sklearn包学习
1首先是sklearn的官网:http://scikit-learn.org/stable/
在官网网址上可以看到很多的demo,下边这张是一张非常有用的流程图,在这个流程图中,可以根据数据集的特征,选择合适的方法。

2.sklearn使用的小例子
import numpy as np
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier iris=datasets.load_iris()
iris_X=iris.data
iris_y=iris.target print(iris_X[:2,:]) #输出数据的前2行,
print(iris_y) X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(iris_X,iris_y,test_size=0.3) #把数据集分为训练集和测试集两个部分一部分是训练集,一部分是测试集,其中测试集占了30%
print(y_train) knn=KNeighborsClassifier()
knn.fit(X_train,y_train)
print(knn.predict(X_test))
print(y_test)
3.sklearn数据集
在上边例子中,直接使用了sklearn的数据集,在这个包中还有很多其他的数据集,数据集的网址:http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/classes.html#module-sklearn.datasets不仅可以使用数据集中的数据,还可以生成虚拟的数据,
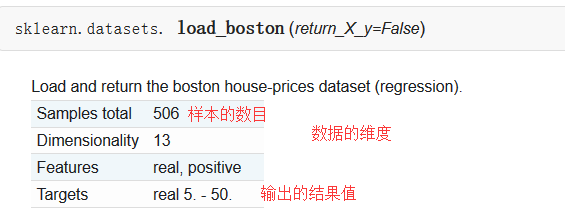
sklearn中自带的数据集,以房屋数据集为例:
sklearn可以生成的数据集,回归模型中使用的数据集为例:

| Parameters: |
n_samples : int, optional (default=100):The number of samples. n_features : int, optional (default=100):The number of features. n_informative : int, optional (default=10):The number of informative features, i.e., the number of features used to build the linear model used to generate the output. n_targets : int, optional (default=1):The number of regression targets, i.e., the dimension of the y output vector associated with a sample. By default, the output is a scalar. bias : float, optional (default=0.0):The bias term in the underlying linear model. effective_rank : int or None, optional (default=None) if not None:The approximate number of singular vectors required to explain most of the input data by linear combinations. Using this kind of singular spectrum in the input allows the generator to reproduce the correlations often observed in practice. if None:The input set is well conditioned, centered and gaussian with unit variance. tail_strength : float between 0.0 and 1.0, optional (default=0.5):The relative importance of the fat noisy tail of the singular values profile if effective_rank is not None. noise : float, optional (default=0.0):The standard deviation of the gaussian noise applied to the output. shuffle : boolean, optional (default=True):Shuffle the samples and the features. coef : boolean, optional (default=False):If True, the coefficients of the underlying linear model are returned. random_state : int, RandomState instance or None, optional (default=None):If int, random_state is the seed used by the random number generator; If RandomState instance, random_state is the random number generator; If None, the random number generator is the RandomState instance used by np.random. |
|---|---|
| Returns: |
X : array of shape [n_samples, n_features]:The input samples. y : array of shape [n_samples] or [n_samples, n_targets]:The output values. coef : array of shape [n_features] or [n_features, n_targets], optional:The coefficient of the underlying linear model. It is returned only if coef is True. |
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #使用以后的数据集进行线性回归
loaded_data=datasets.load_boston()
data_X=loaded_data.data
data_y=loaded_data.target model=LinearRegression()
model.fit(data_X,data_y) print(model.predict(data_X[:4,:]))
print(data_y[:4]) #使用生成线性回归的数据集,最后的数据集结果用散点图表示
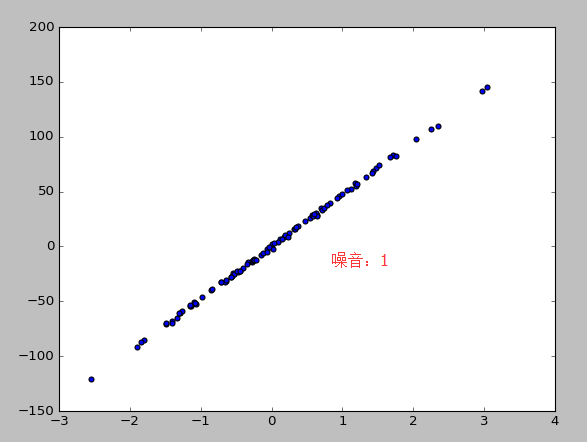
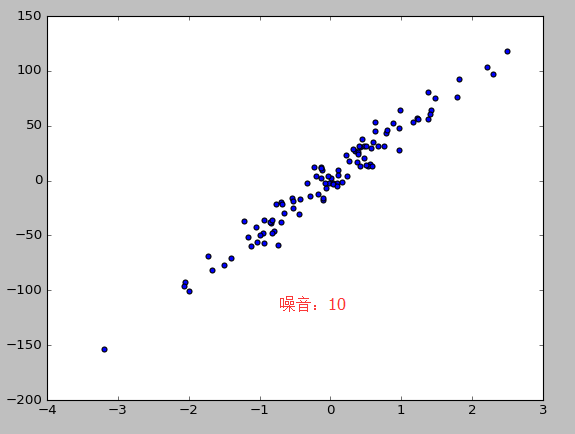
X,y=datasets.make_regression(n_samples=100,n_features=1,n_targets=1,noise=10) #n_samples表示样本数目,n_features特征的数目 n_tragets noise噪音
plt.scatter(X,y)
plt.show()
4。模型的参数
sklearn 的 model 属性和功能都是高度统一的. 你可以运用到这些属性查看 model 的参数和值等等.
