JVM学习(1)——通过实例总结Java虚拟机的运行机制(转)
俗话说,自己写的代码,6个月后也是别人的代码……复习!复习!复习!涉及到的知识点总结如下:
- JVM的历史
- JVM的运行流程简介
- JVM的组成(基于 Java 7)
- JVM调优参数:-Xmx和-Xms
- 逃逸分析(DoEscapeAnalysis )的概念——JVM栈上分配实验
- JVM中client模式(-client)和server模式(-server)的区别
- 查看GC日志的方法
- 使用idea对JVM进行参数输入
- Java栈,Java堆和方法区的交互原理
为了能让递归方法调用的次数更多一些,应该怎么做?
- 1996年 SUN JDK 1.0 Classic VM——纯解释运行,使用外挂进行JIT
- 1997年 JDK1.1 发布——AWT、内部类、JDBC、RMI、反射
- 1998年 JDK1.2 Solaris Exact VM
- JIT 解释器 混合
- Accurate Memory Management 精确内存管理,数据类型敏感
- 提升 GC 性能
- JDK1.2开始称为Java 2,导致了J2SE J2EE J2ME 的出现
- 加入Swing Collections
- 2000年 JDK 1.3 Hotspot (HotSpot 为Longview Technologies开发 被SUN收购)作为默认虚拟机发布——加入JavaSound API
- 2002年 JDK 1.4 Classic VM退出历史舞台(1996年推出的 Classic VM 到2002年出 JDK 1.4 方才退出)——Assert、正则表达式、NIO、IPV6、日志API、加密类库……
- 2004年 JDK1.5 即 JDK5 、J2SE 5 、Java 5 发布了(很重要的一版),是Java语言的发展史上的又一里程碑事件。为了表示这个版本的重要性,JDK 1.5 更名为 5.0
- 泛型
- 注解
- 装箱
- 枚举
- 可变长参数
- Foreach
- 2005年 Java SE 6、JDK 1.6、JDK 6 发布,JavaOne 大会召开,SUN 公司公开 Java SE 6 此时 Java 的各种版本已经更名以取消其中的数字“2”——J2EE更名为Java EE, J2SE更名为Java SE,J2ME更名为Java ME。
- 脚本语言支持
- JDBC 4.0
- Java编译器 API
- 2006年11月13日,SUN 公司宣布 Java 全线采纳 GNU General Public License Version 2,从而公开了 Java 的源代码,并建立OpenJDK——HotSpot 成为Sun JDK 和 OpenJDK 中所带的虚拟机。
- 2008 年 Oracle 收购 BEA——得到JRockit VM。
- 2010 年 Oracle 收购 Sun——得到Hotspot,Oracle 宣布在 JDK 8 时整合 JRockit 和 Hotspot,优势互补,在Hotspot基础上,移植JRockit优秀特性。
- 2011年 JDK 7 发布,延误项目推到JDK 8
- G1
- 动态语言增强
- 64位系统中的压缩指针
- NIO 2.0
- 2014年 JDK 8 发布
- Lambda 表达式
- 语法增强
- Java类型注解
- 2016年 JDK 9 发布——模块化
Java的两大基石:Java 语言规范和 JVM 规范
- –Groovy
- –Clojure
- –Scala
JVM的启动过程是怎样的?
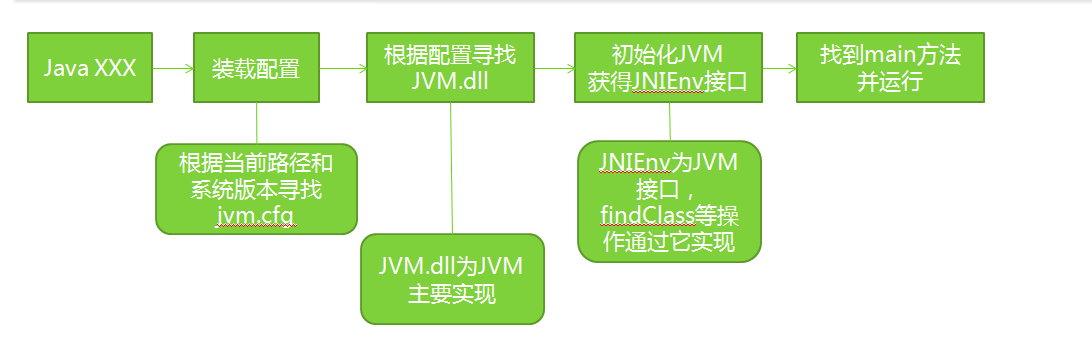
也就是说JVM是如何一步步的找到main方法的……简单总结下,Java虚拟机启动的过程:
- 首先使用 Java 命令启动JVM
- 其次进行JVM配置的装载——根据当前路径和系统的版本去寻找jvm.cfg文件,装载配置。
- 之后会根据加载的配置去寻找JVM.dll文件——JVM的主要实现文件。
- 再后,通过该文件去初始化JVM,并获得相关的接口,比如JNIEnv接口,通过该接口实现findClass操作。
- 最后,通过相关接口(JNIEnv……),找到程序里的main方法,即可进入程序……
如图:
介绍一下 JVM 的基本结构,并说出各个模块的功能?
可以结合这个网络上经典的 JVM 结构图来理解 JVM,当总结完毕,再画一个更加详细的结构图(jdk 7 规范的 JVM):

首先,要知道JVM有一个类加载系统(不然我们的类没法执行),也就是传说中的ClassLoader……Class文件(Java编译之后的)通过类加载器被加载到JVM中,而JVM的内存空间是分区的,主要有如图所示几个区:
- 方法区
- Java 堆
- Java 栈
- 本地方法栈(也就是native方法调用)
而类比物理cpu,JVM也需要一个指针来指向下一条指令的地址,就是图中的PC寄存器,紧接着是执行引擎,用来执行字节码,当然还有一个很重要的模块——GC(垃圾回收器)。下面单独总结下各个主要模块:
- PC寄存器
- 方法区
- Java堆

- Java栈
1 public class Demo {
2 public static int doStaticMethod(int i, long l, float f, Object o, byte b) {
3 return 0;
4 }
5 }
编译之后的具备变量表字节码如下:

1 LOCALVARIABLE i I L0 L1 0
2 LOCALVARIABLE l J L0 L1 1
3 LOCALVARIABLE f F L0 L1 3
4 LOCALVARIABLE o Ljava/lang/Object; L0 L1 4
5 LOCALVARIABLE b B L0 L1 5
6 MAXSTACK = 1
7 MAXLOCALS = 6

可以认为Java栈帧里的局部变量表有很多的槽位组成,每个槽最大可以容纳32位的数据类型,故方法参数里的int i 参数占据了一个槽位,而long l 参数就占据了两个槽(1和2),Object对象类型的参数其实是一个引用,o相当于一个指针,也就是32位大小。byte类型升为int,也是32位大小。如下:

相对再看看实例方法:
public int doInstanceMethod(char c, short s, boolean b) {
return 0;
}
编译之后的具备变量表字节码如下:

