机器学习实战python3 决策树ID3
代码及数据:https://github.com/zle1992/MachineLearningInAction
决策树
优点:计算复杂度不高,输出结果易于理解,对中间值的缺失不敏感,可以处理不相关特征数据。
缺点:可能会产生过度匹配问题。
适用数据类型:数值型和标称型。
创建分支的伪代码函数createBranch()如下所示:
检测数据集中的每个子项是否属于同一分类:
if so return 类标签;
Else
寻找划分数据集的最好特征
划分数据集
创建分支节点
for 每个划分的子集
调用函数createBranch并增加返回结果到分支节点中
return 分支节点
上面的伪代码createBranch是一个递归函数,在倒数第二行直接调用了它自己。后面我们
寄把上面的伪代码转换为Python代码,这里我们需要进一步了解算法是如何划分数据集的。
1决策树构造
1.1创建数据
def createDataSet():
dataSet = [[1, 1, 'yes'],
[1, 1, 'yes'],
[1, 0, 'no'],
[0, 1, 'no'],
[0, 1, 'no']]
labels = ['no surfacing','flippers']
#change to discrete values
return dataSet, labels
1.2信息增益
如果看不明白什么是信息增益(information gain)和墒( entropy ),请不要着急—创门自
诞生的那一天起,就注定会令世人十分费解。
嫡定义为信息的期望值,在明晰这个概念之前,我们必须知道信息的定义。如果待分类的事
务可能划分在多个分类之中,则符号xi,的信息定义为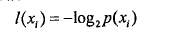
其中P(xi)是选择该分类的概率。
为了计算嫡,我们需要计算所有类别所有可能值包含的信息期望值,通过下面的公式得到:

其中n是分类的数目。
程序:计算给定数据集的香农熵
def calcShannonEnt(dataSet):
numEntries = len(dataSet) #Data 的大小N,N行
labelCount = {}#字典存储 不同类别的个数
for featVec in dataSet :
currentLabel = featVec[-1] #每行的最后一个是类别
if currentLabel not in labelCount.keys():
labelCount[currentLabel] = 0
labelCount[currentLabel] += 1 #原书缩进错误!!!
shannonEnt = 0.0
for key in labelCount:
prob = float(labelCount[key])/numEntries
shannonEnt -= prob *math.log(prob,2) #熵最后外面有个求和符号 !!!
return shannonEnt
1.3划分数据集
程序:划分数据集
def splitDataSet(dataSet,axis,value):
retDataSet = []
for featVec in dataSet:
if featVec[axis] == value:
#去掉axis 这一列
reducedFeatVec = featVec[:axis]
reducedFeatVec.extend(featVec[axis+1: ])
retDataSet.append(reducedFeatVec)
return retDataSet
划分数据集之后,使得划分后的纯度越小。选择信息增益最大的划分。
程序:选择最好的数据集划分方式
def chooseBestFeatureTopSplit(dataSet):
#列数 = len(dataset[0])
#行数 = len(dataset)
numFeatures = len(dataSet[0]) -1 #最后一列是标签
baseEntropy = calcShannonEnt(dataSet) #所有数据的信息熵
bestInfoGainn = 0.0
bestFeature = -1
for i in range(numFeatures):#遍历不同的属性
featList = [example[i] for example in dataSet] #取出每一列
uniqueVals = set(featList)
newEntropy = 0.0
for value in uniqueVals:#在第i个属性里,遍历第i个属性所有不同的属性值
subDataSet = splitDataSet(dataSet,i,value) #划分数据
prob = len(subDataSet)/float(len(dataSet)) #len([[]]) 行数
newEntropy += prob *calcShannonEnt(subDataSet)
infoGain = baseEntropy - newEntropy
if(infoGain > bestInfoGainn):
bestInfoGainn = infoGain
bestFeature = i
return bestFeature
1.4递归构建决策树
def majorityCnt(classList):
classCount ={}
for vote in classList:
if vote not in classCount.keys():
classCount[vote] = 0
classCount[vote] += 1 classCount = sorted(classCount.items(),key=operator.itemgetter(1),reverse=True) #与python2 不同!!!!!!python3 的字典items 就是迭代对象
return classCount[0][0] #返回的是字典第一个元素的key 即 类别标签
def createTree(dataSet,labels):
#mytree 是一个字典,key 是属性值,val 是类别或者是另一个字典,
