【java基础之jdk源码】集合类
最近在整理JAVA 基础知识,从jdk源码入手,今天就jdk中 java.util包下集合类进行理解
先看图
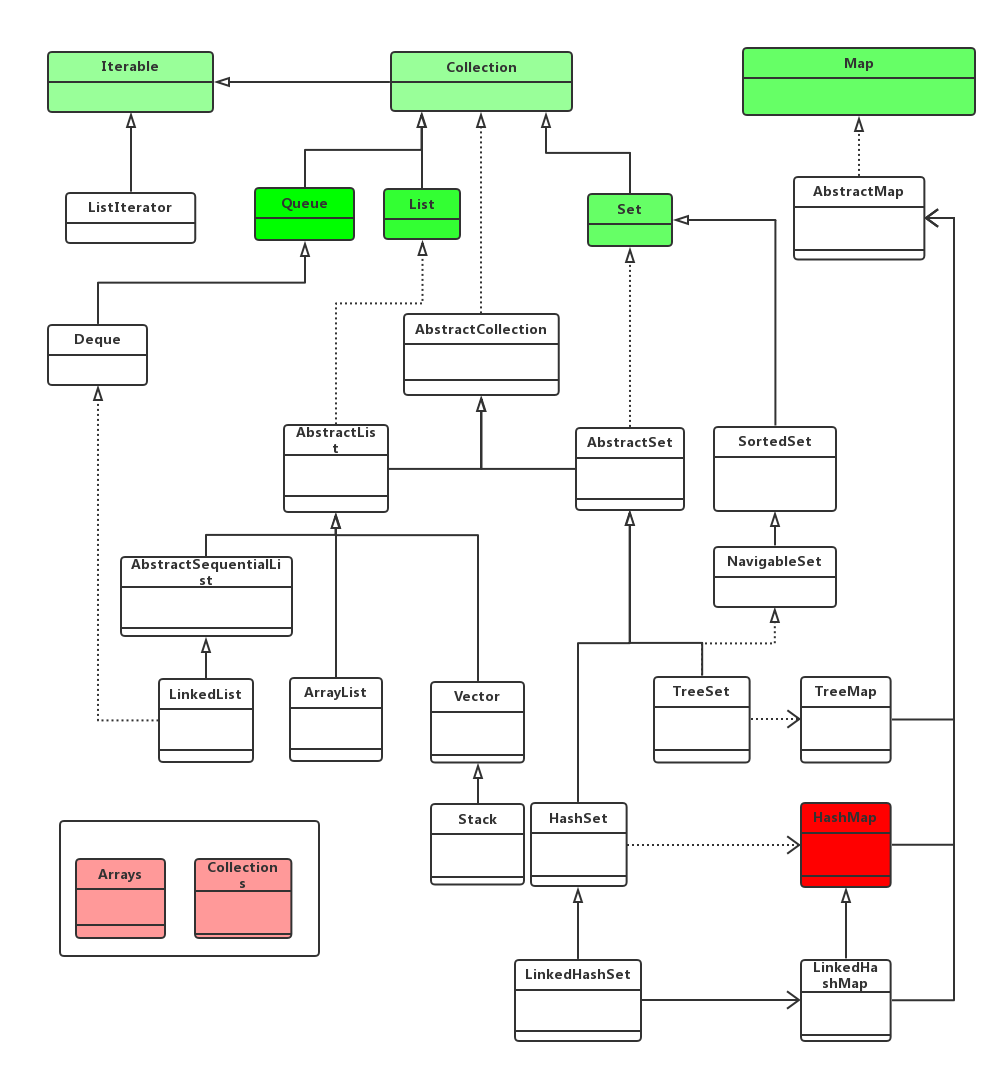
从类图结构可以了解 java.util包下的2个大类:
1、Collecton:可以理解为主要存放的是单个对象
2、Map:可以理解为主要存储key-value类型的对象
一、Collection
Collection继承了Iterate接口,Iterate用于集合内迭代器抽象接口,其子类均实现接口中方法,看下ArrayList下实现:
- /**
- * Returns an iterator over the elements in this list in proper sequence.