1 L1
2 LOCALVARIABLE this LDemo; L0 L1 0
3 LOCALVARIABLE c C L0 L1 1
4 LOCALVARIABLE s S L0 L1 2
5 LOCALVARIABLE b Z L0 L1 3
6 MAXSTACK = 1
7 MAXLOCALS = 4

实例方法的局部变量表和静态方法基本一样,唯一区别就是实例方法在Java栈帧的局部变量表里第一个槽位(0位置)存的是一个this引用(当前对象的引用),后面就和静态方法的一样了。
再看,Java栈里的方法调用组成帧栈的过程:
1 public static int doStaticMethod(int i, long l, float f, Object o, byte b) {
2 return doStaticMethod(i, l, f, o, b);
3 }
如上一个递归调用(栈的内存溢出),当类中方法(静态 or 实例)调用的时候,就会在Java栈里创建一个帧,每一次调用都会产生一个帧,并持续的压入栈顶……一直到Java栈满了,就发生了溢出!或者方法调用结束了,那么对应的Java栈帧就被移除。

注意,一个Java栈帧里除了保存局部变量表外,还会保存操作数栈,返回地址等信息。顺势我在分析下Java栈帧里的操作数栈,理解Java栈帧里的操作数栈前先知道一个结论——因为Java没有寄存器,故所有参数传递使用Java栈帧里的操作数栈。
看一个例子:
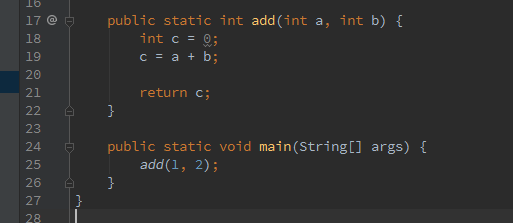
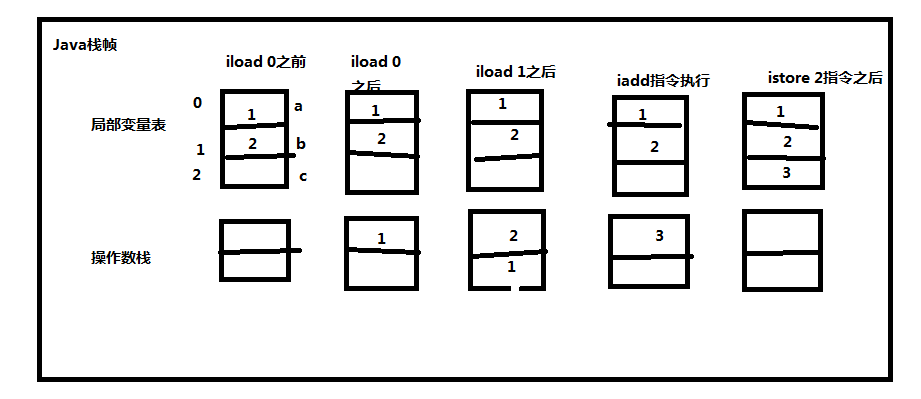
注意,对于局部变量表的槽位,按照从0开始的顺序,依次是方法参数,之后是方法内的局部变量,局部变量0就是a,1就是b,2就是c…… 编译之后的字节码为:

// access flags 0x9
public static add(II)I
L0
LINENUMBER 18 L0 // 对应源代码第18行,以此类推
ICONST_0 // 把常量0 push 到Java栈帧的操作数栈里
ISTORE 2 // 将0从操作数栈pop到局部变量表槽2里(c),完成赋值
L1
LINENUMBER 19 L1
ILOAD 0 // 将局部变量槽位0(a)push 到Java栈帧的操作数栈里
ILOAD 1 // 把局部变量槽1(b)push到操作数栈
IADD // pop出a和b两个变量,求和,把结果push到操作数栈
ISTORE 2 // 把结果从操作数栈pop到局部变量2(a+b的和给c赋值)
L2
LINENUMBER 21 L2
ILOAD 2 // 局部变量2(c)push 到操作数栈
IRETURN // 返回结果
L3
LOCALVARIABLE a I L0 L3 0
LOCALVARIABLE b I L0 L3 1
LOCALVARIABLE c I L1 L3 2
MAXSTACK = 2
MAXLOCALS = 3

发现,整个计算过程的参数传递和操作数栈密切相关!如图:
继续总结,区分Java堆上分配内存和栈上分配内存
回忆c++语言,如下代码:
public void test() {
Demo *demo = new Demo();
// ......
delete demo;
}
new出的对象是在堆中分配内存,每次使用完毕,必须记得手动回收该内存区域,使用了delete运算符,如果一旦这样的分配多了,那么很可能忘记删除,就可能会发生内存泄漏问题,一旦发生就很难发现和解决。如果是这样:
public void test() {
Demo demo;// 使用c++的引用,直接声明一个对象引用,对对象进行操作,操作完毕,不需要我们手动释放内存
}
此时就叫在栈中分配,栈上分配,函数调用完成自动清理内存,不会发生内存泄漏。而堆上分配,每次需要清理空间。
类似的原理,在Java中:

1 public class OnStackTest {
2 /**
3 * alloc方法内分配了两个字节的内存空间
4 */
5 public static void alloc(){
6 byte[] b = new byte[2];
7 b[0] = 1;
8 }
9
10 public static void main(String[] args) {
11 long b = System.currentTimeMillis();
12
13 // 分配 100000000 个 alloc 分配的内存空间
14 for(int i = 0; i < 100000000; i++){
15 alloc();
16 }
17
18 long e = System.currentTimeMillis();
19 System.out.println(e - b);
20 }
21 }

