Exception (2) Java Exception Handling
The Java programming language uses exceptions to handle errors and other exceptional events.An exception is an event that occurs during the execution of a program that disrupts the normal flow of instructions.
- Java Exception Handling Overview
- Exception Handling Keywords
- Exception Hierarchy
- Useful Exception Methods
- Creating Custom Exception Classes
Java Exception Handling Overview
Java Exception handling framework is very robust and easy to understand and use. Exception can arise from different kind of situations such as wrong data entered by user, hardware failure, network connection failure, Database server down etc.
Java being an object oriented programming language, whenever an error occurs while executing a statement, creates an exception object and then the normal flow of the program halts and JRE tries to find someone that can handle the raised exception. The exception object contains a lot of debugging information such as method hierarchy, line number where the exception occurred, type of exception etc. When the exception occurs in a method, the process of creating the exception object and handing it over to runtime environment is called “throwing the exception”.
Once runtime receives the exception object, it tries to find the handler for the exception. Exception Handler is the block of code that can process the exception object. The logic to find the exception handler is simple – starting the search in the method where error occurred, if no appropriate handler found, then move to the caller method and so on. So if methods call stack is A->B->C and exception is raised in method C, then the search for appropriate handler will move from C->B->A. If appropriate exception handler is found, exception object is passed to the handler to process it. The handler is said to be “catching the exception”. If there are no appropriate exception handler found then program terminates printing information about the exception.
Note that Java Exception handling is a framework that is used to handle runtime errors only, compile time errors are not handled by exception handling framework.
Exception Handling Keywords
Java provides specific keywords for exception handling purposes.
- throw – We know that if any exception occurs, an exception object is getting created and then Java runtime starts processing to handle them. Sometime we might want to generate exception explicitly in our code, for example in a user authentication program we should throw exception to client if the password is null. throw keyword is used to throw exception to the runtime to handle it.
- throws – When we are throwing any exception in a method and not handling it, then we need to use throws keyword in method signature to let caller program know the exceptions that might be thrown by the method. The caller method might handle these exceptions or propagate it to it’s caller method using throws keyword. We can provide multiple exceptions in the throws clause and it can be used with main() method also.
- try-catch – We use try-catch block for exception handling in our code. try is the start of the block and catch is at the end of try block to handle the exceptions. We can have multiple catch blocks with a try and try-catch block can be nested also. catch block requires a parameter that should be of type Exception.
- finally – finally block is optional and can be used only with try-catch block. Since exception halts the process of execution, we might have some resources open that will not get closed, so we can use finally block. finally block gets executed always, whether exception occurred or not.
Let’s see a simple programing showing exception handling in java.
package cn.zno.exceptions; import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException; public class Deal { public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException,
IOException {
try {
ariseTest(-1);
ariseTest(-2);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
System.out.println("Releasing resources");
}
ariseTest(1);
} static void ariseTest(int code) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException {
if (code < 0) {
throw new FileNotFoundException("code: " + code);
} else {
throw new IOException("code: " + code);
}
} }
Output of above program is:
java.io.FileNotFoundException: code: -
at cn.zno.exceptions.Deal.ariseTest(Deal.java:)
at cn.zno.exceptions.Deal.main(Deal.java:)
Exception in thread "main" java.io.IOException: code:
Releasing resources
at cn.zno.exceptions.Deal.ariseTest(Deal.java:)
at cn.zno.exceptions.Deal.main(Deal.java:)
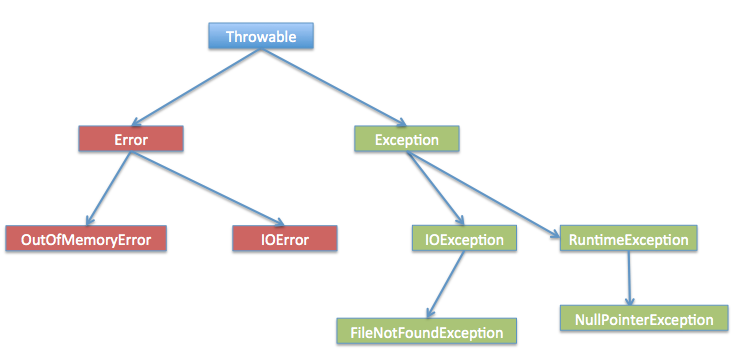
Exception Hierarchy
As stated earlier, when any exception is raised an exception object is getting created. Java Exceptions are hierarchical and inheritance is used to categorize different types of exceptions. Throwable is the parent class of Java Exceptions Hierarchy and it has two child objects – Error and Exception. Exceptions are further divided into checked exceptions and runtime exception.
