分布式计算 要不要把写日志独立成一个Server Remote Procedure Call Protocol
w
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Remote_procedure_call
In distributed computing a remote procedure call (RPC) is when a computer program causes a procedure (subroutine) to execute in another address space (commonly on another computer on a shared network), which is coded as if it were a normal (local) procedure call, without the programmer explicitly coding the details for the remote interaction. That is, the programmer writes essentially the same code whether the subroutine is local to the executing program, or remote.[1] This is a form of client–server interaction (caller is client, executer is server), typically implemented via a request–response message-passing system. The object-oriented programming analog is remote method invocation (RMI). The RPC model implies a level of location transparency, namely that calling procedures is largely the same whether it is local or remote, but usually they are not identical, so local calls can be distinguished from remote calls. Remote calls are usually orders of magnitude slower and less reliable than local calls, so distinguishing them is important.
RPCs are a form of inter-process communication (IPC), in that different processes have different address spaces: if on the same host machine, they have distinct virtual address spaces, even though the physical address space is the same; while if they are on different hosts, the physical address space is different. Many different (often incompatible) technologies have been used to implement the concept.
History and origins[edit]
Response–request protocols date to early distributed computing in the late 1960s, theoretical proposals of remote procedure calls as the model of network operations date to the 1970s, and practical implementations date to the early 1980s. In the 1990s, with the popularity of object-oriented programming, the alternative model of remote method invocation (RMI) was widely implemented, such as in Common Object Request Broker Architecture (CORBA, 1991) and Java remote method invocation. RMIs in turn fell in popularity with the rise of the internet, particularly in the 2000s.
Remote procedure calls used in modern operating systems trace their roots back to the RC 4000 multiprogramming system,[2] which used a request-response communication protocol for process synchronization.[3] The idea of treating network operations as remote procedure calls goes back at least to the 1970s in early ARPANET documents.[4] In 1978, Per Brinch Hansen proposed Distributed Processes, a language for distributed computing based on "external requests" consisting of procedure calls between processes.[5]
Bruce Jay Nelson is generally credited with coining the term "remote procedure call" (1981),[6] and the first practical implementation was by Andrew Birrel and Bruce Nelson, called Lupine, in the Cedar environment at Xerox PARC.[7][8][9] Lupine automatically generated stubs, providing type-safe bindings, and used an efficient protocol for communication.[8] One of the first business uses of RPC was by Xerox under the name "Courier" in 1981. The first popular implementation of RPC on Unix was Sun's RPC (now called ONC RPC), used as the basis for Network File System.
Message passing[edit]
RPC is a kind of request–response protocol. An RPC is initiated by the client, which sends a request message to a known remote server to execute a specified procedure with supplied parameters. The remote server sends a response to the client, and the application continues its process. While the server is processing the call, the client is blocked (it waits until the server has finished processing before resuming execution), unless the client sends an asynchronous request to the server, such as an XHTTP call. There are many variations and subtleties in various implementations, resulting in a variety of different (incompatible) RPC protocols.
An important difference between remote procedure calls and local calls is that remote calls can fail because of unpredictable network problems. Also, callers generally must deal with such failures without knowing whether the remote procedure was actually invoked. Idempotent procedures (those that have no additional effects if called more than once) are easily handled, but enough difficulties remain that code to call remote procedures is often confined to carefully written low-level subsystems.
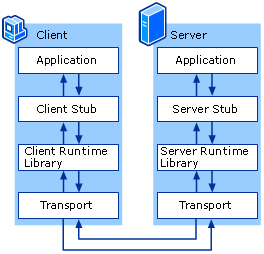
Sequence of events[edit]
- The client calls the client stub. The call is a local procedure call, with parameters pushed on to the stack in the normal way.
- The client stub packs the parameters into a message and makes a system call to send the message. Packing the parameters is called marshalling.
- The client's local operating system sends the message from the client machine to the server machine.
- The local operating system on the server machine passes the incoming packets to the server stub.
- The server stub unpacks the parameters from the message. Unpacking the parameters is called unmarshalling.
- Finally, the server stub calls the server procedure. The reply traces the same steps in the reverse direction.
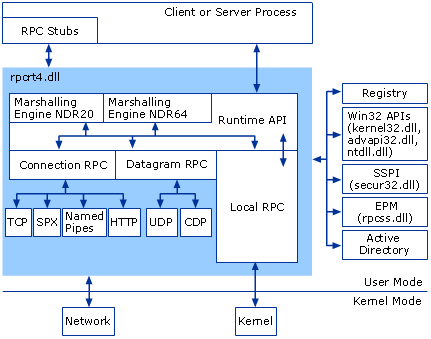
Standard contact mechanisms[edit]
To let different clients access servers, a number of standardized RPC systems have been created. Most of these use an interface description language (IDL) to let various platforms call the RPC. The IDL files can then be used to generate code to interface between the client and servers.
