spark 算子之RDD
map
| map(func) | Return a new distributed dataset formed by passing each element of the source through a function func. |
返回通过函数func传递源的每个元素形成的新的分布式数据集。通过函数得到一个新的分布式数据集。
var rdd = session.sparkContext.parallelize(1 to 10)
rdd.foreach(println)
println("=========================")
rdd.map(x => (x,1)).foreach(println)
结果:
67891012345
=========================
(6,1)(7,1)(8,1)(9,1)(10,1)(1,1)(2,1)(3,1)(4,1)(5,1)
filter
| filter(func) | Return a new dataset formed by selecting those elements of the source on which funcreturns true. |
通过自定义函数对元素进行过滤
val rdd = session.sparkContext.parallelize(1 to 10)
rdd.foreach(print)
val rdd2 = rdd.filter(_>6)
println("=========================")
rdd2.foreach(print)
结果:
67891012345
=========================
78910
filtMap
| flatMap(func) | Similar to map, but each input item can be mapped to 0 or more output items (so func should return a Seq rather than a single item). |
通过自定义函数把RDD中的每一个元素映射成多个元素,返回一个集合。
val ds = session.sparkContext.textFile("D:/公司/test.txt")
ds.foreach(println)
val ds2 = ds.flatMap(x => {
x.toString().split(":")
})
println("===================")
ds2.foreach(println)
结果:
{ "DEVICENAME": "����4", "LID": 170501310, "ADDRESS": "xxxx", "ID": 230001160 }
===================
{ "DEVICENAME"
"����4", "LID"
170501310, "ADDRESS"
"xxxx", "ID"
230001160 }
mapFunction
| mapPartitions(func) | Similar to map, but runs separately on each partition (block) of the RDD, so func must be of type Iterator<T> => Iterator<U> when running on an RDD of type T. |
类型map.不过是分区进行。类似于批量。
mapPartitionsWithIndex
| mapPartitionsWithIndex(func) | Similar to mapPartitions, but also provides func with an integer value representing the index of the partition, so func must be of type (Int, Iterator<T>) => Iterator<U> when running on an RDD of type T. |
sample
| sample(withReplacement, fraction, seed) | Sample a fraction fraction of the data, with or without replacement, using a given random number generator seed. |
采集一个RDD的随机样本。
其中包含三个参数
replacement 布尔类型,表示是否重样。
fraction 返回的比例数 介于0到1。如原来RDD数10,fraction=0.5,那么将返回一个长度为5的随机RDD。
seed 表示随机比例。默认为long的最大值。如果此值为恒值(不随机),那么返回的RDD相等。
union
| union(otherDataset) | Return a new dataset that contains the union of the elements in the source dataset and the argument. |
将两个RDD合并,不去重。
intersection
| intersection(otherDataset) | Return a new RDD that contains the intersection of elements in the source dataset and the argument. |
返回两个RDD的交集。去重。
var rdd = session.sparkContext.parallelize(1 to 10)
rdd.foreach(println)
val rdd2 = rdd.sample(true, 0.5)
println("==============")
rdd2.foreach(println)
val rdd3 = rdd.intersection(rdd2)
println("==============")
rdd3.foreach(println)
结果:
==============
89955
==============
958
distinct
| distinct([numTasks])) | Return a new dataset that contains the distinct elements of the source dataset. |
对RDD进行去重。参数为任务数。
其内部实现原理对元素进行分组,然后取第一个。
/**
* Return a new RDD containing the distinct elements in this RDD.