- Errors Errors are exceptional scenarios that are out of scope of application and it’s not possible to anticipate and recover from them, for example hardware failure, JVM crash or out of memory error. That’s why we have a separate hierarchy of errors and we should not try to handle these situations. Some of the common Errors are OutOfMemoryError and StackOverflowError.
- Checked Exceptions Checked Exceptions are exceptional scenarios that we can anticipate in a program and try to recover from it, for example FileNotFoundException. We should catch this exception and provide useful message to user and log it properly for debugging purpose. Exception is the parent class of all Checked Exceptions and if we are throwing a checked exception, we must catch it in the same method or we have to propagate it to the caller using throws keyword.
- Runtime Exception Runtime Exceptions are cause by bad programming, for example trying to retrieve an element from the Array. We should check the length of array first before trying to retrieve the element otherwise it might throw ArrayIndexOutOfBoundException at runtime. RuntimeException is the parent class of all runtime exceptions. If we are throwing any runtime exception in a method, it’s not required to specify them in the method signature throws clause. Runtime exceptions can be avoided with better programming.
Useful Exception Methods
Exception and all of it’s subclasses doesn’t provide any specific methods and all of the methods are defined in the base class Throwable. The exception classes are created to specify different kind of exception scenarios so that we can easily identify the root cause and handle the exception according to it’s type. Throwable class implements Serializable interface for interoperability.
Some of the useful methods of Throwable class are:
- public synchronized Throwable getCause() Returns the cause of this throwable.
- public String getLocalizedMessage() Creates a localized description of this throwable. Subclasses may override this method in order to produce a locale-specific message. For subclasses that do not override this method, the default implementation returns the same result as getMessage().
- public String getMessage() Returns the detail message string of this throwable and the message can be provided while creating the exception through it’s constructor.
- public void printStackTrace() Prints this throwable and its backtrace to the standard error stream.
- public String toString() This method returns the information about Throwable in String format, the returned String contains the name of Throwable class and localized message.
Creating Custom Exception Classes
Java provides a lot of exception classes for us to use but sometimes we may need to create our own custom exception classes to notify the caller about specific type of exception with appropriate message and any custom fields we want to introduce for tracking, such as error codes. For example, let’s say we write a method to process only text files, so we can provide caller with appropriate error code when some other type of file is sent as input.
MyException.java
package cn.zno.exceptions;
public class MyException extends Exception {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private ErrorCode errorCode = ErrorCode.UNKNOWN;
public MyException(String message, ErrorCode errorCode) {
super(message);
this.errorCode = errorCode;
}
public ErrorCode getErrorCode() {
return errorCode;
}
public enum ErrorCode {
BAD_FILE_TYPE, FILE_NOT_FOUND_EXCEPTION, FILE_CLOSE_EXCEPTION, UNKNOWN
}
}
Deal.java
package cn.zno.exceptions;
import cn.zno.exceptions.MyException.ErrorCode;
public class Deal {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
processFile();
} catch (MyException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println(e.getErrorCode());
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
static void processFile() throws MyException {
throw new MyException("Bad File Type, notify user", ErrorCode.BAD_FILE_TYPE);
}
}
cn.zno.exceptions.MyException: Bad File Type, notify user
at cn.zno.exceptions.Deal.processFile(Deal.java:)
at cn.zno.exceptions.Deal.main(Deal.java:)
BAD_FILE_TYPE
Bad File Type, notify user
Notice that we can have a separate method to process different types of error codes that we get from different methods, some of them gets consumed because we might not want to notify user for that or some of them we will throw back to notify user for the problem.
Here I am extending Exception so that whenever this exception is being produced, it has to be handled in the method or returned to the caller program, if we extends RuntimeException, there is no need to specify it in the throws clause. This is a design decision but I always like checked exceptions because I know what exceptions I can get when calling any method and take appropriate action to handle them.
Exception (2) Java Exception Handling的更多相关文章
- Exception (3) Java exception handling best practices
List Never swallow the exception in catch block Declare the specific checked exceptions that your me ...