https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/远程过程调用
远程过程调用(英语:Remote Procedure Call,缩写为 RPC)是一个计算机通信协议。该协议允许运行于一台计算机的程序调用另一台计算机的子程序,而程序员无需额外地为这个交互作用编程。
信息传递
远程过程调用是一个分布式计算的客户端-服务器(Client/Server)的例子,它简单而又广受欢迎。远程过程调用总是由客户端对服务器发出一个执行若干过程请求,并用客户端提供的参数。执行结果将返回给客户端。
标准化的沟通机制
为了允许不同的客户端均能访问服务器,许多标准化的 RPC 系统应运而生了。其中大部分采用接口描述语言(Interface Description Language,IDL),方便跨平台的远程过程调用。
要不要把写日志独立成一个Server,需考虑吞吐量,可靠性和负载。在非极高并发的情况下,本地磁盘写比RPC请求可靠性要高(失败率更低),而你丢给LogServer,它最终也还是要保存成文件的。吞吐量则是,本地磁盘的写入速度会不会跟不上数据的产生速度。负载则充分考虑机器的负载能力,例如有些服务器CPU占用很高,但是磁盘IO却很闲,这时写本地文件可充分利用闲置的IO资源。又或者某些服务器本身IO就很繁忙,但网络很闲,就可以考虑把数据通过网络丢给另外的服务去处理更好。
分布式计算 要不要把写日志独立成一个Server Remote Procedure Call Protocol的更多相关文章
- How To Write In Sharepoint Log File 怎么对自定义的MOSS代码写日志
How To Write In Sharepoint Log File 怎么对自定义的MOSS代码写日志 Add Microsoft.Office.Server dll in your project ...
- 咏南中间件更新日志--将数据库配置独立成DBCONFIG.EXE
咏南中间件更新日志--将数据库配置独立成DBCONFIG.EXE.
- .NET Core的日志[5]:利用TraceSource写日志
从微软推出第一个版本的.NET Framework的时候,就在“System.Diagnostics”命名空间中提供了Debug和Trace两个类帮助我们完成针对调试和跟踪信息的日志记录.在.NET ...
- Spring 使用 SLF4J代替 Commons Logging 写日志 异常
项目的日志更换成slf4j和logback后,发现项目无法启动.错误提示 Caused by: java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: Lorg/apache/commons/ ...
- 利用TraceSource写日志
利用TraceSource写日志 从微软推出第一个版本的.NET Framework的时候,就在“System.Diagnostics”命名空间中提供了Debug和Trace两个类帮助我们完成针对调试 ...
- C#多线程写日志
由于程序是3层架构的,所有多线程记录日志成了比较棘手的问题,以前还真就没有在意过写日志的问题,认为不过是写文件罢了~~!如今发现原来要实现文件共享,并且能够使多线程同时操作日志还不能相互冲突,真的很麻 ...
- aspnetcore进程内托管的坑-非常规方法解决Log4Net不写日志的问题
问题描述:Log4Net,本地测试一切正常,发布后,无法自动创建文件夹和日志文件,无法写入文件. 一.在项目中配置Log4Net 请参考我的上一篇博客 <aspnetcore配置log4net并 ...
- python语言(六)mock接口开发、发邮件、写日志、新Excel操作
一.urllib模块 urllib模块是一个标准模块,直接import urllib即可,在python3里面只有urllib模块,在python2里面有urllib模块和urllib2模块. url ...
- PostgreSQL 预写日志机制(WAL)
关于持久性 持久性是指,事务提交后,对系统的影响必须是永久的,即使系统意外宕机,也必须确保事务提交时的修改已真正永久写入到永久存储中. 最简单的实现方法,当然是在事务提交后立即刷新事务修改后的数据到磁 ...
随机推荐
- Microsoft SQL Server Data Tools - Business Intelligence for Visual Studio 2013 SSIS
VS2012 SSDTBI_VS2012_x86_CHS.exe http://www.microsoft.com/zh-CN/download/details.aspx?id=36843 VS201 ...
- Eclipse中屏蔽日志
如何在Eclipse中屏蔽日志 //屏蔽日志 Eclipse Java import org.apache.log4j.Level; import org.apache.log4j.Logger; L ...
- 用jquery制作一个简单的导航栏
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title> ...
- ORACLE 存储过程实例 [备忘录]
统计报表:用户登录量(平台点击量)每月月初定时任务统计前一个月的登陆次数.登陆账号数.账号总数. 使用存储过程把查询的值存储到表 RP_MONTH_CLICK 中. create or replace ...
- makefile之call函数
call函数是唯一一个可以创建定制化参数函数的引用函数. 支持对自定义函数的引用; 支持将一个变量定义为一个复杂的表达式,用call函数根据不同的参数对它进行展开来获取不同的结果; 函数语法: $(c ...
- gcc 编译动态库和静态库
Linux C 编程入门之一:gcc 编译动态库和静态库 cheungmine 2012 参考: C程序编译过程浅析 http://blog.csdn.net/koudaidai/article/de ...
- WOW模型导出到Unity3D使用教程
最近又重操旧业.搞起了Unity3D.对WOW的模型怨念很深. 于是写了一个教程帮助其他人一起提取wow的模型..哈哈..希望能帮助到大家哈哈.. 我自己的百度网盘里面附加.有兴趣的大家下载看看.文档 ...
- TaskTracker学习笔记
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/androidlushangderen/article/details/41477061 上次分析完JobTracker通过TaskScheduler如 ...
- 第二百四十二节,Bootstrap列表组面板和嵌入组件
Bootstrap列表组面板和嵌入组件 学习要点: 1.列表组组件 2.面板组件 3.响应式嵌入组件 本节课我们主要学习一下 Bootstrap 的三个组件功能:列表组组件.面板组件. 响应 式嵌入组 ...
- 网络I/O:Socket→RMI
★Socket Socket编程可能大家都很熟,所以就不多讨论了,只是说通过socket把数据保存到远端服务器或从网络socket读取数据也不失为一种值得考虑的方式. ★RMI RMI机制其实就是RP ...
