Cortex-M3 / M4 Hard Fault Handler (转载)
转自大伟的,感谢大伟的帮助调试:http://www.cnblogs.com/shangdawei/archive/2013/04/30/3052491.html
http://blog.frankvh.com/2011/12/07/cortex-m3-m4-hard-fault-handler/
If you’re seeing a Hard Fault exception on your Cortex M3 or Cortex M4 processor, this handler and information may help. I can’t take credit for it – this code was provided by Joseph Yiu on a few different forums, as well as in his book (Definitive Guide to the ARM Cortex M3). I’m simply providing some assistance on how to install and use it.
Hard Fault Handler Installation
These instructions work for an STM32F2xx or STM32F4xx processor using a GNU-based toolchain (eg Yagarto or Sourcery G++). They should work with other processors and toolchains but may require a small tweak – no doubt your compiler will be pleased to tell you if it’s not happy! As always with programming, the following is not the only way to do it – it’s simply the way I did it. If you want to rearrange things or do things a bit differently then feel free.
Joseph’s hard fault handler is in two pieces – a small piece of assembly, and a small piece of C. You need the processor’s hardfault exception vector to jump to the assembly, and then the assembly code will itself call the C code.
Here’s the assembly code. It extracts the location of the stack frame, then passes it as a pointer to the C code, which is named hard_fault_handler_c.

- .syntax unified
- .cpu cortex-m3
- .thumb
- .global HardFault_Handler
- .extern hard_fault_handler_c
- HardFault_Handler:
- TST LR, #4
- ITE EQ
- MRSEQ R0, MSP
- MRSNE R0, PSP
- B hard_fault_handler_c

For those of you using the IAR tool chain, the assembly stub must be specified in a modules and section to compile and link properly. Below is the code that I used to apply this example to the IAR tool chain:

- MODULE HARDFAULT_MOD
- SECTION HARDFAULT_SECT : CODE(2)
- THUMB
- PUBLIC HardFault_Handler
- EXTERN HardFault_Handler_C
- HardFault_Handler:
- TST LR, #4
- ITE EQ
- MRSEQ R0, MSP
- MRSNE R0, PSP
- B HardFault_Handler_C
- END


- void HardFault_Handler( void )
- {
- __ASM(“TST LR, #4″);
- __ASM(“ITE EQ”);
- __ASM(“MRSEQ R0, MSP”);
- __ASM(“MRSNE R0, PSP”);
- __ASM(“B hard_fault_handler_c”);
- }

This assembly needs to be immediately called when the hard fault exception occurs.
If you look at the vectors list, you’ll see something like this:

- g_pfnVectors:
- .word _estack
- .word Reset_Handler
- .word NMI_Handler
- .word HardFault_Handler
- .word MemManage_Handler
- .word BusFault_Handler
- .word UsageFault_Handler
- etc

Given that the name in the vector table is HardFault_Handler, we give the assembler code that name (and declare the name as a global so the linker can find it). If your vector table contains a different name, then change the name of the assembler code to suit.
You need to include this bit of assembler in your build. Just save the assembler code in its own .s file (eg: hardfault.s) and then include it in your build, the same way as your other .s files (like that startup file) are.
Now we need to add the C code. Here it is:

- // From Joseph Yiu, minor edits by FVH
- // hard fault handler in C,
- // with stack frame location as input parameter
- // called from HardFault_Handler in file xxx.s
- void hard_fault_handler_c (unsigned int * hardfault_args)
- {
- unsigned int stacked_r0;
- unsigned int stacked_r1;
- unsigned int stacked_r2;
- unsigned int stacked_r3;
- unsigned int stacked_r12;
- unsigned int stacked_lr;
- unsigned int stacked_pc;
- unsigned int stacked_psr;
- stacked_r0 = ((unsigned long) hardfault_args[0]);
- stacked_r1 = ((unsigned long) hardfault_args[1]);
- stacked_r2 = ((unsigned long) hardfault_args[2]);
- stacked_r3 = ((unsigned long) hardfault_args[3]);
- stacked_r12 = ((unsigned long) hardfault_args[4]);
- stacked_lr = ((unsigned long) hardfault_args[5]);
- stacked_pc = ((unsigned long) hardfault_args[6]);
- stacked_psr = ((unsigned long) hardfault_args[7]);
- printf ("\n\n[Hard fault handler - all numbers in hex]\n");
- printf ("R0 = %x\n", stacked_r0);
- printf ("R1 = %x\n", stacked_r1);
- printf ("R2 = %x\n", stacked_r2);
- printf ("R3 = %x\n", stacked_r3);
- printf ("R12 = %x\n", stacked_r12);
- printf ("LR [R14] = %x subroutine call return address\n", stacked_lr);
- printf ("PC [R15] = %x program counter\n", stacked_pc);
- printf ("PSR = %x\n", stacked_psr);
- printf ("BFAR = %x\n", (*((volatile unsigned long *)(0xE000ED38))));
- printf ("CFSR = %x\n", (*((volatile unsigned long *)(0xE000ED28))));
- printf ("HFSR = %x\n", (*((volatile unsigned long *)(0xE000ED2C))));
- printf ("DFSR = %x\n", (*((volatile unsigned long *)(0xE000ED30))));
- printf ("AFSR = %x\n", (*((volatile unsigned long *)(0xE000ED3C))));
- printf ("SCB_SHCSR = %x\n", SCB->SHCSR);
- while (1);
- }

