@bzoj - 4356@ Ceoi2014 Wall
@description@
给出一个N*M的网格图,有一些方格里面存在城市,其中首都位于网格图的左上角。
你可以沿着网络的边界走,要求你走的路线是一个环并且所有城市都要被你走出来的环圈起来,即想从方格图的外面走到任意一个城市一定要和你走的路线相交。
你沿着方格的边界走是需要费用的,不同的边界费用可能不同,求最小代价。
1<=N,M<=400,走过边界的代价为正整数且不超过10^9
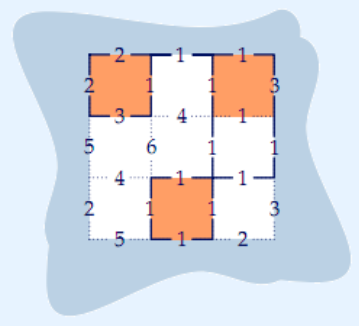
Sample Input
3 3
1 0 1
0 0 0
0 1 0
2 1 1 3
5 6 1 1
2 1 1 3
2 1 1
3 4 1
4 1 1
5 1 2
Sample Output
22
HINT
@solution@
人类智慧题。
首先路径可能重复经过边或者点这件事很难描述,而且本身很不自然。
我们将走过一条边看成两种,一种从左/上侧经过,一种从右/下侧经过(竖着的边就是左右侧,横着的边就是上下侧)。
比如下图就是转变后的例子:
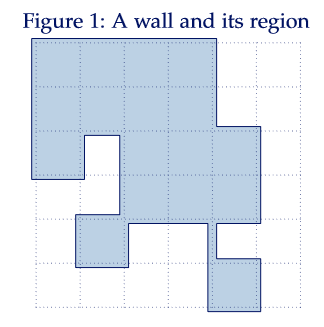
这样就不会经过重边重点,而且可以很自然地描述包含一条边/一个格点的概念。
假如没有额外限制,就只是找一个简单最小环(并且一定包含左上角,因为左上角一定有一个城市)。
如果左上角的格点为 (0, 0),那么跑一个从 (0, 1) 到 (1, 0) 的最短路即可。
但是我怎么表达包含一个城市的概念。
假如只有左上角有城市,则只要确定起点为 (0, 1) 终点为 (1, 0) 就可以包含左上角的城市了。
假如城市与城市之间有些割不断的联系,那么我跑最短路时不横断这些联系,既然我已经包含了左上角,就可以保证所有城市都在最小环里面了。
有一个结论:左上角的格点到城市的左上角的最短路一定会被包含其中。
直观地理解:
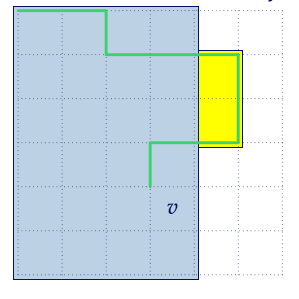
假如蓝色是一种方案,绿色是最短路。当我把黄色区域加入进去过后,因为是最短路,所以方案一定不会变差(否则绿色就不是最短路了)。
即我们总可以用最短路代替边界。
那么建出最短路树,只要不横断这些树边就一定合法了。
具体实现,我们将一个格点拆成四个,建出一个类似于如下的图:
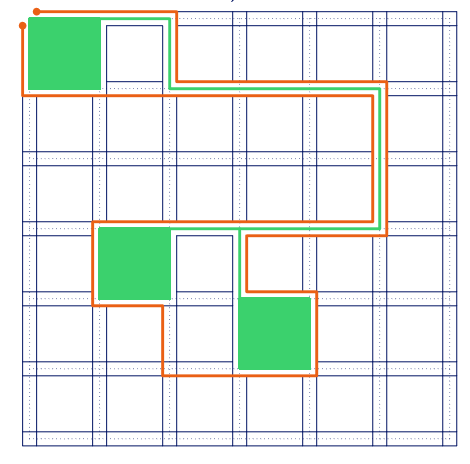
拆出来的四个点之间,如果不会横断最短路就连边权为 0 的边。
同时需要注意,一个城市四个角对应的点不向其他点连边。
左上角的格点拆出来的对应左上角的那个点不连边,跑左上角的格点对应的右上角到左上角的格点对应左下角的那个点的最短路。
两个相邻格点之间也要连,边权即原图中边的边权。
@accepted code@
#include<cstdio>
#include<queue>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define rep(G, x) for(Graph::edge *p = G.adj[x];p;p = p->nxt)
typedef long long ll;
const int MAXN = 400 + 5;
const int MAXV = 4*MAXN*MAXN;
const int MAXE = 16*MAXV + 5;
const ll INF = (1LL<<60);
struct Graph{
struct edge{
int to, dis;
edge *nxt;
}edges[MAXE + 5], *adj[MAXV + 5], *ecnt;
Graph() {ecnt = edges;}
void addedge(int u, int v, int w) {
edge *p = (++ecnt);
p->to = v, p->dis = w, p->nxt = adj[u], adj[u] = p;
p = (++ecnt);
p->to = u, p->dis = w, p->nxt = adj[v], adj[v] = p;
// printf("! %d %d %d\n", u, v, w);
}
void clear(int n) {
ecnt = edges;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
adj[i] = NULL;
}
}G;
int hp[MAXV + 5], pre[MAXV + 5];
ll f[MAXV + 5], dis[MAXV + 5];
void update(int x, ll k, const int &n) {
f[x] = k;
while( x ) {
hp[x] = x;
if( (x<<1) <= n && f[hp[x<<1]] < f[hp[x]] )
hp[x] = hp[x<<1];
if( (x<<1|1) <= n && f[hp[x<<1|1]] < f[hp[x]] )
hp[x] = hp[x<<1|1];
x >>= 1;
}
}
void dijkstra(int s, const int &n) {
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
dis[i] = f[i] = INF, hp[i] = i;
update(s, dis[s] = 0, n);
while( f[hp[1]] != INF ) {
int x = hp[1]; update(x, INF, n);
rep(G, x) {
if( dis[x] + p->dis < dis[p->to] ) {