alloc方法内的b(new)分配的内存按照之前理论,我开始认为是分到了Java堆,那么如果系统的内存空间不够,是不是会发生内存泄漏?!下面做一个实验来验证。
再实验之前先总结几个JVM调优的参数和一些需要使用的概念:
- -XX:功能开关
- -Xms:minimum memory size for pile and heap
- -Xmx:maximum memory size for pile and heap
- 打印GC日志——我还需要使用JVM的一个查看GC日志的参数:-XX:+PrintGC(当GC发生时打印信息)
- JVM的server模式和client模式
- 逃逸分析
举例:对JVM堆内存进行基本的配置可以使用哪个命令参数?
-Xms 10m,表示JVM Heap(堆内存)最小尺寸10MB,最开始只有 -Xms 的参数,表示 `初始` memory size(m表示memory,s表示size),属于初始分配10m,-Xms表示的 `初始` 内存也有一个 `最小` 内存的概念(其实常用的做法中初始内存采用的也就是最小内存)。
-Xmx 10m,表示JVM Heap(堆内存)最大允许的尺寸10MB,按需分配。如果 -Xmx 不指定或者指定偏小,也许出现java.lang.OutOfMemory错误,此错误来自JVM不是Throwable的,无法用try...catch捕捉。
JVM的server模式和client模式的区别是什么?
-client,-server 两个参数可以设置JVM使用何种运行模式,client模式启动较快,但运行性能和内存管理效率不如server模式,通常用于客户端程序。相反server模式启动比client慢,但可获得更高的运行性能,常用语服务器程序。
windows上,缺省的虚拟机类型为client模式(使用java -verson命令查看),如果要使用server模式,就需要在启动虚拟机时加-server参数,以获得更高性能,对服务器端应用,推荐采用server模式,尤其是多个CPU的系统。
在Linux,Solaris上缺省采用server模式。
官方这样介绍:JVM Server模式与client模式启动,最主要的差别在于:-Server模式启动时,速度较慢,但是一旦运行起来后,性能将会有很大的提升。JVM工作在Server模式可以大大提高性能,但应用的启动会比client模式慢大概10%。当该参数不指定时,虚拟机启动检测主机是否为服务器,如果是,则以Server模式启动,否则以client模式启动,Java 5.0检测的根据是至少2个CPU和最低2GB内存。
综上,当JVM用于启动GUI界面的交互应用时适合于使用client模式,当JVM用于运行服务器后台程序时建议用Server模式。
JVM在client模式默认-Xms是1M,-Xmx是64M;
JVM在Server模式默认-Xms是128M,-Xmx是1024M。可以通过运行:java -version来查看jvm默认工作在什么模式。
什么是JVM 的逃逸分析(Escape Analysis)?
所谓逃逸分析,是JVM的一种内存分配的优化方式,一些参考书上这样写到:在编程语言的编译优化原理中,分析指针动态范围的方法称之为逃逸分析。通俗一点讲,就是当一个对象的指针被多个方法或线程引用时,我们称这个指针发生了逃逸。而用来分析这种逃逸现象的方法,就称之为逃逸分析。
我们知道java对象是在堆里分配的,在Java栈帧中,只保存了对象的指针。当对象不再使用后,需要依靠GC来遍历引用树并回收内存,如果对象数量较多,将给GC带来较大压力,也间接影响了应用的性能。减少临时对象在堆内分配的数量,无疑是最有效的优化方法,接下来,举一个场景来阐述。
假设在方法体内,声明了一个局部变量,且该变量在方法执行生命周期内未发生逃逸(在方法体内,未将引用暴露给外面)。按照JVM内存分配机制,首先会在堆里创建变量类的实例,然后将返回的对象指针压入调用栈,继续执行。这是优化前,JVM的处理方式。
逃逸分析优化 – 栈上分配,优化原理:JVM分析找到未逃逸的变量(在方法体内,未将引用暴露给外面),将变量类的实例化内存直接在栈里分配(无需进入堆),分配完成后,继续在调用栈内执行,最后线程结束,栈空间被回收,局部变量也被回收。这是优化后的处理方式,对比可以看出,主要区别在栈空间直接作为临时对象的存储介质。从而减少了临时对象在堆内的分配数量。
如下例子是发生了逃逸的局部对象变量:

1 class A {
2 public static B b;
3
4 // 给全局变量赋值,发生逃逸
5 public void globalVariablePointerEscape() {
6 b = new B();
7 }
8
9 // 方法返回值,发生逃逸
10 public B methodPointerEscape() {
11 return new B();
12 }
13
14 // 实例引用传递,发生逃逸
15 public void instancePassPointerEscape() {
16 methodPointerEscape().printClassName(this);
17 }
18 }
19
20 class B {
21 public void printClassName(A a) {
22 System.out.println(a.class.getName());
23 }

记住一个结论:启用逃逸分析的运行性能6倍于未启用逃逸分析的程序。逃逸分析是JVM层面的工作,JVM做了逃逸分析,这样没有逃逸的对象就可以被优化,从而减少堆的大小并减少GC。如果JVM没有加逃逸分析,就算自己优化了代码,也不会有效果。
JVM中启用逃逸分析需要安装jdk1.6.0_14+版本,运行java时传递jvm参数 -XX:+DoEscapeAnalysis,取消逃逸分析把+改为-。
下面回到之前的实验代码,如下:

1 public class OnStackTest {
2 /**
3 * alloc方法内分配了两个字节的内存空间
4 */
5 public static void alloc(){
6 byte[] b = new byte[2];
7 b[0] = 1;
8 }
9
10 public static void main(String[] args) {
11 long b = System.currentTimeMillis();
12
13 // 分配 100000000 个 alloc 分配的内存空间
14 for(int i = 0; i < 100000000; i++){
15 alloc();
16 }
17
18 long e = System.currentTimeMillis();
19 System.out.println(e - b);
20 }
21 }

我启用逃逸分析(可以看出b引用的对象没有逃逸),并设置在服务端模式下运行程序(性能较高),修改JVM堆内存最小(初始化)为10m,最大可用也为10m,且打印GC作为实验结果。如下在idea设置JVM参数:
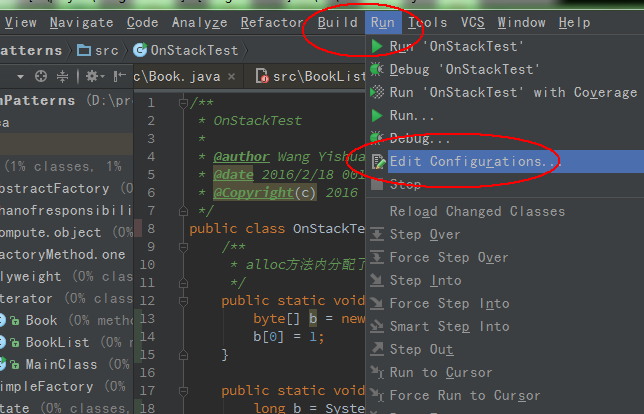
进入菜单之后,在如下地方填写JVM参数,在JVM启动时,传递给jvm
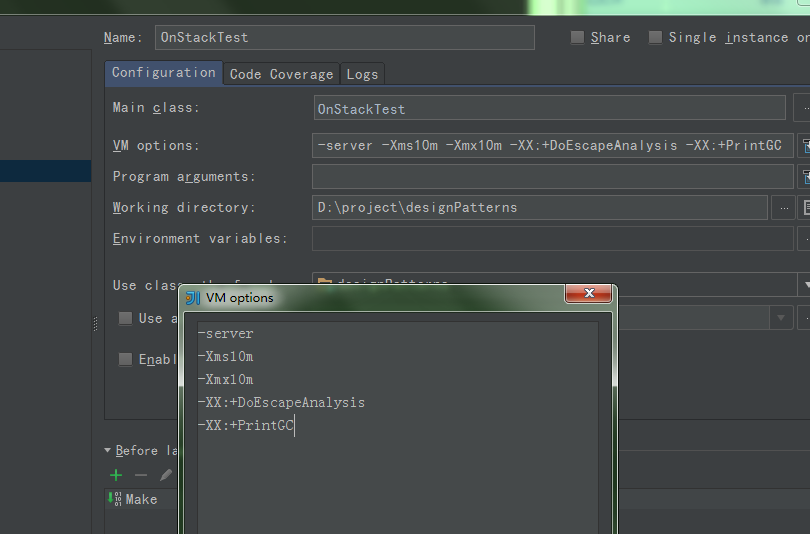
运行结果:
[GC (Allocation Failure) 2816K->727K(9984K), 0.0049897 secs]
23
Process finished with exit code 0
得知,运行了23ms,没有GC发生。作为对比,我不用任何参数配置,也不进行逃逸分析,且本机在win下,默认是客户端模式运行程序如下结果:

发现运行了1285ms!间接的证明了之前的理论是有效果的。
再进行实验,只是取消逃逸分析,其他不变,如下:
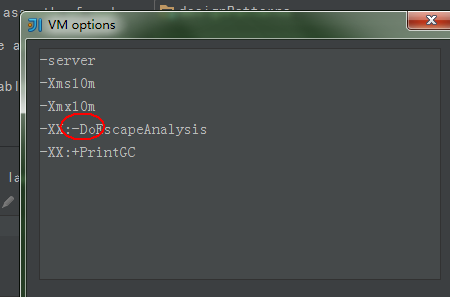
运行结果:(数据很多……)

1 [GC (Allocation Failure) 2816K->726K(9984K), 0.0331335 secs]
2 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3542K->742K(9984K), 0.0005698 secs]
3 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3558K->734K(9984K), 0.0016077 secs]
4 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3550K->798K(9984K), 0.0004902 secs]
5 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3614K->798K(9984K), 0.0003673 secs]
6 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3614K->798K(8960K), 0.0003434 secs]
7 [GC (Allocation Failure) 2590K->826K(9472K), 0.0003698 secs]
8 [GC (Allocation Failure) 2618K->834K(9472K), 0.0001611 secs]
9 [GC (Allocation Failure) 2626K->842K(9472K), 0.0002289 secs]
10 [GC (Allocation Failure) 2634K->830K(9472K), 0.0004765 secs]
11 [GC (Allocation Failure) 2622K->838K(9472K), 0.0001281 secs]
12 [GC (Allocation Failure) 2630K->842K(9472K), 0.0002448 secs]
13 [GC (Allocation Failure) 2634K->830K(9472K), 0.0004815 secs]
14 [GC (Allocation Failure) 2622K->862K(9472K), 0.0001148 secs]
15 [GC (Allocation Failure) 2654K->870K(9472K), 0.0001238 secs]
16 [GC (Allocation Failure) 2662K->846K(9472K), 0.0004488 secs]
17 [GC (Allocation Failure) 2638K->846K(9472K), 0.0001138 secs]
18 [GC (Allocation Failure) 2638K->846K(9728K), 0.0001107 secs]
19 [GC (Allocation Failure) 2894K->846K(9472K), 0.0001126 secs]
20 [GC (Allocation Failure) 2894K->846K(9728K), 0.0001760 secs]
21 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3150K->846K(9728K), 0.0002964 secs]
22 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3150K->846K(9728K), 0.0087972 secs]
23 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3150K->846K(9728K), 0.0003353 secs]
24 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3150K->846K(9728K), 0.0002302 secs]
25 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3150K->846K(9728K), 0.0001739 secs]
26 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3150K->846K(9728K), 0.0242303 secs]
27 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3150K->846K(9728K), 0.0002367 secs]
28 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3150K->846K(9728K), 0.0006995 secs]
29 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3150K->846K(9728K), 0.0004961 secs]
30 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3150K->846K(9984K), 0.0003110 secs]
31 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3406K->846K(9728K), 0.0001449 secs]
32 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3406K->846K(9984K), 0.0008167 secs]
33 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003906 secs]
34 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0013368 secs]
35 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002305 secs]
36 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001524 secs]
37 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001204 secs]
38 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002497 secs]
39 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003225 secs]
40 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001652 secs]
41 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0005384 secs]
42 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001642 secs]
43 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001477 secs]
44 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001524 secs]
45 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0307698 secs]
46 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002871 secs]
47 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002777 secs]
48 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0004491 secs]
49 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001592 secs]
50 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002547 secs]
51 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001779 secs]
52 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001729 secs]
53 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002858 secs]
54 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002815 secs]
55 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0005290 secs]
56 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001300 secs]
57 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0009583 secs]
58 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0010292 secs]
59 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0004983 secs]
60 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001568 secs]
61 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001518 secs]
62 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001496 secs]
63 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002003 secs]
64 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0012879 secs]
65 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001667 secs]
66 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001536 secs]
67 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001493 secs]
68 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003064 secs]
69 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0009474 secs]
70 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003213 secs]
71 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001571 secs]
72 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0006827 secs]
73 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002308 secs]
74 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003011 secs]
75 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002933 secs]
76 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001437 secs]
77 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001219 secs]
78 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0031484 secs]
79 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0009044 secs]
80 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0015364 secs]
81 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001592 secs]
82 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001536 secs]
83 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003567 secs]
84 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0034899 secs]
85 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0007984 secs]
86 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002221 secs]
87 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001512 secs]
88 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001900 secs]
89 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0010519 secs]
90 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0006379 secs]
91 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001596 secs]
92 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0028863 secs]
93 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0009128 secs]
94 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0018132 secs]
95 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0014058 secs]
96 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003375 secs]
97 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0242166 secs]
98 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003141 secs]
99 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0014105 secs]
100 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0036604 secs]
101 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001819 secs]
102 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003639 secs]
103 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0388277 secs]
104 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002578 secs]
105 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0422050 secs]
106 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002790 secs]
107 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0216289 secs]
108 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003148 secs]
109 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0004597 secs]
110 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002221 secs]
111 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0010382 secs]
112 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0005007 secs]
113 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002096 secs]
114 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002174 secs]
115 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001847 secs]
116 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001456 secs]
117 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0016282 secs]
118 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002905 secs]
119 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001860 secs]
120 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001527 secs]
121 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0006133 secs]
122 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0006961 secs]
123 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0116160 secs]
124 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001832 secs]
125 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0010460 secs]
126 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0019464 secs]
127 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001508 secs]
128 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001387 secs]
129 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002112 secs]
130 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0015038 secs]
131 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002211 secs]
132 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001723 secs]
133 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001568 secs]
134 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002609 secs]
135 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002124 secs]
136 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001418 secs]
137 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001459 secs]
138 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001437 secs]
139 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0026791 secs]
140 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001888 secs]
141 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001549 secs]
142 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0015837 secs]
143 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0007751 secs]
144 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001720 secs]
145 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002445 secs]
146 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0006690 secs]
147 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0022680 secs]
148 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002034 secs]
149 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003042 secs]
150 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0023358 secs]
151 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0261819 secs]
152 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0562080 secs]
153 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0038828 secs]
154 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002578 secs]
155 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001667 secs]
156 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001257 secs]
157 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0006065 secs]
158 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001816 secs]
159 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0098407 secs]
160 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0008547 secs]
161 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002445 secs]
162 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002227 secs]
163 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0312876 secs]
164 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001739 secs]
165 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002389 secs]
166 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001493 secs]
167 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001524 secs]
168 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001452 secs]
169 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0016608 secs]
170 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002037 secs]
171 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001512 secs]
172 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001605 secs]
173 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001328 secs]
174 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0004706 secs]
175 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002118 secs]
176 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001505 secs]
177 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003088 secs]
178 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001499 secs]
179 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001440 secs]
180 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001465 secs]
181 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002040 secs]
182 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0008777 secs]
183 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003480 secs]
184 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002606 secs]
185 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001546 secs]
186 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001521 secs]
187 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001568 secs]
188 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0004861 secs]
189 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001561 secs]
190 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001412 secs]
191 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002622 secs]
192 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002087 secs]
193 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0006870 secs]
194 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001602 secs]
195 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001844 secs]
196 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002348 secs]
197 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001477 secs]
198 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001480 secs]
199 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0006174 secs]
200 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001555 secs]
201 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0020238 secs]
202 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0004790 secs]
203 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001577 secs]
204 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001515 secs]
205 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0008786 secs]
206 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0011626 secs]
207 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0004457 secs]
208 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0023560 secs]
209 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001683 secs]
210 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001540 secs]
211 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003378 secs]
212 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001480 secs]
213 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001456 secs]
214 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001745 secs]
215 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001443 secs]
216 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001409 secs]
217 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0004668 secs]
218 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0008223 secs]
219 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0004224 secs]
220 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001617 secs]
221 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001782 secs]
222 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003191 secs]
223 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002367 secs]
224 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001452 secs]
225 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001409 secs]
226 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001462 secs]
227 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002852 secs]
228 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001496 secs]
229 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001437 secs]
230 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0008024 secs]
231 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0007720 secs]
232 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001608 secs]
233 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001515 secs]
234 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001434 secs]
235 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001502 secs]
236 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001428 secs]
237 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0004314 secs]
238 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003427 secs]
239 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001418 secs]
240 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001449 secs]
241 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001216 secs]
242 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001449 secs]
243 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0025109 secs]
244 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001704 secs]
245 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001897 secs]
246 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001611 secs]
247 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001527 secs]
248 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001480 secs]
249 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0037686 secs]
250 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001624 secs]
251 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0005269 secs]
252 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002270 secs]
253 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0009918 secs]
254 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0006550 secs]
255 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003197 secs]
256 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003328 secs]
257 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002861 secs]
258 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0414909 secs]
259 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001748 secs]
260 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001617 secs]
261 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001244 secs]
262 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002342 secs]
263 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002308 secs]
264 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001449 secs]
265 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001505 secs]
266 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001530 secs]
267 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001449 secs]
268 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002606 secs]
269 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001540 secs]
270 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001801 secs]
271 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002292 secs]
272 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001633 secs]
273 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001521 secs]
274 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001496 secs]
275 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0007707 secs]
276 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003502 secs]
277 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001596 secs]
278 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001490 secs]
279 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0007953 secs]
