[Scikit-learn] 1.5 Generalized Linear Models - SGD for Classification
NB: 因为softmax,NN看上去是分类,其实是拟合(回归),拟合最大似然。
多分类参见:[Scikit-learn] 1.1 Generalized Linear Models - Logistic regression & Softmax
感知机采用的是形式最简单的梯度
Perceptron and SGDClassifier share the same underlying implementation.In fact, Perceptron() is equivalent to SGDClassifier(loss=”perceptron”, eta0=1, learning_rate=”constant”, penalty=None).
1.5. Stochastic Gradient Descent
- 1.5.1. Classification
- 1.5.2. Regression
- 1.5.3. Stochastic Gradient Descent for sparse data
- 1.5.4. Complexity
- 1.5.5. Tips on Practical Use
- 1.5.6. Mathematical formulation
- 1.5.7. Implementation details
损失函数
需要一些背景知识,参见斯坦福 CS231n - CNN for Visual Recognition 2 - lecture3
参考:斯坦福CS231n - CNN for Visual Recognition 2 - lecture3 Optimization
一、Loss function 计算
Linear SVM classifier的一个例子。
(1) 计算损失函数:Multiclass SVM loss
一个批次,三张图片,分别得到如下的预测值;而后计算loss。

与"另外两个"的比较:
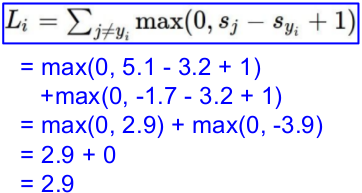
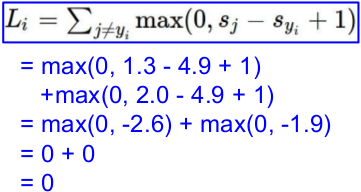
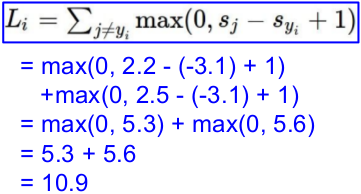
L = (2.9 + 0 + 10.9)/3
= 4.6
(2) 正则化

典型例子说服你:我们当然prefer后一个,w2 。
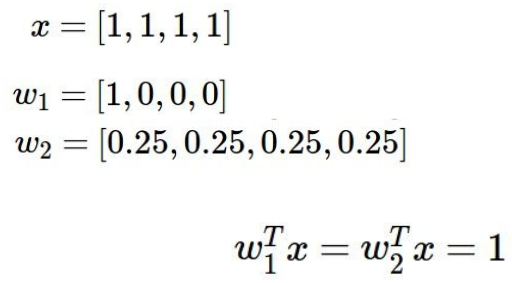
二、其他loss function
Ref: Loss functions for classification

三、loss计算对比
(a) Softmax classifier 的 Softmax's Loss 计算:

(b) Linear SVM classifier 的 hinge loss 计算:
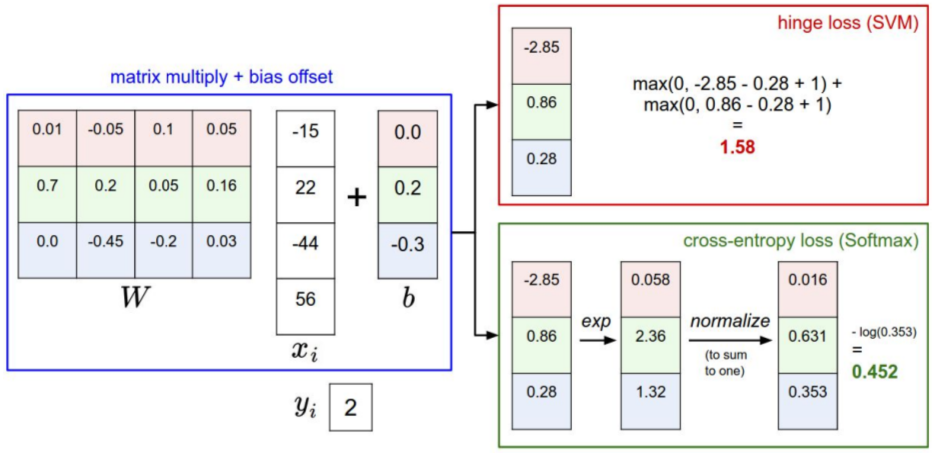

通过该演示体会:http://vision.stanford.edu/teaching/cs231n-demos/linear-classify/
梯度下降
一、逻辑回归
两种损失函数
第一步,逻辑回归的损失函数可以是“得分差”,当然也可以是其他。
第二步,利用“得分差”来进行梯度下降,进行参数优化。
常见有选择两种损失函数,如下:
(1)最小二乘损失函数:逻辑回归与梯度下降法全部详细推导
(2)交叉熵损失函数:机器学习算法 --- 逻辑回归及梯度下降(正统策略)
两个函数接口
Softmax参见:[Scikit-learn] 1.1 Generalized Linear Models - Logistic regression & Softmax
LogisticRegression (交叉熵损失,迭代) versus SGDClassifier(loss="log")
the major difference is the optimization algorithm:
Question: Liblinear/Coordinate Descent vs. Stochastic Gradient Descent.