- *
- * <p>The returned iterator is <a href="#fail-fast"><i>fail-fast</i></a>.
- *
- * @return an iterator over the elements in this list in proper sequence
- */
- public Iterator<E> iterator() {
- return new Itr(); // 返回内部类实例
- }
- /**
- * An optimized version of AbstractList.Itr
- */
- private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
- int cursor; // index of next element to return 指向下一个位置索引id
- int lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no such 指向上一个位置索引id
- int expectedModCount = modCount;
- public boolean hasNext() {
- return cursor != size;
- }
- @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
- public E next() {
- checkForComodification();
- int i = cursor;
- if (i >= size)
- throw new NoSuchElementException();
- Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
- if (i >= elementData.length)
- throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
- cursor = i + 1;
- return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
- }
- public void remove() {
- if (lastRet < 0)
- throw new IllegalStateException();
- checkForComodification();
- try {
- ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet);
- cursor = lastRet;
- lastRet = -1;
- expectedModCount = modCount;
- } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
- throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
- }
- }
- @Override
- @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
- public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> consumer) {
- Objects.requireNonNull(consumer);
- final int size = ArrayList.this.size;
- int i = cursor;
- if (i >= size) {
- return;
- }
- final Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
- if (i >= elementData.length) {
- throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
- }
- while (i != size && modCount == expectedModCount) {
- consumer.accept((E) elementData[i++]);
- }
- // update once at end of iteration to reduce heap write traffic
- cursor = i;
- lastRet = i - 1;
- checkForComodification();
- }
- final void checkForComodification() {
- if (modCount != expectedModCount)
- throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
- }
- }
1、List
特点:有序结果、顺序遍历、索引、允许有重复值
(1) ArrayList
以上特点实现:
- transient Object[] elementData; // List内部存储对象数组结果
- public boolean add(E e) {
- ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
- elementData[size++] = e;
- return true;
- }
- // 添加对象时先识别是否越界,没有越界则数组对象当前索引值的下一个添
- // 添加对象时,不识别重复,所以有序允许重复值
- /**
- * Removes all of the elements from this list. The list will
- * be empty after this call returns.
- */
- public void clear() {
- modCount++;
- // clear to let GC do its work
- for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
- elementData[i] = null;
- size = 0;
- }
- // 清空List时顺序遍历值置为null
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
return elementData(index);
}
E elementData(int index) {
return (E) elementData[index];
}
其中 remove方法 :
- public E remove(int index) { // 按索引删除对象
- rangeCheck(index); // 校验输入索引id是否越界,若越界则抛出运行时异常 IndexOutOfBoundsException
- modCount++;
- E oldValue = elementData(index);
- int numMoved = size - index - 1; // 定位到索引的下一位
- if (numMoved > 0)
- System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
- numMoved); //调用native方法实现数组位置左移
- elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
- // 末尾元素置空
- return oldValue;
- }
- public boolean remove(Object o) {// 按对象删除
- if (o == null) {
- for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
- if (elementData[index] == null) {
- fastRemove(index);
- return true;
- }
- } else {
- for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
- if (o.equals(elementData[index])) { // 识别对象相等使用equals方法,使用时注意重写equals方法
- fastRemove(index);
- return true;
- }
- }
- return false;
- }
- /*
- * Private remove method that skips bounds checking and does not
- * return the value removed.