update(p->to, dis[p->to] = dis[x] + p->dis, n);
pre[p->to] = x;
}
}
}
}
int id[MAXN + 5][MAXN + 5], cnt;
int A[MAXN + 5][MAXN + 5], B[MAXN + 5][MAXN + 5], C[MAXN + 5][MAXN + 5];
bool tg[MAXV + 5];
queue<int>que;
int ind(int x, int p) {
return (x - 1) * 4 + p;
}
bool check(int x, int y) {
return (pre[x] == y && tg[x]) || (pre[y] == x && tg[y]);
}
int main() {
int N, M; scanf("%d%d", &N, &M);
for(int i=1;i<=N;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=M;j++)
scanf("%d", &A[i][j]);
for(int i=1;i<=N+1;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=M+1;j++)
id[i][j] = (++cnt);
for(int i=1;i<=N;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=M+1;j++) {
scanf("%d", &B[i][j]);
G.addedge(id[i][j], id[i+1][j], B[i][j]);
}
for(int i=1;i<=N+1;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=M;j++) {
scanf("%d", &C[i][j]);
G.addedge(id[i][j], id[i][j+1], C[i][j]);
}
dijkstra(1, cnt);
for(int i=1;i<=N;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=M;j++)
if( A[i][j] ) que.push(id[i][j]), tg[id[i][j]] = true;
while( !que.empty() ) {
int f = que.front(); que.pop();
if( !tg[pre[f]] )
que.push(pre[f]), tg[pre[f]] = true;
}
G.clear(cnt);
for(int i=1;i<=N;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=M+1;j++) {
if( !A[i][j-1] )
G.addedge(ind(id[i][j], 3), ind(id[i+1][j], 2), B[i][j]);
if( !A[i][j] )
G.addedge(ind(id[i][j], 4), ind(id[i+1][j], 1), B[i][j]);
}
for(int i=1;i<=N+1;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=M;j++) {
if( !A[i-1][j] )
G.addedge(ind(id[i][j], 1), ind(id[i][j+1], 2), C[i][j]);
if( !A[i][j] )
G.addedge(ind(id[i][j], 4), ind(id[i][j+1], 3), C[i][j]);
}
for(int i=1;i<=N+1;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=M+1;j++) {
if( i == 1 && j == 1 ) continue;
if( !(check(id[i][j], id[i-1][j]) || A[i-1][j] || A[i-1][j-1]) )
G.addedge(ind(id[i][j], 1), ind(id[i][j], 2), 0);
if( !(check(id[i][j], id[i][j-1]) || A[i][j-1] || A[i-1][j-1]) )
G.addedge(ind(id[i][j], 2), ind(id[i][j], 3), 0);
if( !(check(id[i][j], id[i+1][j]) || A[i][j-1] || A[i][j]) )
G.addedge(ind(id[i][j], 3), ind(id[i][j], 4), 0);
if( !(check(id[i][j], id[i][j+1]) || A[i-1][j] || A[i][j]) )
G.addedge(ind(id[i][j], 4), ind(id[i][j], 1), 0);
}
dijkstra(ind(1, 1), ind(cnt, 4));
printf("%lld\n", dis[ind(1, 3)]);
}
@details@
只用了 N 没有用 M 这个变量的人一定不止我一个人吧。
所以 2014 年出的题我现在还是不会。
@bzoj - 4356@ Ceoi2014 Wall的更多相关文章
- BZOJ4356 : Ceoi2014 Wall
求出左上角到每个需要保护的点左上角的最短路树,那么最优解一定圈住了它们. 然后将每个点拆成四个点,四个点之间如果没跨越最短路树的树边,那就连0权边. 每个需要保护的点四周4个点都不可通行,求出最短路即 ...