280 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001611 secs]
281 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0021666 secs]
282 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0006077 secs]
283 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002563 secs]
284 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0026175 secs]
285 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001683 secs]
286 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001555 secs]
287 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0010453 secs]
288 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003885 secs]
289 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0039067 secs]
290 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0014680 secs]
291 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0022773 secs]
292 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001661 secs]
293 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003710 secs]
294 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0007968 secs]
295 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0080853 secs]
296 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0025979 secs]
297 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002874 secs]
298 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0540315 secs]
299 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001829 secs]
300 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0019299 secs]
301 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0007213 secs]
302 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0078775 secs]
303 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0250296 secs]
304 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001785 secs]
305 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001680 secs]
306 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001639 secs]
307 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001642 secs]
308 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001611 secs]
309 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001210 secs]
310 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001543 secs]
311 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001434 secs]
312 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001639 secs]
313 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002606 secs]
314 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001465 secs]
315 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001291 secs]
316 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001151 secs]
317 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002186 secs]
318 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0006012 secs]
319 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0007088 secs]
320 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0004672 secs]
321 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0005147 secs]
322 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002700 secs]
323 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003088 secs]
324 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003070 secs]
325 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0005085 secs]
326 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0052988 secs]
327 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0068434 secs]
328 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0176566 secs]
329 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003431 secs]
330 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0307346 secs]
331 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0137013 secs]
332 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0027712 secs]
333 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003462 secs]
334 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0004687 secs]
335 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0010341 secs]
336 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002821 secs]
337 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0006945 secs]
338 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002513 secs]
339 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0057389 secs]
340 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0011175 secs]
341 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001717 secs]
342 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001536 secs]
343 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0145414 secs]
344 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0160925 secs]
345 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0009216 secs]
346 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0159631 secs]
347 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0290430 secs]
348 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001788 secs]
349 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001707 secs]
350 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003807 secs]
351 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001767 secs]
352 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0006457 secs]
353 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0005219 secs]
354 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003151 secs]
355 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002469 secs]
356 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002964 secs]
357 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003092 secs]
358 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002342 secs]
359 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002255 secs]
360 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001795 secs]
361 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002246 secs]
362 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002840 secs]
363 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001692 secs]
364 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0005001 secs]
365 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001266 secs]
366 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0007371 secs]
367 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002656 secs]
368 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001250 secs]
369 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001465 secs]
370 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001471 secs]
371 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001306 secs]
372 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001340 secs]
373 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002625 secs]
374 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0033540 secs]
375 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001652 secs]
376 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001586 secs]
377 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001266 secs]
378 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0022947 secs]
379 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0024166 secs]
380 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001583 secs]
381 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001515 secs]
382 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001449 secs]
383 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003387 secs]
384 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001925 secs]
385 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002429 secs]
386 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001480 secs]
387 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001459 secs]
388 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0006382 secs]
389 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002899 secs]
390 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001543 secs]
391 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001608 secs]
392 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002644 secs]
393 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003546 secs]
394 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002445 secs]
395 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001490 secs]
396 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001449 secs]
397 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002351 secs]
398 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001574 secs]
399 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002445 secs]
400 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001431 secs]
401 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001462 secs]
402 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001477 secs]
403 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002933 secs]
404 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002743 secs]
405 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001602 secs]
406 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001521 secs]
407 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0005987 secs]
408 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002115 secs]
409 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0057542 secs]
410 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003654 secs]
411 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0006186 secs]
412 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0004364 secs]
413 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0026546 secs]
414 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0298837 secs]
415 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001987 secs]
416 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003437 secs]
417 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001527 secs]
418 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001639 secs]
419 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001518 secs]
420 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002911 secs]
421 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002130 secs]
422 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0005589 secs]
423 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0006149 secs]
424 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0033363 secs]
425 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002908 secs]
426 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002283 secs]
427 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0031547 secs]
428 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0176105 secs]
429 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0103212 secs]
430 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0004591 secs]
431 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0004448 secs]
432 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0068689 secs]
433 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0006339 secs]
434 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001767 secs]
435 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001558 secs]
436 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001561 secs]
437 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0034837 secs]
438 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003017 secs]
439 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002578 secs]
440 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001627 secs]
441 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0005045 secs]
442 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001586 secs]
443 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001449 secs]
444 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003368 secs]
445 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002507 secs]
446 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001306 secs]
447 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001997 secs]
448 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003555 secs]
449 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001767 secs]
450 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001518 secs]
451 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001683 secs]
452 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001614 secs]
453 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0005026 secs]
454 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001720 secs]
455 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001505 secs]
456 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001614 secs]
457 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001770 secs]
458 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001176 secs]
459 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001216 secs]
460 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002924 secs]
461 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001574 secs]
462 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001378 secs]
463 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001546 secs]
464 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001490 secs]
465 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001409 secs]
466 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0030663 secs]
467 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002572 secs]
468 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0253565 secs]
469 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0034722 secs]
470 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0007384 secs]
471 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001701 secs]
472 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002376 secs]
473 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0010111 secs]
474 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001555 secs]
475 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0004874 secs]
476 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0011909 secs]
477 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0011402 secs]
478 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0006597 secs]
479 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0004606 secs]
480 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0142543 secs]
481 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0104319 secs]
482 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0101361 secs]
483 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003993 secs]
484 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0005073 secs]
485 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003689 secs]
486 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0015545 secs]
487 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002068 secs]
488 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0008438 secs]
489 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002426 secs]
490 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002264 secs]
491 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001512 secs]
492 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001166 secs]
493 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002099 secs]
494 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001045 secs]
495 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0007010 secs]
496 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0006068 secs]
497 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001608 secs]
498 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001306 secs]
499 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0009097 secs]
500 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0005219 secs]
501 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0004196 secs]
502 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0007172 secs]
503 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0263185 secs]
504 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0007054 secs]
505 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001860 secs]
506 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001173 secs]
507 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002989 secs]
508 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001166 secs]
509 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001151 secs]
510 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001686 secs]
511 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001070 secs]
512 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001169 secs]
513 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003023 secs]
514 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002090 secs]
515 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003350 secs]
516 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0005281 secs]
517 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003297 secs]
518 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0008161 secs]
519 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001642 secs]
520 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003029 secs]
521 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002320 secs]
522 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001117 secs]
523 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001157 secs]
524 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0081105 secs]
525 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003459 secs]
526 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001760 secs]
527 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001449 secs]
528 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001337 secs]
529 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0129219 secs]
530 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001564 secs]
531 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001452 secs]
532 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001459 secs]
533 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001788 secs]
534 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001145 secs]
535 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001132 secs]
536 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001135 secs]
537 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002665 secs]
538 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001415 secs]
539 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001151 secs]
540 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001400 secs]
541 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001064 secs]
542 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001281 secs]
543 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001045 secs]
544 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0003275 secs]
545 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0009041 secs]
546 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001555 secs]
547 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001092 secs]
548 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001104 secs]
549 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001247 secs]
550 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001120 secs]
551 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001126 secs]
552 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001110 secs]
553 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001095 secs]
554 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001123 secs]
555 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001110 secs]
556 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001847 secs]
557 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001107 secs]
558 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001079 secs]
559 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001496 secs]
560 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001132 secs]
561 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0001107 secs]
562 [GC (Allocation Failure) 3662K->846K(9984K), 0.0002034 secs]
563 1755
564
565 Process finished with exit code 0

