Java核心复习 —— J.U.C 并发工具类
一、CountDownLatch
文档描述
A synchronization aid that allows one or more threads to wait until* a set of operations being performed in other threads completes.
是一个同步帮助工具,允许一个或多个线程等待一系列其他线程操作完后,再执行。
count down 倒计时
latch 插锁
在Java中Latch结尾的也叫 闭锁

用法
| 方法名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| await() | 线程会被挂起,它会等待直到count值为0才继续执行 |
简单示例
public class CountDownLatchDemo {
private static final ExecutorService threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(50, 100,
5, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<>(),
new BasicThreadFactory.Builder().namingPattern("thread-%d").build());
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(10);
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
threadPool.execute(() -> {
System.out.println("test-"+new Random().nextInt());
countDownLatch.countDown();
});
}
countDownLatch.await();
System.out.println("end");
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}

应用场景
同事A需要执行任务A,进行A类数据的收集
同事B需要执行任务B,进行B类数据的收集
项目经理需要等到A和B的数据都收集齐之后,进行统计,然后向上汇报。
public class CountDownLatchDemo2 {
private static final ExecutorService threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(50, 100,
5, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<>(),
new BasicThreadFactory.Builder().namingPattern("thread-%d").build());
public static void main(String[] args) {
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(2);
// 收集数据A
threadPool.execute(new TaskA(countDownLatch));
// 收集数据B
threadPool.execute(new TaskB(countDownLatch));
try {
countDownLatch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 进行统计工作
System.out.println("进行统计工作");
// 向上汇报
System.out.println("向上汇报");
System.out.println("任务结束");
threadPool.shutdown();
}
static class TaskA implements Runnable {
private CountDownLatch countDownLatch;
public TaskA(CountDownLatch countDownLatch) {
this.countDownLatch = countDownLatch;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println("执行任务A-----------");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
System.out.println("执行任务A完成");
countDownLatch.countDown();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
static class TaskB implements Runnable {
private CountDownLatch countDownLatch;
public TaskB(CountDownLatch countDownLatch) {
this.countDownLatch = countDownLatch;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println("执行任务B-----------");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(7);
System.out.println("执行任务B完成");
countDownLatch.countDown();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
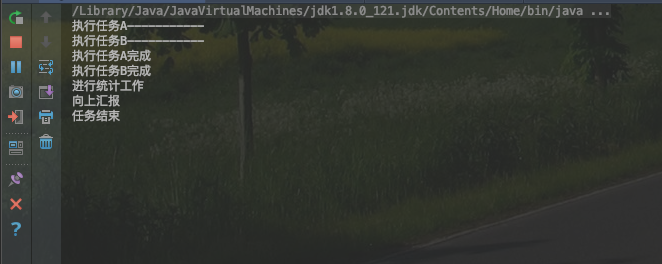
运行结果
二、Semaphore

文档描述
A counting semaphore. Conceptually, a semaphore maintains a set of* permits. Each {@link #acquire} blocks if necessary until a permit is* available, and then takes it. Each {@link #release} adds a permit,* potentially releasing a blocking acquirer.* However, no actual permit objects are used; the {@code Semaphore} just* keeps a count of the number available and acts accordingly.**
Semaphores are often used to restrict the number of threads than can* access some (physical or logical) resource. For example, here is* a class that uses a semaphore to control access to a pool of items:
用于控制并发量。
用法
| 方法名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| acquire() | 从该信号量获取一个许可,在获取许可前线程将一直阻塞 |
| release() | 释放一个许可,将其返回给信号量 |
简单示例
public class SemaphoreDemo {
private static final ExecutorService threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(20, 100,
1, TimeUnit.MINUTES,
new SynchronousQueue<>(),
new BasicThreadFactory.Builder().namingPattern("thread-%d").build());
private static volatile int count = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(3);
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
threadPool.execute(() -> {
try {
semaphore.acquire();
System.out.println("test--" + count);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
count++;