- */
- private void fastRemove(int index) {
- modCount++; // 删除元素时,modCount值变更
- int numMoved = size - index - 1;
- if (numMoved > 0)
- System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
- numMoved);
- elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
- }
可以看到ArrayList中对数组进行,操作时常用到System.arraycopy
- java.lang.System下
public static native void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos,- Object dest, int destPos,
- int length);
还有在 java.util.Arrays下数组copy方法,最终也是调用System.arraycopy方法
- public static <T> T[] copyOf(T[] original, int newLength) {
- return (T[]) copyOf(original, newLength, original.getClass());
- }
- public static <T,U> T[] copyOf(U[] original, int newLength, Class<? extends T[]> newType) {
- @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
- T[] copy = ((Object)newType == (Object)Object[].class)
- ? (T[]) new Object[newLength]
- : (T[]) Array.newInstance(newType.getComponentType(), newLength);
- System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
- Math.min(original.length, newLength));
- return copy;
- }
示例:
- package jdk.array;
- import java.util.ArrayList;
- import java.util.Arrays;
- import java.util.Iterator;
- public class ArrayListTest1 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- ArrayList<String> l1 = new ArrayList<>();
- l1.add("s1");
- l1.add("s2");
- l1.add("s1");
- l1.add("s2");
- l1.add("s2");
- l1.add("s2");
- l1.add("s3");
- l1.add("s3");
- l1.add("s3");
- // 使用容器迭代器遍历List
- Iterator<String> iterator = l1.iterator();
- while (iterator.hasNext()) {
- String str = iterator.next();
- if ("s1".equals(str)) {
- iterator.remove(); // 迭代器内部方法remove()
- }
- }
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(l1.toArray()));
- // 使用 for循环遍历List
- for(int i = 0 ; i < l1.size(); i++) {
- if ("s2".equals(l1.get(1))) {
- l1.remove(i);
- i--;
- }
- }
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(l1.toArray()));
- // 使用foreach遍历List
- for (String str : l1) {
- if ("s3".equals(str)) {
- l1.remove(str); // ArrayList内部方法remove(Object)
- }
- }
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(l1.toArray()));
- }
- }

可以看到出现异常:ConcurrentModificationException,出现该异常原因是:
“快速失败”也就是fail-fast,它是Java集合的一种错误检测机制。当创建Iterator后,在Iterator使用还没有结束时,改变(删除或增添新项)集合元素就会出现上面的错误
看看ArrayList的排序方法:sort(Comparator<? super E> c)
- public void sort(Comparator<? super E> c) {
- final int expectedModCount = modCount;
- Arrays.sort((E[]) elementData, 0, size, c);
- if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
- throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
- }
- modCount++;
- }
- public static <T> void sort(T[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
- Comparator<? super T> c) {
- if (c == null) {
- sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex);
- } else {
- rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
- if (LegacyMergeSort.userRequested)
- legacyMergeSort(a, fromIndex, toIndex, c);
- else
- TimSort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex, c, null, 0, 0);
- }
- }
示例:
- package jdk.array;
- import java.util.ArrayList;
- import java.util.Arrays;
- import java.util.Comparator;
- import java.util.Iterator;
- public class ArrayListTest2 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- ArrayList<String> l1 = new ArrayList<>();
- l1.add("s1");
- l1.add("s2");
- l1.add("s1");
- l1.add("s2");
- l1.add("s2");
- l1.add("s2");
- l1.add("s3");
- l1.add("s3");
- l1.add("s3");
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(l1.toArray()));
- l1.sort(null);
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(l1.toArray()));
- l1.sort(new Comparator() {
- @Override
- public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
- return -((String) o1).compareTo((String) o2);
- }
- });
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(l1.toArray()));
- }
- }

(2)LinkedList
- public class LinkedList<E>
- extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
- implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
- // 实现了Deque接口,可以做队列使用
- /**
- * Pointer to first node.
- * Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
- * (first.prev == null && first.item != null)
- */
- transient Node<E> first;
- /**
- * Pointer to last node.
- * Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
- * (last.next == null && last.item != null)
- */
- transient Node<E> last;
- /**
- * Constructs an empty list.
- */
- public LinkedList() {
- }
- // 集合对象存储结构,通过当前节点的前后节点,维护顺序集合(双向链表结构)
- private static class Node<E> {
- E item;
- Node<E> next;
- Node<E> prev;
- Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
- this.item = element;
- this.next = next;
- this.prev = prev;
- }
- }
以上为 LinkedList的内部存储结构,以Node存储。
在看下集合元素插入、删除及获取方法实现:
- public boolean add(E e) {
- linkLast(e);
- return true;
- }
- /**
- * Links e as last element.