果不其然,不仅运行速度慢了很多,且可以推断出变量b指向的对象在Java堆里分配内存了。就如之前理论,逃逸分析是JVM层面的工作,如果JVM不进行逃逸分析,那么即使优化了代码,也是在堆中分配内存(因为发生了大量的GC日志记录~!),而之前的进行逃逸分析运行不仅速度很快,且没有任何GC记录,说明逃逸分析之后b是在Java栈帧里分配的内存,方法调用完毕自动清理内存,不会发生内存泄漏,也不GC!
对Java栈——栈上分配优化的小结:
- 必须是小对象(一般几十个bytes),且必须是在没有逃逸的情况下,如果JVM使用了逃逸分析优化,则该小对象可以直接分配在栈上,因为栈的空间不大(一般也就到1m封顶了),更没有堆大。
- 直接分配在栈上,方法调用完毕,Java栈帧就立即被移除,故内存可以自动回收,减轻GC压力。
- 大对象(栈的空间不允许)或者逃逸的对象无法在栈上分配(即使启动了JVM的逃逸分析优化,且因为Java栈是线程私有的,不共享,局部对象变量被其他线程或者方法引用了肯定不能在栈分配内存)
总结到这里不禁有一个疑问,为什么方法调用(包括其他编程语言的函数调用等)需要使用栈?
占坑,留在下一个单元进行总结。
对JVM基本结构的小结,再次回忆上文提到的JVM的基本结构:

现在单独拿出红色框里的方法区,Java堆,Java栈区,来看看三者之间如何交互。
且前面也说了Java堆是全局共享的,几乎所有的对象都保存到了Java堆,堆是发生GC的主要区域。
而Java栈是线程私有的,且每个线程启动都会创建一个Java栈,栈内还有帧,Java栈中的每个帧都保存一个方法调用的局部变量、操作数栈、指向常量池的指针等,且每一次方法调用都会创建一个帧,并压栈。
还有方法区,它是保存JVM装载的类的信息的,比如类型的常量池、类中的字段,类中的方法信息、方法的字节码(bytecode)等,注意这不是绝对的!比如:JDK 6 时,String等字符串常量的信息是置于方法区中的,但是到了JDK 7 时,已经移动到了Java堆。
所以,方法区也好,Java堆也罢,到底保存了什么,其实没有具体定论,要结合不同的JVM版本来分析,因为技术是发展的!不过一般认为,方法区就是保存了JVM装载的类的信息。
下面再看一个(网上找的)更加细致的JVM内存结构图(以后会经常看到):
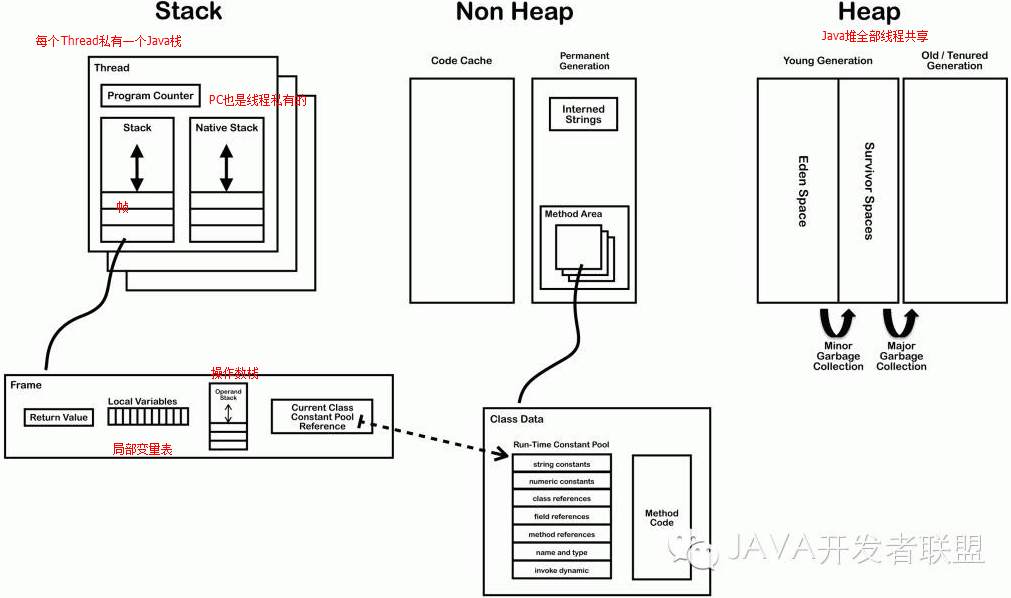
进阶:实例说明JVM的栈、堆、和方法区的交互
看上图有些复杂,下面用一个例子(来源于互联网)帮助总结他们三者之间的交互原理。