semaphore.release();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
}
}
应用场景
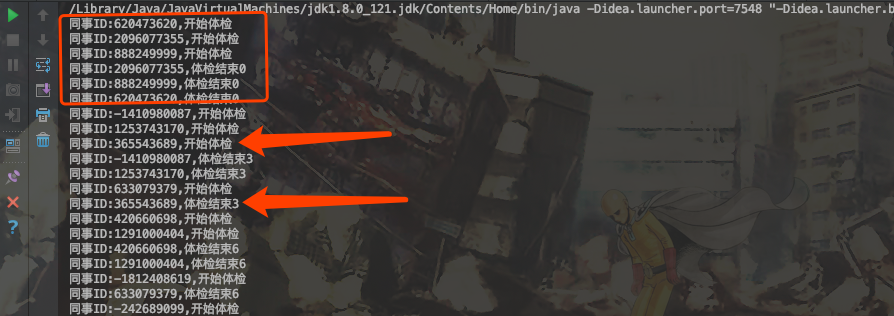
公司有100个人需要体检,医院每次最多只能体检3人。
当有3个人在体检时,其他人只能等待,有1个人体检完,下一个人可以补上。
public class SemaphoreDemo {
private static final ExecutorService threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(20, 100,
1, TimeUnit.MINUTES,
new SynchronousQueue<>(),
new BasicThreadFactory.Builder().namingPattern("thread-%d").build());
private static volatile int count = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(3);
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
threadPool.execute(() -> {
try {
String id = new Random().nextInt() + "";
semaphore.acquire();
System.out.println("同事ID:" + id + ",开始体检");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3L);
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(new Random(10000).nextInt());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("同事ID:" + id + ",体检结束" + count);
count++;
semaphore.release();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
}
}
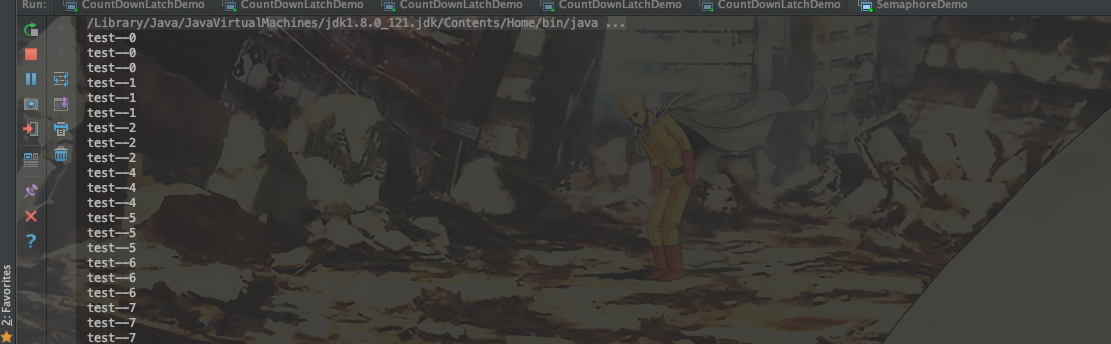
运行结果
三、CyclicBarrier
概念

和闭锁不同的是,栅栏是用来等待线程的,闭锁是用来等待时间。
当指定线程数都到达某个点,才开始执行后续的操作。
就好比有10个人赛跑,要跑400米,在100米设置一个栅栏,当这10个人都到达了这个栅栏的时候,才取消栅栏,全部放行。
简单示例
public class CyclicBarrierDemo {
private static final ExecutorService threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(50, 100,
1, TimeUnit.MINUTES,
new SynchronousQueue<>(),
new BasicThreadFactory.Builder().namingPattern("thread-%d").build());
public static void main(String[] args) {
CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier = new CyclicBarrier(10);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
threadPool.execute(() -> {
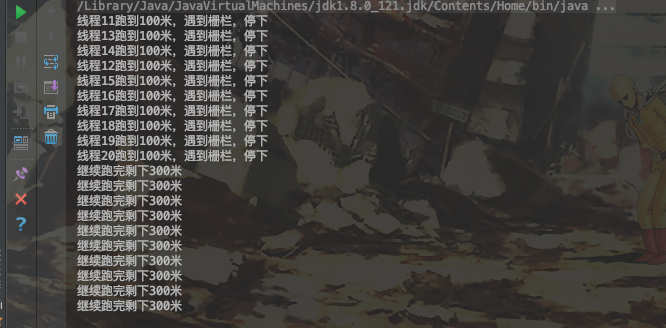
System.out.println("线程" + Thread.currentThread().getId() + "跑到100米,遇到栅栏,停下");
try {
cyclicBarrier.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (BrokenBarrierException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("继续跑完剩下300米");
});
}
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}
应用场景
还用上面CountDownLatch的例子,
同事A需要执行任务A,进行A类数据的收集
同事B需要执行任务B,进行B类数据的收集
项目经理需要等到A和B的数据都收集齐之后,进行统计,然后向上汇报。
public class CyclicBarrierDemo2 {
private static final ExecutorService threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(50, 100,
5, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<>(),
new BasicThreadFactory.Builder().namingPattern("thread-%d").build());
private static volatile boolean flag = false;
public static void main(String[] args) {
CyclicBarrier cb = new CyclicBarrier(2);
// 收集数据A
threadPool.execute(new TaskA(cb));
// 收集数据B
threadPool.execute(new TaskB(cb));
threadPool.shutdown();
}
static class TaskA implements Runnable {
private CyclicBarrier cb;
public TaskA(CyclicBarrier cb) {
this.cb = cb;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
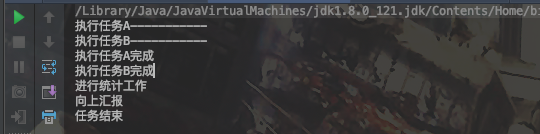
System.out.println("执行任务A-----------");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
System.out.println("执行任务A完成");
cb.await();
if(!flag){
flag = true;
System.out.println("进行统计工作");
System.out.println("向上汇报");
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (BrokenBarrierException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
static class TaskB implements Runnable {
private CyclicBarrier cb;
public TaskB(CyclicBarrier cb) {
this.cb = cb;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println("执行任务B-----------");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(7);
System.out.println("执行任务B完成");
cb.await();
if(!flag){
flag = true;
System.out.println("进行统计工作");
System.out.println("向上汇报");
System.out.println("任务结束");
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (BrokenBarrierException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
运行结果
Java核心复习 —— J.U.C 并发工具类的更多相关文章
- Java核心复习——J.U.C AbstractQueuedSynchronizer
第一眼看到AbstractQueuedSynchronizer,通常都会有这几个问题. AbstractQueuedSynchronizer为什么要搞这么一个类? 这个类是干什么的.有什么用? 这个类 ...
