Android 4 学习(18):搜索
参考《Professional Android 4 Development》
搜索
通过下面这几种方式可以给应用程序添加搜索功能:
- Search Bar

- Search View

- Quick Search Box

可搜索的Content Provider
首先,要在res./xml目录下创建一个xml文件,例如:
<?xml version=”1.0” encoding=”utf-8”?>
<searchable xmlns:android=”http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android” android:label=”@string/app_name” android:hint=”@string/search_hint”>
</searchable>
其中,Label一般是应用程序的名称。
为应用程序创建Search Activity
Search Activity和普通的Activity不同,它是一直在back stack的栈顶,每次有新的search activity创建时,不会有将其简单的入栈,因为用户是不会希望按返回键时返回自己前面的查询结果。为了表明该Activity可以被搜索,需要将android.intent.action.SEARCH加入到自己的Intent Filter中,同时需要将前面创建的searchable的xml文件加到meta-data标签中:
<activity android:name=”.DatabaseSkeletonSearchActivity” android:label=”Element Search” android:launchMode=”singleTop”>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name=”android.intent.action.SEARCH” />
<category android:name=”android.intent.category.DEFAULT” />
</intent-filter>
<meta-data android:name=”android.app.searchable” android:resource=”@xml/searchable” />
</activity>
用户进行搜索后,可以在搜索结果中继续搜索,而这种操作会生成新的Intent,而这些Intent可以通过onNewIntent handler来处理:
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// Get the launch Intent
parseIntent(getIntent());
}
@Override
protected void onNewIntent(Intent intent) {
super.onNewIntent(intent);
parseIntent(getIntent());
}
private void parseIntent(Intent intent) {
// If the Activity was started to service a Search request, extract the search query.
if (Intent.ACTION_SEARCH.equals(intent.getAction())) {
String searchQuery = intent.getStringExtra(SearchManager.QUERY);
// Perform the search
performSearch(searchQuery);
}
}
设置默认的Serach Provider
在应用程序中,最好设置一个Activity,让所有的搜索结果都从这个Activity中出来,设置方法也简单,将下面的配置加到程序配置中就可以了:
<meta-data android:name=”android.app.default_searchable” android:value=”.DatabaseSkeletonSearchActivity” />
使用Cursor Loader的Search Activity示例
import android.app.ListActivity;
import android.app.LoaderManager;
import android.app.SearchManager;
import android.content.ContentUris;
import android.content.CursorLoader;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.Loader;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.net.Uri;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.SimpleCursorAdapter;
public class DatabaseSkeletonSearchActivity extends ListActivity implements LoaderManager.LoaderCallbacks<Cursor> {
private static String QUERY_EXTRA_KEY = “QUERY_EXTRA_KEY”;
private SimpleCursorAdapter adapter;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// Create a new adapter and bind it to the List View
adapter = new SimpleCursorAdapter(this, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, null, new String[] { MyContentProvider.KEY_COLUMN_1_NAME }, new int[] { android.R.id.text1 }, 0);
setListAdapter(adapter);
// Initiate the Cursor Loader
getLoaderManager().initLoader(0, null, this);
// Get the launch Intent
parseIntent(getIntent());
}
@Override
protected void onNewIntent(Intent intent) {
super.onNewIntent(intent);
parseIntent(getIntent());
}
private void parseIntent(Intent intent) {
// If the Activity was started to service a Search request, extract the search query.
if (Intent.ACTION_SEARCH.equals(intent.getAction())) {
String searchQuery = intent.getStringExtra(SearchManager.QUERY);
// Perform the search
performSearch(searchQuery);
}
}
// Execute the search.
private void performSearch(String query) {
// Pass the search query as an argument to the Cursor Loader
Bundle args = new Bundle();
args.putString(QUERY_EXTRA_KEY, query);
// Restart the Cursor Loader to execute the new query.
getLoaderManager().restartLoader(0, args, this);
}
public Loader<Cursor> onCreateLoader(int id, Bundle args) {
String query = “0”;
// Extract the search query from the arguments.
if (args != null)
query = args.getString(QUERY_EXTRA_KEY);
// Construct the new query in the form of a Cursor Loader.