- */
- void linkLast(E e) {
- final Node<E> l = last; // 保存最后个节点
- final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);// 新增节点
- last = newNode; // 将新节点置为最后节点
- if (l == null)
- first = newNode;
- else
- l.next = newNode;
- size++;
- modCount++;
- }
- public E remove() {
- return removeFirst(); // 去掉首节点
- }
- public E removeFirst() {
- final Node<E> f = first;
- if (f == null)
- throw new NoSuchElementException();
- return unlinkFirst(f);
- }
- private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) {
- // assert f == first && f != null;
- final E element = f.item;
- final Node<E> next = f.next;
- f.item = null;
- f.next = null; // help GC
- first = next;
- if (next == null)
- last = null;
- else
- next.prev = null;
- size--;
- modCount++;
- return element;
- }
- // 入栈方法
- public void push(E e) {
- addFirst(e);
- }
- // 出栈方法
- public E pop() {
- return removeFirst();
- }
- // 入队
- public boolean offer(E e) {
- return add(e);
- }
- public boolean add(E e) {
- linkLast(e);
- return true;
- }
- // 出队
- public E poll() {
- final Node<E> f = first;
- return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f);
- }
- //随机访问集合对象
- public E get(int index) {
- checkElementIndex(index);
- return node(index).item;
- }
- /**
- * Returns the (non-null) Node at the specified element index.
- */
- Node<E> node(int index) {
- // assert isElementIndex(index);
- // 识别 index id离首节点近还是尾节点近,减少遍历
- if (index < (size >> 1)) {
- Node<E> x = first;
- for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) // 0(i)
- x = x.next;
- return x;
- } else {
- Node<E> x = last;
- for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) // 0(i)
- x = x.prev;
- return x;
- }
- }
通过以上源码理解 ArrayList 和 LinkedList 区别类似数据结构中 数组及链表结构区别 ,新增、删除 和 随机访问存在 效率上的差别:
ArrayList是最常用的集合,其内部实现是一个数组,ArrayList的大小是可以动态扩充的。对于元素的随机访问效率高,其访问的时间复杂度为O(1),对于数据的插入与删除,从尾部操作效率高,时间复杂度和随机访问一样是O(1),若是从头部操作则效率会比较低,因为从头部插入或删除时需要移动后面所有元素,其时间复杂度为O(n-i)(n表示元素个数,i表示元素位置)
LinkList对于随机访问效率是比较低的,因为它需要从头开始索引,所以其时间复杂度为O(i)。但是对于元素的增删,LinkList效率高,因为只需要修改前后指针即可,其时间复杂度为O(1)。
(3)Vector
与ArrayList类型,内部也是使用数据来存储对象,但是线程安全的,因为实现方法重写的时候,全部加上了同步关键字:synchronized;(一般不建议使用,性能消耗)
(4)Stack
- public
- class Stack<E> extends Vector<E> {
- /**
- * Creates an empty Stack.
- */
- public Stack() {
- }
2、Queue
遵循FIFO(先入先出规则),内部出栈入栈方法,主要区别在于是否是阻塞入队或出队
3、Set
- public class HashSet<E>
- extends AbstractSet<E>
- implements Set<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
- /**
- * Constructs a new, empty set; the backing <tt>HashMap</tt> instance has
- * default initial capacity (16) and load factor (0.75).