- Java核心复习——J.U.C LinkedBlockingQueue源码分析
参考文档 LinkedBlockingQueue和ArrayBlockingQueue的异同
- Java核心复习——J.U.C ArrayBlockingQueue源码分析
介绍 依赖关系 源码 构造方法 public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity) { this(capacity, false);//默认构造非公平的有界队列 } pub ...
- Java并发指南9:AQS共享模式与并发工具类的实现
一行一行源码分析清楚 AbstractQueuedSynchronizer (三) 转自:https://javadoop.com/post/AbstractQueuedSynchronizer-3 ...
- Java并发编程-并发工具类及线程池
JUC中提供了几个比较常用的并发工具类,比如CountDownLatch.CyclicBarrier.Semaphore. CountDownLatch: countdownlatch是一个同步工具类 ...
- Java并发(十六):并发工具类——Exchanger
Exchanger(交换者)是一个用于线程间协作的工具类.Exchanger用于进行线程间的数据交换.它提供一个同步点,在这个同步点两个线程可以交换彼此的数据.这两个线程通过exchange方法交换数 ...
- Java并发(十五):并发工具类——信号量Semaphore
先做总结: 1.Semaphore是什么? Semaphore(信号量)是用来控制同时访问特定资源的线程数量,它通过协调各个线程,以保证合理的使用公共资源. 把它比作是控制流量的红绿灯,比如XX马路要 ...
- Java并发(十四):并发工具类——CountDownLatch
先做总结: 1.CountDownLatch 是什么? CountDownLatch 允许一个或多个线程等待其他线程(不一定是线程,某个操作)完成之后再执行. CountDownLatch的构造函数接 ...
- Java并发(十三):并发工具类——同步屏障CyclicBarrier
先做总结 1.CyclicBarrier 是什么? CyclicBarrier 的字面意思是可循环使用(Cyclic)的屏障(Barrier).它要做的事情是,让一组线程到达一个屏障(也可以叫同步点) ...
随机推荐
- SR开启时LOG_MODE必须是normal
SR开启时LOG_MODE必须是normal 需要一个初始化备份,
- S3C2440 gpio + main
相关文章:http://blog.csdn.net/zhangxuechao_/article/details/77990854 举例 start.S .globl _start _start: /* ...
- stm32 CAN通信 TJA1040
CAN协议特点 1.多主控制 所有单元都可以发送消息,根据标识符(Identifier简称ID)决定优先级.仲裁获胜(被判定为优先级最高)的单元可继续发送消息,仲裁失利的单元则立刻停止发送而进行接收工 ...
- Cknife流量分析
本文首发:https://<img src=1 onerror=\u006coc\u0061tion='j\x61v\x61script:\x61lert\x281\x29'>testde ...
- [Abp vNext微服务实践] - 框架分析
一.简介 abp vNext新框架的热度一直都很高,于是最近上手将vNext的微服务Demo做了一番研究.我的体验是,vNext的微服务架构确实比较成熟,但是十分难以上手,对于没有微服务开发经验的.n ...
- 数组中的reduce
reduce方法第一次对我的感觉是很鸡肋,但是深入了解,才发现其中的奥妙,是个非常强大且实用的方法 var arr = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]; var sum = arr.reduce( ( ...
- 使用DateTimeFormatter替换线程不安全的SimpleDateFormat
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/baofeidyz/article/details/81307478 如何让SimpleDateFormat保持安全运行? 方案一 每次都去new这种 ...
- 【恐怖的数组模拟】Secret Poems - HihoCoder - 1632
Secret Poems - HihoCoder - 1632 图一 图二 Following the order indicated by arrows, you can get “THISISAV ...
- String字符串常量池简介
直接贴代码---> public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { /** * 为了提升字符串的访问效率,在程序中使用了 ...
- ask confirm shell
#/bin/bash BASEDIR=$(cd $() && pwd) cd $BASEDIR>/dev/null usage="Usage: $0 -o/--org ...
