Cartographer源码阅读(9):图优化的前端——闭环检测
约束计算
闭环检测的策略:搜索闭环,通过匹配检测是否是闭环,采用了分支定界法。
前已经述及PoseGraph的内容,此处继续。位姿图类定义了pose_graph::ConstraintBuilder constraint_builder_对象。
1.ConstraintBuilder类图
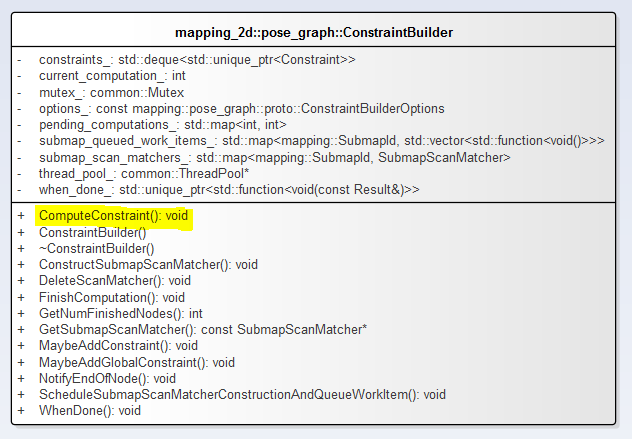
定义了SubmapScanMatcher的键值对。
// Map of already constructed scan matchers by 'submap_id'.
std::map<mapping::SubmapId, SubmapScanMatcher> submap_scan_matchers_ GUARDED_BY(mutex_);
SubmapScanMatcher结构体定义如下:
struct SubmapScanMatcher
{
const ProbabilityGrid* probability_grid;
std::unique_ptr<scan_matching::FastCorrelativeScanMatcher>
fast_correlative_scan_matcher;
};
注意ConstraintBuilder::ComputeConstraint方法,MaybeAddConstraint和MaybeAddGlobalConstraint都调用了该方法。
void ConstraintBuilder::ComputeConstraint(
const mapping::SubmapId& submap_id, const Submap* const submap,
const mapping::NodeId& node_id, bool match_full_submap,
const mapping::TrajectoryNode::Data* const constant_data,
const transform::Rigid2d& initial_relative_pose,
std::unique_ptr<ConstraintBuilder::Constraint>* constraint) {
const transform::Rigid2d initial_pose =
ComputeSubmapPose(*submap) * initial_relative_pose;
const SubmapScanMatcher* const submap_scan_matcher =
GetSubmapScanMatcher(submap_id); // The 'constraint_transform' (submap i <- node j) is computed from:
// - a 'filtered_gravity_aligned_point_cloud' in node j,
// - the initial guess 'initial_pose' for (map <- node j),
// - the result 'pose_estimate' of Match() (map <- node j).
// - the ComputeSubmapPose() (map <- submap i)
float score = .;
transform::Rigid2d pose_estimate = transform::Rigid2d::Identity(); // Compute 'pose_estimate' in three stages:
// 1. Fast estimate using the fast correlative scan matcher.
// 2. Prune if the score is too low.
// 3. Refine.
if (match_full_submap) {
if (submap_scan_matcher->fast_correlative_scan_matcher->MatchFullSubmap(
constant_data->filtered_gravity_aligned_point_cloud,
options_.global_localization_min_score(), &score, &pose_estimate)) {
CHECK_GT(score, options_.global_localization_min_score());
CHECK_GE(node_id.trajectory_id, );
CHECK_GE(submap_id.trajectory_id, );
} else {
return;
}
} else {
if (submap_scan_matcher->fast_correlative_scan_matcher->Match(
initial_pose, constant_data->filtered_gravity_aligned_point_cloud,
options_.min_score(), &score, &pose_estimate)) {
// We've reported a successful local match.
CHECK_GT(score, options_.min_score());
} else {
return;
}
}
{
common::MutexLocker locker(&mutex_);
score_histogram_.Add(score);
} // Use the CSM estimate as both the initial and previous pose. This has the
// effect that, in the absence of better information, we prefer the original
// CSM estimate.