问题:线性梯度下降 vs 随机梯度下降
If your problem is high dimensional (10K or more) and you have a large
number of examples (100K or more) you should choose the latter -
otherwise, LogisticRegression should be fine.高维,更高的数据:随机梯度下降
反之:Liblinear/Coordinate梯度下降
迭代即可,
Both are not proper multinomial logistic regression models;LogisticRegression does not care and simply computes the probability
estimates of each OVR classifier and normalized to make sure they sum
to one. You could do the same for SGDClassifier(loss='log') but you
have to implement it on your own. You should be aware of the fact that
SGDClassifier(n_jobs > 1) uses multiple processes, thus, if your
dataset (``X``) is too large (more than 50% of your RAM) you'll run
into troubles.
二、梯度下降实践
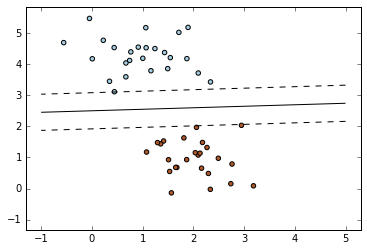
SGD + Linear SVM classifier
=========================================
SGD: Maximum margin separating hyperplane
========================================= Plot the maximum margin separating hyperplane within a two-class
separable dataset using a linear Support Vector Machines classifier
trained using SGD.
"""
print(__doc__) import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.linear_model import SGDClassifier
from sklearn.datasets.samples_generator import make_blobs # we create 50 separable points
X, Y = make_blobs(n_samples=50, centers=2, random_state=0, cluster_std=0.60)
# 生成样本(上),即刻训练(下)
# fit the model
clf = SGDClassifier(loss="hinge", alpha=0.01, n_iter=200, fit_intercept=True)
clf.fit(X, Y) # plot the line, the points, and the nearest vectors to the plane
xx = np.linspace(-1, 5, 10)
yy = np.linspace(-1, 5, 10) X1, X2 = np.meshgrid(xx, yy)
Z = np.empty(X1.shape)
for (i, j), val in np.ndenumerate(X1):
x1 = val
x2 = X2[i, j]
p = clf.decision_function([[x1, x2]])
Z[i, j] = p[0]
levels = [-1.0, 0.0, 1.0]
linestyles = ['dashed', 'solid', 'dashed']
colors = 'k'
plt.contour(X1, X2, Z, levels, colors=colors, linestyles=linestyles)
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=Y, cmap=plt.cm.Paired) plt.axis('tight')
plt.show()
Result:
SGDClassifier 的重要参数
具体的损失函数可以通过 loss 参数来设置。SGDClassifier 支持以下几种损失函数:
loss="hinge": (soft-margin) linear Support Vector Machine,loss="modified_huber": smoothed hinge loss,loss="log": logistic regression,- and all regression losses below.
上述中前两个损失函数lazy的,它们只有在某个样本违反了margin(间隔)限制才会更新模型参数,这样的训练过程非常有效,并且可以应用在稀疏模型上,甚至当使用了L2罚项的时候。
具体的罚项可以通过 penalty 参数。SGD支持一下几种罚项:
penalty="l2": L2 norm penalty oncoef_.penalty="l1": L1 norm penalty oncoef_.penalty="elasticnet": Convex combination of L2 and L1;(1 - l1_ratio) * L2 + l1_ratio * L1.