- Java exception handling best practices--转载
原文地址:http://howtodoinjava.com/2013/04/04/java-exception-handling-best-practices/ This post is anothe ...
- Java AOP nested exception is java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: org/aopalliance/aop/Advice || Error creating bean with name 'org.springframework.aop.aspectj.AspectJPointcutAdvisor#0' 两个异常解决办法
贴出applicationContext.xml <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans ...
- nested exception is java.lang.RuntimeException: Error parsing Mapper XML. Cause: java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Result Maps collection already contains value for
org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCreationException: Error creating bean with name 'daoSupport': ...
- myeclipse启动tomcat会出现 a java exception has occured错误 的解决方法
在浏览器中可以打开tomcat,结果在myeclipse启动tomcat会出现 a java exception has occured错误 ,之后出现一个Classloader.class的文件,关 ...
- Spring 整合 Flex (BlazeDS)无法从as对象 到 Java对象转换的异常:org.springframework.beans.ConversionNotSupportedException: Failed to convert property value of type 'java.util.Date' to required type 'java.sql.Timestamp' for property 'wfsj'; nested exception is java.lang.Ill
异常信息如下: org.springframework.beans.ConversionNotSupportedException: Failed to convert property value ...
- jedis:exception is java.lang.VerifyError: Bad type on operand stack
项目中需要用到缓存,经过比较后,选择了redis,客户端使用jedis连接,也使用到了spring提供的spring-data-redis.配置正确后启动tomcat,发现如下异常: ======== ...
- Spring系列: 使用aop报错:nested exception is java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: org/aspectj/weaver/reflect/ReflectionWorld$Refle
写了个最简单的aop例子 配置文件如下 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns ...
- Could not load resource factory class [Root exception is java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: org.apache.tomcat.dbcp.dbcp.BasicDataSourceFactory]
WARNING: Failed to register in JMX: javax.naming.NamingException: Could not load resource factory cl ...
随机推荐
- POJ1159解题心得
题目:http://poj.org/problem?id=1159 刚开始,从样例的特征去思考.总让我从回文数的角度去思考,想出几个方案,可都用了数据去检验,发现不行.如:ABCDDCB,BACDCA ...
- [知识整理]Linux系统WIFI知识的一些整理
前段时间接触了wifi,主要是在linux系统下做预研.开发.本文根据个人收集资料及研究经验做了一些基本入门级别的引子,旨在对wifi有一个很基础的入门的认知,比如知道wifi模块硬件接口有哪些,了解 ...
- 【UVa】11882 Biggest Number(dfs+剪枝)
题目 题目 分析 典型搜索,考虑剪枝. 统计一下联通分量. 1.本位置能够达到所有的点的数量加上本已有的点,还没有之前的结果长,直接返回. 2.当本位置能够达到所有的点的数量加上本已有的点与之 ...
- poj 3518 Prime Gap
Prime Gap Time Limit: 5000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 7392 Accepted: 4291 Descrip ...
- [Python] Regular Expressions
1. regular expression Regular expression is a special sequence of characters that helps you match or ...
- NLTK与自然语言处理基础
NLTK (Natural Language Toolkit) NTLK是著名的Python自然语言处理工具包,但是主要针对的是英文处理.NLTK配套有文档,有语料库,有书籍. NLP领域中最常用的一 ...
- clutter recoder
cin >> ch; cin.get(ch);区别读取输入是否忽略空格.制表等; char ch; ; cout << "Enter characters;enter ...
- pipenv 简要指南
pipenv 简要指南 pipenv是requests作者的一个项目, 整合了virtualenv, pip, pipfile, 用于更方便地为项目建立虚拟环境并管理虚拟环境中的第三方模块. 安装 直 ...
- 我的Linux之路——windows10用WMware安装CentOS6.9 虚拟机详细步骤
出自:http://blog.51cto.com/13438667/2059926 一.安装环境 windows10操作系统物理机VMware Workstation 软件(可以在网上下载)CentO ...
- Elasticsearch-PHP 搜索操作
搜索操作 好吧,这不叫elasticsearch的不劳而获!让我们来谈谈PHP客户端中的搜索操作. 客户端允许你通过REST API访问所有的查询和公开的参数,尽可能的遵循命名规则.让我们来看一些例子 ...