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #使用以后的数据集进行线性回归
loaded_data=datasets.load_boston()
data_X=loaded_data.data
data_y=loaded_data.target model=LinearRegression()
model.fit(data_X,data_y) print(model.predict(data_X[:4,:]))
print(data_y[:4]) #参数
print(model.coef_) #如果y=0.1x+0.3 则此行输出的结果为0.1
print(model.intercept_) #此行输出的结果为0.3
print(model.get_params()) #模型定义时定义的参数,如果没有定义则返回默认值
print(model.score(data_X,data_y)) #给训练模型打分,注意用在LinearR中使用R^2 conefficient of determination打分
输出的结果:
[ 30.00821269 25.0298606 30.5702317 28.60814055]
[ 24. 21.6 34.7 33.4]
[ -1.07170557e-01 4.63952195e-02 2.08602395e-02 2.68856140e+00
-1.77957587e+01 3.80475246e+00 7.51061703e-04 -1.47575880e+00
3.05655038e-01 -1.23293463e-02 -9.53463555e-01 9.39251272e-03
-5.25466633e-01]
36.4911032804
{'fit_intercept': True, 'normalize': False, 'n_jobs': 1, 'copy_X': True}
0.740607742865
5.标准化:normalization
normalization 在数据跨度不一的情况下对机器学习有很重要的作用.特别是各种数据属性还会互相影响的情况之下. Scikit-learn 中标准化的语句是 preprocessing.scale() . scale 以后, model 就更能从标准化数据中学到东西.
from sklearn import preprocessing #进行标准化数据时,需要引入个包
import numpy as np
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
from sklearn.datasets.samples_generator import make_classification
from sklearn.svm import SVC
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt X,y=make_classification(n_samples=300,n_features=2,n_redundant=0,n_informative=2,random_state=22,n_clusters_per_class=1,scale=100) #X=preprocessing.minmax_scale(X,feature_range=(-1,1))
X=preprocessing.scale(X) #0.966666666667 没有 0.477777777778
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(X,y,test_size=0.3)
clf=SVC()
clf.fit(X_train,y_train)
print(clf.score(X_test,y_test)) plt.scatter(X[:,0],X[:,1],c=y)
plt.show() a=np.array([[10,2.7,3.6],
[-100,5,-2],
[120,20,40]],dtype=np.float64) #每一列代表一个属性
print(a) #标准化之前a
print(preprocessing.scale(a)) #标准化之后的a
6.交叉验证 cross validation(1)
sklearn 中的 cross validation 交叉验证 对于我们选择正确的 model 和model 的参数是非常有帮助的. 有了他的帮助, 我们能直观的看出不同 model 或者参数对结构准确度的影响.
