01Hadoop二次排序
我的目的:
示例:
2012,01,01,35
2011,12,23,-4
2012,01,01,43
2012,01,01,23
2011,12,23,5
2011,4,1,2
2011,4,1,56
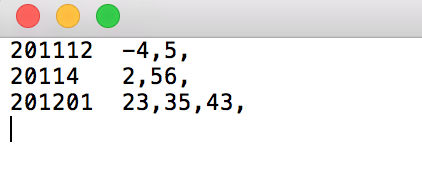
结果:
201112 -4,5
20114 2,56
201201 23,35,43
正式实现:
代码结构:

分为以下的步骤:
(1)编写封装类,把上述的字段分装进去。
package com.book.test; import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Writable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable; public class DataTemperaturePair implements Writable,WritableComparable<DataTemperaturePair> {
//年-月
private Text yearMoth=new Text();
//温度
private IntWritable temperature=new IntWritable();
//日期
private Text day=new Text(); public DataTemperaturePair()
{
}
public Text getYearMoth() {
return yearMoth;
}
public Text getDay() {
return day;
}
public void setDay(Text day) {
this.day = day;
}
public void setYearMoth(Text yearMoth) {
this.yearMoth = yearMoth;
}
public IntWritable getTemperature() {
return temperature;
}
public void setTemperature(IntWritable temperature) {
this.temperature = temperature;
}
//这俩个函数是必须要写的,不然在reduce端,这个分装类拿不到
public void readFields(DataInput input) throws IOException {
String readuf=input.readUTF(); int readuf3=input.readInt();
String readuf2=input.readUTF();
this.yearMoth=new Text(readuf); this.temperature=new IntWritable(readuf3);
this.day=new Text(readuf2); }
//这俩个函数是必须要写的,不然在reduce端,这个分装类拿不到
public void write(DataOutput output) throws IOException
{ output.writeUTF(yearMoth.toString()); output.writeInt(temperature.get()); output.writeUTF(day.toString()); } public int compareTo(DataTemperaturePair that) {
int compareValue=this.yearMoth.compareTo(that.yearMoth); if(compareValue==0) {
compareValue=temperature.compareTo(that.temperature);
} //升序
return compareValue;
}
(2)编写分区器
为什么要自定义这个分区器呢?
因为我们的key是自己写的一个对象,我们想按照这个对象里面的Yearmoth来分到一个区。
package com.book.test; import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner; /**
* 自定义的分区器
* @author Sxq
*
*/
public class DataTemperaturePartition extends Partitioner<DataTemperaturePair, NullWritable> { @Override
public int getPartition(DataTemperaturePair pair, NullWritable text, int numberOfPartotions) {
return Math.abs(pair.getYearMoth().hashCode()%numberOfPartotions);
} }
(3)编写比较器
决定数据分入到哪个分组
package com.book.test; import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparator; public class DataTemperatureGroupingComparator extends WritableComparator { public DataTemperatureGroupingComparator() {
super(DataTemperaturePair.class,true);
} @Override
public int compare(WritableComparable a, WritableComparable b) { DataTemperaturePair v1=(DataTemperaturePair)a;
DataTemperaturePair v2=(DataTemperaturePair)b;
return v1.getYearMoth().compareTo(v2.getYearMoth());
} }
(4)写驱动类
package com.book.test; import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Iterator; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import com.guigu.shen.flowsun.FlowCountSort;
public class Cmain {
static class mapper1 extends Mapper<LongWritable,Text, DataTemperaturePair, IntWritable>
{
DataTemperaturePair dataTemperaturePair=new DataTemperaturePair();
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value,
Mapper<LongWritable, Text, DataTemperaturePair, IntWritable>.Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String valuestring=value.toString();
String[] lines=valuestring.split(",");
String yymm=lines[0]+lines[1]; dataTemperaturePair.setYearMoth(new Text(yymm)); IntWritable temparature=new IntWritable(Integer.valueOf(lines[3]));
dataTemperaturePair.setTemperature(temparature);
dataTemperaturePair.setDay(new Text(lines[2])); context.write(dataTemperaturePair, temparature);
} } static class reduce1 extends Reducer<DataTemperaturePair, IntWritable, Text, Text>
{ @Override
protected void reduce(DataTemperaturePair KEY, Iterable<IntWritable> VALUE,
Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
StringBuffer sortedTemperaturelist=new StringBuffer(); Iterator<IntWritable> iterator=VALUE.iterator(); while(iterator.hasNext())
{ sortedTemperaturelist.append(iterator.next());
sortedTemperaturelist.append(",");
}
context.write(KEY.getYearMoth(), new Text(sortedTemperaturelist.toString())); }
} public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Configuration conf=new Configuration();
Job job=Job.getInstance(conf);
job.setJarByClass(Cmain.class);
job.setMapperClass(mapper1.class);
job.setReducerClass(reduce1.class); job.setMapOutputKeyClass(DataTemperaturePair.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class); job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
job.setGroupingComparatorClass(DataTemperatureGroupingComparator.class);
job.setPartitionerClass(DataTemperaturePartition.class); //指定输入的数据的目录
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("/Users/mac/Desktop/temperature.txt")); FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("/Users/mac/Desktop/flowresort")); boolean result=job.waitForCompletion(true);
System.exit(result?0:1);
} }
结果:
成功了
01Hadoop二次排序的更多相关文章
- MapReduce二次排序
默认情况下,Map 输出的结果会对 Key 进行默认的排序,但是有时候需要对 Key 排序的同时再对 Value 进行排序,这时候就要用到二次排序了.下面让我们来介绍一下什么是二次排序. 二次排序原理 ...