1 public class Sample {
2 private String name;
3
4 public Sample(String name) {
5 this.name = name;
6 }
7
8 public void printName() {
9 System.out.println(this.name);
10 }
11 }
12
13 public class AppMain {
14
15 public static void main(String[] args) {
16 Sample test1 = new Sample("测试1");
17 Sample test2 = new Sample("测试2");
18
19 test1.printName();
20 test2.printName();
21 }
22 }

众所周知,通常Java程序都要从main方法进入,故一般情况下Java程序都有一个main方法,而它本身也是一个线程(主线程),自然就对应一个Java栈,main方法也就对应一个Java的栈帧了。而根据之前JVM结构的分析,我们知道类会被JVM装载,那么JVM装载的类的信息放在了方法区里(包括字段信息,方法本身的字节码等,当然main方法也不例外),而方法体内的局部变量(包括形参),本例是对象的引用,统一放到Java栈帧里。而对象本身存放到了Java堆。如下注释:

1 /**
2 * AppMain
3 *
4 * 程序运行时,JVM把AppMain这个类的信息(装载的)全部放入方法区保存
5 *
6 * @author Wang Yishuai.
7 * @date 2016/2/19 0019.
8 * @Copyright(c) 2016 Wang Yishuai,USTC,SSE.
9 */
10 public class AppMain {
11
12 // main方法本身的字节码也放入方法区保存
13 public static void main(String[] args) {
14 // test引用保存到Java栈帧,类Sample的对象存入Java堆
15 Sample test1 = new Sample("测试 1");
16 Sample test2 = new Sample("测试 2");
17
18 test1.printName();
19 test2.printName();
20 }
21 }
22
23 public class Sample {
24 /**
25 * 类的字段信息也存入了方法区
26 */
27 private String name;
28
29 /**
30 * main方法里new本类实例之后,Sample构造器作为一个方法,它的形参name,name引用存入栈,name引用的字符串对象放入堆
31 *
32 * @param name String
33 */
34 public Sample(String name) {
35 this.name = name;
36 }
37
38 /**
39 * printName 放入了方法区保存
40 */
41 public void printName() {
42 System.out.println(this.name);
43 }
44 }

画成图就是这样:类中方法本身(字节码)存放在方法区,Java栈里的对象引用指向了Java堆里的对象,之后堆里的对象需要的类的信息要去方法区里(非堆区)读取。
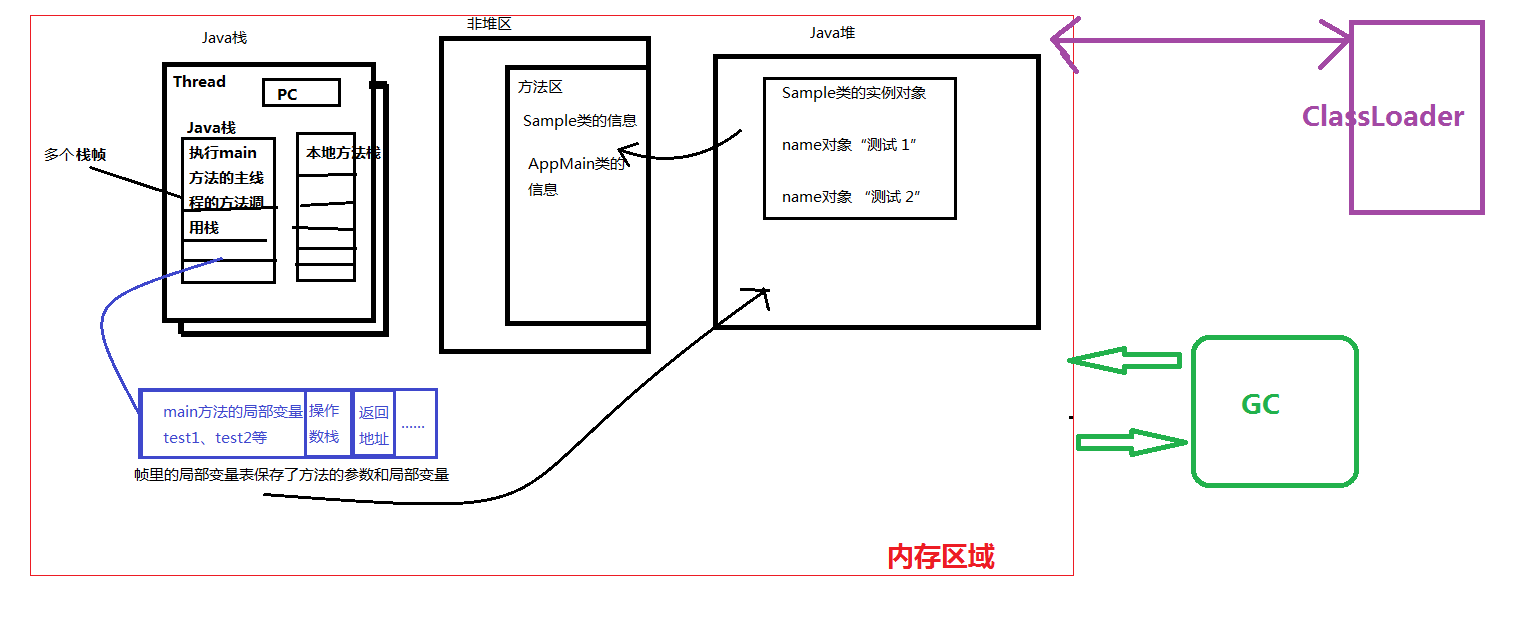
问题:为了能让递归方法调用的次数更多一些,应该怎么做呢?
众所周知,递归是指函数直接或间接地调用自己,传统地递归过程就是函数调用,涉及返回地址、函数参数、寄存器值等压栈(在x86-64上通常用寄存器保存函数参数),这样做的缺点有二:
- 效率低,占内存
- 如果递归链过长,可能会statck over flow(栈区的空间通常是OS设定好的,通常只有几M)

1 int fib_1(int n) {
2 int a = 1;
3 int b = 1 ;
4
5 for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
6 int a_ = b;
7 int b_ = a + b;
8 a = a_ ;
9 b = b_ ;
10 }
11
12 return a
13 }

使用递归实现:

1 int fib_2(int n) {
2 if (n <= 1) {
3 return 1 ;
4 } else {
5 return fib_2(n - 1) + fib_2(n - 2) ;
6 }
7 }

后来人们发现,对于该递归而言,一些压栈操作并无必要,递归中的子问题规模几乎不变,每次只减去了1或者2。如果画一个递归树,会发现很多相同的子树!!!说明该实现浪费了很多内存和时间,当解决Fn-1问题时,计算了Fn-2和Fn-3,解决Fn问题时,计算了Fn-1和Fn-2,实际上我只需要计算一次Fn-2就ok了。优化——使用自底向上的算法:线性递归