- */
- public HashSet() {
- map = new HashMap<>();
- }
- // Set 集合对象存储在 Map的 key中
- public boolean contains(Object o) {
- return map.containsKey(o);
- }
- // 添加对象到Set集合中
- public boolean add(E e) {
- return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
- }
- // 删除Set集合中对象
- public boolean remove(Object o) {
- return map.remove(o)==PRESENT;
- }
实际Set集合的实现依赖于Map的实现,通过Map的 key值唯一性来实现
二、Map
1、HashMap:基于Map接口实现、允许null 键值、无序、非同步
一起看下HashMap的实现
- // map 内部对象链表存储结构
- static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
- final int hash;
- final K key;
- V value;
- Node<K,V> next; // 下一节点
- Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
- this.hash = hash;
- this.key = key;
- this.value = value;
- this.next = next;
- }
- public final K getKey() { return key; }
- public final V getValue() { return value; }
- public final String toString() { return key + "=" + value; }
- // 重写hashCode方法
- public final int hashCode() {
- return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value);
- }
- public final V setValue(V newValue) {
- V oldValue = value;
- value = newValue;
- return oldValue;
- }
- // 重写 equals方法
- public final boolean equals(Object o) {
- if (o == this)
- return true;
- if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
- Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;
- if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) &&
- Objects.equals(value, e.getValue()))
- return true;
- }
- return false;
- }
- }
- transient Node<K,V>[] table; // 用数组保存多条链表的首节点
- // 获取 key所对应的存储JNode的 value值
- public V get(Object key) {
- Node<K,V> e;
- return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;
- }
- // 识别是否存在key所对应的 Node
- public boolean containsKey(Object key) {
- return getNode(hash(key), key) != null;
- }
- // map 内部对象链表存储结构
- static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
- final int hash;
- final K key;
- V value;
- Node<K,V> next; // 下一节点
- Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
- this.hash = hash;
- this.key = key;
- this.value = value;
- this.next = next;
- }
- public final K getKey() { return key; }
- public final V getValue() { return value; }
- public final String toString() { return key + "=" + value; }
- // 重写hashCode方法
- public final int hashCode() {
- return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value);
- }
- public final V setValue(V newValue) {
- V oldValue = value;
- value = newValue;
- return oldValue;
- }
- // 重写 equals方法
- public final boolean equals(Object o) {
- if (o == this)
- return true;
- if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
- Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;
- if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) &&
- Objects.equals(value, e.getValue()))
- return true;
- }
- return false;
- }
- }
- transient Node<K,V>[] table; // 用数组保存多条链表的首节点
- // 获取 key所对应的存储JNode的 value值
- public V get(Object key) {
- Node<K,V> e;
- return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;
- }
- // 识别是否存在key所对应的 Node
- public boolean containsKey(Object key) {
- return getNode(hash(key), key) != null;
- }
- // 插入 对象
- public V put(K key, V value) {
- return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
- }
- // 调用的内部方法,
- final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
- boolean evict) {
- // tab 为map内首节点集合
- Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
- // 先识别table是否为空,为空则初始化,hashmap内存存储延迟加载在这里体现
- if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
- n = (tab = resize()).length;
- // 通过hash值以长度做按位与,识别读取元素的存储在tab中的位置
- if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
- // 若tab所在链表首节点为空,则直接构造新节点
- tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
- else {
- // tab所在链表首节点不为空,则遍历p所在链表或红黑树,找到可以存储的位置
- Node<K,V> e; K k;
- if (p.hash == hash &&
- ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
- e = p;
- else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
- e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
- else {
- for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
- if ((e = p.next) == null) {
