mnist手写数字识别——深度学习入门项目(tensorflow+keras+Sequential模型)
前言
今天记录一下深度学习的另外一个入门项目——《mnist数据集手写数字识别》,这是一个入门必备的学习案例,主要使用了tensorflow下的keras网络结构的Sequential模型,常用层的Dense全连接层、Activation激活层和Reshape层。还有其他方法训练手写数字识别模型,可以基于pytorch实现的,《Pytorch实现基于卷积神经网络的面部表情识别(详细步骤)》 这篇就是基于pytorch实现,pytorch里也封装了mnist的数据集,实现方法应该类似,正在学习中……
这一篇记录则是基于keras的Sequential模型实现的。
1、mnist手写数字真面目
我们使用离线下载的数据集进行导入,一定程度上解决了从远程加载数据缓慢的问题,这里有两种数据集提供给大家,分别是:
- mnist.npz数据集
它是把手写数字的图像数据和对应标签集成在一起,而且训练集与测试集也在里面,使用的时候无需拆分文件,只需要简单代码划分数据,可直接下载本地 mnist手写数字识别数据集npz文件.zip - mnist.zip数据集
它包含了两个压缩包,分别是训练集和测试集(文件名:mnist_traint_data.zip和mnist_test_data.zip),每个数据集解压后里面分别是数据和对应的标签,所以最后由4个文件,可直接下载本地 mnist训练数据+测试数据(手写数字识别).zip
1.1、mnist.npz(集成)数据集
下载好mnist手写数字识别数据集npz文件.zip之后,解压得到mnist.npz之后,我们这里开始写代码看看手写数字图像的真面目。
显示图像代码:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt def load_mnist(): # 自定义加载数据
path = r'D:\mnist_data\mnist.npz' # 放置mnist.npz的目录。注意斜杠
f = np.load(path)
x_train, y_train = f['x_train'], f['y_train'] # 代码实现分离数据集里面的训练集和测试集以及对应标签
x_test, y_test = f['x_test'], f['y_test'] # x_train为训练数据,y_train为对应标签 f.close() # 关闭文件
return (x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) def main():
(X_train, y_train_label), (test_image, test_label) = load_mnist() #后续可以显示训练数据的数字或者测试数据的 fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=5, ncols=5, sharex=True, sharey=True) # 显示图像
ax = ax.flatten()
for i in range(25):
img = X_train[i].reshape(28, 28)
# img = X_train[y_train_label == 8][i].reshape(28, 28) # 显示标签为8的数字图像
ax[i].set_title(y_train_label[i])
ax[i].imshow(img, cmap='Greys', interpolation='nearest')
ax[0].set_xticks([])
ax[0].set_yticks([])
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show() if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
效果如下:
也可以花样输出:
代码:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt def load_mnist():
path = r'D:\mnist_data\mnist.npz' # 放置mnist.npz的目录。注意斜杠
f = np.load(path)
x_train, y_train = f['x_train'], f['y_train'] # 代码实现分离数据集里面的训练集和测试集以及对应标签
x_test, y_test = f['x_test'], f['y_test'] # x_train为训练数据,y_train为对应标签 f.close() # 关闭文件
return (x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) def main():
(X_train, y_train_label), (test_image, test_label) = load_mnist()
plt.subplot(221)#显示图像
plt.imshow(X_train[0], cmap=plt.get_cmap('Accent'))
plt.subplot(222)
plt.imshow(X_train[1], cmap=plt.get_cmap('gray'))
plt.subplot(223)
plt.imshow(X_train[2], cmap=plt.get_cmap('Blues'))
plt.subplot(224)
plt.imshow(X_train[3], cmap=plt.get_cmap('Oranges'))
plt.show() if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
图像显示:
1.2、mnist数据集(训练测试数据与标签分离)
这里介绍第二中方法,也就是数据集是分离的,下载好mnist训练数据+测试数据(手写数字识别).zip之后,解压得到文件如图:
进去解压得到:
可以看到分别是训练集和测试集,包括数据和标签。
这种方法比较麻烦,没想到吧!^_ ^ ,大家可以选择第一种步骤简单
最后得到:
导入时候需要用到的是这些.gz文件。
显示图像代码:
import gzip
import os
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt local_file = 'D:\mnist_data'
files = ['train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz', 'train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz',
't10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz', 't10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz'] def load_local_mnist(filename):# 加载文件
paths = []
file_read = []
for file in files:
paths.append(os.path.join(filename, file))
for path in paths:
file_read.append(gzip.open(path, 'rb'))
# print(file_read) train_labels = np.frombuffer(file_read[1].read(), np.uint8, offset=8)#文件读取以及格式转换
train_images = np.frombuffer(file_read[0].read(), np.uint8, offset=16) \
.reshape(len(train_labels), 28, 28)
test_labels = np.frombuffer(file_read[3].read(), np.uint8, offset=8)
test_images = np.frombuffer(file_read[2].read(), np.uint8, offset=16) \
.reshape(len(test_labels), 28, 28)
return (train_images, train_labels), (test_images, test_labels) def main():
