Ural Sport Programming Championship 2015
Ural Sport Programming Championship 2015
A - The First Day at School
题目描述:给出课程安排,打印一个课程表。
solution
暴力模拟。
B - Maths
题目描述:给定一个数\(n\),找出一个序列\(a_i\)满足\(\forall i \in [2, n], \sum_{j=1}^{j \leq i} a_j\) 有\(a_i\)个约数。
solution
暴力搜索,发现和不会超过\(2 \times 10^6\), 数字不会超过\(200\),而且直接搜索即可很快求出答案。
时间复杂度:\(O(能过)\)
C - History
题目描述:求出从\(A\)年到\(B\)年中有\(1\)~\(12\)个黑色星期五的分别有多少年。
solution
显然有循环,模拟一下发现2800年左右有循环,因此只需要求出循环中每一年有多少个黑色星期五,然后求答案,求一下前缀和即可。
时间复杂度:\(O(2800 \times 12)\)
D - Chemistry
题目描述:给出\(n\)个杯子,每个杯子有一升的水,每次从一个杯子向另一个杯子倒水,使得后一个杯子的水变成原来的两倍,求出一种操作方案,使得最终有一个杯子有\(m\)升水,或无解。
solution
不会,本来想着好像二分那样弄就行,但发现会有副产品利用的情况,而且情况有些复杂。
E - 3D-modeling
题目描述:给定空间中的两条线段,问是否存在一条直线,使得一条线段绕直线转某个角度即可得到另一条直线,求出这条直线和对应的角度。
solution
不会
F - Physics
题目描述:有两个\(v(t)\)函数\(v_1, v_2\),这两个函数都是折线函数,令\(h(t)=max(v_1(t), v_2(t)), g(t)=min(v_1(t), v_2(t))\),给出\(h(t), g(t)\)的起点、终点、转折点,求出\(v_1(t), v_2(t)\),使得两个函数所代表的位移相等。\(v_1, v_2\)重合点不超过\(30\)个。
solution
求出所有的重合点,假设开始时\(v_1=h, v_2=g\),而只有遇到重合点的时候,\(v_1, v_2\)才有可能交换,即重合点将函数分成了若干段,每一段中的函数不能相交,因此可以分开前后两个部分进行搜索,然后判断是否存在一种方案使得合起来的位移等于总位移的一半。
注意:有可能\(h(t1) \neq g(t1)\),但\(v_1(t1) = v_2(t1)\)
时间复杂度:\(O(2 \times 2^{15})\)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;typedef long long LL;const int maxn=int(2e6)+100;int T, n, m;pair<int, int> h[maxn], g[maxn], tmp[maxn];vector< pair<int, int> > v1, v2, cp;map<LL, int> cnt;LL sumh[maxn], sumg[maxn];int block;bool vis[maxn];void read(){scanf("%d", &T);scanf("%d", &n);for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i)scanf("%d%d" , &h[i].first, &h[i].second);scanf("%d", &m);for (int i=1; i<=m; ++i)scanf("%d%d", &g[i].first, &g[i].second);}void crosspoint(){for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i) tmp[i]=h[i];int tmpn=n;n=1;for (int i=2; i<=tmpn; ++i)for (int j=tmp[i-1].first+1; j<=tmp[i].first; ++j)if (LL(j-tmp[i-1].first)*(tmp[i].second-tmp[i-1].second)%(tmp[i].first-tmp[i-1].first)==0)h[++n]=make_pair(j, LL(j-tmp[i-1].first)*(tmp[i].second-tmp[i-1].second)/(tmp[i].first-tmp[i-1].first)+tmp[i-1].second);/*puts("h:");for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i) printf("%d %d\n", h[i].first, h[i].second);*/for (int i=1; i<=m; ++i) tmp[i]=g[i];int tmpm=m;m=1;for (int i=2; i<=tmpm; ++i)for (int j=tmp[i-1].first+1; j<=tmp[i].first; ++j)if (LL(j-tmp[i-1].first)*(tmp[i].second-tmp[i-1].second)%(tmp[i].first-tmp[i-1].first)==0)g[++m]=make_pair(j, LL(j-tmp[i-1].first)*(tmp[i].second-tmp[i-1].second)/(tmp[i].first-tmp[i-1].first)+tmp[i-1].second);/*puts("g:");for (int i=1; i<=m; ++i) printf("%d %d\n", g[i].first, g[i].second);*/for (int i=1, j=1; i<=n && j<=m; ++i){while (j<=m && g[j].first<h[i].first) ++j;if (j>m) continue;if (h[i].first==g[j].first && h[i].second==g[j].second)cp.push_back(h[i]);}if (h[n].second!=g[m].second) cp.push_back(h[n]);/*puts("cp:");for (auto &i:cp) printf("%d %d\n", i.first, i.second);*/}void calc_sum(){block=cp.size();LL s=0;for (int i=2, j=0; i<=n; ++i){while (j<cp.size() && cp[j].first<h[i].first) ++j;s+=LL(h[i-1].second+h[i].second)*(h[i].first-h[i-1].first);if (j>=cp.size()) continue;if (cp[j].first==h[i].first) sumh[j]=s, s=0;}s=0;for (int i=2, j=0; i<=m; ++i){while (j<cp.size() && cp[j].first<g[i].first) ++j;s+=LL(g[i-1].second+g[i].second)*(g[i].first-g[i-1].first);if (j>=cp.size()) continue;if (cp[j].first==g[i].first) sumg[j]=s, s=0;}/*for (int i=0; i<block; ++i) printf("%lld ", sumh[i]);for (int i=0; i<block; ++i) printf("%lld ", sumg[i]);*/}inline LL det(pair<int, int> b, pair<int, int> c, pair<int, int> o){return (b.first-o.first)*(c.second-o.second)-(b.second-o.second)*(c.first-o.first);}void print(LL sett){for (int i=0, j=1, k=1; i<block; ++i){if (sett>>i & 1){while (j<=n && h[j].first<=cp[i].first) v1.push_back(h[j++]);while (k<=m && g[k].first<=cp[i].first) v2.push_back(g[k++]);}else{while (j<=n && h[j].first<=cp[i].first) v2.push_back(h[j++]);while (k<=m && g[k].first<=cp[i].first) v1.push_back(g[k++]);}}for (int i=0; i<v1.size(); ++i) vis[i]=true;for (int i=2; i<v1.size(); ++i)if (det(v1[i-2], v1[i-1], v1[i])==0) vis[i-1]=false;int ans=0;for (int i=0; i<v1.size(); ++i) ans+=vis[i];printf("%d\n", ans);for (int i=0; i<v1.size(); ++i)if (vis[i]) printf("%d %d\n", v1[i].first, v1[i].second);for (int i=0; i<v2.size(); ++i) vis[i]=true;for (int i=2; i<v2.size(); ++i)if (det(v2[i-2], v2[i-1], v2[i])==0) vis[i-1]=false;ans=0;for (int i=0; i<v2.size(); ++i) ans+=vis[i];printf("%d\n", ans);for (int i=0; i<v2.size(); ++i)if (vis[i]) printf("%d %d\n", v2[i].first, v2[i].second);}void solve(){crosspoint();calc_sum();LL total=0;for (int i=0; i<block; ++i) total+=sumh[i]+sumg[i];total/=2;for (int i=0; i<1<<(block/2); ++i){LL s=0;for (int j=0; j<block/2; ++j)if (i>>j & 1) s+=sumh[j];else s+=sumg[j];cnt[s]=i;}for (int i=0; i<1<<(block-block/2); ++i){LL s=0;for (int j=0; j<block-block/2; ++j)if (i>>j & 1) s+=sumh[block/2+j];else s+=sumg[block/2+j];if (cnt.count(total-s)){print(cnt[total-s]|(i<<(block/2)));return;}}}int main(){read();solve();return 0;}