- p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
- if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
- treeifyBin(tab, hash);
- break;
- }
- if (e.hash == hash &&
- ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
- break;
- p = e;
- }
- }
- if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
- V oldValue = e.value;
- if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
- e.value = value;
- afterNodeAccess(e);
- return oldValue;
- }
- }
- ++modCount;
- if (++size > threshold)
- resize();
- afterNodeInsertion(evict);
- return null;
- }
可以看到,在HashMap中存储的结构下, Node类型的数组保存头部节点(单链表)或根节点(红黑树),先以 Node的key的hash值与数组长度做位与运算(hash碰撞),初始
时使用单链表存储新插入对象(newNode),当链表长度超过8时,会将链表结构转为红黑树结构存储(treeifyBin方法)
- final void treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] tab, int hash) {
- int n, index; Node<K,V> e;
- if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY)
- resize();
- else if ((e = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
- // 找到需要转换的 单链表 e,遍历单链表,转换为TreeNode,保存前后节点关系
- TreeNode<K,V> hd = null, tl = null;
- do {
- TreeNode<K,V> p = replacementTreeNode(e, null);
- if (tl == null)
- hd = p;
- else {
- p.prev = tl;
- tl.next = p;
- }
- tl = p;
- } while ((e = e.next) != null);
- //让桶的第一个元素指向新建的红黑树头结点,以后这个桶里的元素就是红黑树而不是链表了
- if ((tab[index] = hd) != null)
- hd.treeify(tab);
- }
- }
先将单链表转换为 treenode,在调用 treeify方法构造红黑树
2、LinkedHashMap
继承HashMap,HashMap是无序集合,而LinkedHashMap为有序集合
- public class LinkedHashMap<K,V>
- extends HashMap<K,V>
- implements Map<K,V>
构造LinkedHashMap.EntreyNode<K,V> 继承 HashMap.Node<K,V> 实现双向链表
- static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Node<K,V> {
- Entry<K,V> before, after; // before 保存前置节点,after保存后置节点
- Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
- super(hash, key, value, next);
- }
- }
- /**
- * The head (eldest) of the doubly linked list.
- */
- transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> head; // 头节点
- /**
- * The tail (youngest) of the doubly linked list.
- */
- transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> tail; // 尾部节点
- // 重写HashMap的 创建新节点方法
- Node<K,V> newNode(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> e) {
- LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p =
- new LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e);
- linkNodeLast(p); // 将新节点放到尾部节点,从而保证顺序
- return p;
- }
- // link at the end of list
- private void linkNodeLast(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p) {
- LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last = tail;
- tail = p;
- if (last == null)
- head = p;
- else {
- p.before = last;
- last.after = p;
- }
- }
3、TreeMap
TreeMap直接使用红黑树结构存储集合元素,根据键 做排序,排序规则按内部 comparator 对象的实例对象的排序规则,若comparator为空,则按自然排序
- public class TreeMap<K,V>
- extends AbstractMap<K,V>
- implements NavigableMap<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
- {
- /**
- * The comparator used to maintain order in this tree map, or
- * null if it uses the natural ordering of its keys.
- *
- * @serial
- */
- private final Comparator<? super K> comparator; // 对象比较接口
- private transient Entry<K,V> root; // 根节点
root的实现逻辑为 TreeMap.Entrey<K,V> 继承 Map.Entrey<K,V> 实现 ,与HashMap.TreeNode<K,V>实现类似
- static final class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
- K key;
- V value;
- Entry<K,V> left;
- Entry<K,V> right;
- Entry<K,V> parent;
- boolean color = BLACK;
所以TreeMap put和get方法就是以键先进行红黑树的查找后操作
4、HashTable
HashTable和HashMap数据结构类似,主要区别为HashTable中操作集合元素对象的方法都加上了 同步关键字(synchronized), 所以说线程安全的及集合
【java基础之jdk源码】集合类的更多相关文章
- 【java基础之jdk源码】Object
最新在整体回归下java基础薄弱环节,以下为自己整理笔记,若有理解错误,请批评指正,谢谢. java.lang.Object为java所有类的基类,所以一般的类都可用重写或直接使用Object下方法, ...
- Jdk源码-集合类主要原理和解析
写在前面 熟悉Jdk原理的重要性不言而喻,作为Java开发者或者面试者,了解其实现原理也显得更为装逼,在Java读书计划我写到了,它是面试中最基础的一部分,所以单独拿出来做个总结,为了更好滴理解和学习 ...
- Java基础(八)--String(源码)、StringBuffer、StringBuilder
String源码:基于jdk1.8 public final class String implements Serializable, Comparable<String>, CharS ...
- Java基础try-with-resource语法源码分析
众所周知,所有被打开的系统资源,比如流.文件或者Socket连接等,都需要被开发者手动关闭,否则随着程序的不断运行,资源泄露将会累积成重大的生产事故. 在Java的江湖中,存在着一种名为finally ...