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = load_local_mnist(local_file) fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=6, ncols=6, sharex=True, sharey=True)#显示图像
ax = ax.flatten()
for i in range(36):
img=x_test[i].reshape(28,28)
# img = x_train[y_train == 8][i].reshape(28, 28) # 显示标签为8的数字图像
ax[i].set_title(y_train[i])
ax[i].imshow(img, cmap='Greys', interpolation='nearest')
ax[0].set_xticks([])
ax[0].set_yticks([])
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show() if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
输出结果:
2、Sequential模型训练
这里实现主要使用了tensorflow下的keras网络结构的Sequential模型,常用层的Dense全连接层、Activation激活层和Reshape层。tensorflow安装有问题可参考《初入机器学习,安装tensorflow包等问题总结》
模型比较简单,网络搭建以及模型选择的损失函数、优化器可见代码。
import numpy as np
import os
import gzip
from tensorflow import keras
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import SGD
from tensorflow_core.python.keras.utils import np_utils
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Dropout, Activation local_file = 'D:\mnist_data'
files = ['train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz', 'train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz',
't10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz', 't10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz'] def load_local_mnist(filename): # 加载文件
paths = []
file_read = []
for file in files:
paths.append(os.path.join(filename, file))
for path in paths:
file_read.append(gzip.open(path, 'rb'))
# print(file_read) train_labels = np.frombuffer(file_read[1].read(), np.uint8, offset=8) # 文件读取以及格式转换
train_images = np.frombuffer(file_read[0].read(), np.uint8, offset=16) \
.reshape(len(train_labels), 28, 28)
test_labels = np.frombuffer(file_read[3].read(), np.uint8, offset=8)
test_images = np.frombuffer(file_read[2].read(), np.uint8, offset=16) \
.reshape(len(test_labels), 28, 28)
return (train_images, train_labels), (test_images, test_labels) def load_data():# 加载模型需要的数据
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = load_local_mnist(local_file)
number = 10000
x_train = x_train[0:number]
y_train = y_train[0:number]
x_train = x_train.reshape(number, 28 * 28)
x_test = x_test.reshape(x_test.shape[0], 28 * 28)
x_train = x_train.astype('float32')
x_test = x_test.astype('float32') y_train = np_utils.to_categorical(y_train, 10)
y_test = np_utils.to_categorical(y_test, 10)
x_train = x_train
x_test = x_test x_train = x_train / 255
x_test = x_test / 255
return (x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) (X_train, Y_train), (X_test, Y_test) = load_data()
model = keras.Sequential()# 模型选择
model.add(Dense(input_dim=28 * 28, units=690,
activation='relu')) # tanh activation:Sigmoid、tanh、ReLU、LeakyReLU、pReLU、ELU、maxout
model.add(Dense(units=690, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dense(units=690, activation='relu')) # tanh
model.add(Dense(units=10, activation='relu'))
model.compile(loss='mse', optimizer=SGD(lr=0.1),
metrics=['accuracy']) # loss:mse,categorical_crossentropy,optimizer: rmsprop 或 adagrad、SGD(此处推荐)
model.fit(X_train, Y_train, batch_size=100, epochs=20)
result = model.evaluate(X_test, Y_test)
print('TEST ACC:', result[1])
经过稍微调优,发现输入层激活函数使用relu和tanh效果好,其他网络层使用relu。另外,损失函数使用了MSE(均方误差),优化器使用 SGD(随即梯度下降),学习率learning rate调到0.1,度量常用正确率。
参数batch_size=100, epochs=20,增加参数更新以及训练速度。
以上参数以及选择训练效果如下:
使用优化器为adagrad效果:
大家也可以自行各种尝试,优化器和损失函数选择,参数调优等,进一步提高正确率。
这里提供另一种写法,模型构建类似。
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import datasets, layers, optimizers, models, metrics
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import SGD import os os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '' # 忽略tensorflow版本警告
(xs, ys), _ = datasets.mnist.load_data()
print('datasets:', xs.shape, ys.shape, xs.min(), xs.max()) # tf.compat.v1.enable_eager_execution()
tf.enable_eager_execution()
xs = tf.convert_to_tensor(xs, dtype=tf.float32) / 255.
