更早被调用。
对所有Bean都有效,即在每个Bean实例化前后都会调用BeanPostProcessor中指定的方法;
scope为per-container(即application);
可以有多个BeanPostProcessor,可以给其指定优先级,将按优先级调用;
The
BeanPostProcessorinterface defines callback methods that you can implement to provide your own (or override the container’s default) instantiation logic, dependency resolution logic, and so forth.The post-processor gets a callback from the container both before container initialization methods (such as
InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet()or any declaredinitmethod) are called, and after any bean initialization callbacks.
示例:
@Bean
public MyBeanPostProcessor getMyBeanPostProcessor() {
return new MyBeanPostProcessor();
} // The BeanPostProcessor interface defines callback methods that you can
// implement to provide your own (or override the container’s default)
// instantiation logic, dependency resolution logic, and so forth.
//
public static class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor { @Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {//在每个Bean Initialization前将执行此方法
System.err.println(beanName + " BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization");
return bean;
} @Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {//在每个Bean Initialization后将执行此方法
System.err.println(beanName + " BeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization");
return bean;
}
}
应用:可借此来扩展或修改Spring容器的功能,如:
BeanValidationPostProcessor、MethodValidationPostProcessor等对Bean做验证。
@Autowired、@Value、@Resource、@Inject等注解就是由BeanPostProcessor的实现类AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor处理的。故若自定义了BeanFactory并覆盖默认实现,则这些注解可能就不生效了。CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类似。
3.1.4 LifeCycle Callback - BeanFactoryPostProcessor callback
BeanFactoryPostProcessor与BeanPostProcessor类似,区别:
BeanPostProcessor是在Bean instantiate之后在接下来的initialize前后执行
BeanFactoryPostProcessor是在Bean instantiate前后执行,此时任何Bean都尚未instantiate。
可见BeanFactoryPostProcessor比BeanPostProcessor更早被调用。此外,BeanFactoryPostProcessor中的方法只会被执行一次(在所有Bean instantiate之前)。
作用:
用于修改Bean Definition(此时所有Bean Definition都已load到BeanFactory,但都未创建出Bean)。典型应用是Spring中配置文件的解析,如PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer、PropertyResourceConfigurer、PropertyOverrideConfigurer
BeanFactoryPostProcessoroperates on the bean configuration metadata. That is, the Spring IoC container lets aBeanFactoryPostProcessorread the configuration metadata and potentially change it before the container instantiates any beans
用于往容器添加Bean(手动注册Bean),示例:
法1:通过BeanFactoryPostProcessor手动添加Bean
public static class MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
beanFactory.registerSingleton("myTestObj", new Object());//手动注册手动创建的对象到Spring容器,作为一个Bean。其他地方可以@Autowired取该Bean
System.err.println(this + " BeanFactory PostProcessor beanFactory is " + beanFactory);
}
}
法2:直接通过通过ApplicationContext注入
ApplicationContext ctx = SpringApplication.run(new Class<?>[] { StoreMain.class }, args);
System.err.println(ctx);// org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext
String customBeanName = "myBeanA";
((DefaultListableBeanFactory) ((ConfigurableApplicationContext) ctx).getBeanFactory()).registerBeanDefinition(
customBeanName, BeanDefinitionBuilder.genericBeanDefinition(Object.class).getRawBeanDefinition());// 通过Application获取BeanFactory从而注入Bean
System.err.println(ctx.getBean(customBeanName));// java.lang.Object@1e14ed59,读取到的注入的Bean
3.2 Aware Interfaces
作用:可以理解成一种设计模式,使得Bean能收到容器的通知,从而在Bean内部能够获得自身或外部的某些信息。Bean只要实现Aware接口就能收到对应的通知。
示例:ApplicationContextAware、BeanNameAware、ApplicationContextAware、MessageSourceAware等等。示例:
@Configuration
class CustomBeanLifecycle { /** 以下为Aware(通知)模式 demo */
@Bean(name = "studentZhang")
public StudentModel getStudetnModel() {
return new StudentModel();
} public static class StudentModel
implements BeanNameAware, BeanFactoryAware, ApplicationContextAware, BeanClassLoaderAware {
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name) {
System.err.println(this + " beanName is " + name);//输出为 studentZhang
} @Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
System.err.println(this + " applicationContext is " + applicationContext);
} @Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.err.println(this + " beanFactory is " + beanFactory);
} @Override
public void setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader classLoader) {
System.err.println(this + " classLoader is " + classLoader);
} }
}
Note again that using these interfaces ties your code to the Spring API and does not follow the Inversion of Control style. As a result, we recommend them for infrastructure beans that require programmatic access to the container.
原理:对于一个Bean,如果是想了某Aware接口,则Spring容器会自动调用Bean实例中该接口的方法,从这角度看实际上相当于注册了个回调函数。
缺点及解决:使用这些接口违反了“IOC”原则——相当于由Bean负责设置依赖的对象。解决:可以不使用这些接口,而是直接通过Autowired等注入,如 @Autoweired private ApplicationContext ctx;
3.3 Annotation-based Container Configuration
@Configuration、@Bean、@Import、@Scope、@Lazy、@DependsOn、@ComponentScan。@ComponentScan用于指定扫描策略如路径等。
@PostConstruct、@PreDestroy
@Autowired、@Value、@Resource、@Primary、@Qualifiers
@Component、@Controller、@RestController、@Service、@Repository等(所谓sterotype annotation),被这些修饰的类会被自动扫描为Bean,可通过@ComponentScan useDefaultFilters=false禁用默认行为
详情可参阅该文档最后一部分:https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/current/spring-framework-reference/core.html#beans-annotation
3.4 Java-based Container Configuration
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext、AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext
4. 参考资料
(推荐阅读官方文档,写得比较全面易懂)
https://blog.csdn.net/ivan820819/article/details/79744797 (什么是IOC/DI)
https://blog.csdn.net/javazejian/article/details/54561302(Spring IOC使用)
https://www.cnblogs.com/ITtangtang/p/3978349.html(Spring IOC源码解读)
https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/current/spring-framework-reference/core.html(Spring IOC官方文档)
Spring IOC小记的更多相关文章
- Spring IOC 特性有哪些,不会读不懂源码!