- bzoj AC倒序
Search GO 说明:输入题号直接进入相应题目,如需搜索含数字的题目,请在关键词前加单引号 Problem ID Title Source AC Submit Y 1000 A+B Problem ...
- BZOJ 1665: [Usaco2006 Open]The Climbing Wall 攀岩
题目 1665: [Usaco2006 Open]The Climbing Wall 攀岩 Time Limit: 5 Sec Memory Limit: 64 MBSubmit: 197 Sol ...
- 【BZOJ】1665: [Usaco2006 Open]The Climbing Wall 攀岩(spfa)
http://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=1665 这题只要注意到“所有的落脚点至少相距300”就可以大胆的暴力了. 对于每个点,我们枚举比他的x ...
- BZOJ 1113 Wall ——计算几何
凸包第一题. 自己认为自己写的是Andrew 其实就是xjb写出来居然过掉了测试. 刚开始把pi定义成了int,调了半天 #include <map> #include <cmath ...
- 【BZOJ】【2120】数颜色 & 【2453】维护队列
莫队算法 分块大法吼 这题乍一看跟HH的项链很像啊……只是多了一个修改操作……然而我就不会做了
- [Usaco2006 Open]The Climbing Wall 攀岩
Description One of the most popular attractions at the county fair is the climbing wall. Bessie want ...
- BZOJ 2127: happiness [最小割]
2127: happiness Time Limit: 51 Sec Memory Limit: 259 MBSubmit: 1815 Solved: 878[Submit][Status][Di ...
- [poj1113][Wall] (水平序+graham算法 求凸包)
Description Once upon a time there was a greedy King who ordered his chief Architect to build a wall ...
随机推荐
- python条件变量之生产者与消费者操作实例分析
python条件变量之生产者与消费者操作实例分析 本文实例讲述了python条件变量之生产者与消费者操作.分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下: 互斥锁是最简单的线程同步机制,面对复杂线程同步问题,Pyth ...
- PYTHON网络爬虫与信息提取[信息的组织与提取](单元五)
1 三种信息类型的简介 xml : extensible markup language 与html非常相似 现有html后有xml xml是html发展来的 扩展 通用 json 类型 javas ...
- SPOJ GSS5
GSS5 - Can you answer these queries V #tree You are given a sequence A[1], A[2], ..., A[N] . ( |A[i] ...
- 洛谷3128 [USACO15DEC]最大流Max Flow——树上差分
题目:https://www.luogu.org/problemnew/show/P3128 树上差分.用离线lca,邻接表存好方便. #include<iostream> #includ ...
- Total Number of Unicorn Companies: 188
https://www.cbinsights.com/research-unicorn-companies Total Number of Unicorn Companies: 188 Total ...
- js判断类型为数字的方法实现总汇——原生js判断isNumber()
方法一[推荐]: 最容易想到的是用typeof来判断是否是number类型 ,但是如果为NaN会被认为也是number类型,因此我们需要使用isNaN来排除NaN的情况. function isNum ...
- Katalon系列二十:读写Excle
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFSheet import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook Fil ...
- json格式示例
案例一: {key:value,key:value} class Person{ String firstname = "张"; String lastname = "三 ...
- 51nod1196 字符串的数量
用N个不同的字符(编号1 - N),组成一个字符串,有如下要求:(1) 对于编号为i的字符,如果2 * i > n,则该字符可以作为结尾字符.如果不作为结尾字符而是中间的字符,则该字符后面可以接 ...
- awss3
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage; import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; import java.io ...