db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((xs, ys))
db = db.batch(100).repeat(20) network = models.Sequential([layers.Dense(256, activation='relu'),
layers.Dense(256, activation='relu'),
layers.Dense(256, activation='relu'),
layers.Dense(10)])
network.build(input_shape=(None, 28 * 28))
network.summary() optimizer = optimizers.SGD(lr=0.01)
acc_meter = metrics.Accuracy()# 度量正确率 for step, (x, y) in enumerate(db): with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
# [b, 28, 28] => [b, 784] 784维=24*24
x = tf.reshape(x, (-1, 28 * 28))#-1的含义,数组新的shape属性应该要与原来的配套,根据剩下的维度计算出数组的另外一个shape属性值。
# [b, 784] => [b, 10]
out = network(x)
# [b] => [b, 10]
y_onehot = tf.one_hot(y, depth=10) # 独热编码,y = 0 对应的输出是[1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0],范围0-9,depth深度10层表示10个数字
# [b, 10]
loss = tf.square(out - y_onehot)# 计算模型预测与实际的损失
# [b]
loss = tf.reduce_sum(loss) / 32 acc_meter.update_state(tf.argmax(out, axis=1), y)
grads = tape.gradient(loss, network.trainable_variables)# 计算梯度
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, network.trainable_variables)) if step % 200 == 0:
print(step, 'loss:', float(loss), 'acc:', acc_meter.result().numpy())
acc_meter.reset_states()
最后正确率比上面好一点,如图: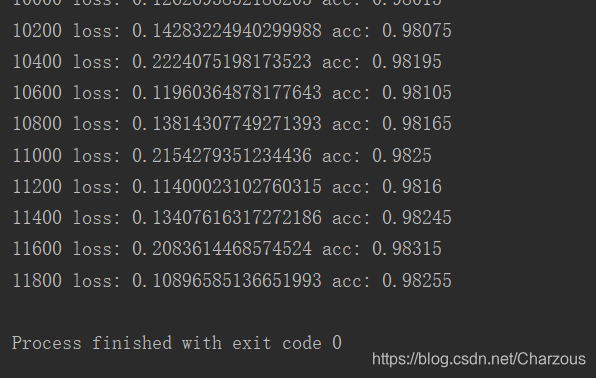
写在后面
经过这次学习,感觉收获了许多,之前只是在理论知识上的理解,现在配合代码实践,模型训练,理解更加深刻,还存在不足,欢迎大家指正交流,这个过程的详细步骤,希望能帮助跟我一样入门需要的伙伴,记录学习过程,感觉总结一下很好,继续加油!
我的CSDN博客:mnist手写数字识别深度学习入门项目(tensorflow+keras+Sequential模型)
我的博客园:mnist手写数字识别——深度学习入门项目(tensorflow+keras+Sequential模型)
mnist手写数字识别——深度学习入门项目(tensorflow+keras+Sequential模型)的更多相关文章
- 深度学习之 mnist 手写数字识别
深度学习之 mnist 手写数字识别 开始学习深度学习,先来一个手写数字的程序 import numpy as np import os import codecs import torch from ...
- 用MXnet实战深度学习之一:安装GPU版mxnet并跑一个MNIST手写数字识别
用MXnet实战深度学习之一:安装GPU版mxnet并跑一个MNIST手写数字识别 http://phunter.farbox.com/post/mxnet-tutorial1 用MXnet实战深度学 ...
- Pytorch入门——手把手教你MNIST手写数字识别
MNIST手写数字识别教程 要开始带组内的小朋友了,特意出一个Pytorch教程来指导一下 [!] 这里是实战教程,默认读者已经学会了部分深度学习原理,若有不懂的地方可以先停下来查查资料 目录 MNI ...