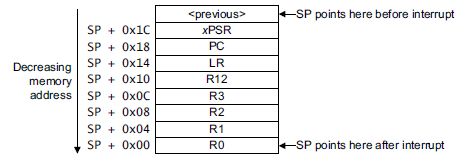
This code goes wherever the existing (previous) Hard Fault Handler went. In our example, the vector table pointed to a function called HardFault_Handler. We are replacing that function with the assembler code, so the original HardFault_Handler function needs to be commented out (otherwise we’ll have two functions with the same name). For the STM32F2xx all exception handlers are found in the file: stm32f2xx_it.c So comment out the function HardFault_Handler() from that C file, and paste the C code for Joseph’s hard_fault_handler_c() into the same file.
That’s it. In summary, you commented out the old hard fault handler, and you added in some assembly code and some C code instead. Try building your project and see what happens.
Note that this code will only work if the main stack pointer hasn’t been badly corrupted prior to the hard fault occurring – if the stack pointer is off in never-never land then the C handler may not work. In my experience this has never been a problem.
Cortex-M3 / M4 Hard Fault Handler (转载)的更多相关文章
- 【ARM-Linux开发】ARM7 ARM9 ARM Cortex M3 M4 有什么区别
ARM7 ARM9 ARM Cortex M3 M4 区别 arm7 arm9 可以类比386和奔腾, 不同代,arm9相比arm7指令集和性能都有所增强,arm7和arm9都有带mmu和无mmu的版 ...
- ARM 架构、ARM7、ARM9、STM32、Cortex M3 M4 、51、AVR 之间有什么区别和联系?(转载自知乎)
ARM架构: 由英国ARM公司设计的一系列32位的RISC微处理器架构总称,现有ARMv1~ARMv8种类. ARM7: 一类采用ARMv3或ARMv4架构的,使用冯诺依曼结构的内核. ...
- 【freertos】002-posix模拟器设计与cortex m3异常处理
目录 前言 posix 标准接口层设计 模拟器的系统心跳 模拟器的task底层实质 模拟器的任务切换原理 cortex M3/M4异常处理 双堆栈指针 双操作模式 栈帧 EXC_RETURN 前言 如 ...
- ARM Cortex M3(V7-M架构)硬件启动程序 一
Cortex-m3启动代码分析笔记 启动代码文件名是STM32F10X.S,它的作用先总结下,然后再分析. 启动代码作用一般是: 1)堆和栈的初始化: 2)中断向量表定义: 3)地址重映射及中断向量表 ...
- Implementation of Serial Wire JTAG flash programming in ARM Cortex M3 Processors
Implementation of Serial Wire JTAG flash programming in ARM Cortex M3 Processors The goal of the pro ...
- ARM Cortex M3系列GPIO口介绍(工作方式探讨)
一.Cortex M3的GPIO口特性 在介绍GPIO口功能前,有必要先说明一下M3的结构框图,这样能够更好理解总线结构和GPIO所处的位置. Cortex M3结构框图 从图中可以看出 ...
- IBM X3650 M3/M4的服务器装系统
IBM X3650 M3/M4的服务器一般都有两块以上的硬盘.所以如果没有做RAID,那首先应该做好raid 磁盘阵列.本文装系统的前提是RAID已经做好. 一般安装系统的方式为先在IBM官网下载对应 ...
- STM32学习之路入门篇之指令集及cortex——m3的存储系统
STM32学习之路入门篇之指令集及cortex——m3的存储系统 一.汇编语言基础 一).汇编语言:基本语法 1.汇编指令最典型的书写模式: 标号 操作码 操作数1, 操作数2,... ...
- T-SQL - 习题02_将数据表year|month|amount查询成year|m1|m2|m3|m4的样式
时间:2017-09-11 整理:byzqy 题目:有个年度统计表,结构如下: 怎么样把这个表,查询成这样一个结果: 这是在面试过程中遇到的一个关于数据库的题,没有一点思路,不知它考查到的知识点是什么 ...
随机推荐
- [NOIP2002] 提高组 洛谷P1033 自由落体
题目描述 在高为 H 的天花板上有 n 个小球,体积不计,位置分别为 0,1,2,….n-1.在地面上有一个小车(长为 L,高为 K,距原点距离为 S1).已知小球下落距离计算公式为 d=1/2*g* ...
- ST 表学习
作用:ST算法是用来求解给定区间RMQ的最值,本文以最小值为例 举例: 给出一数组A[0~5] = {5,4,6,10,1,12},则区间[2,5]之间的最值为1. 方法:ST算法分成两部分:离线预处 ...
- 12.1——类的定义与声明,隐含的this指针
类的定义与声明: (1)将const放在成员函数的形参列表之后,可以将将成员函数声明为常量,而它的意思是函数不能改变所操作的数据成员 这里必须在声明和定义处都加上const. (2)成员函数有一个隐含 ...
- vagrant的学习 之 打包分发
vagrant的学习 之 打包分发 一.打包Box: (1)关闭虚拟机. vagrant halt (2)打包: vagrant package 这样打包出来的文件叫package.box. 指定生成 ...
- [Bzoj3611][Heoi2014]大工程(虚树)
3611: [Heoi2014]大工程 Time Limit: 60 Sec Memory Limit: 512 MBSubmit: 2000 Solved: 837[Submit][Status ...
- win8,win10里面内置的IE浏览器网银无法输入密码
win8,win10里面内置的IE浏览器网银无法输入密码,安装控件也没效果,部分网银直接导致IE崩溃,只需要简单设置即可解决. 方法/步骤 1 打开IE浏览器,点击右上角的小齿轮图标,在下拉菜单中 ...
- 异步SOCKET分包和组包的一种通用算法
unit uPackage;// 应用协议// cxg 2016-9-23// 包=包头+包体 interface uses SysUtils, Classes, PeachCtrl.Net.Iocp ...
- SeaGlass:手工搭建伪基站监控系统
“伪基站”即假基站,设备一般由主机和笔记本电脑或手机组成,通过短信群发器.短信发信机等相关设备能够搜取以其为中心.一定半径范围内的手机卡信息,利用2G移动通信的缺陷,通过伪装成运营商的基站,冒用他人手 ...
- 微信小程序 自定义组件(stepper)
项目目录: 步骤一:创建组件 声明这一组文件为自定义组件 stepper.json { "component": true, "usingComponents" ...
- Codeforces Round #253 (Div. 1) A Borya and Hanabi
A. Borya and Hanabi time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard ...