G - Physical Education
题目描述:给定一个数字\(n\),将\(1\)到\(n\)重新排序:按各个位的数字的和从小到大排,相同的按预案数字从小到大排,问排序后的位置与原数字一样的数有多少个。
solution
先做一个数位\(dp\),求出各个位的数字的和各有多少个,然后按这个进行分组,每一组最多只有可能有一个数字的位置与原数字的位置相同,这是因为在同一组中,相邻的数字的差事大于\(1\)的,因此不可能有两个数字的位置与原位置相同,如果有,那么这两个位置之间的数字的差必须都是\(1\)。
如果用新数列减去旧数列,则在同一组中,得到的数列是递增的,而我们要找的是是否存在一个等于零的位置,如果存在,则答案加一。这里可以用二分,每次二分用数位\(dp\)求出和与当前组的和一样的,小于等于某个数的数字有多少个,就可以判断是否存在。
时间复杂度:\(O(81 \times log(10^9) \times 9*10*81)\)
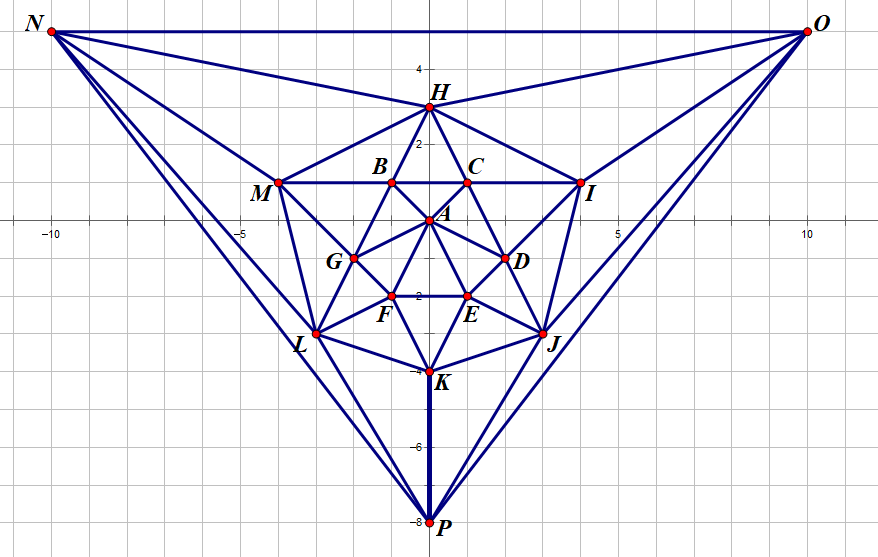
H - Biology
题目描述:在平面上找出\(16\)个点,然后构成一个平面图,使得该图中的简单环超过\(3\times10^5\)个。
solution
直接上图。
J - Urban Geography
题目描述:给出一个图,\(n\)个点,\(m\)条边,选择一些边,使得构成一颗生成树,而且选择的边的权值的最大值与最小值的差最小,输出方案。
solution
用\(LCT\)维护生成树,将边从小到大排序,然后逐条边添加进去,每次添加后把环里面的最小边删掉,更新答案。
时间复杂度:\(O(nlogn)\)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;const int maxn=int(5e4)+100;const int inf=0x7fffffff;struct node{node *son[2], *fa;node *maxid;int value, num;bool reverse;node(){son[0]=son[1]=fa=NULL;maxid=NULL;value=inf;num=0;reverse=false;}void update(){maxid=this;if (son[0] && son[0]->maxid->value<maxid->value) maxid=son[0]->maxid;if (son[1] && son[1]->maxid->value<maxid->value) maxid=son[1]->maxid;}void down(){if (!reverse) return;if (son[0]){son[0]->reverse^=1;swap(son[0]->son[0], son[0]->son[1]);}if (son[1]){son[1]->reverse^=1;swap(son[1]->son[0], son[1]->son[1]);}reverse=false;}void rotate(int id){node *y=fa;node *z=y->fa;fa=z;if (z && (z->son[0]==y || z->son[1]==y)) z->son[z->son[1]==y]=this;y->son[id]=son[id^1];if (son[id^1]) son[id^1]->fa=y;son[id^1]=y;y->fa=this;y->update();update();}void splay(){node *x=this;while (x->fa && (x->fa->son[0]==x || x->fa->son[1]==x)){node *y=x->fa;node *z=y->fa;if (z && (z->son[0]==y || z->son[1]==y)) z->down();y->down(); x->down();if (!z || (z->son[0]!=y && z->son[1]!=y)) x->rotate(y->son[1]==x);else{bool L=z->son[1]==y, R=y->son[1]==x;if (L^R) x->rotate(R), x->rotate(L);else y->rotate(L), x->rotate(R);}}x->down();x->update();}node *expose(){node *x=this;node *y=NULL;for (; x!