Linux驱动之LED驱动编写
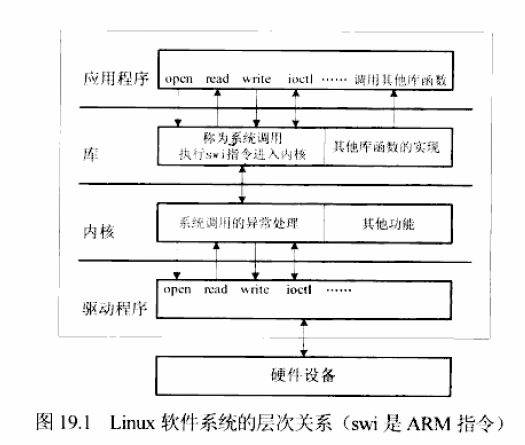
从上到下,一个软件系统可以分为:应用程序、操作系统(内核)、驱动程序。结构图如下:我们需要做的就是写出open、read、write等驱动层的函数。一个LED驱动的步骤如下:
5、编写Makefile,编译驱动代码与测试代码,在开发板上运行
1、查看原理图,确定需要控制的IO端口
打开原理图,确定需要控制的IO端口为GPF4、GPF5、GPF6。


2、查看芯片手册,确定IO端口的寄存器地址,可以看到它的基地址为0x56000050

3、编写驱动代码,编写驱动代码的步骤如下:
1)、编写出口、入口函数。
a、首先利用register_chrdev函数如果第一个参数为0的话那么会自动分配一个主设备号为Firstmajor ;第二个参数firstled_drv会是这个字符设备的名称可以利用命令cat /proc/devices看到;第三个参数是它的first_drv_fops结构体,这个结构体是字符设备中最主要的,后面再说明。
b、接着利用class_create函数创建一个firt_drv_class类。它的第一个参数指向这个模块,第二个参数为类的名称。再利用class_device_create创建四个设备节点,第一个参数为类、第三个参数为设备号,第五个参数为设备节点的名称,第六个参数为次设备号。这样的话会在加载驱动之后自动在/dev目录下创建四个设备文件。
c、ioremap函数重映射函数,将物理地址转换成虚拟地址
d、a-c为驱动入口函数,在驱动出口函数会将a-c创建的东西全部删除。
e、module_init与module_exit表示在insmod与rmmod的时候内核会调用first_ledsdrv_init与first_ledsdrv_exit
/*
* 执行insmod命令时就会调用这个函数
*/
static int __init first_ledsdrv_init(void)
{
int minor;//次设备号
Firstmajor = register_chrdev(, "firstled_drv", &first_drv_fops);//注册first_drv_fops结构体到字符设备驱动表,0表示自动分配主设备号
if(Firstmajor<)
{
printk(" first_drv can't register major number\n");
return Firstmajor;
} firt_drv_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "leds");//创建类 firt_drv_class_dev[] = class_device_create(firt_drv_class, NULL, MKDEV(Firstmajor, ), NULL, "leds");//创建设备节点
if (unlikely(IS_ERR(firt_drv_class_dev[])))
return PTR_ERR(firt_drv_class_dev[]); for(minor=;minor<;minor++)
{
firt_drv_class_dev[minor] = class_device_create(firt_drv_class, NULL, MKDEV(Firstmajor, minor), NULL, "led%d",minor);//创建设备节点
if (unlikely(IS_ERR(firt_drv_class_dev[minor])))
return PTR_ERR(firt_drv_class_dev[minor]);
} gpfcon = ioremap(0x56000050 , );//重映射,将物理地址变换为虚拟地址
gpfdat = gpfcon + ; printk("firstdrv module insmoded\n");
return ;
} /*
* 执行rmmod命令时就会调用这个函数
*/
static void __exit first_ledsdrv_exit(void)
{
int i;
for(i=;i<;i++)
class_device_unregister(firt_drv_class_dev[i]);//删除设备节点 class_destroy(firt_drv_class);//删除类 iounmap(gpfcon);//删除重映射分配的地址 unregister_chrdev(Firstmajor, "firstled_drv");//将rst_drv_fops结构体从字符设备驱动表中删除
printk("firstdrv module rmmod\n");
} /* 这两行指定驱动程序的初始化函数和卸载函数 */
module_init(first_ledsdrv_init);
module_exit(first_ledsdrv_exit);
2)、添加file_operations 结构体,这个是字符设备驱动的核心结构,所有的应用层调用的函数最终都会调用这个结构下面定义的函数。
static struct file_operations first_drv_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE, /* 这是一个宏,推向编译模块时自动创建的__this_module变量 */
.open = first_ledsdrv_open,
.write = first_ledsdrv_write,
};
其中THIS_MODULE在linux/module.h中定义,它执向__this_module的地址
extern struct module __this_module;
#define THIS_MODULE (&__this_module)
而__this_module这个变量是在编译的时候由modpost程序生成的,它的结构如下:
struct module __this_module
__attribute__((section(".gnu.linkonce.this_module"))) = {
.name = KBUILD_MODNAME,
.init = init_module,
#ifdef CONFIG_MODULE_UNLOAD
.exit = cleanup_module,
#endif
};
3)、分别编写file_operations 结构体下的open、wrtie函数。当应用程序调用系统调用led设备的open与write时最终内核会定位到驱动层的open与write函数。
其中open函数的功能是根据打开的设备文件初始化相应的io口为输出口
static int first_ledsdrv_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
int minor = MINOR(inode->i_rdev);//取得次设备号,根据次设备号来配置IO端口 switch(minor)
{
case :
*gpfcon &= ~(( << ) | ( << ) | ( << ));//先清0 :8,9,10,11,12,13
*gpfcon |= (( << ) | ( << ) | ( << ));//再置1:8,10,12break;
printk("initialize leds\n");
break;
case :
*gpfcon &= ~(( << ) );//先清0 :8,9,10,11,12,13
*gpfcon |= (( << ));//再置1:8,10,12break;
printk("initialize led1\n");
break;
case :
*gpfcon &= ~( ( << ));//先清0 :8,9,10,11,12,13
*gpfcon |= ( ( << ) );//再置1:8,10,12break;
printk("initialize led2\n");
break;
case :
*gpfcon &= ~(( << ));//先清0 :8,9,10,11,12,13
*gpfcon |= (( << ));//再置1:8,10,12break;
printk("initialize led3\n");
break;
default:break;
} // printk("hello this is open\n");
return ;
}
write函数的功能是根据设备文件以及向设备写入的值来操作相应的IO口做相应的动作
static ssize_t first_ledsdrv_write(struct file *file, const char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t * ppos)
{
char val;
int ret;
int minor = MINOR(file->f_dentry->d_inode->i_rdev);//根据文件取出次设备号 ret = copy_from_user(&val, buf, count);//ret返回0表示拷贝成功 if(!ret)
{
switch(minor)
{
case :
if(val==)
{
*gpfdat &= ~(( << ) | (<<) | (<<));//点灯
printk("leds on\n");
}
else if(val == )
{
*gpfdat |= (( << ) | (<<) | (<<));//灭灯
printk("leds off\n");
}
break;
case :
if(val==)
{
*gpfdat &= ~(( << ));//点灯
printk("led1 on\n");
}
else if(val == )
{
*gpfdat |= (( << ));//灭灯
printk("led1 off\n");
}
break;
case :
if(val==)
{
*gpfdat &= ~((<<));//点灯
printk("led2 on\n");
}
else if(val == )
{
*gpfdat |= ((<<));//灭灯
printk("led2 off\n");
}
break;
case :
if(val==)
{
*gpfdat &= ~((<<));//点灯
printk("led3 on\n");
}
else if(val == )
{
*gpfdat |= ((<<));//灭灯
printk("led3 off\n");
}
break;
default:break;
}
}
else
printk("copy from user wrong!!!!%d %d\n",ret,count);
// printk("hello this is write\n");
return ;
}
4)、下面是整个LED驱动的整体代码
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <asm/io.h> //含有iomap函数iounmap函数
#include <asm/uaccess.h>//含有copy_from_user函数
#include <linux/device.h>//含有类相关的处理函数 static struct class *firt_drv_class;//类
static struct class_device *firt_drv_class_dev[];//类下面的设备
static int Firstmajor; static unsigned long *gpfcon = NULL;
static unsigned long *gpfdat = NULL; static int first_ledsdrv_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