*/
def distinct(numPartitions: Int)(implicit ord: Ordering[T] = null): RDD[T] = withScope {
map(x => (x, null)).reduceByKey((x, y) => x, numPartitions).map(_._1)
}
var rdd = session.sparkContext.parallelize(1 to 10)
val rdd2 = rdd.sample(true, 0.5)
rdd2.foreach(print)
println("====================")
val rdd3 = rdd2.distinct(10)
rdd3.foreach(print)
结果:
7792224
==============
4279
groupByKey
| groupByKey([numTasks]) | When called on a dataset of (K, V) pairs, returns a dataset of (K, Iterable<V>) pairs. Note: If you are grouping in order to perform an aggregation (such as a sum or average) over each key, using reduceByKey or aggregateByKey will yield much better performance. Note: By default, the level of parallelism in the output depends on the number of partitions of the parent RDD. You can pass an optional numTasks argument to set a different number of tasks. |
对一个(k,v)对的数据集进行k的分组,并返回一个v的集合。此算子使用前提是一个(k,v)对的RDD。
官方的建议是,如果要进行类似操作,最好使用reduceByKey 或者aggregateByKey 。
相当于group by ,它不可以自定义函数。如果在这个基础上需要做count等运算,需要使用reduceByKey 或者aggregateByKey 。
groupBy
groupBy和groupByKey略有不同。1:groupby可以自定义key;2:在返回值上,groupby返回的是[key,{key:value1,key:value2}],而groupByKey返回的是[key,{value1,value2}]
val seq = Seq[String]("spark", "hadoop", "spark")
val rdd = session.sparkContext.parallelize(seq)
val rdd2 = rdd.map(x => (x, 1)).groupBy(_._1)//默认元素为key,此时同groupByKey,但返回值略有不同
rdd2.foreach(println)
println("==============")
val rdd4 = rdd.map(x => (x, 1)).groupBy(x => {
x._1 + new Random().nextInt(100);//可以自定义key
})
rdd4.foreach(println)
println("==============")
val rdd3 = rdd.map(x => (x, 1)).groupByKey()//默认元素为key
rdd3.foreach(println)
结果:
(spark,CompactBuffer((spark,1), (spark,1)))
(hadoop,CompactBuffer((hadoop,1)))
==============
(spark92,CompactBuffer((spark,1)))
(hadoop72,CompactBuffer((hadoop,1)))
(spark46,CompactBuffer((spark,1)))
==============
(spark,CompactBuffer(1, 1))
(hadoop,CompactBuffer(1))
reduceByKey
| reduceByKey(func, [numTasks]) | When called on a dataset of (K, V) pairs, returns a dataset of (K, V) pairs where the values for each key are aggregated using the given reduce function func, which must be of type (V,V) => V. Like in groupByKey, the number of reduce tasks is configurable through an optional second argument. |
针对一个(K,V)对的RDD,返回一个对K去重的值。这个具体的值是什么样,取决于第一个参数。
val seq = Seq[String]("spark", "hadoop", "spark")
val rdd = session.sparkContext.parallelize(seq)
val rdd2 = rdd.map(x => (x, 1)).reduceByKey(_+_)
rdd2.foreach(println)
结果:
(spark,2)
(hadoop,1)
小结:groupBy groupByKey reduceByKey
1:groupBy可以自定义key;2:在返回值上,groupBy返回的是[key,{key:value1,key:value2}],而groupByKey返回的是[key,{value1,value2}]
2:reduceByKey(func, [numTasks])的第一个参数为自定义函数,可以对结果进行再处理。groupBy([numTasks])和groupByKey([numTasks])都不能自定义函数,如实现wordcount的功能,需额外使用算子或自定义实现。
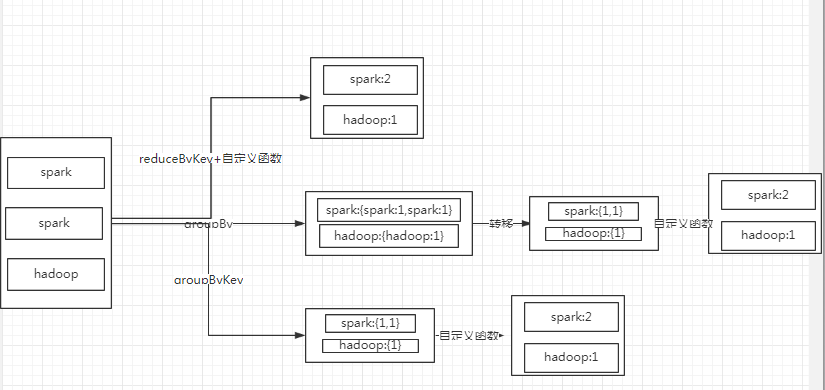
3:reduceByKey和groupByKey内部原理不一样。这一点在官方注释上已经讲得很明白。reduceByKey会经过类似于Map与reduce之间的combiner操作(similarly to a "combiner" in MapReduce.)。会将各个节点上的数据进行合并之后再进行传输。
reduceByKey
/**
* Merge the values for each key using an associative and commutative reduce function. This will
* also perform the merging locally on each mapper before sending results to a reducer, similarly
* to a "combiner" in MapReduce. Output will be hash-partitioned with the existing partitioner/
* parallelism level.