#如果val 是类标签,则该子节点就是叶子节点
#如果val是另一个数据字典,则该节点是一个判断节点
classList = [example[-1] for example in dataSet]
if classList.count(classList[0]) == len(classList): #类别完全相同,停止划分
return classList[0]
if len(dataSet[0])==1: #完全划分
return majorityCnt(classList)
bestFeat = chooseBestFeatureTopSplit(dataSet)
bestFeatLabel = labels[bestFeat]
myTree = {bestFeatLabel:{}}
del(labels[bestFeat]) #
featValues = [example[bestFeat] for example in dataSet] # 某属性的所有取值
uniqueVals = set(featValues)
for value in uniqueVals :
subLabels = labels[:]
myTree[bestFeatLabel][value] = createTree(splitDataSet(dataSet,bestFeat,value),subLabels)
return myTree
2在Python中使用Matplotlib注解绘制树形图
2.1使用文本注解绘制树节点
#定义文本框跟箭头格式
decisionNode = dict(boxstyle="sawtooth", fc="0.8")
leafNode = dict(boxstyle="round4", fc="0.8")
arrow_args = dict(arrowstyle="<-")
def plotNode(nodeTxt, centerPt, parentPt, nodeType):
createPlot.ax1.annotate(nodeTxt, xy=parentPt, xycoords='axes fraction',
xytext=centerPt, textcoords='axes fraction',
va="center", ha="center", bbox=nodeType, arrowprops=arrow_args )
2.2构造注解树
程序:获得叶子节点数与深度
def getNumLeafs(myTree):
numLeafs = 0
firstStr = list(myTree)[0]#找到第一个节点
secondDict = myTree[firstStr] #第二个节点
for key in secondDict.keys(): #第二节点的字典的key
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__=='dict': #判断第二节点是否为字典
numLeafs += getNumLeafs(secondDict[key]) #第二节点是字典 ,递归调用getNum
else :numLeafs += 1 #第二节点不是字典,说明此节点是最后一个节点
return numLeafs def getTreeDepth(myTree):
maxDepth = 0
firstStr = list(myTree)[0]#找到第一个节点
secondDict = myTree[firstStr] #第二个节点
for key in secondDict.keys(): #第二节点的字典的key
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__=='dict': #判断第二节点是否为字典
thisDepth = 1 + getTreeDepth(secondDict[key]) #第二节点是字典 ,递归调用getNum
else :thisDepth = 1 #第二节点不是字典,说明此节点是最后一个节点
if thisDepth > maxDepth: maxDepth =thisDepth
return maxDepth
程序:plotTree
def plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, txtString):#在父子节点间填充文本信息
xMid = (parentPt[0]-cntrPt[0])/2.0 + cntrPt[0]
yMid = (parentPt[1]-cntrPt[1])/2.0 + cntrPt[1]
createPlot.ax1.text(xMid, yMid, txtString, va="center", ha="center", rotation=30) def plotTree(myTree, parentPt, nodeTxt):
numLeafs = getNumLeafs(myTree) #叶子节点个数
depth = getTreeDepth(myTree) #树的高度
firstStr = list(myTree)[0] #!!!!!!!与py2不同
cntrPt = (plotTree.xOff + (1.0 + float(numLeafs))/2.0/plotTree.totalW, plotTree.yOff) #按照叶子结点个数划分x轴
plotMidText(cntrPt,parentPt,nodeTxt)
plotNode(firstStr,cntrPt,parentPt,decisionNode)
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff - 1.0/plotTree.totalD #plotTree.yOff 全局变量
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__ =='dict':
plotTree(secondDict[key],cntrPt,str(key))# 第二节点是字典,递归调用plotTree
else:
plotTree.xOff = plotTree.xOff + 1.0/plotTree.totalW #x方向计算结点坐标
plotNode(secondDict[key], (plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, leafNode)#绘制子节点
plotMidText((plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, str(key))#添加文本信息
plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff + 1.0/plotTree.totalD #下次重新调用时恢复y
def createPlot(inTree):
fig = plt.figure(1, facecolor='white')
fig.clf()
axprops = dict(xticks=[], yticks=[])
createPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111, frameon=False, **axprops) # no ticks
# createPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111, frameon=False) #ticks for demo puropses
plotTree.totalW = float(getNumLeafs(inTree))
plotTree.totalD = float(getTreeDepth(inTree))
plotTree.xOff = -0.5 / plotTree.totalW
plotTree.yOff = 1.0
plotTree(inTree, (0.5, 1.0), '')
plt.show()
程序:测试
def retrieveTree(i):
listOfTrees =[{'no surfacing': {0: 'no', 1: {'flippers': {0: 'no', 1: 'yes'}}}},
{'no surfacing': {0: 'no', 1: {'flippers': {0: {'head': {0: 'no', 1: 'yes'}}, 1: 'no'}}}}
]
return listOfTrees[i]
if __name__ == '__main__':
tree = retrieveTree(0)
createPlot(tree)
3测试算法:使用决策树执行分类
使用决策树预测隐形眼镜类型
程序:使用决策树分类函数
def classify(inputTree,featLabels,testVec):
firstStr = list(inputTree.keys())[0]
secondDict = inputTree[firstStr]
featIndex = featLabels.index(firstStr) #将标签转化成索引
for key in secondDict.keys():
if testVec[featIndex] == key:
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__=='dict':
classLabel = classify(secondDict[key],featLabels,testVec)
else : classLabel = secondDict[key]#到达叶子节点,返回标签
return classLabel
程序:使用pickle保存模型
def storeTree(inputTree,filename):
with open(filename,'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(inputTree,f)
def grabTree(filename):
with open(filename,'rb') as f:
t = pickle.load(f)
return t
程序:主程序
if __name__ == '__main__':
#
dataSet,labels = createDataSet()
tree = createTree(dataSet,labels)
storeTree(tree,"tree.model")
tree = grabTree("tree.model")
treePlotter.createPlot(tree) #读取txt文件,预测隐形眼镜的类型
with open('lenses.txt') as f:
lenses = [inst.strip().split('\t') for inst in f.readlines()]
lensesLabels = ['age','prescript','astigmastic','tearRate']
lensesTree = createTree(lenses,lensesLabels)
treePlotter.createPlot(lensesTree)
机器学习实战python3 决策树ID3的更多相关文章
- 【Python机器学习实战】决策树和集成学习(一)
摘要:本部分对决策树几种算法的原理及算法过程进行简要介绍,然后编写程序实现决策树算法,再根据Python自带机器学习包实现决策树算法,最后从决策树引申至集成学习相关内容. 1.决策树 决策树作为一种常 ...
- 机器学习实战python3 K近邻(KNN)算法实现
台大机器技法跟基石都看完了,但是没有编程一直,现在打算结合周志华的<机器学习>,撸一遍机器学习实战, 原书是python2 的,但是本人感觉python3更好用一些,所以打算用python ...
- 机器学习实战:决策树的存储读写文件报错(Python3)
错误原因:pickle模块存储的是二进制字节码,需要以二进制的方式进行读写 1. 报错一:TypeError: write() argument must be str, not bytes 将决策树 ...