- 默认的设置是
penalty="l2"。L1罚项会导致稀疏的解,使大多数稀疏为0。弹性网络解决了当属性高度相关情况下L1罚项的不足。参数l1_ratio控制 L1 和 L2 罚项的凸组合。
三、多类分类
SGDClassifier 通过组合多个“one versus all(OVA)”形式的二分类器来支持多类分类。
"Softmax 回归 vs. k 个二元分类器 —— 这一选择取决于你的类别之间是否互斥"
对于  类中每个类别,二分类器通过判别该类和其它
类中每个类别,二分类器通过判别该类和其它  类来学习。
类来学习。
通过随机梯度下降解线性分类问题。
"""
========================================
Plot multi-class SGD on the iris dataset
======================================== Plot decision surface of multi-class SGD on iris dataset.
The hyperplanes corresponding to the three one-versus-all (OVA) classifiers
are represented by the dashed lines. """
print(__doc__) import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.linear_model import SGDClassifier # import some data to play with
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data[:, :2] # we only take the first two features. We could
# avoid this ugly slicing by using a two-dim dataset
y = iris.target
colors = "bry" # shuffle 洗牌
idx = np.arange(X.shape[0])
np.random.seed(13)
np.random.shuffle(idx)
X = X[idx]
y = y[idx] # standardize
mean = X.mean(axis=0)
std = X.std(axis=0)
X = (X - mean) / std h = .02 # step size in the mesh clf = SGDClassifier(alpha=0.001, n_iter=100).fit(X, y) # create a mesh to plot in
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1
y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() + 1
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h),
np.arange(y_min, y_max, h)) # Plot the decision boundary. For that, we will assign a color to each
# point in the mesh [x_min, x_max]x[y_min, y_max].
Z = clf.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
# Put the result into a color plot
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
cs = plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, cmap=plt.cm.Paired)
plt.axis('tight') # Plot also the training points
for i, color in zip(clf.classes_, colors):
idx = np.where(y == i)
plt.scatter(X[idx, 0], X[idx, 1], c=color, label=iris.target_names[i],
cmap=plt.cm.Paired)
plt.title("Decision surface of multi-class SGD")
plt.axis('tight') # Plot the three one-against-all classifiers
xmin, xmax = plt.xlim()
ymin, ymax = plt.ylim()
coef = clf.coef_
intercept = clf.intercept_ def plot_hyperplane(c, color):
def line(x0):
return (-(x0 * coef[c, 0]) - intercept[c]) / coef[c, 1] plt.plot([xmin, xmax], [line(xmin), line(xmax)],
ls="--", color=color) for i, color in zip(clf.classes_, colors):
plot_hyperplane(i, color)
plt.legend()
plt.show()
Result:

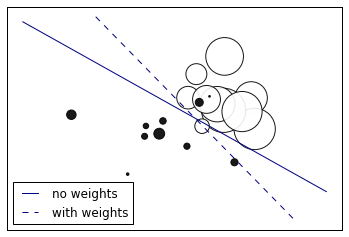
四、考虑权重的二分类
"""
=====================
SGD: Weighted samples
===================== Plot decision function of a weighted dataset, where the size of points
is proportional to its weight.
"""
print(__doc__) import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import linear_model # we create 20 points
np.random.seed(0)
X = np.r_[np.random.randn(10, 2) + [1, 1], np.random.randn(10, 2)]
y = [1] * 10 + [-1] * 10
sample_weight = 100 * np.abs(np.random.randn(20))
# and assign a bigger weight to the last 10 samples
sample_weight[:10] *= 10 # plot the weighted data points
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(-4, 5, 500), np.linspace(-4, 5, 500))
plt.figure()
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, s=sample_weight, alpha=0.9, cmap=plt.cm.bone) #散点图 ## fit the unweighted model
clf = linear_model.SGDClassifier(alpha=0.01, n_iter=100)
clf.fit(X, y)
Z = clf.decision_function(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
no_weights = plt.contour(xx, yy, Z, levels=[0], linestyles=['solid']) ## fit the weighted model
clf = linear_model.SGDClassifier(alpha=0.01, n_iter=100)
clf.fit(X, y, sample_weight=sample_weight)
Z = clf.decision_function(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
samples_weights = plt.contour(xx, yy, Z, levels=[0], linestyles=['dashed']) plt.legend([no_weights.collections[0], samples_weights.collections[0]],
["no weights", "with weights"], loc="lower left") plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
plt.show()
Result:
End.
[Scikit-learn] 1.5 Generalized Linear Models - SGD for Classification的更多相关文章
- [Scikit-learn] 1.5 Generalized Linear Models - SGD for Regression
梯度下降 一.亲手实现“梯度下降” 以下内容其实就是<手动实现简单的梯度下降>. 神经网络的实践笔记,主要包括: Logistic分类函数 反向传播相关内容 Link: http://pe ...