=NULL; y=x, x=x->fa){x->splay();x->son[1]=y;x->update();}return y;}node *askroot(){node *x=expose();while (x->son[0]) x=x->son[0];x->splay();return x;}void evert(){expose();splay();reverse=true;swap(son[0], son[1]);}void cut(node *x, node *y){x->evert();y->expose();splay();x->fa=y->fa=NULL;}void clear(){son[0]=son[1]=fa=NULL;maxid=NULL;value=inf;num=0;reverse=false;}};struct LINK{int x, y, dis;int num;bool operator < (const LINK b) const{return dis<b.dis;}};int n, m;LINK edge[maxn];node tree[maxn*2];set< pair<int, int> > len;bool vis[maxn];void read(){scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);for (int i=1; i<=m; ++i){edge[i].num=i;scanf("%d%d%d", &edge[i].x, &edge[i].y, &edge[i].dis);}}node *askmin(node *x, node *y){x->evert();y->expose();x->splay();return x->maxid;}void connect(node *x, node *y, int v, int idx){node *z=tree+n+idx;z->value=v;z->num=idx;z->fa=x;y->evert();y->fa=z;}void solve(){sort(edge+1, edge+1+m);int block=n;int minnum=inf;int ans;for (int i=1; i<=m; ++i){node *u=tree+edge[i].x;node *v=tree+edge[i].y;len.insert(make_pair(edge[i].dis, i));if (u->askroot()!=v->askroot())connect(u, v, edge[i].dis, i), block--;else{node *x=askmin(u, v);len.erase(make_pair(x->value, x->num));x->cut(tree+edge[x->num].x, tree+edge[x->num].y);connect(u, v, edge[i].dis, i);}if (block!=1) continue;int tmp=len.begin()->first;if (edge[i].dis-tmp<minnum){minnum=edge[i].dis-tmp;ans=i;}}for (int i=1; i<=n+m; ++i) (tree+i)->clear();for (int i=1; i<=ans; ++i){node *u=tree+edge[i].x;node *v=tree+edge[i].y;vis[i]=true;if (u->askroot()!=v->askroot())connect(u, v, edge[i].dis, i), block--;else{node *x=askmin(u, v);x->cut(tree+edge[x->num].x, tree+edge[x->num].y);vis[x->num]=false;connect(u, v, edge[i].dis, i);}}for (int i=1; i<=m; ++i)if (vis[i]) printf("%d ", edge[i].num);}int main(){read();solve();return 0;}
K - Scholarship
solution
按题目说的做。
Ural Sport Programming Championship 2015的更多相关文章
- German Collegiate Programming Contest 2015 计蒜课
// Change of Scenery 1 #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> ...
- Nordic Collegiate Programming Contest 2015 B. Bell Ringing
Method ringing is used to ring bells in churches, particularly in England. Suppose there are 6 bells ...
- Nordic Collegiate Programming Contest 2015 G. Goblin Garden Guards
In an unprecedented turn of events, goblins recently launched an invasion against the Nedewsian city ...
- Nordic Collegiate Programming Contest 2015 E. Entertainment Box
Ada, Bertrand and Charles often argue over which TV shows to watch, and to avoid some of their fight ...