*/
def reduceByKey(func: (V, V) => V): RDD[(K, V)] = self.withScope {
reduceByKey(defaultPartitioner(self), func)
}
groupByKey
/**
* Group the values for each key in the RDD into a single sequence. Allows controlling the
* partitioning of the resulting key-value pair RDD by passing a Partitioner.
* The ordering of elements within each group is not guaranteed, and may even differ
* each time the resulting RDD is evaluated.
*
* @note This operation may be very expensive. If you are grouping in order to perform an
* aggregation (such as a sum or average) over each key, using `PairRDDFunctions.aggregateByKey`
* or `PairRDDFunctions.reduceByKey` will provide much better performance.
*
* @note As currently implemented, groupByKey must be able to hold all the key-value pairs for any
* key in memory. If a key has too many values, it can result in an [[OutOfMemoryError]].
*/
def groupByKey(partitioner: Partitioner): RDD[(K, Iterable[V])] = self.withScope {
// groupByKey shouldn't use map side combine because map side combine does not
// reduce the amount of data shuffled and requires all map side data be inserted
// into a hash table, leading to more objects in the old gen.
val createCombiner = (v: V) => CompactBuffer(v)
val mergeValue = (buf: CompactBuffer[V], v: V) => buf += v
val mergeCombiners = (c1: CompactBuffer[V], c2: CompactBuffer[V]) => c1 ++= c2
val bufs = combineByKeyWithClassTag[CompactBuffer[V]](
createCombiner, mergeValue, mergeCombiners, partitioner, mapSideCombine = false)
bufs.asInstanceOf[RDD[(K, Iterable[V])]]
}

示例一个用三种方法实现经典的wordcount的例子。
val seq = Seq[String]("spark", "hadoop", "spark")
val rdd = session.sparkContext.parallelize(seq)
//reduceByKey
val rdd_reduceByKey = rdd.map((_,1)).reduceByKey(_+_).foreach(println)
//groupby
val rdd_groupby = rdd.map((_,1)).groupBy(_._1).map(x=>{
(x._1,x._2.map(x => {x._2}))
}).map(x => (x._1,x._2.sum)).foreach(println)
//groupByKey
val rdd_groupByKey = rdd.map((_,1)).groupByKey().map(x=>(x._1,x._2.sum)).foreach(println)
结果:
(spark,2)
(hadoop,1)
aggregateByKey
| aggregateByKey(zeroValue)(seqOp, combOp, [numTasks]) | When called on a dataset of (K, V) pairs, returns a dataset of (K, U) pairs where the values for each key are aggregated using the given combine functions and a neutral "zero" value. Allows an aggregated value type that is different than the input value type, while avoiding unnecessary allocations. Like in groupByKey, the number of reduce tasks is configurable through an optional second argument. |
此函数类似于reduceByKey。它提供了三个参数。第一个参数是一个初始值。后两个参数为自定义函数。
在kv对的RDD中,,按key将value进行分组合并,合并时,将每个value和初始值作为seq函数的参数,进行计算,返回的结果作为一个新的kv对,然后再将结果按照key进行合并,最后将每个分组的value传递给combine函数进行计算(先将前两个value进行计算,将返回结果和下一个value传给combine函数,以此类推),将key与计算结果作为一个新的kv对输出。在client模式下,注意设置master的core数。
/**
* a:param1 b:rdd._2
*/
def seqs(a:Int,b:Int) : Int =b def comb(a: Int, b: Int): Int = a+b def aggregateByKey(session : SparkSession){
val seq = Seq[String]("spark", "hadoop", "spark")
val rdd = session.sparkContext.parallelize(seq).map((_,1))
//("spark",1)
rdd.aggregateByKey(2)(seqs, comb).foreach(println)
}
结果:
(spark,2)
(hadoop,1)
sortByKey sortBy