- [Scikit-learn] 1.1 Generalized Linear Models - Logistic regression & Softmax
二分类:Logistic regression 多分类:Softmax分类函数 对于损失函数,我们求其最小值, 对于似然函数,我们求其最大值. Logistic是loss function,即: 在逻 ...
- 广义线性模型(Generalized Linear Models)
前面的文章已经介绍了一个回归和一个分类的例子.在逻辑回归模型中我们假设: 在分类问题中我们假设: 他们都是广义线性模型中的一个例子,在理解广义线性模型之前需要先理解指数分布族. 指数分布族(The E ...
- Andrew Ng机器学习公开课笔记 -- Generalized Linear Models
网易公开课,第4课 notes,http://cs229.stanford.edu/notes/cs229-notes1.pdf 前面介绍一个线性回归问题,符合高斯分布 一个分类问题,logstic回 ...
- [Scikit-learn] 1.1 Generalized Linear Models - from Linear Regression to L1&L2
Introduction 一.Scikit-learning 广义线性模型 From: http://sklearn.lzjqsdd.com/modules/linear_model.html#ord ...
- Popular generalized linear models|GLMM| Zero-truncated Models|Zero-Inflated Models|matched case–control studies|多重logistics回归|ordered logistics regression
============================================================== Popular generalized linear models 将不同 ...
- Regression:Generalized Linear Models
作者:桂. 时间:2017-05-22 15:28:43 链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/xingshansi/p/6890048.html 前言 本文主要是线性回归模型,包括: ...
- Generalized Linear Models
作者:桂. 时间:2017-05-22 15:28:43 链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/xingshansi/p/6890048.html 前言 主要记录python工具包:s ...
- [Scikit-learn] 1.1 Generalized Linear Models - Comparing various online solvers
数据集分割 一.Online learning for 手写识别 From: Comparing various online solvers An example showing how diffe ...
随机推荐
- springmvc,hibernate整合时候出现Cannot load JDBC driver class 'com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
原因:不清楚是什么原因,哪位知道可以给我留言,不胜感激! 解决方法: 1.把mysql的驱动包放到你项目的WEB-INF目录下的lib目录中2.要mysql的驱动包放在tomcat/lib目录下
- WCF错误处理
介绍 WCF(Windows Communication Foundation) -异常处理:一般Exception的处理,FaultException和FaultException<T> ...
- ES使用org.elasticsearch.client.transport.NoNodeAvailableException: No node available
1) 端口错 client = new TransportClient().addTransportAddress(new InetSocketTransportAddress(ipAddress, ...
- python----四种内置数据结构(dict、list、tuple、set)
1.dict 无序,可更改 2.tuple 有序,不可更改 3.list 有序,可更改(增加,删除) 4.set 无序,可能改 {元素1,元素2,元素3.....}和字典一样都是用大括号定义,不过不同 ...
- email.py
import os import argparse import yaml import smtplib import csv from email.mime.multipart import MIM ...
- 006_STM32程序移植之_SYN6288语音模块
1. 测试环境:STM32C8T6 2. 测试模块:SYN6288语音模块 3. 测试接口: SYN6288语音模块: VCC------------------3.3V GND----------- ...
- 威尔逊定理x
威尔逊定理 在初等数论中,威尔逊定理给出了判定一个自然数是否为素数的充分必要条件.即:当且仅当p为素数时:( p -1 )! ≡ -1 ( mod p ),但是由于阶乘是呈爆炸增长的,其结论对于实际操 ...
- 通过zabbix来监控树莓派
安装zabbix-agent(4.0版本) 配置zabbix-agent(使用主动模式) 使用zabbix-sender(主动推送自定义数据) 以下 执行命令和相关配置文件: wget https:/ ...
- JVM备忘点(1.8以前)
1.内存结构 左边两个线程共享,右边三个线程私有. 方法区:.class文件的类信息.常量.static变量.即时编译器编译后的代码(动态代理).HotSpot将方法区称为永久代 堆:分为新生代和老年 ...
- P3469 割点的应用
https://www.luogu.org/problem/P3469 题目就是说封锁一个点,会导致哪些点(对)连不通: 用tarjan求割点,如果这个点是割点,那么不能通行的点对数就是(乘法法则)儿 ...
