树的平衡 AVL Tree
本篇随笔主要从以下三个方面介绍树的平衡:
1):BST不平衡问题
2):BST 旋转
3):AVL Tree
一:BST不平衡问题的解析
之前有提过普通BST的一些一些缺点,例如BST的高度是介于lgN和N之间的,如果是N的的话,显然效率很低,不是我们需要的;但是在实际情况中,BST的高度h = N的情况却经常出现,例如下图所示。在BST中search,insert的running time都等于BST的高度h,我们肯定希望高度h越小越好,best case就是lgN。下图的example 2的情况,我们会称之为这个BST是不平衡的。 所以如果遇到这种不平衡的BST,我们如何解决呢?如何将不平衡的BST转化成平衡的BST呢?如何将BST的高度h从N转化成lgN呢?
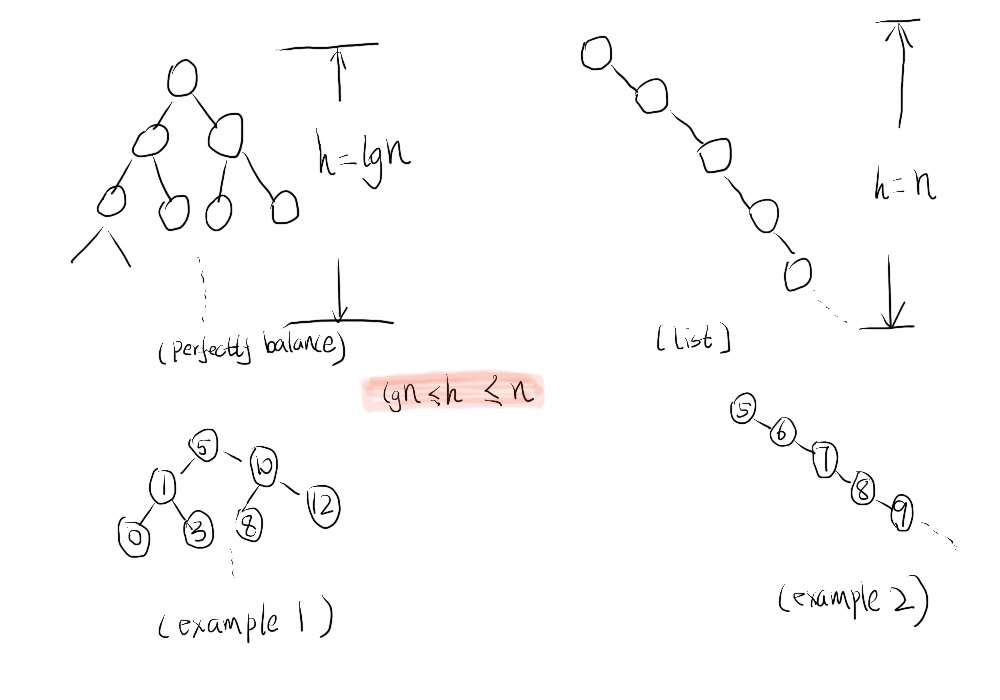
二:树的平衡
下面我们就来介绍一下树的旋转 rotation。BST是可以经过一些旋转操作后,仍然保持BST的结构不变的,即对于每一个node,该node的left child的值总是小于这个node的值,而该node的right child的值总是大于这个node的值。经过总结,这个旋转主要可以分为4中模式,这四种模式如下面的两图所示:
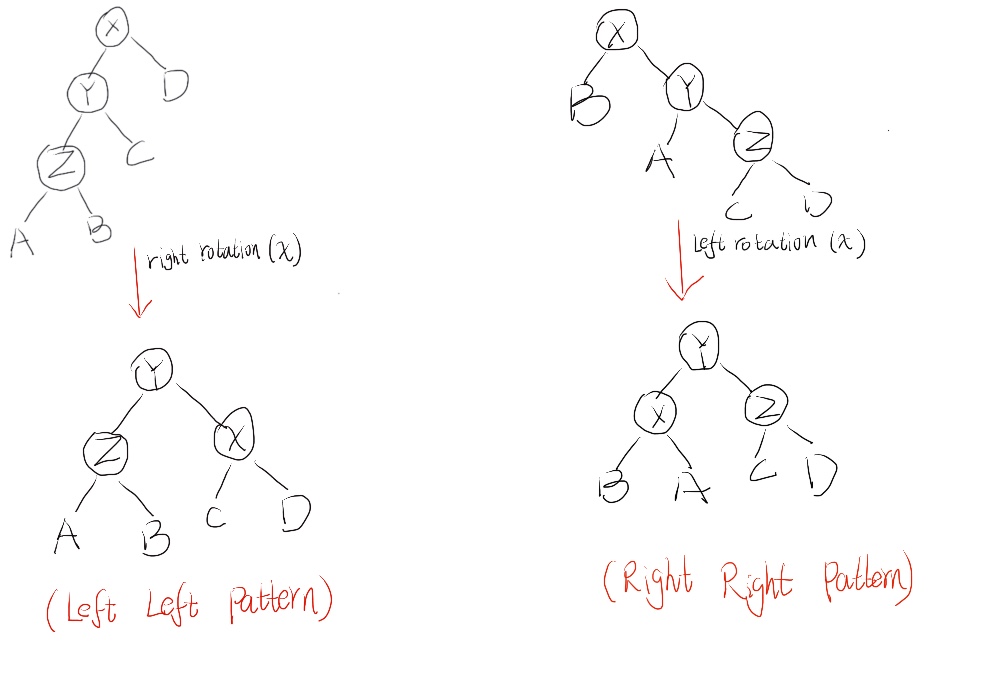
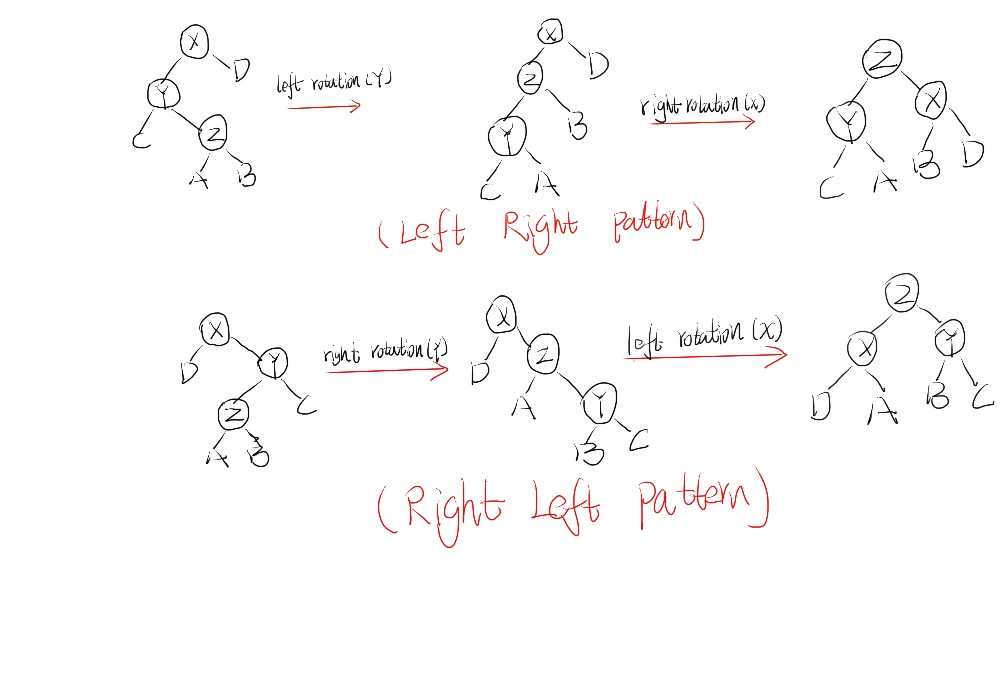