- 基于tensorflow的MNIST手写数字识别(二)--入门篇
http://www.jianshu.com/p/4195577585e6 基于tensorflow的MNIST手写字识别(一)--白话卷积神经网络模型 基于tensorflow的MNIST手写数字识 ...
- Android+TensorFlow+CNN+MNIST 手写数字识别实现
Android+TensorFlow+CNN+MNIST 手写数字识别实现 SkySeraph 2018 Email:skyseraph00#163.com 更多精彩请直接访问SkySeraph个人站 ...
- Tensorflow实现MNIST手写数字识别
之前我们讲了神经网络的起源.单层神经网络.多层神经网络的搭建过程.搭建时要注意到的具体问题.以及解决这些问题的具体方法.本文将通过一个经典的案例:MNIST手写数字识别,以代码的形式来为大家梳理一遍神 ...
- 持久化的基于L2正则化和平均滑动模型的MNIST手写数字识别模型
持久化的基于L2正则化和平均滑动模型的MNIST手写数字识别模型 觉得有用的话,欢迎一起讨论相互学习~Follow Me 参考文献Tensorflow实战Google深度学习框架 实验平台: Tens ...
- Tensorflow之MNIST手写数字识别:分类问题(1)
一.MNIST数据集读取 one hot 独热编码独热编码是一种稀疏向量,其中:一个向量设为1,其他元素均设为0.独热编码常用于表示拥有有限个可能值的字符串或标识符优点: 1.将离散特征的取值扩展 ...
- 第三节,CNN案例-mnist手写数字识别
卷积:神经网络不再是对每个像素做处理,而是对一小块区域的处理,这种做法加强了图像信息的连续性,使得神经网络看到的是一个图像,而非一个点,同时也加深了神经网络对图像的理解,卷积神经网络有一个批量过滤器, ...
随机推荐
- HashMap等集合初始化时应制定初始化大小
阿里巴巴开发规范中,推荐用户在初始化HashMap时,应指定集合初始值大小. 一.原因 这个不用多想,肯定是效率问题,那为什么会造成效率问题呢? 当我们new一个HashMap没有对其容量进行初始化的 ...
- 数据可视化之powerBI入门(十)认识Power BI的核心概念:度量值
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/64150720 本文学习PowerBI最重要的概念:度量值 初学Power BI一般都会对度量值比较困惑,毕竟对长期接触Excel的人来说, ...
- [Qt2D绘图]-06QPainter的复合模式&&双缓冲绘图&&绘图中的其他问题
本篇读书笔记主要记录QPainter的复合模式&&双缓冲绘图&&绘图中的其他问题 大纲: 复合模式 双缓冲绘图 绘图中的其他问题 ...
- Ethical Hacking - NETWORK PENETRATION TESTING(11)
Securing your Network From the Above Attacks. Now that we know how to test the security of all known ...
- P1433 吃奶酪(洛谷)状压dp解法
嗯?这题竟然是个绿题. 这个题真的不(很)难,我们只是不会计算2点之间的距离,他还给出了公式,这个就有点…… 我们直接套公式去求出需要的值,然后普通的状压dp就可以了. 是的状压dp. 这个题的数据加 ...
- 技术小菜比入坑 LinkedList,i 了 i 了
先看再点赞,给自己一点思考的时间,思考过后请毫不犹豫微信搜索[沉默王二],关注这个长发飘飘却靠才华苟且的程序员.本文 GitHub github.com/itwanger 已收录,里面还有技术大佬整理 ...
- 【翻译】Scriban README 文本模板语言和.NET引擎
scriban Scriban是一种快速.强大.安全和轻量级的文本模板语言和.NET引擎,具有解析liquid模板的兼容模式 Github https://github.com/lunet-io/sc ...
- Laravel 5.4 使用 Mail 发送邮件获取验证码功能(使用的配置邮箱为126邮箱)
<?php namespace App\Modules\Liveapi\Http\Controllers\Personnel; use App\Modules\Liveapi\Http\Cont ...
- 给Django Admin添加验证码和多次登录尝试限制
Django自带的Admin很好用,但是放到生产环境总还差了点什么= = 看看admin的介绍: Django奉行Python的内置电池哲学.它自带了一系列在Web开发中用于解决常见问题或需求的额外的 ...
- BuuCTF Web Writeup
WarmUp index.php <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> ...