String[] projection = {MyContentProvider.KEY_ID, MyContentProvider.KEY_COLUMN_1_NAME};
String where = MyContentProvider.KEY_COLUMN_1_NAME + “ LIKE \”%” + query + “%\””;
String[] whereArgs = null;
String sortOrder = MyContentProvider.KEY_COLUMN_1_NAME + “ COLLATE LOCALIZED ASC”;
// Create the new Cursor loader.
return new CursorLoader(this, MyContentProvider.CONTENT_URI, projection, where, whereArgs, sortOrder);
}
public void onLoadFinished(Loader<Cursor> loader, Cursor cursor) {
// Replace the result Cursor displayed by the Cursor Adapter with the new result set.
adapter.swapCursor(cursor);
}
public void onLoaderReset(Loader<Cursor> loader) {
// Remove the existing result Cursor from the List Adapter.
adapter.swapCursor(null);
}
}
大部分情况下,我们需要响应对搜索结果的click事件,因此需要重写onListItemClick方法:
@Override
protected void onListItemClick(ListView listView, View view, int position, long id) {
super.onListItemClick(listView, view, position, id);
// Create a URI to the selected item.
Uri selectedUri = ContentUris.withAppendedId(MyContentProvider.CONTENT_URI, id);
// Create an Intent to view the selected item.
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW);
intent.setData(selectedUri);
// Start an Activity to view the selected item.
startActivity(intent);
}
使用Search View Widget
Android 3.0后推出了Search View Widget以替代Search Activity。将Search View绑定到searchable activity中,首先要获取searchableInfo:
// Use the Search Manager to find the SearchableInfo related to this Activity.
SearchManager searchManager = (SearchManager)getSystemService(Context.SEARCH_SERVICE);
SearchableInfo searchableInfo = searchManager.getSearchableInfo(getComponentName());
// Bind the Activity’s SearchableInfo to the Search View
SearchView searchView = (SearchView)findViewById(R.id.searchView);
searchView.setSearchableInfo(searchableInfo);
本地Android Content Provider
Android中提供了一些本地的Content Provider,包括下面这些:
- Media Store
- Browser
- Contacts Contract
- Calendar
- Call Log
使用Media Store Content Provider
MediaStore类有Audio,Video和Image子类,这些子类又有含有uri信息的子类。每个子类中uri信息是这么存储的:
- MediaStore.<mediatype>.Media.EXTERNAL_CONTENT_URI
- MediaStore.<mediatype>.Media.INTERNAL_CONTENT_URI
下面是一个示例:
// Get a Cursor over every piece of audio on the external volume,
// extracting the song title and album name.
String[] projection = new String[] {
MediaStore.Audio.AudioColumns.ALBUM,
MediaStore.Audio.AudioColumns.TITLE
};
Uri contentUri = MediaStore.Audio.Media.EXTERNAL_CONTENT_URI;
Cursor cursor = getContentResolver().query(contentUri, projection, null, null, null);
// Get the index of the columns we need.
int albumIdx = cursor.getColumnIndexOrThrow(MediaStore.Audio.AudioColumns.ALBUM);
int titleIdx = cursor.getColumnIndexOrThrow(MediaStore.Audio.AudioColumns.TITLE);
// Create an array to store the result set.
String[] result = new String[cursor.getCount()];
// Iterate over the Cursor, extracting each album name and song title.
while (cursor.moveToNext()) {
// Extract the song title.
String title = cursor.getString(titleIdx);
// Extract the album name.
String album = cursor.getString(albumIdx);
result[cursor.getPosition()] = title + “ (“ + album + “)”;
}
// Close the Cursor.
cursor.close();
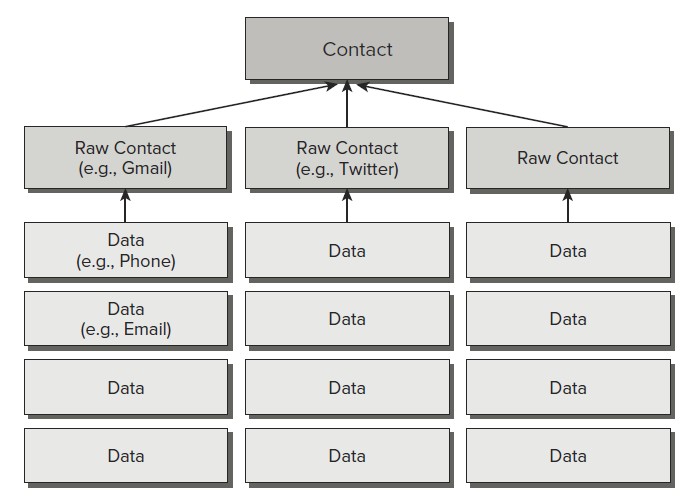
使用Contacts Contract Content Provider
Contacts Contract Provider使用三层模型存储数据:
Android 4 学习(18):搜索的更多相关文章
- Android Animation学习(二) ApiDemos解析:基本Animatiors使用
Animator类提供了创建动画的基本结构,但是一般使用的是它的子类: ValueAnimator.ObjectAnimator.AnimatorSet ApiDemos中Animation部分是单独 ...