- JDK源码学习笔记——Object
一.源码解析 public class Object { /** * 一个本地方法,具体是用C(C++)在DLL中实现的,然后通过JNI调用 */ private static native void ...
- 从JDK源码角度看java并发的公平性
JAVA为简化开发者开发提供了很多并发的工具,包括各种同步器,有了JDK我们只要学会简单使用类API即可.但这并不意味着不需要探索其具体的实现机制,本文从JDK源码角度简单讲讲并发时线程竞争的公平性. ...
- 一点一点看JDK源码(三)java.util.ArrayList 前偏
一点一点看JDK源码(三)java.util.ArrayList liuyuhang原创,未经允许禁止转载 本文举例使用的是JDK8的API 目录:一点一点看JDK源码(〇) 1.综述 ArrayLi ...
- 一点一点看JDK源码(六)java.util.LinkedList前篇之链表概要
一点一点看JDK源码(六)java.util.LinkedList前篇之链表概要 liuyuhang原创,未经允许禁止转载 本文举例使用的是JDK8的API 目录:一点一点看JDK源码(〇) 1.什么 ...
- Java是如何实现自己的SPI机制的? JDK源码(一)
注:该源码分析对应JDK版本为1.8 1 引言 这是[源码笔记]的JDK源码解读的第一篇文章,本篇我们来探究Java的SPI机制的相关源码. 2 什么是SPI机制 那么,什么是SPI机制呢? SPI是 ...
随机推荐
- VC创建多级目录
BOOL ForceCreateDirectory(string strDir) { BOOL bRet = FALSE; //确保以"\"结尾,以创建最后一个目录 ...
- 有限状态机(Finite-state machine)
var menu = { // 当前状态 currentState: 'hide', // 绑定事件 initialize: function() { var self = this; self.on ...
- 前言《iOS网络高级编程:iPhone和iPad的企业应用开发》(书籍学习)
本书内容: 在客户端设备与服务器之间执行HTTP请求 管理客户端设备与服务器之间的数据负载 处理HTTP请求的错误 保护网络通信 改进网络通信的性能 执行Socket层的通信 实现推送通知 单个设备上 ...
- CSS 简介、语法、派生选择器、id 选择器、类选择器、属性选择器
CSS 概述 CSS 指层叠样式表 (Cascading Style Sheets) 样式定义如何显示 HTML 元素 样式通常存储在样式表中 把样式添加到 HTML 4.0 中,是为了解决内容与表现 ...
- 递归求和1到n
一般的方法 #include<stdio.h> int sum(int n){ if(n==1) return 1; else return n+sum(n-1);} int main(v ...
- Unity3D在NGUI中使用mask
过程是这样的:最近一直想做一个头像的mask效果,后来发现原来unity的mask需要用shader来写,网上找了不少资料,也能实现,不过大多数都是用render texture作为相机投影的text ...
- Java Swing paint repaint update 方法的关系
Java Swing paint repaint update 方法的关系: 参考:http://blog.csdn.net/xiaoliangmeiny/article/details/691665 ...
- Vue.js自定义指令的用法与实例
市面上大多数关于Vue.js自定义指令的文章都在讲语法,很少讲实际的应用场景和用例,以致于即便明白了怎么写,也不知道怎么用.本文不讲语法,就讲自定义指令的用法. 自定义指令是用来操作DOM的.尽管Vu ...
- 从零开始学习C#——HelloWorld(一)
从零开始学习C# 老规矩Hello World 您的第一个程序 visual studio 如何使用就不说了 //编程的开始,Hello World! program in C# using Syst ...
- Struct 和 Union 的详细区别
Union: 共用体 Struct:结构体 两者的区别: 1:共用体和结构体都是由多个不同的数据类型成员组成, 但在任何同一时刻, 共用体只存放一个被选中的成员, 而结构体则存放所有的成员变量. 2: ...
