POJ 3463 Sightseeing 题解
题目
Tour operator Your Personal Holiday organises guided bus trips across the Benelux. Every day the bus moves from one city S to another city F. On this way, the tourists in the bus can see the sights alongside the route travelled. Moreover, the bus makes a number of stops (zero or more) at some beautiful cities, where the tourists get out to see the local sights.
Different groups of tourists may have different preferences for the sights they want to see, and thus for the route to be taken from S to F. Therefore, Your Personal Holiday wants to offer its clients a choice from many different routes. As hotels have been booked in advance, the starting city S and the final city F, though, are fixed. Two routes from S to F are considered different if there is at least one road from a city A to a city B which is part of one route, but not of the other route.
There is a restriction on the routes that the tourists may choose from. To leave enough time for the sightseeing at the stops (and to avoid using too much fuel), the bus has to take a short route from S to F. It has to be either a route with minimal distance, or a route which is one distance unit longer than the minimal distance. Indeed, by allowing routes that are one distance unit longer, the tourists may have more choice than by restricting them to exactly the minimal routes. This enhances the impression of a personal holiday.
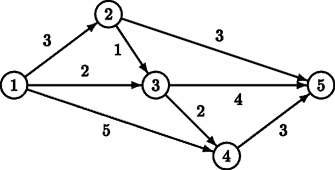
For example, for the above road map, there are two minimal routes from S = 1 to F = 5: 1 → 2 → 5 and 1 → 3 → 5, both of length 6. There is one route that is one distance unit longer: 1 → 3 → 4 → 5, of length 7.
Now, given a (partial) road map of the Benelux and two cities S and F, tour operator Your Personal Holiday likes to know how many different routes it can offer to its clients, under the above restriction on the route length.
输入格式
The first line of the input file contains a single number: the number of test cases to follow. Each test case has the following format:
One line with two integers N and M, separated by a single space, with \(2 ≤ N ≤ 1,000\) and \(1 ≤ M ≤ 10, 000\): the number of cities and the number of roads in the road map.
M lines, each with three integers A, B and L, separated by single spaces, with \(1 ≤ A, B ≤ N, A ≠ B\) and \(1 ≤ L ≤ 1,000\), describing a road from city \(A\) to city \(B\) with length \(L\).
The roads are unidirectional. Hence, if there is a road from \(A\) to \(B\), then there is not necessarily also a road from \(B\) to \(A\). There may be different roads from a city A to a city B.
One line with two integers \(S\) and \(F\), separated by a single space, with \(1 ≤ S, F ≤ N\) and \(S ≠ F\): the starting city and the final city of the route.
There will be at least one route from \(S\) to \(F\).
输出格式
For every test case in the input file, the output should contain a single number, on a single line: the number of routes of minimal length or one distance unit longer. Test cases are such, that this number is at most 109 = 1,000,000,000.
输入样例
25 81 2 31 3 21 4 52 3 12 5 33 4 23 5 44 5 31 55 62 3 13 2 13 1 104 5 25 2 75 2 74 1
输出样例
32
代码
实际上就是最短路, 但是增加了一个次长路, 也很好解决
在Dijkstra更新时, 每次构建一个新路径, 做一下判断, 不仅更新最短路, 还要更新次短路
记录源点到某点的最短路和次短路
如果新路径小于最短路, 那么新路径变成最短路, 原来的最短路变成次短路;
如果新路径等于最短路, 那么最短路方法数+1
如果新路径大于最短路小于次短路, 更新次短路
如果新路径等于次短路, 那么次短路方法数+1
代码
#include <cstdio>#include <cstring>using namespace std;const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f, VM = 1010, EM = 10010;struct Edge { int to, next, w; } edges[EM << 1];int dis[VM][2], head[VM], num[VM][2], n, m, cnt;bool vis[VM][2];void add(int u, int v, int w) { edges[++cnt] = (Edge){v, head[u], w}, head[u] = cnt; }void Dijkstra(int s, int e) {memset(vis, false, sizeof(vis));memset(num, 0, sizeof(num));for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) dis[i][0] = INF, dis[i][1] = INF;dis[s][0] = 0, num[s][0] = 1;int p, flag;for (int i = 1; i <= 2 * n - 1; i++) {int minn = INF;for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {if (!vis[j][0] && minn > dis[j][0]) {flag = 0;minn = dis[p = j][0];} else if (!vis[j][1] && minn > dis[j][1]) {flag = 1;minn = dis[p = j][1];}}if (minn == INF) break;vis[p][flag] = true;for (int j = head[p]; j; j = edges[j].next) {int v = edges[j].to;if (dis[v][0] > minn + edges[j].w) {dis[v][1] = dis[v][0];num[v][1] = num[v][0];dis[v][0] = minn + edges[j].w;num[v][0] = num[p][flag];} else if (dis[v][0] == minn + edges[j].w)num[v][0] += num[p][flag];else if (dis[v][1] > minn + edges[j].w) {dis[v][1] = minn + edges[j].w;num[v][1] = num[p][flag];} else if (dis[v][1] == minn + edges[j].w)num[v][1] += num[p][flag];}}if (dis[e][1] == dis[e][0] + 1) num[e][0] += num[e][1];printf("%d\n", num[e][0]);}int main() {int T;scanf("%d", &T);while (T--) {cnt = 0;memset(head, -1, sizeof(head));scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);int u, v, w;while (m--) {scanf("%d%d%d", &u, &v, &w);add(u, v, w);}int s, e;scanf("%d%d", &s, &e);Dijkstra(s, e);}return 0;}
POJ 3463 Sightseeing 题解的更多相关文章
- poj 3463 Sightseeing( 最短路与次短路)
http://poj.org/problem?id=3463 Sightseeing Time Limit: 2000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissio ...