- 【Python机器学习实战】决策树和集成学习(二)——决策树的实现
摘要:上一节对决策树的基本原理进行了梳理,本节主要根据其原理做一个逻辑的实现,然后调用sklearn的包实现决策树分类. 这里主要是对分类树的决策进行实现,算法采用ID3,即以信息增益作为划分标准进行 ...
- 【Python机器学习实战】决策树与集成学习(七)——集成学习(5)XGBoost实例及调参
上一节对XGBoost算法的原理和过程进行了描述,XGBoost在算法优化方面主要在原损失函数中加入了正则项,同时将损失函数的二阶泰勒展开近似展开代替残差(事实上在GBDT中叶子结点的最优值求解也是使 ...
- 03机器学习实战之决策树CART算法
CART生成 CART假设决策树是二叉树,内部结点特征的取值为“是”和“否”,左分支是取值为“是”的分支,右分支是取值为“否”的分支.这样的决策树等价于递归地二分每个特征,将输入空间即特征空间划分为有 ...
- 【Python机器学习实战】决策树与集成学习(四)——集成学习(2)GBDT
本打算将GBDT和XGBoost放在一起,但由于涉及内容较多,且两个都是比较重要的算法,这里主要先看GBDT算法,XGBoost是GBDT算法的优化和变种,等熟悉GBDT后再去理解XGBoost就会容 ...
- 【Python机器学习实战】决策树与集成学习(六)——集成学习(4)XGBoost原理篇
XGBoost是陈天奇等人开发的一个开源项目,前文提到XGBoost是GBDT的一种提升和变异形式,其本质上还是一个GBDT,但力争将GBDT的性能发挥到极致,因此这里的X指代的"Extre ...
- 机器学习实战 - python3 学习笔记(一) - k近邻算法
一. 使用k近邻算法改进约会网站的配对效果 k-近邻算法的一般流程: 收集数据:可以使用爬虫进行数据的收集,也可以使用第三方提供的免费或收费的数据.一般来讲,数据放在txt文本文件中,按照一定的格式进 ...
随机推荐
- 《Linux实验要求》
实验 1:登录和使用基本的 Linux 命令 实验环境: 安装了 Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.0 可运行系统,并且是成功验证系统. 有另外一个无特权用户 student,密码 ...
- 集成学习AdaBoost算法——学习笔记
集成学习 个体学习器1 个体学习器2 个体学习器3 ——> 结合模块 ——>输出(更好的) ... 个体学习器n 通常,类似求平均值,比最差的能好一些,但是会比最好的差. 集成可能提 ...
- JavaScript入门之函数返回值
函数返回值 <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head lang="en"> <meta charset="UTF ...
- JavaScript------表单约束验证DOM方法
<input id="id1" type="number" min="100" max="300" require ...
- Hadoop单机安装配置过程:
1. 首先安装JDK,必须是sun公司的jdk,最好1.6版本以上. 最后java –version 查看成功与否. 注意配置/etc/profile文件,在其后面加上下面几句: export JAV ...
- tomcat启动后,页面浏览时报错 Unable to compile class for JSP的解决方案
转:tomcat启动后,页面浏览时报错 Unable to compile class for JSP的解决方案 检查tomcat与web工程对应版本,tomcat中对应版本的jar包拷贝到web工程 ...
- ArcGIS 相同要素类的多Shp文件或多要素合并
- @Override错误
导入一个项目,项目所有类报 @Override 有错误,去掉就不报错了,原因?在 Java Compiler 将 Enable project specific setting 选中 然后再选择1 ...
- 170330、Spring中你不知道的注入方式
前言 在Spring配置文件中使用XML文件进行配置,实际上是让Spring执行了相应的代码,例如: 使用<bean>元素,实际上是让Spring执行无参或有参构造器 使用<prop ...
- 基于注解的形式配置Bean
基于注解的方式配置Bean:也就说我们在每个Bean的类名前面注解一下,Spring会自动帮我们扫描Bean放进IOC容器中 I基于注解的方式配置Bean(没有依赖关系的Bean)有两个步骤: 1组件 ...