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier iris=load_iris()
iris_X=iris.data
iris_y=iris.target #直接训练
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(iris_X,iris_y,random_state=4) #把数据集分为训练集和测试集两个部分一部分是训练集,一部分是测试集,其中测试集占了30%
knn=KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=5)
knn.fit(X_train,y_train)
print(knn.score(X_test,y_test)) #0.973684210526 #交叉验证
from sklearn.cross_validation import cross_val_score
knn=KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=5)
score=cross_val_score(knn,iris_X,iris_y,cv=5,scoring='accuracy') #c分成几组 scoring是准确度
print(score)
print(score.mean()) import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
k_range=range(1,31)
k_score=[]
for k in k_range:
knn=KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=k)
#score=cross_val_score(knn,iris_X,iris_y,cv=10,scoring='accuracy')#for classification 精度
loss=-cross_val_score(knn,iris_X,iris_y,cv=10,scoring='mean_squared_error') #for regression 损失函数
#k_score.append(score.mean())
k_score.append(loss.mean())
plt.plot(k_range,k_score)
plt.xlabel("Value of K for KNN")
plt.ylabel("Cross-validates Accuracy")
plt.show()
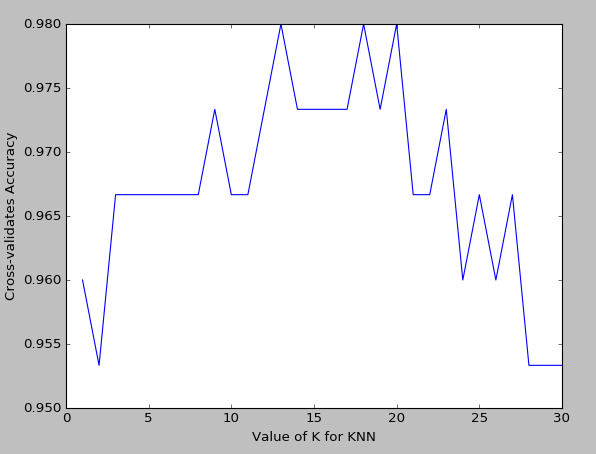
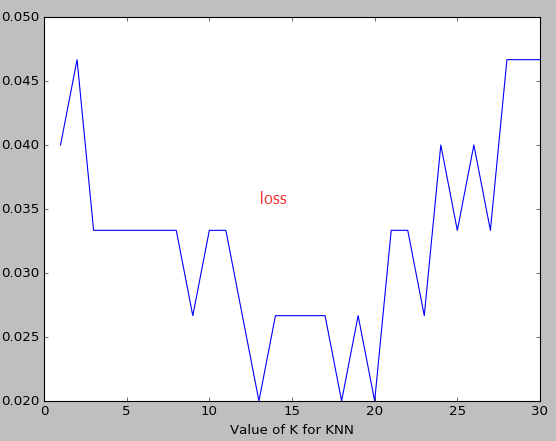
k越大越容易underfitting而不是overfitting
如果想要对不同的机器学习模型来计算,可能需要把knn的值换一下
7.交叉验证 cross validation(2)
sklearn.learning_curve 中的 learning curve 可以很直观的看出我们的 model 学习的进度,对比发现有没有 overfitting 的问题.然后我们可以对我们的 model 进行调整,克服 overfitting 的问题.
from sklearn.learning_curve import learning_curve #可视化学习的整个过程
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
from sklearn.svm import SVC
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np digits=load_digits()
X=digits.data
y=digits.target
train_sizes,train_loss,test_loss=learning_curve(
SVC(gamma=0.1),X,y,cv=10,scoring="mean_squared_error",
train_sizes=[0.1,0.25,0.5,0.75,1]) #记录的点是学习过程中的10%,25%等等的点
train_loss_mean= (-1)*np.mean(train_loss,axis=1)
test_loss_mean= (-1)*np.mean(test_loss,axis=1) plt.plot(train_sizes,train_loss_mean,"o-",color="r",label="Training")