这四种rotation的方式是由BST的特性所决定的,至于为什么这样旋转是是正确的,也是由BST的特点所确定的,我在这就不证明了。只要大家记住BST可以有这4中旋转模式即可。其实上面所示的rotation过程,都是为了平衡树的目的。 那么现在有一个问题来了,我们说了这么多平衡,不平衡的概念,前面我们都是通过直观的感受来体味平衡或者不平衡,那么到底有什么明确的指标可以指明一个BST到底是平衡还是不平衡的呢???这个指标到底是什么呢?那么下面就要解释AVL Tree的概念了。
三:AVL Tree
首先AVL Tree要满足以下2个条件:
1. AVL Tree遵循BST的结构;即left child 小于当前node, right child大于当前node。
2.每一个node的2个 child nodes的高度相差不大于1。
根据上面的条件,我们可以看出AVL Tree其本质是一种特殊的BST。所以我们现在有一个定性的指标来判断一个BST是不是平衡的了,这个指标就是上面2个条件。当然了BST中有很多指标来判读一个BST是不是平衡的,我们这里只是用AVL Tree作为其中之一个指标,你也可以用其他的指标方法。
所以AVL Tree是平衡的,其高度是h=lgN;
在AVL Tree中,每一个node的高度等于取其2个child node 的较大的高度值加1,即max[left child height, right child height]+1; 若node==NULL,则其高度默认为-1.