- Android:学习AIDL,这一篇文章就够了(下)
前言 上一篇博文介绍了关于AIDL是什么,为什么我们需要AIDL,AIDL的语法以及如何使用AIDL等方面的知识,这一篇博文将顺着上一篇的思路往下走,接着介绍关于AIDL的一些更加深入的知识.强烈建议 ...
- Android WiFiDirect 学习(二)——Service Discovery
Service Discovery 简介 在Android WifiDirect学习(一 )中,简单介绍了如何使用WifiDirect进行搜索——连接——传输. 这样会有一个问题,那就是你会搜索到到附 ...
- Android 数字签名学习笔记
Android 数字签名学习笔记 在Android系统中,所有安装到系统的应用程序都必有一个数字证书,此数字证书用于标识应用程序的作者和在应用程序之间建立信任关系,如果一个permission的pro ...
- Android 布局学习之——Layout(布局)具体解释二(常见布局和布局參数)
[Android布局学习系列] 1.Android 布局学习之--Layout(布局)具体解释一 2.Android 布局学习之--Layout(布局)具体解释二(常见布局和布局參数) ...
- 我的Android 4 学习系列之数据库和Content Provider
目录 创建数据库和使用SQLite 使用Content Provider.Cusor和Content Value来存储.共享和使用应用程序数据 使用Cursor Loader异步查询Content P ...
- 我的Android 4 学习系列之文件、保存状态和首选项
目录 使用Shared Preference 保留简单的应用程序数据 保存回话间的Activity实例数据 管理应用程序首选项和创建Preference Screen 保存并加载文件以及管理本地文件系 ...
- Android 自定义支持快速搜索筛选的选择控件(一)
Android 自定义支持快速搜索筛选的选择控件 项目中遇到选择控件选项过多,需要快速查找匹配的情况. 做了简单的Demo,效果图如下: 源码地址:https://github.com/whieenz ...
- Android JNI学习(四)——JNI的常用方法的中文API
本系列文章如下: Android JNI(一)——NDK与JNI基础 Android JNI学习(二)——实战JNI之“hello world” Android JNI学习(三)——Java与Nati ...
随机推荐
- python爬虫入门(6)-Scrapy基本使用
源码:链接:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1dEK82hb 密码:9flo 创建项目 scrapy startpro ...
- Vmware无法正常打开
VMware的问题 VMware总是搞一些事情,比如隔三差五就打不开了.那么怎么办呢?以前总要把Vm的安装程序重新开始一遍,然后选择修复 但是呢?这样太麻烦了,前几月做web开发的时候接触了Apach ...
- 【剑指offer】n个骰子的点数,C++实现
# 题目 # 思路 # 代码
- 使用 MSBuild 响应文件 (rsp) 来指定 dotnet build 命令行编译时的大量参数
在为开源项目 easiwin/MSTestEnhancer 进行持续集成编译时,需要在编译命令中传入较多的参数.这对于新接手此项目的人来说,成本还是高了一点儿.本文将介绍 MSBuild 响应文件 ( ...
- Ecel 粘贴图片并调整大小,移到底层
Sub Click() ActiveSheet.Pictures.Paste.Select Selection.ShapeRange.ScaleWidth 1.4, msoTrueSelection. ...
- 【数据库】sql连表查询
SQL总结 连表查询 连接查询包括合并.内连接.外连接和交叉连接,如果涉及多表查询,了解这些连接的特点很重要. 只有真正了解它们之间的区别,才能正确使用. 1.Union UNION 操作符用于合并两 ...
- STMM32 ‘&’ 操作
if(0x04 == (new_cfg&0x04)){ sys_cfg_msg.pps_cfg = ; cn_save_data[cn_save_index_stp].hash= ; sys_ ...
- 【转】MFC对话框和控件
原文网址:http://www.cnblogs.com/tiwlin/archive/2013/05/08/3067966.html 对话框和控件 对话框是Windows应用程序中一种常用的资源,其主 ...
- (二)Fiddler抓取Firefox、Chrome浏览器上的https协议
Fiddler抓取Firefox.Chrome浏览器上的https协议 安装Fiddler后默认只抓取http协议,如果是https协议的话,浏览器就会提示"您的链接并不安全". ...
- 修改配置文件matplotlibrc,让Matplotlib显示中文
matplotlib默认不支持中文显示,网上的解决办法有好多种,但是大多数都是通过在代码中指定字体,虽然也能实现,但是多出那么几行代码让人觉得很恶心. 本文介绍一种通过修改配置文件matplotlib ...