ceres::Solver::Summary unused_summary;
ceres_scan_matcher_.Match(pose_estimate.translation(), pose_estimate,
constant_data->filtered_gravity_aligned_point_cloud,
*submap_scan_matcher->probability_grid,
&pose_estimate, &unused_summary); const transform::Rigid2d constraint_transform =
ComputeSubmapPose(*submap).inverse() * pose_estimate;
constraint->reset(new Constraint{submap_id,
node_id,
{transform::Embed3D(constraint_transform),
options_.loop_closure_translation_weight(),
options_.loop_closure_rotation_weight()},
Constraint::INTER_SUBMAP}); if (options_.log_matches()) {
std::ostringstream info;
info << "Node " << node_id << " with "
<< constant_data->filtered_gravity_aligned_point_cloud.size()
<< " points on submap " << submap_id << std::fixed;
if (match_full_submap) {
info << " matches";
} else {
const transform::Rigid2d difference =
initial_pose.inverse() * pose_estimate;
info << " differs by translation " << std::setprecision()
<< difference.translation().norm() << " rotation "
<< std::setprecision() << std::abs(difference.normalized_angle());
}
info << " with score " << std::setprecision() << . * score << "%.";
LOG(INFO) << info.str();
}
}
这里出现了scan_matching::FastCorrelativeScanMatcher,另一种扫描匹配的方法。论文中介绍的分支定界法就在这个类中实现。
以上FastCorrelativeScanMatcher::Match和FastCorrelativeScanMatcher::MatchFullSubmap方法都调用了FastCorrelativeScanMatcher::MatchWithSearchParameters方法。
FastCorrelativeScanMatcher::MatchWithSearchParameters调用了FastCorrelativeScanMatcher::BranchAndBound方法。
|
Tips:总结一下出现的几种扫描匹配的方法? RealTimeCorrelativeScanMatcher FastCorrelativeScanMatcher |
bool FastCorrelativeScanMatcher::MatchWithSearchParameters(
SearchParameters search_parameters,
const transform::Rigid2d& initial_pose_estimate,
const sensor::PointCloud& point_cloud, float min_score, float* score,
transform::Rigid2d* pose_estimate) const
{
CHECK_NOTNULL(score);
CHECK_NOTNULL(pose_estimate); const Eigen::Rotation2Dd initial_rotation = initial_pose_estimate.rotation();
const sensor::PointCloud rotated_point_cloud = sensor::TransformPointCloud(
point_cloud,
transform::Rigid3f::Rotation(Eigen::AngleAxisf(
initial_rotation.cast<float>().angle(), Eigen::Vector3f::UnitZ())));
const std::vector<sensor::PointCloud> rotated_scans =
GenerateRotatedScans(rotated_point_cloud, search_parameters);
const std::vector<DiscreteScan> discrete_scans = DiscretizeScans(
limits_, rotated_scans,
Eigen::Translation2f(initial_pose_estimate.translation().x(),
initial_pose_estimate.translation().y()));
search_parameters.ShrinkToFit(discrete_scans, limits_.cell_limits()); const std::vector<Candidate> lowest_resolution_candidates =
ComputeLowestResolutionCandidates(discrete_scans, search_parameters);
const Candidate best_candidate = BranchAndBound(
discrete_scans, search_parameters, lowest_resolution_candidates,
precomputation_grid_stack_->max_depth(), min_score);//分支定界法
if (best_candidate.score > min_score) {
*score = best_candidate.score;
*pose_estimate = transform::Rigid2d(
{initial_pose_estimate.translation().x() + best_candidate.x,
initial_pose_estimate.translation().y() + best_candidate.y},
initial_rotation * Eigen::Rotation2Dd(best_candidate.orientation));
return true;
}
return false;
}
2.分支定界法
FastCorrelativeScanMatcher::BranchAndBound,......
Candidate FastCorrelativeScanMatcher::BranchAndBound(
const std::vector<DiscreteScan>& discrete_scans,
const SearchParameters& search_parameters,
const std::vector<Candidate>& candidates, const int candidate_depth,
float min_score) const
{
if (candidate_depth == )
{
// Return the best candidate.
return *candidates.begin();
} Candidate best_high_resolution_candidate(, , , search_parameters);
best_high_resolution_candidate.score = min_score;
for (const Candidate& candidate : candidates)
{
if (candidate.score <= min_score) { break; }
std::vector<Candidate> higher_resolution_candidates;
const int half_width = << (candidate_depth - );
for (int x_offset : {, half_width})
{
if (candidate.x_index_offset + x_offset >
search_parameters.linear_bounds[candidate.scan_index].max_x) {
break;
}
for (int y_offset : {, half_width}) {
if (candidate.y_index_offset + y_offset >
search_parameters.linear_bounds[candidate.scan_index].max_y) {
break;
}
higher_resolution_candidates.emplace_back(
candidate.scan_index, candidate.x_index_offset + x_offset,
candidate.y_index_offset + y_offset, search_parameters);
}
}
ScoreCandidates(precomputation_grid_stack_->Get(candidate_depth - ),
discrete_scans, search_parameters,
&higher_resolution_candidates);
best_high_resolution_candidate = std::max(
best_high_resolution_candidate,
BranchAndBound(discrete_scans, search_parameters,
higher_resolution_candidates, candidate_depth - ,
best_high_resolution_candidate.score));
}
return best_high_resolution_candidate;
}
Cartographer源码阅读(9):图优化的前端——闭环检测的更多相关文章
- Cartographer源码阅读(1):程序入口
带着几个思考问题: (1)IMU数据的使用,如何融合,Kalman滤波? (2)图优化的具体实现,闭环检测的策略? (3)3D激光的接入和闭环策略? 1. 安装Kdevelop工具: http://b ...