| sortByKey([ascending], [numTasks]) | When called on a dataset of (K, V) pairs where K implements Ordered, returns a dataset of (K, V) pairs sorted by keys in ascending or descending order, as specified in the boolean ascending argument. |
聚合排序。sortBy针对RDD,sortByKey针对(K,V)对的RDD。排序的问题,在client模式下,注意设置master的core数。
val seq = Seq[String]("spark", "hadoop", "apark","spark", "hadoop", "spark")
val rdd = session.sparkContext.parallelize(seq)
rdd.sortBy(x=>x, true,1).foreach(println)
rdd.map((_,1)).sortByKey(true,1).foreach(println)
结果:
apark
hadoop
hadoop
spark
spark
spark
===============
(apark,1)
(hadoop,1)
(hadoop,1)
(spark,1)
(spark,1)
(spark,1)
join leftOuterJoin rightOuterJoin fullOuterJoin
| join(otherDataset, [numTasks]) | When called on datasets of type (K, V) and (K, W), returns a dataset of (K, (V, W)) pairs with all pairs of elements for each key. Outer joins are supported through leftOuterJoin, rightOuterJoin, and fullOuterJoin. |
join相当于inner join。其它参照sql。
cogroup
| cogroup(otherDataset, [numTasks]) | When called on datasets of type (K, V) and (K, W), returns a dataset of (K, (Iterable<V>, Iterable<W>)) tuples. This operation is also called groupWith. |
cogroup类似全外连接,即fullOuterJoin。不同的是,cogroup会根据key做分组聚合。而且cogroup可以连接多个RDD。
val seq = Seq[String]("spark", "hadoop", "apark", "spark", "hadoop", "spark")
val seq2 = Seq[String]("spark1", "hadoop", "apark1")
val rdd = session.sparkContext.parallelize(seq).map((_,1))
val rdd2 = session.sparkContext.parallelize(seq2).map((_,1))
rdd.fullOuterJoin(rdd2).foreach(println)
println("===================")
rdd.cogroup(rdd2).collect().foreach(println)
结果:
(apark,(Some(1),None))
(apark1,(None,Some(1)))
(spark1,(None,Some(1)))
(spark,(Some(1),None))
(spark,(Some(1),None))
(spark,(Some(1),None))
(hadoop,(Some(1),Some(1)))
(hadoop,(Some(1),Some(1)))
===================
(spark1,(CompactBuffer(),CompactBuffer(1)))
(spark,(CompactBuffer(1, 1, 1),CompactBuffer()))
(hadoop,(CompactBuffer(1, 1),CompactBuffer(1)))
(apark1,(CompactBuffer(),CompactBuffer(1)))
(apark,(CompactBuffer(1),CompactBuffer()))
cartesian
| cartesian(otherDataset) | When called on datasets of types T and U, returns a dataset of (T, U) pairs (all pairs of elements). |
笛卡尔积。
pipe
| pipe(command, [envVars]) | Pipe each partition of the RDD through a shell command, e.g. a Perl or bash script. RDD elements are written to the process's stdin and lines output to its stdout are returned as an RDD of strings. |
调用外部程序。
coalesce
| coalesce(numPartitions) | Decrease the number of partitions in the RDD to numPartitions. Useful for running operations more efficiently after filtering down a large dataset. |
repartition
| repartition(numPartitions) | Reshuffle the data in the RDD randomly to create either more or fewer partitions and balance it across them. This always shuffles all data over the network. |
两个函数都是对RDD进行重分区。coalesce带有是否进行shuffle的参数,而repartition强制使用shuffle。
spark 算子之RDD的更多相关文章
- Spark算子与RDD基本转换
map 将一个RDD中的每个数据项,通过map中的函数映射变为一个新的元素. 输入分区与输出分区一对一,即:有多少个输入分区,就有多少个输出分区. flatMap 属于Transformation算子 ...
- (转)Spark 算子系列文章
http://lxw1234.com/archives/2015/07/363.htm Spark算子:RDD基本转换操作(1)–map.flagMap.distinct Spark算子:RDD创建操 ...