int minor = MINOR(inode->i_rdev);//取得次设备号,根据次设备号来配置IO端口 switch(minor)
{
case :
*gpfcon &= ~(( << ) | ( << ) | ( << ));//先清0 :8,9,10,11,12,13
*gpfcon |= (( << ) | ( << ) | ( << ));//再置1:8,10,12break;
printk("initialize leds\n");
break;
case :
*gpfcon &= ~(( << ) );//先清0 :8,9,10,11,12,13
*gpfcon |= (( << ));//再置1:8,10,12break;
printk("initialize led1\n");
break;
case :
*gpfcon &= ~( ( << ));//先清0 :8,9,10,11,12,13
*gpfcon |= ( ( << ) );//再置1:8,10,12break;
printk("initialize led2\n");
break;
case :
*gpfcon &= ~(( << ));//先清0 :8,9,10,11,12,13
*gpfcon |= (( << ));//再置1:8,10,12break;
printk("initialize led3\n");
break;
default:break;
} // printk("hello this is open\n");
return ;
} static ssize_t first_ledsdrv_write(struct file *file, const char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t * ppos)
{
char val;
int ret;
int minor = MINOR(file->f_dentry->d_inode->i_rdev);//根据文件取出次设备号 ret = copy_from_user(&val, buf, count);//ret返回0表示拷贝成功 if(!ret)
{
switch(minor)
{
case :
if(val==)
{
*gpfdat &= ~(( << ) | (<<) | (<<));//点灯
printk("leds on\n");
}
else if(val == )
{
*gpfdat |= (( << ) | (<<) | (<<));//灭灯
printk("leds off\n");
}
break;
case :
if(val==)
{
*gpfdat &= ~(( << ));//点灯
printk("led1 on\n");
}
else if(val == )
{
*gpfdat |= (( << ));//灭灯
printk("led1 off\n");
}
break;
case :
if(val==)
{
*gpfdat &= ~((<<));//点灯
printk("led2 on\n");
}
else if(val == )
{
*gpfdat |= ((<<));//灭灯
printk("led2 off\n");
}
break;
case :
if(val==)
{
*gpfdat &= ~((<<));//点灯
printk("led3 on\n");
}
else if(val == )
{
*gpfdat |= ((<<));//灭灯
printk("led3 off\n");
}
break;
default:break;
}
}
else
printk("copy from user wrong!!!!%d %d\n",ret,count);
// printk("hello this is write\n");
return ;
} static struct file_operations first_drv_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE, /* 这是一个宏,推向编译模块时自动创建的__this_module变量 */
.open = first_ledsdrv_open,
.write = first_ledsdrv_write,
}; /*
* 执行insmod命令时就会调用这个函数
*/
static int __init first_ledsdrv_init(void)
{
int minor;//次设备号
Firstmajor = register_chrdev(, "firstled_drv", &first_drv_fops);//注册first_drv_fops结构体到字符设备驱动表,0表示自动分配主设备号
if(Firstmajor<)
{
printk(" first_drv can't register major number\n");
return Firstmajor;
} firt_drv_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "leds");//创建类 firt_drv_class_dev[] = class_device_create(firt_drv_class, NULL, MKDEV(Firstmajor, ), NULL, "leds");//创建设备节点
if (unlikely(IS_ERR(firt_drv_class_dev[])))
return PTR_ERR(firt_drv_class_dev[]); for(minor=;minor<;minor++)
{
firt_drv_class_dev[minor] = class_device_create(firt_drv_class, NULL, MKDEV(Firstmajor, minor), NULL, "led%d",minor);//创建设备节点