plt.plot(train_sizes,test_loss_mean,"o-",color="g",label="Cross-validation") plt.xlabel("Training examples")
plt.ylabel("Loss")
plt.legend(loc="best")
plt.show()
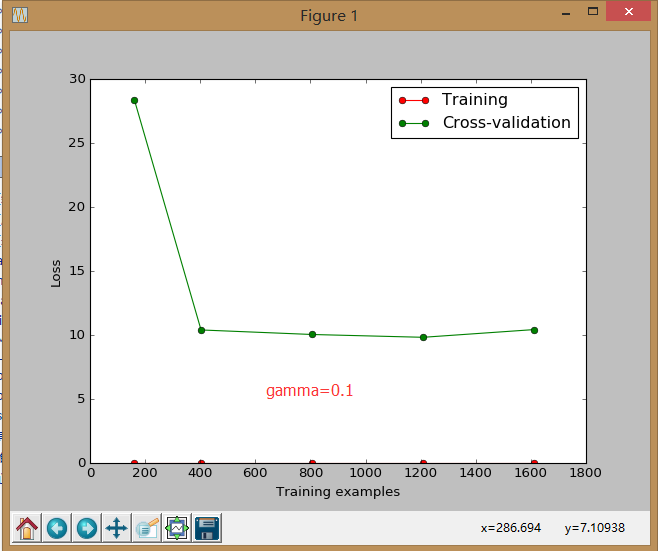
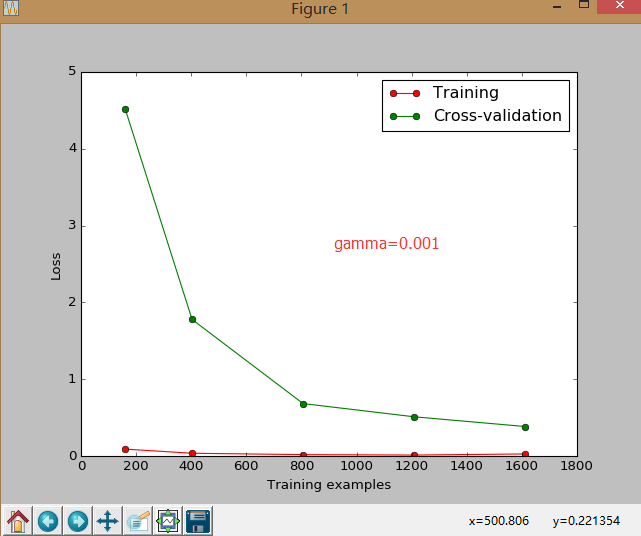
8.交叉验证 cross validation(3)
连续三节的 cross validation让我们知道在机器学习中 validation 是有多么的重要, 这一次的 sklearn 中我们用到了 sklearn.learning_curve 当中的另外一种, 叫做 validation_curve, 用这一种 curve 我们就能更加直观看出改变 model 中的参数的时候有没有 overfitting 的问题了.这也是可以让我们更好的选择参数的方法.
from sklearn.learning_curve import validation_curve #可视化学习的整个过程
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
from sklearn.svm import SVC
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np digits=load_digits()
X=digits.data
y=digits.target
gamma_range=np.logspace(-6,-2.3,5)#从-6到-2.3取5个点
train_loss,test_loss=validation_curve(
SVC(),X,y,param_name="gamma",param_range=gamma_range,cv=10,scoring="mean_squared_error")
train_loss_mean= (-1)*np.mean(train_loss,axis=1)
test_loss_mean= (-1)*np.mean(test_loss,axis=1) plt.plot(gamma_range,train_loss_mean,"o-",color="r",label="Training")
plt.plot(gamma_range,test_loss_mean,"o-",color="g",label="Cross-validation") plt.xlabel("gamma")
plt.ylabel("Loss")
plt.legend(loc="best")
plt.show()
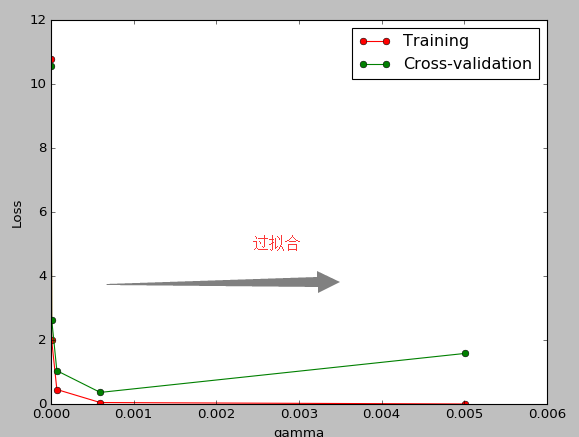
9,存储模型:
我们练习好了一个 model 以后总需要保存和再次预测, 所以保存和读取我们的 sklearn model 也是同样重要的一步.本文采用了两种方法来存储
from sklearn import svm
from sklearn import datasets clf=svm.SVC()
iris=datasets.load_iris()
X,y=iris.data,iris.target
clf.fit(X,y) #method1:pickle
import pickle
#save
with open('save/clf.pickle','wb')as f:
pickle.dump(clf,f) #restore
with open('save/clf.pickle','rb') as f:
clf=pickle.load(f)
print(clf.predict(X[0:1])) #method2:joblib
from sklearn.externals import joblib
#save
joblib.dump(clf,'save/clf.pkl')
clf3=joblib.load('save/clf.pkl')
print(clf3.predict(X[0:1]))
youtube学习 :
周莫烦:https://www.youtube.com/user/MorvanZhou
个人主页:https://morvanzhou.github.io/tutorials/
源码:https://github.com/MorvanZhou
sklearn包学习的更多相关文章
- R语言爬虫初尝试-基于RVEST包学习
注意:这文章是2月份写的,拉勾网早改版了,代码已经失效了,大家意思意思就好,主要看代码的使用方法吧.. 最近一直在用且有维护的另一个爬虫是KINDLE 特价书爬虫,blog地址见此: http://w ...