作者:小傅哥 博客:https://bugstack.cn 沉淀.分享.成长,让自己和他人都能有所收获! 一.前言 多线程.锁.JVM调优,都背出花啦,怎么一写代码还是乱糟糟? 为什么这些无论从书本. ...
- 【初探Spring】------Spring IOC(三):初始化过程---Resource定位
我们知道Spring的IoC起到了一个容器的作用,其中装得都是各种各样的Bean.同时在我们刚刚开始学习Spring的时候都是通过xml文件来定义Bean,Spring会某种方式加载这些xml文件,然 ...
- 【初探Spring】------Spring IOC(一)
IOC:Inversion of Control(控制反转).IOC它所体现的并不是一种技术,而是一种思想,一种将设计好的对象交给容器来管理的思想.IOC的核心思想就体现在控制.反转这两个词上面,要理 ...
- spring ioc
spring ioc是spring的核心之一,也是spring体系的基础,那么spring ioc所依赖的底层技术是什么的?反射,以前我们开发程序的时候对象之间的相互调用需要用new来实现,现在所有的 ...
- Spring IoC源码解析——Bean的创建和初始化
Spring介绍 Spring(http://spring.io/)是一个轻量级的Java 开发框架,同时也是轻量级的IoC和AOP的容器框架,主要是针对JavaBean的生命周期进行管理的轻量级容器 ...
- spring笔记6 spring IOC的中级知识
1,spring ioc的整体流程,xml配置 spring ioc初始化的流程结合上图 步骤编号 完成的工作 1 spring容器读取配置文件,解析称注册表 2 根据注册表,找到相应的bean实现类 ...
- 谈谈对Spring IOC的理解(转)
学习过Spring框架的人一定都会听过Spring的IoC(控制反转) .DI(依赖注入)这两个概念,对于初学Spring的人来说,总觉得IoC .DI这两个概念是模糊不清的,是很难理解的,今天和大家 ...
- 自己动手编写spring IOC源码
前言:对于spring IOC概念不是很了解的朋友可以阅读我上一篇博客--轻松理解spring IOC(这两篇博客也是由于我的个人原因导致现在才发布,惭愧啊).通过这篇博客的理解之后,相信大家会对sp ...
- spring ioc 源码解析
什么是ioc? 通俗的解释是:(spring)框架中,完成对象的创建和注入的容器. springIOC体系结构: spring IOC的创建是典型的工厂模式,这一系列的bean工厂如上所示. 其核心是 ...
随机推荐
- gradle 多模块Springboot项目 compile project引用其他模块的坑
本来以为子项目中compile project(':xxx'),就能引用其他模块了,因为之后idea也没在引用时候标红 然而我gradle build的时候,居然各种找不到引用模块的类 最后在stac ...
- HTML+css基础 css选择器 选择器的权重
css选择器 选择器的权重 在css中,哪个选择器的权重高,就走谁的样式 标签选择器的权重是1 class选择器的权重是10 Id选择器的权重是100 行间样式的权重是1000 带有关键字 !imp ...
- CSS改变浏览器默认滚动条样式
前言 最近总是看到某网站滚动条不是浏览器默认样式,而是自定义样式 比如我博客的滚动条,自定义滚动条样式和hover前后的效果 顿时来了兴致和有一个疑问,这是怎么实现的呢? 解决 注:经测试,目 ...
- ubuntu16.04跑通Mask R-CNN Demo
1. 下载源码: git clone https://github.com/matterport/Mask_RCNN 2. 安装依赖项(其实就是程序的运行环境) 我是用conda新建的虚拟环境. (1 ...
- php CI如何实现全站静态生成html,动态创建目录
php CI如何实现全站静态生成html,动态创建目录CodeIgniter框架生成HTML的方法 public function out_html($code) { $data['articles' ...
- 在vue里使用codemirror的两种用法
这是我自己做的一个左边点击对应的标题,右边显示相应代码的一个功能.代码显示这里用的是vue-codemirror插件. 第一种用法: 1.安装:npm install vue-codemirror - ...
- filebeat + ELK 部署篇
ELK Stack Elasticsearch:分布式搜索和分析引擎,具有高可伸缩.高可靠和易管理等特点.基于 Apache Lucene 构建,能对大容量的数据进行接近实时的存储.搜索和分析操作.通 ...
- Telegram APIs中文介绍
Telegram APIs 我们为开发者提供了两种API,Bot API (机器人API) 允许你很轻松地用Telegram的接口创建程序,Telegram API 和DLib 允许你创建定制自己的T ...
- python中杀死线程
有时候有这样的需要,在某种情况下,需要在主线程中杀死之前创建的某个线程,可以使用下面的方法,通过调用python内置API,在线程中抛出异常,使线程退出. import threading impor ...
- python 类 专有方法
__init__ : 构造函数,在生成对象时调用 __del__ : 析构函数,释放对象时使用 __repr__ : 打印,转换 __setitem__ : 按照索引赋值 __getitem__: 按 ...