- Cartographer源码阅读(3):程序逻辑结构
Cartographer早期的代码在进行3d制图的时候使用了UKF方法,查看现有的tag版本,可以转到0.1.0和0.2.0查看,包含kalman_filter文件夹. 文件夹中的pose_track ...
- Cartographer源码阅读(5):PoseGraph位姿图
PoseGraph位姿图 mapping2D::PoseGraph类的注释: // Implements the loop closure method called Sparse Pose Adju ...
- Cartographer源码阅读(6):LocalTrajectoryBuilder和PoseExtrapolator
LocalTrajectoryBuilder意思是局部轨迹的构建,下面的类图中方法的参数没有画进去. 注意其中的三个类:PoseExtrapolator类,RealTimeCorrelativeSca ...
- Cartographer源码阅读(4):Node和MapBuilder对象2
MapBuilder的成员变量sensor::Collator sensor_collator_; 再次阅读MapBuilder::AddTrajectoryBuilder方法.首先构造了mappin ...
- Cartographer源码阅读(8):imu_tracker
IMU的输入为imu_linear_acceleration 和 imu_angular_velocity 线加速和角速度.最终作为属性输出的是方位四元数. Eigen::Quaterniond ...
- Cartographer源码阅读(2):Node和MapBuilder对象
上文提到特别注意map_builder_bridge_.AddTrajectory(x,x),查看其中的代码.两点: 首先是map_builder_.AddTrajectoryBuilder(...) ...
- Cartographer源码阅读(7):轨迹推算和位姿推算的原理
其实也就是包括两个方面的内容:类似于运动模型的位姿估计和扫描匹配,因为需要计算速度,所以时间就有必要了! 1. PoseExtrapolator解决了IMU数据.里程计和位姿信息进行融合的问题. 该类 ...
- 【原】SDWebImage源码阅读(四)
[原]SDWebImage源码阅读(四) 本文转载请注明出处 —— polobymulberry-博客园 1. 前言 SDWebImage中主要实现了NSURLConnectionDataDelega ...
随机推荐
- RabbitMQ 学习专栏
RabbitMQ 官网:http://www.rabbitmq.com/ 原创博文 1.揭开消息中间件RabbitMQ的神秘面纱 2. RabbitMQ 服务器之下载安装 3. RabbitMQ 之修 ...
- Android PopupWindow 仿微信弹出效果
项目中,我须要PopupWindow的时候特别多,这个东西也特别的好使,所以我今天给大家写一款PopupWindow 仿微信弹出效果.这样大家直接拿到项目里就能够用了! 首先让我们先看效果: 那么我首 ...
- 【Spark深入学习 -15】Spark Streaming前奏-Kafka初体验
----本节内容------- 1.Kafka基础概念 1.1 出世背景 1.2 基本原理 1.2.1.前置知识 1.2.2.架构和原理 1.2.3.基本概念 1.2.4.kafka特点 2.Kafk ...
- ffmpeg中av_log的实现分析
[时间:2017-10] [状态:Open] [关键词:ffmpeg,avutil,av_log, 日志输出] 0 引言 FFmpeg的libavutil中的日志输出的接口整体比较少,但是功能还是不错 ...
- hdoj:2061
#include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; int main() { int n,k; double ...
- 蜕变成蝶~Linux设备驱动中的阻塞和非阻塞I/O
今天意外收到一个消息,真是惊呆我了,博客轩给我发了信息,说是俺的博客文章有特色可以出本书,,这简直让我受宠若惊,俺只是个大三的技术宅,写的博客也是自己所学的一些见解和在网上看到我一些博文以及帖子里综合 ...
- echarts网络拓扑图
option = { title: { text: '' }, tooltip: {}, animationDurationUpdate: 1500, animationEasingUpdate: ' ...
- C# 客户端篇之实现Restful Client开发(RestSharp帮助类)
上篇文章<C# 服务端篇之实现RestFul Service开发(简单实用)>讲解到,如果开发一个简单的Restful风格的Service,也提到了简单创建一个Restful Client ...
- 获取当前目录绝对路径,参考canal run.sh里面的方式
case "`uname`" in Darwin) bin_abs_path=`cd $(dirname $0); pwd` ;; Linux) bin_abs_path=$(re ...
- VMPlayer Ubuntu 16.04 Copy and Paste with Host 主机与宿机之间的复制粘贴
使用Ubuntu的虚拟机时如果不能主机之间进行复制粘粘,会非常非常的不方便,所以我们需要安装vmware tools,使用如下的代码(注意第二句一定要有,不然还是不能复制粘贴): sudo apt-g ...