1 int fib_3(int n) {
2 int fib_rec(int a , int b , int n) {
3 if (n <= 1) {
4 return 1 ;
5 } else {
6 return a + fib_rec(b , a + b , n - 1)
7 }
8 }
9
10 return fib_rec(1 , 1 , n)
11 }

依次计算Fn,F0、F1、F2、F3……Fn,花费线性时间,因为我的输入是线性的。不过还不是更好的,线性递归每次调用时,针对上一次调用的结果,它不进行收集(保存),只能依靠顺次的展开,这样也很消耗内存。下面引出一个概念——尾递归:尾递归,它比线性递归多一个参数,这个参数是上一次调用函数得到的结果,尾递归每次调用都在收集结果,避免了线性递归不收集结果只能依次展开,消耗内存的坏处。如下:

1 int fib_4(int n) {
2 int fib_iter(int a , int b , int n) {
3 if (n == 0) {
4 return a;
5 } else {
6 return fib_iter(b , a + b , n - 1) ;
7 }
8 }
9
10 return fib_iter(1 , 1 , n) ;
11 }

尾递归的情况是下层计算结果对上层“无用”(上一层运算已经做完,不依赖后续的递归),为了效率,直接将下一层需要的空间覆盖在上一层上,尾递归和一般的递归不同在对内存的占用,普通递归创建stack累积而后计算收缩,尾递归只会占用恒量的内存(和迭代一样)。通俗的说,尾递归是把变化的参数传递给递归函数的变量了。
怎么写尾递归?形式上只要最后一个return语句是单纯函数就可以。如:
return tailrec(x+1);
而
return tailrec(x+1) + x;
则不可以。因为无法更新tailrec()函数内的实际变量,只是新建一个栈。
function story() {
从前有座山,山上有座庙,庙里有个老和尚,一天老和尚对小和尚讲故事:story(),小和尚听了,找了块豆腐撞死了 // 非尾递归,下一个函数结束以后此函数还有后续,所以必须保存本身的环境以供处理返回值。
}
尾递归:
function story() {
从前有座山,山上有座庙,庙里有个老和尚,一天老和尚对小和尚讲故事:story() // 尾递归,进入下一个函数不再需要上一个函数的环境了,得出结果以后直接返回。
}
综上,可以尽可能高效的利用栈空间,增加递归调研数。
http://www.cnblogs.com/kubixuesheng/p/5199200.html
JVM学习(1)——通过实例总结Java虚拟机的运行机制(转)的更多相关文章
- JVM学习001通过实例总结Java虚拟机的运行机制
JVM学习(1)——通过实例总结Java虚拟机的运行机制-转载http://www.cnblogs.com/kubixuesheng/p/5199200.html 文章转载自:http://www.c ...
- JVM学习(1)——通过实例总结Java虚拟机的运行机制
俗话说,自己写的代码,6个月后也是别人的代码……复习!复习!复习!涉及到的知识点总结如下: JVM的历史 JVM的运行流程简介 JVM的组成(基于 Java 7) JVM调优参数:-Xmx和-Xms ...
- JVM学习(1)——通过实例总结Java虚拟机的运行机制-转载http://www.cnblogs.com/kubixuesheng/p/5199200.html
JVM系类的文章全部转载自:http://www.cnblogs.com/kubixuesheng/p/5199200.html 特别在此声明.那位博主写的真的很好 ,感谢!! 俗话说,自己写的代码, ...
- Java虚拟机及运行时数据区
1.Java虚拟机的定义 Java虚拟机(Java Virtual Machine),简称JVM.当我们说起Java虚拟机时,可能指的是如下三种不同的东西: 抽象的虚拟机规范 规范的具体实现 一个运行 ...
- Java虚拟机_运行时数据区
Java虚拟机在执行Java程序的过程中会把它所管理的内存划分为若干个不同的数据区域. 这些区域都有各自的用途.各自的创建和销毁的时间,有的区域随着虚拟机进程的启动而存在,有些区域则是依赖用户线程启动 ...
- 【Java虚拟机】运行时数据区
Java在执行Java程序的过程中会把它所管理的内存划分为若干个不同的数据区域.这些区域都有各自的用途.创建和销毁的时间,有一些是随虚拟机的启动而创建,随虚拟机的退出而销毁,有些则是与线程一一对应,随 ...
- Java虚拟机如何运行Java字节码
一.Java的class文件的内容 1.首先编写一个简单的代码 public class StringDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { S ...
- 《Java疯狂讲义》(第3版)学习笔记 2 - Java语言的运行机制
内容 1.高级语言的运行机制 2.Java 语言的运行机制 1.高级语言的运行机制 高级语言主要分为编译型语言和解释型语言两类. 编译型语言是指使用专门的编译器.针对特定平台(操作系统)将高级语言源代 ...
- java虚拟机规范-运行时栈帧
前言 java虚拟机是java跨平台的基石,本文的描述以jdk7.0为准,其他版本可能会有一些微调. 引用 java虚拟机规范 java虚拟机规范-运行时数据区 java内存运行时的栈帧结构 java ...
随机推荐
- IIS总提示输入用户名和密码
解决办法: 第一步,在"运行"中输入"gpedit.msc"调出组策略设置. 找到计算机配置-管理模块-windows 组件-internet控制面板-安全页- ...
- CentOS修改yum更新源
1. 在修改前先备份该文件 cp /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo.bak 2. 修改更新源配置文 ...
- css 简单 返回顶部 代码及注释说明
1. 最简单的静态返回顶部,点击直接跳转页面顶部,常见于固定放置在页面底部返回顶部功能 方法一:用命名锚点击返回到顶部预设的id为top的元素 html代码 <a href="#top ...
- POJ 1205 Water Treatment Plants(递推)
题意 建设一条河岸的污水处理系统 河岸有n个城市 每一个城市都能够自己处理污水 V 也能够把污水传到相邻的城市处理 >或< 除了你传给我我也传给你这样的情况 其他都是 ...
- .NET 单点登录
<appSettings> <!--是否启用单点登录接口--> <add key="IsStartCas" value="f ...
- Chrome应用技巧之代码整理。
我们有时候在看别人站点代码时往往是经过压缩的,代码都在一行上了,调试非常是困难,今天给大家介绍一种基本Chrome浏览器的代码整理方法.请看图:
- oracle 包,函数,过程,块的创建和执行及在java中执行(转)
SQL> create or replace procedure sp_guocheng1 is--如果有这个名字就替换 2 begin--执行部分 3 insert into guoc ...
- Java Map 迭代
Map迭代 有两种 道路 遍历 Map该方法: 1 Set<K> KeySet(): 获取全部的键,得到set集合,迭代, 通过get( key)获取值! 2 Se ...
- twisted是python实现的基于事件驱动的异步网络通信构架。
网:https://twistedmatrix.com/trac/ http://www.cnblogs.com/wy-wangyan/p/5252271.html What is Twisted? ...
- Saltstack 安装使用
Saltstack是一个具备puppet与func功能为一身的集中化,轻量级的自动化运维管理工具,使用python编写,功能非常强大,可以使用EPEL快速安装.相比较puppet,安装和配置更加容易和 ...