if (unlikely(IS_ERR(firt_drv_class_dev[minor])))
return PTR_ERR(firt_drv_class_dev[minor]);
} gpfcon = ioremap(0x56000050 , );//重映射,将物理地址变换为虚拟地址
gpfdat = gpfcon + ; printk("firstdrv module insmoded\n");
return ;
} /*
* 执行rmmod命令时就会调用这个函数
*/
static void __exit first_ledsdrv_exit(void)
{
int i;
for(i=;i<;i++)
class_device_unregister(firt_drv_class_dev[i]);//删除设备节点 class_destroy(firt_drv_class);//删除类 iounmap(gpfcon);//删除重映射分配的地址 unregister_chrdev(Firstmajor, "firstled_drv");//将rst_drv_fops结构体从字符设备驱动表中删除
printk("firstdrv module rmmod\n");
} /* 这两行指定驱动程序的初始化函数和卸载函数 */
module_init(first_ledsdrv_init);
module_exit(first_ledsdrv_exit); MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");//不加的话加载会有错误提醒
MODULE_AUTHOR("andylu");//作者
MODULE_VERSION("0.0.0");//版本
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("S3C2410/S3C2440 LED Driver");//简单的描述
4、确定应用程序功能,编写测试代码。应用程序功能为打开不同设备文件操作不同的IO口。代码如下:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h> /*
* ledtest <dev> <on|off>
*/
void print_usage(char *file)
{
printf("Usage:\n");
printf("%s <dev> <on|off>\n",file);
printf("eg. \n");
printf("%s /dev/leds on\n", file);
printf("%s /dev/leds off\n", file);
printf("%s /dev/led1 on\n", file);
printf("%s /dev/led1 off\n", file);
} int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd;
char* filename=NULL;
char val; filename = argv[]; fd = open(filename, O_RDWR);//打开dev/firstdrv设备文件
if (fd < )//小于0说明没有成功
{
printf("error, can't open %s\n", filename);
return ;
} if(argc !=)
{
print_usage( argv[]);//打印用法
} if(!strcmp(argv[], "on"))
val = ;
else
val = ; write(fd, &val, );//操作LED return ;
}
5、编写Makefile,编译驱动代码与测试代码,在开发板上运行
Makefile源码如下:
KERN_DIR = /work/system/linux-2.6.22.6 all:
make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules //M='pwd'表示当前目录。这句话的意思是利用内核目录下的Makefile规则来编译当前目录下的模块 clean:
make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules clean
rm -rf modules.order obj-m +=first_drv.o//调用内核目录下Makefile编译时需要用到这个参数
1)、然后在当前目录下make后编译出first_drv.ko文件
2)、arm-linux-gcc -o first_test first_test.c编译出first_test测试程序
3)、cp first_drv.ko first_test /work/nfs_root将编译出来的文件拷贝到开发板挂接的网络文件系统上
4)、执行insmod first_drv.ko加载驱动。
5)、./first_test /dev/leds on测试程序,灯全部被点亮,成功运行。
Linux驱动之LED驱动编写的更多相关文章
- linux驱动之LED驱动
通过之前的学习,了解到linux驱动编写的流程是:先通过注册函数注册我们编写的入口函数,然后在入口函数中获取设备号->注册字符设备->自动创建设备节点->获取设备树信息,最后通过销毁 ...
- 【Linux 驱动】简单字符设备驱动架构(LED驱动)
本文基于icool210开发板,内核版本:linux2.6.35: 驱动代码: (1)头文件:led.h #ifndef __LED_H__ #define __LED_H__ #define LED ...
- linux驱动之LED驱动_1
步骤: 1.框架 2.完好硬件的操作: a.看原理图.引脚 b.看2440手冊 c.写代码: IO口须要用ioremap映射 我的板子电路例如以下所看到的 1.配置GPBCON 寄存器,配置输出 ...