当在构建AVL Tree的过程中,向其中insert node的时候,首先第一步跟BST insert一样,然后第二步是要检查insert后node的2个children之间的高度差,然后根据相应的高度差来判断相应的rotation的pattern,经过旋转后,使整个Tree仍然保持AVL Tree的特性,即满足上面的2个条件,所以仍然是平衡的。由于insert,search的操作的时间复杂度在BST中都是等于树的高度,AVL Tree作为一种特殊的BST,insert, search的操作的时间复杂度自然也是等于AVL的高度h=lgN. 这样的时间复杂度还是可以让我们满意的,其效率也要远远高于O(N)。AVL Tree的C++ 实现过程如下面的代码所示,以下代码实现了AVL Tree的insertion, sorting, rotation等功能。代码仅供学习交流等非盈利使用,不能用于商业目的,作者保留追溯的权利。
#include "AVLTree.hpp"
using namespace std; AVL_Tree::AVL_Tree(){ this->root = NULL;
} void AVL_Tree::setRoot(Node *root){ this->root = root;
}
Node *AVL_Tree::getRoot(){ return this->root;
} /*
* height of tree or subtree
*
* a node's height equals the max of node's left child's height and node's right child's height plus 1
*
*parameters:
1, node;//the node that we want to measure with
*
*return: the height of the node
*/
int AVL_Tree::height(Node *node){ int h = -; if (node != NULL) { int l_height = height(node->getLeft());
int r_height = height(node->getRight());
h = std::max(l_height,r_height) + ;
} return h;
}
/*
* the height difference of two children nodes
*
*parameters:
* 1, node;//the node which we want to know the differences of its two children
*
*return: int; the height difference of the two children nodes
*/ int AVL_Tree::heightDiff(Node *node){ int l_height = height(node->getLeft());
int r_height = height(node->getRight()); return l_height-r_height; } /*
*
*4 types of rotations
*
*1)left left pattern
*2)left right pattern
*3)right right pattern
*4)right left pattern
*
*/
void AVL_Tree::ll_rotation(Node *node){ int value = node->getData();
Node *temp = node->getLeft(); node->setData(temp->getData());
node->setLeft(temp->getLeft()); temp->setData(value);
temp->setLeft(temp->getRight());
temp->setRight(node->getRight());
node->setRight(temp); }
void AVL_Tree::lr_rotation(Node *node){ Node *temp = node->getLeft();
node->setLeft(temp->getRight());
temp->setRight(temp->getRight()->getLeft());
node->getLeft()->setLeft(temp);
ll_rotation(node); }
void AVL_Tree::rr_rotation(Node *node){ int value = node->getData();
Node *temp = node->getRight(); node->setData(temp->getData());
node->setRight(temp->getRight()); temp->setData(value);
temp->setRight(temp->getLeft());
temp->setLeft(node->getLeft());
node->setLeft(temp); }
void AVL_Tree::rl_rotation(Node *node){ Node *temp = node->getRight();
node->setRight(temp->getLeft());
temp->setLeft(node->getRight()->getRight());
node->getRight()->setRight(temp);
rr_rotation(node); } /*
*Description: balancing the node whoes two children nodes' height difference is greater than 1 or smaller than -1
*
*parameters:
* 1, node;//the node which we want to rotate with, it is the polar point of the rotation
*
*
*return: void
*
*
*
*/
void AVL_Tree::balance(Node *node){ int balance_factor = heightDiff(node);//differences of the node's two sub nodes. if (balance_factor>) {//left side is heavy if (heightDiff(node->getLeft())>) {//left left case ll_rotation(node); }else{//left right case lr_rotation(node);
} }else if (balance_factor<-){//right side heavy if (heightDiff(node->getRight())<) {//right right case rr_rotation(node); }else{//right left case rl_rotation(node);
} }
} /*
* Description: insert a node into the AVL tree and keep the whole structure balanced after inserting
*
*Parameters:
* 1, Node *node;//the node which needs to be inserted
* 2, Node *root;//the root of the tree or subtree;
*
*Return: Node *;//the parent node of the inserted node;
*/ Node *AVL_Tree::insert(Node *node, Node *root){ if (this->root == NULL) { Node *root = new Node();
root->setLeft(NULL);
root->setRight(NULL);
root->setData(node->getData());
this->root = root; return root;
} if (root == NULL) { return node; }else if(node->getData() < root->getData()){ root->setLeft(insert(node, root->getLeft()));
balance(root); }else if (node->getData()>=root->getData()){ root->setRight(insert(node, root->getRight()));
balance(root);
} return root;
} /*
*Description: print out the sorted nodes of the AVL tree of AVL subtree
*
*parameters:
* 1, Node *node;//the root of the AVL tree of AVL subtree
*
*
*/
void AVL_Tree::inorderSort(Node *node){ if (node == NULL) { return;
} inorderSort(node->getLeft());
std::cout<<node->getData()<<" ";
inorderSort(node->getRight()); }
树的平衡 AVL Tree的更多相关文章
- PAT Advanced 1066 Root of AVL Tree (25) [平衡⼆叉树(AVL树)]
题目 An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, the heights of the two child ...