- POJ - 3463 Sightseeing 最短路计数+次短路计数
F - Sightseeing 传送门: POJ - 3463 分析 一句话题意:给你一个有向图,可能有重边,让你求从s到t最短路的条数,如果次短路的长度比最短路的长度多1,那么在加上次短路的条数. ...
- poj 3463 Sightseeing——次短路计数
题目:http://poj.org/problem?id=3463 当然要给一个点记最短路和次短路的长度和方案. 但往优先队列里放的结构体和vis竟然也要区分0/1,就像把一个点拆成两个点了一样. 不 ...
- POJ 3463 Sightseeing (次短路经数)
Sightseeing Time Limit: 2000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions:10005 Accepted: 3523 Descr ...
- POJ 3463 Sightseeing 【最短路与次短路】
题目 Tour operator Your Personal Holiday organises guided bus trips across the Benelux. Every day the ...
- poj 3463 Sightseeing(次短路+条数统计)
/* 对dij的再一次理解 每个点依旧永久标记 只不过这里多搞一维 0 1 表示最短路还是次短路 然后更新次数相当于原来的两倍 更新的时候搞一下就好了 */ #include<iostream& ...
- POJ 3463 Sightseeing
最短路+次短路(Dijkstra+priority_queue) 题意是要求你找出最短路的条数+与最短路仅仅差1的次短路的条数. 開始仅仅会算最短路的条数,和次短路的长度.真是给次短路条数跪了.ORZ ...
- POJ 3463 Sightseeing (次短路)
题意:求两点之间最短路的数目加上比最短路长度大1的路径数目 分析:可以转化为求最短路和次短路的问题,如果次短路比最短路大1,那么结果就是最短路数目加上次短路数目,否则就不加. 求解次短路的过程也是基于 ...
- POJ 1637 Sightseeing tour(最大流)
POJ 1637 Sightseeing tour 题目链接 题意:给一些有向边一些无向边,问能否把无向边定向之后确定一个欧拉回路 思路:这题的模型很的巧妙,转一个http://blog.csdn.n ...
随机推荐
- ReentrantReadWriteLock源码分析及理解
本文结构 读写锁简介:介绍读写锁.读写锁的特性以及类定义信息 公平策略及Sync同步器:介绍读写锁提供的公平策略以及同步器源码分析 读锁:介绍读锁的一些常用操作和读锁的加锁.解锁的源码分析 写锁:介绍 ...
- react使用Echarts绘制高亮可点击选中的省市地图
最近做项目遇到一个需求,需要显示广东省各个地级市的地图,并且鼠标移入高亮显示,鼠标点击可以选中某个地级市.在网上查阅了大量资料之后,最后选择了使用echarts实现该需求.在此记录一下,希望可以帮到有 ...
- redis 数据删除策略和逐出算法
数据存储和有效期 在 redis 工作流程中,过期的数据并不需要马上就要执行删除操作.因为这些删不删除只是一种状态表示,可以异步的去处理,在不忙的时候去把这些不紧急的删除操作做了,从而保证 redis ...
- 封装find_element
因为find_element_by_id,find_element_by_name底层都是用find_element实现元素查找 #!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: ...
- Numpy中的广播机制,数组的广播机制(Broadcasting)
这篇文章把numpy中的广播机制讲的十分透彻: https://jakevdp.github.io/PythonDataScienceHandbook/02.05-computation-on-arr ...
- PytorchMNIST(使用Pytorch进行MNIST字符集识别任务)
都说MNIST相当于机器学习界的Hello World.最近加入实验室,导师给我们安排了一个任务,但是我才刚刚入门呐!!没办法,只能从最基本的学起. Pytorch是一套开源的深度学习张量库.或者我倾 ...
- 如何用Python从海量文本抽取主题?
摘自https://www.jianshu.com/p/fdde9fc03f94 你在工作.学习中是否曾因信息过载叫苦不迭?有一种方法能够替你读海量文章,并将不同的主题和对应的关键词抽取出来,让你谈笑 ...
- VUE+ELEMENT-UI的后台项目封装组件--查询form的封装
最近项目打算重构,项目的模块几乎都是以后台查询展示的传统的增删改差模式,所以卑微的我想要自己封装一下查询form,先上效果图 子组件页面: <template> <div class ...
- 多语言工作者の十日冲刺<10/10>
这个作业属于哪个课程 软件工程 (福州大学至诚学院 - 计算机工程系) 这个作业要求在哪里 团队作业第五次--Alpha冲刺 这个作业的目标 团队进行Alpha冲刺--第十天(05.09) 作业正文 ...
- awk 命令使用入门
Linux 下处理和分析文本文件内容,AWK 命令是一个强有力的工具.特别是文件内容是以行和列的形式排版的时候,AWK 就是命令行界的 Excel 啊! 简单的 awk 命令可以直接在命令行中使用,复 ...