- spark算子之DataFrame和DataSet
前言 传统的RDD相对于mapreduce和storm提供了丰富强大的算子.在spark慢慢步入DataFrame到DataSet的今天,在算子的类型基本不变的情况下,这两个数据集提供了更为强大的的功 ...
- Spark操作算子本质-RDD的容错
Spark操作算子本质-RDD的容错spark模式1.standalone master 资源调度 worker2.yarn resourcemanager 资源调度 nodemanager在一个集群 ...
- Spark(四)【RDD编程算子】
目录 测试准备 一.Value类型转换算子 map(func) mapPartitions(func) mapPartitions和map的区别 mapPartitionsWithIndex(func ...
- Spark计算模型-RDD介绍
在Spark集群背后,有一个非常重要的分布式数据架构,即弹性分布式数据集(Resilient Distributed DataSet,RDD),它是逻辑集中的实体,在集群中的多台集群上进行数据分区.通 ...
- Spark算子总结及案例
spark算子大致上可分三大类算子: 1.Value数据类型的Transformation算子,这种变换不触发提交作业,针对处理的数据项是Value型的数据. 2.Key-Value数据类型的Tran ...
- Spark 核心概念 RDD 详解
RDD全称叫做弹性分布式数据集(Resilient Distributed Datasets),它是一种分布式的内存抽象,表示一个只读的记录分区的集合,它只能通过其他RDD转换而创建,为此,RDD支持 ...
- Spark 核心概念RDD
文章正文 RDD全称叫做弹性分布式数据集(Resilient Distributed Datasets),它是一种分布式的内存抽象,表示一个只读的记录分区的集合,它只能通过其他RDD转换而创建,为此, ...
随机推荐
- Geoserver 发布shp格式地图服务
本文实践参考https://blog.csdn.net/zj3172172173/article/details/53336704 第一步: 安装geoserver . 自己去官方下载一个安装包 第二 ...
- arduino uno r3的数据类型
char 一个字节,存储一个字符值.字符文字用单引号写成:'A' unsigned char 无符号,一个字节 byte 一个字节,无符号数, int 2字节,这产生-32768至32767的范围. ...
- redis 5.0.3 讲解、集群搭建
REDIS 一 .redis 介绍 不管你是从事Python.Java.Go.PHP.Ruby等等... Redis都应该是一个比较熟悉的中间件.而大部分经常写业务代码的程序员,实际工作中或许只用到了 ...
- Python——列表、元祖、字典、集合的基本操作
列表 1. 列表——增 (1)append li = ['xcsd', 'cdc', [1, 5, 2], 'eht', '辛辰'] li.append('nihao') print(li) #['x ...
- Red-Gate.NET.Reflector.v8.0.1.308(内含注册机Keygen与注册图解)
Red-Gate.NET.Reflector.v8.0.1.308(内含注册机Keygen与注册图解) 反编译神器 内含软件安装包.注册机及插件集合. 这里说下注册方法,注意不要在联网的情况下注册 ...
- [转]SQL server2008 导入超大SQL脚本文件(超过10M)
同事给我一个sqlserver的学习库,sql脚本导出有300m,gui执行有内存溢出的错误报出来,所以问了一下度娘,学而时习之:) 1. SQL server2008 导入超大SQL脚本文件(超过1 ...
- Excel技巧--单列变多行
当上图的单列转变成多行时,可以这么做: 1.在第一行输入A2.A3,向右拖拉第一行: 2.第二行按第一行最右顺序,写下A12,再向右拖拉出第二行: 3.选择这两行,再拖拉出一串连续顺序的多行来: 4. ...
- LiveBindings如何绑定一个对象(转)
原文 http://www.malcolmgroves.com/blog/?p=1084 一.新建VCL工程加入TAdapterBingSource控件 二.定一个TPerson类 MyPerson ...
- 【动态规划】最大连续子序列和,最大子矩阵和,最大m子段和
1.最大字段和问题 求一个序列最大连续子序列之和. 例如序列[-1,-2,-3,4,5,-6]的最大子段和为4 + 5 = 9. ①枚举法 int MaxSum(int n,int *a){ int ...
- bui框架nav导航图标一览
权限 .nav-permission 仓库 .nav-storage 库存 .nav-inventory 用户 .nav-user 订单 .nav-order 商品 . ...