- AVL树 高度平衡的二叉查找树
1.What is AVL tree? AVL tree 是一种特殊的二叉查找树,,首先我们要在树中引入平衡因子balance,表示结点右子树的高度减去左子树的高度差(右-左),对于一棵AVL树要么它 ...
- AVL树(平衡二叉查找树)
首先要说AVL树,我们就必须先说二叉查找树,先介绍二叉查找树的一些特性,然后我们再来说平衡树的一些特性,结合这些特性,然后来介绍AVL树. 一.二叉查找树 1.二叉树查找树的相关特征定义 二叉树查找树 ...
- PAT 1066 Root of AVL Tree[AVL树][难]
1066 Root of AVL Tree (25)(25 分) An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, ...
- PAT甲级——1123 Is It a Complete AVL Tree (完全AVL树的判断)
嫌排版乱的话可以移步我的CSDN:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44385565/article/details/89390802 An AVL tree is a sel ...
- 树的平衡之AVL树——错过文末你会后悔,信我
学习数据结构应该是一个循序渐进的过程: 当我们学习数组时,我们要体会数组的优点:仅仅通过下标就可以访问我们要找的元素(便于查找). 此时,我们思考:假如我要在第一个元素前插入一个新元素?采用数组需要挪 ...
- 04-树5 Root of AVL Tree + AVL树操作集
平衡二叉树-课程视频 An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, the heights of the tw ...
- 判断AVL树是否平衡
AVL树是高度的平衡二插搜索树,其左子树和右子树的高度之差不超过1(树中的左子树和右子树都是AVL树),维持这个高度之差就要控制它的平衡因子.那么判断一颗AVL树是否平衡就需要判断它的左子树和右子树高 ...
- 1066 Root of AVL Tree (25分)(AVL树的实现)
An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, the heights of the two child sub ...
随机推荐
- webservice wsdl语法基础
XML-WSDL基础知识 WSDL 1.1. WSDL 简介 1.1.1. 概述 WSDL 指网络服务描述语言 (Web Services Description Language) WSDL ...
- C. New Year and Rating
C. New Year and Rating time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input stand ...
- 三目运算的使用&bytes类型转str类型
一.三目运算的使用 就像c语言中有三目运算符一样,python中也有三目运算符,废话不多说直接上代码 a=3 c=4 b=a if a>c else c print(b) 意思就和 if a&g ...
- js 添加事件 attachEvent 和 addEventListener 的区别
1.addEventListener 适用w3c标准方法addEventListener绑定事件,如下,事件的执行顺序和绑定顺序一致,执行顺序为method1->method2->meth ...
- 原生addClass 方法 添加类函数
function addClass(id,new_class){ var i,n=0; new_class=new_class.split(","); ...
- display:none,float小秘密
一个元素不管是块元素还是行内元素 在添加了 display:none 之后,就变成了不可见的块元素,可以给他添加长度和高度 在float之后内联元素也会隐性成为 inline-block ...
- luogu P1563 玩具谜题
https://www.luogu.org/problemnew/show/1563 题目: 小南有一套可爱的玩具小人, 它们各有不同的职业. 有一天, 这些玩具小人把小南的眼镜藏了起来. 小南发现玩 ...
- [转载] Netty
转载自http://lippeng.iteye.com/blog/1907279 Netty是什么? 本质:JBoss做的一个Jar包 目的:快速开发高性能.高可靠性的网络服务器和客户端程序 优点:提 ...
- 【手记】让Fiddler抓取入站请求,或者叫用Fiddler做反向代理
注意:本文不涉及HTTPS的场景 最近在弄公众号开发,除了主动去调公众号接口,还存在公众号后台要反过来调你的情形,攻受转换一线间.对于回调的情况,想要知道对方是怎样来请求的很有必要.此前经常用Fidd ...
- Oracle存储过程和自定义函数
新博客文章链接,欢迎大家评论探讨 概述 存储过程和存储函数是指存储在数据库中供所有用户程序调用的子程序叫存储过程.存储函数. 异同点: 存储过程和存储函数的相同点:完成特定功能的程序. 存储过程和存储 ...