- 字符设备驱动之Led驱动学习记录
一.概述 Linux内核就是由各种驱动组成的,内核源码中大约有85%的各种渠道程序的代码.一般来说,编写Linux设备驱动大致流程如下: 1.查看原理图,数据手册,了解设备的操作方法. 2.在内核中找 ...
- 字符设备驱动之LED驱动
实现 ①编写驱动框架 ②编写硬件实现代码 (在Linux系统下操作硬件,需要操作虚拟地址,因此需要先把物理地址转换为虚拟地址 ioremap()) 如何实现单个灯的操作: 实现方法之一--操作次设备号 ...
- Linux驱动之按键驱动编写(中断方式)
在Linux驱动之按键驱动编写(查询方式)已经写了一个查询方式的按键驱动,但是查询方式太占用CPU,接下来利用中断方式编写一个驱动程序,使得CPU占有率降低,在按键空闲时调用read系统调用的进程可以 ...
- Linux驱动之按键驱动编写(查询方式)
在Linux驱动之LED驱动编写已经详细介绍了一个驱动的编写过程,接着来写一个按键驱动程序,主要是在file_operations结构中添加了一个read函数.还是分以下几步说明 1.查看原理图,确定 ...
- linux模块驱动之led(ioremap)
一:led内核驱动 (1)在编写led内核驱动时,我们首先要进行内核裁剪,因为友善之臂将LED灯的驱动默认加载到内核中,所以编写模块驱动程序前就要先把原先的LED灯驱动裁剪掉: led驱动在源码里面的 ...
- (笔记)linux设备驱动--LED驱动
linux设备驱动--LED驱动 最近正在学习设备驱动开发,因此打算写一个系列博客,即是对自己学习的一个总结,也是对自己的一个督促,有不对,不足,需要改正的地方还望大家指出,而且希望结识志同道合的朋友 ...
随机推荐
- android Button、TabLayout英文自动改小写为大写的问题
如果是Button自动大写问题,直接设置Button的 textAllCaps="false" 即可: 如果是TabLayout出现全大写问题,先在style.xml加入属性: & ...
- Android 操作UI线程的一些方法
我们经常会在后台线程中去做一些耗时的操作,比如去网络取数据.但是当数据取回来,需要显示到页面上的时候,会遇到一些小麻烦,因为我们都知道,android的UI页面是不允许在其他线程直接操作的.下面总结4 ...
- java的特点
java是一种跨平台.适合于分布式计算机环境的面向对象编程语言.具有以下特性:简单性.面向对象.分布性.解释性.可靠.安全.平台无关.可移植性.高性能.多线程.动态性等特点. 面向过程和面向对象可以用 ...
- myEclips 中的项目复制重命名
现在有个项目Pj ,要复制一个Pu 一,退出 myEclips. 二,找到Pj备份一份到其他目录. 三,进入myEclips,F2修改项目名Pj至Pu. 四,将备份拷贝回原目录. 五,将Pj重新引进m ...
- bind,call,applay的区别
方法调用模式: 当一个函数被保存为对象的一个方法时,如果调用表达式包含一个提取属性的动作,那么它就是被当做一个方法来调用,此时的this被绑定到这个对象. var a = 1 var obj1 = { ...
- react input的几个坑
[react input的几个坑] 1.input标签中设置value后,input进入controlled模式,valuechange由自动变为手动,导致input无法编辑.如: <input ...
- MySQL 按指定字段自定义列表排序
问题描述 大家都知道, mysql 中按某字段升序排列的 SQL 为 (以 id 为例, 下同): SELECT * FROM `MyTable` WHERE `id` IN (1, 7, 3, 5) ...
- jdk各版本名称
- Android笔记:intent
一.显式intent如下:(1)在intent构造函数传入两个activity文件名Intent intent = new Intent(FirstActivity.this, SecondActiv ...
- 98. Validate Binary Search Tree (Tree; DFS)
Given a binary tree, determine if it is a valid binary search tree (BST). Assume a BST is defined as ...