- Nordic Collegiate Programming Contest 2015 D. Disastrous Downtime
You're investigating what happened when one of your computer systems recently broke down. So far you ...
- 2019-2020 10th BSUIR Open Programming Championship. Semifinal
2019-2020 10th BSUIR Open Programming Championship. Semifinal GYM链接https://codeforces.com/gym/103637 ...
- URAL 1227 Rally Championship(树的直径)(无向图判环)
1227. Rally Championship Time limit: 1.0 secondMemory limit: 64 MB A high-level international rally ...
- Gym100814B Gym100814F Gym100814I(异或) ACM International Collegiate Programming Contest, Egyptian Collegiate Programming Contest (2015) Arab Academy for Science and Technology
今日份的训练题解,今天写出来的题没有昨天多,可能是因为有些事吧... Gym100814B 这个题就是老师改卷子,忘带标准答案了,但是他改了一部分卷子,并且确定自己改的卷子没出错,他想从改过的卷子里把 ...
- ACM Arabella Collegiate Programming Contest 2015 F. Palindrome 并查集
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/gym/100676/attachments 题意: 给一个字符串,有一些约束条件,两个位置要相同,有一些是问号,求最后有多少种方案回文? 分析: ...
随机推荐
- 转---秒杀多线程第五篇 经典线程同步 关键段CS
上一篇<秒杀多线程第四篇 一个经典的多线程同步问题>提出了一个经典的多线程同步互斥问题,本篇将用关键段CRITICAL_SECTION来尝试解决这个问题. 本文首先介绍下如何使用关键段,然 ...
- OSPF协议介绍及配置 (上)
OSPF协议介绍及配置 (上) 一.OSPF概述 回顾一下距离矢量路由协议的工作原理:运行距离矢量路由协议的路由器周期性的泛洪自己的路由表,通过路由的交互,每台路由器都从相邻的路由器学习到路由,并且加 ...
- [BZOJ1195]最短母串
1195: [HNOI2006]最短母串 Time Limit: 10 Sec Memory Limit: 32 MB Description 给定n个字符串(S1,S2,„,Sn),要求找到一个最 ...
- Django之form表单提交并验证
1.提交的时候会报错 2. 需要在setting里面注释掉一句话,关闭跨站请求检查. 3. 注释掉以后,理论上就不报错了.可我还是卡壳了. 4. 通过在网上找方法,修复错误. 原因:表单action字 ...
- unity3D 涂涂乐使用shader实现上色效果
unity3D 涂涂乐使用shader实现上色效果 之前我博文里面发过一个简单的通过截图方式来实现的模型上色方法,但是那个方法不合适商用,因为你需要对的很准确才可以把贴图完美截取下来,只要你手抖了一下 ...
- Linux系统启动详解(一)
本篇主要以Centos为例,讲述整个Linux系统启动过程,包括了grub引导,initramfs流程,/sbin/init执行rc.sysinit及rc的大体流程. 另外,本篇有一个实例来说明,将整 ...
- mac os 启动服务命令 launchctl
参考苹果开发者网址 https://developer.apple.com/library/mac/documentation/MacOSX/Conceptual/BPSystemStartup/Ch ...
- 解题:SCOI 2008 天平
题面 我们很容易想到差分约束,但是我们建出来图之后好像并不好下手,因为我们只能得到砝码间的大小关系,并不能容易地得到每个砝码的具体重量. 于是我们有了一种神奇的思路:既然得不到具体重量我们就不求具体重 ...
- 【bzoj3170】[Tjoi2013]松鼠聚会
3170: [Tjoi2013]松鼠聚会 Time Limit: 10 Sec Memory Limit: 128 MBSubmit: 1670 Solved: 885[Submit][Statu ...
- shell中的引用
By francis_hao Mar 31,2018 引用,用来移除某个字符或单词对于shell的特殊含义 每个元字符对于shell都有特殊含义,可分割单词,如果想使用其本身的含义就需要用到 ...