- sklearn包中有哪些数据集你都知道吗?
注册了博客园一晃有3个月了,同时接触机器学习也断断续续的算是有1个月了.今天就用机器学习神器sklearn包的相关内容作为我的开篇文章吧. 本文将对sklearn包中的数据集做一个系统介绍,并简单说一 ...
- Python: 安装 sklearn 包出现错误的解决方法
今天在安装 Python 的 sklearn 包时出现了 Cannot uninstall 'numpy' 和 Cannot uninstall 'scipy' 错误,下面记录了我尝试了很多网上的方法 ...
- sklearn包
sklearn官方学习资料 https://scikit-learn.org/stable/user_guide.html 1 Supervised learning监督学习 1.1 线性模型 1.2 ...
- sklearn包源码分析(二)——ensemble(未完成)
网络资源 sklearn包tree模型importance解析
- 调用sklearn包中的PLA算法[转载]
转自:https://blog.csdn.net/u010626937/article/details/72896144#commentBox 1.Python的机器学习包sklearn中也包含了感知 ...
- java.util.concurrent包学习笔记(一)Executor框架
类图: 其实从类图我们能发现concurrent包(除去java.util.concurrent.atomic 和 java.util.concurrent.locks)中的内容并没有特别多,大概分为 ...
- Ubuntu16.04下安装配置numpy,scipy,matplotlibm,pandas 以及sklearn+深度学习tensorflow配置+Keras2.0.6(非Anaconda环境)
1.ubuntu镜像源准备(防止下载过慢): 参考博文:http://www.cnblogs.com/top5/archive/2009/10/07/1578815.html 步骤如下: 首先,备份一 ...
- Go中sync包学习
前面刚讲到goroutine和channel,通过goroutine启动一个协程,通过channel的方式在多个goroutine中传递消息来保证并发安全.今天我们来学习sync包,这个包是Go提供的 ...
随机推荐
- [转]android ANR产生原因和解决办法
ANR (Application Not Responding) ANR定义:在Android上,如果你的应用程序有一段时间响应不够灵敏,系统会向用户显示一个对话框,这个对话框称作应用程序无响应(AN ...
- tpshop全局公共方法
TPshop 全局公告函数库 前后台可用 这里只列出有哪些方法, 简单描述, 具体的函数体查看 Application\Common\Common\function.php 文件 <?php ...
- QA:Initialization of bean failed; nested exception is java.lang.AbstractMethodError
Q: <hibernate.version>5.2.10.Final</hibernate.version><dependency> <groupId> ...
- unity---各种资源对应的格式
我们打包AssetBundle后,Unity3D会根据文件的后缀名将文件转换为特定的类型对象存储起来,我们后期获取时需要根据这些类型取出打包的数据,这里记录下不同后缀文件打包后的类型. 文本格式 支持 ...
- IDEA VS 快捷键 大全
[参考]IntelliJ IDEA 常用 黄金 快捷键 总结 不断更新 一.VS常用快捷键 (01).快速插入foreach.try等循环:Tab + Tab; (02).回到光标前一位置: ...
- python 程序构架浅析
定义:通常的 Python 程序的构架是指:将一个程序分割为源代码文件的集合以及将这些部分连接在一起的方法. python的程序构架可表示为: 一个python程序就是一个模块的系统.它有一个顶层文件 ...
- TensoFlow的tf.reshape()
tf.reshape(tensor,shape,name=None) 函数的作用是将tensor变换为参数shape形式,其中的shape为一个列表形式,特殊的是列表可以实现逆序的遍历,即list(- ...
- oracle long类型转换成varchar2
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION LONG_TO_CHAR( in_rowid rowid,in_owner varchar,in_table_name varchar,in_co ...
- 如何将数组中的后面m个数移动为前面m个数
思路分析: 可以通过递归的方法实现调整: (1)将前n-m个元素的顺序颠倒. (2)将后面m个元素的顺序颠倒. (3)将n个元素的顺序全部颠倒. 通过以上3个步骤的执行,就可以把数组的元素颠倒. 代码 ...
- 7 -- Spring的基本用法 -- 8... 抽象Bean与子Bean;Bean继承与Java继承的区别;容器中的工厂Bean;获得Bean本身的id;强制初始化Bean
7.8 深入理解容器中的Bean 7.8.1 抽象Bean与子Bean 把多个<bean.../>配置中相同的信息提取出来,集中成配置模版------这个配置模版并不是真正的Bean,因此 ...