- Hadoop Mapreduce分区、分组、二次排序过程详解[转]
原文地址:Hadoop Mapreduce分区.分组.二次排序过程详解[转]作者: 徐海蛟 教学用途 1.MapReduce中数据流动 (1)最简单的过程: map - reduce (2) ...
- Hadoop.2.x_高级应用_二次排序及MapReduce端join
一.对于二次排序案例部分理解 1. 分析需求(首先对第一个字段排序,然后在对第二个字段排序) 杂乱的原始数据 排序完成的数据 a,1 a,1 b,1 a,2 a,2 [排序] a,100 b,6 == ...
- Hadoop学习笔记: MapReduce二次排序
本文给出一个实现MapReduce二次排序的例子 package SortTest; import java.io.DataInput; import java.io.DataOutput; impo ...
- Spark基础排序+二次排序(java+scala)
1.基础排序算法 sc.textFile()).reduceByKey(_+_,).map(pair=>(pair._2,pair._1)).sortByKey(false).map(pair= ...
- (转)MapReduce二次排序
一.概述 MapReduce框架对处理结果的输出会根据key值进行默认的排序,这个默认排序可以满足一部分需求,但是也是十分有限的.在我们实际的需求当中,往往有要对reduce输出结果进行二次排序的需求 ...
- MapReduce自定义二次排序流程
每一条记录开始是进入到map函数进行处理,处理完了之后立马就入自定义分区函数中对其进行分区,当所有输入数据经过map函数和分区函数处理完之后,就调用自定义二次排序函数对其进行排序. MapReduce ...
- Hadoop MapReduce 二次排序原理及其应用
关于二次排序主要涉及到这么几个东西: 在0.20.0 以前使用的是 setPartitionerClass setOutputkeyComparatorClass setOutputValueGrou ...
- hadoop2.2编程:mapreduce编程之二次排序
mr自带的例子中的源码SecondarySort,我重新写了一下,基本没变. 这个例子中定义的map和reduce如下,关键是它对输入输出类型的定义:(java泛型编程) public static ...
随机推荐
- vue插槽,也就是子页面、父页面相互传值的另一写法
父页面: <template> <div class="parent"> <p>父组件</p> <child> < ...
- 考前停课集训 Day7 嘞
Day7 正如一个大佬提醒的那样,棕名是会被嘲讽的 果然…… 在洛谷里…… 算了. 不必在意. 马上就要退役了. NOIP,开始的地方,也是结束的地方. 如果一群OIer比你小 还会嘲讽你, 你就该退 ...
- 编程菜鸟的日记-初学尝试编程-寻找等长数组A与B(所含元素相同,顺序不同)相匹配的元素即a[i]=b[j]
#include <iostream> using namespace std; void matching(int a[],int b[],int N) { int i=0; while ...
- JSOUP 请求JSON
JSOUP请求JSON Document doc = Jsoup .connect(Constant.DATA_URL) .header("Accept", "*/*&q ...
- ASP.NET Core使用Razor页面
ASP.NET Core使用Razor页面 Razor是ASP.NET的页面引擎,在ASP.NET MVC 3以后被广泛使用,我在之前的博客中有所介绍,需要更多了解的朋友请移步[Razor语法] 在A ...
- ssh-keygen 基本用法
ssh-keygen命令用于为"ssh"生成.管理和转换认证密钥,它支持RSA和DSA两种认证密钥. ssh-keygen(选项) -b:指定密钥长度: -e:读取openssh的 ...
- 解决 docker 报错: Error starting daemon: error initializing graphdriver: backing file system is unsupported for this graph driver
CentOS 7.5 x64下 sudo yum install docker -y systemctl enable docker systemctl start docker 发现启动失败 jou ...
- mysql函数之SUBSTRING_INDEX(str,"/",-1)
SUBSTRING_INDEX的用法: •SUBSTRING_INDEX(str,delim,count) 在定界符 delim 以及count 出现前,从字符串str返回自字符串.若count为正值 ...
- Chrome 开发者控制台中,你可能意想不到的功能
Chrome 有内置的开发者工具.它拥有丰富的特性,比如元素(Elements).网络(Network)和安全(Security).今天,我们主要关注一下 JavaScript 控制台. 当我最初写代 ...
- shell编程学习笔记(九):Shell中的case条件判断
除了可以使用if条件判断,还可以使用case 以下蓝色字体部分为Linux命令,红色字体的内容为输出的内容: # cd /opt/scripts # vim script08.sh 开始编写scrip ...
