Shiro源码分析之Subject和SecurityManager
Subject
毫无疑问,Subject是Shiro最重要的一个概念。
“Subject”只是一个安全术语,意味着应用程序用户的特定于安全性的“视图”。Shiro Subject实例代表单个应用程序用户的安全状态和相关操作。
创建
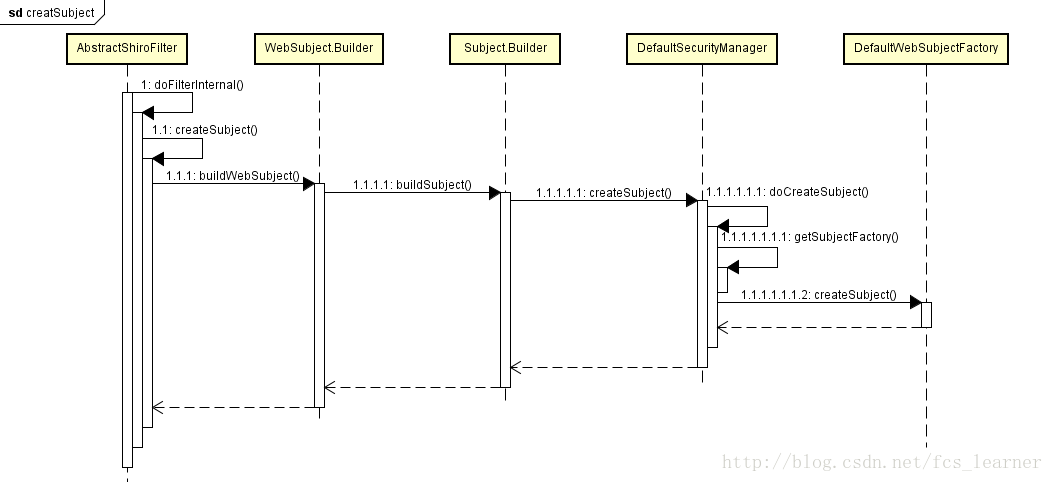
初次创建是在AbstractShiroFilter#doFilterInternal方法中:
final Subject subject = createSubject(request, response);
protected WebSubject createSubject(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response) {
return new WebSubject.Builder(getSecurityManager(), request, response).buildWebSubject();
}创建的时候传入安全管理器,Subject.Builder是这样操作的:
public Builder(SecurityManager securityManager) {
if (securityManager == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("SecurityManager method argument cannot be null.");
}
this.securityManager = securityManager;
this.subjectContext = newSubjectContextInstance();
if (this.subjectContext == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Subject instance returned from 'newSubjectContextInstance' " +
"cannot be null.");
}
this.subjectContext.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
}
public Subject buildSubject() {
return this.securityManager.createSubject(this.subjectContext);
}这个安全管理器还是我们指定的那个DefaultWebSecurityManager,一路传过去的。这个subjectContext参数是一个DefaultSubjectContext,子接口中的Builder覆盖了父类的方法,实际赋予的是一个DefaultWebSubjectContext。
protected Subject doCreateSubject(SubjectContext context) {
return getSubjectFactory().createSubject(context);
}subjectFactory是安全管理器DefaultWebSecurityManager中默认的DefaultWebSubjectFactory:
public DefaultWebSecurityManager() {
super();
((DefaultSubjectDAO) this.subjectDAO).setSessionStorageEvaluator(new DefaultWebSessionStorageEvaluator());
this.sessionMode = HTTP_SESSION_MODE;
setSubjectFactory(new DefaultWebSubjectFactory());
setRememberMeManager(new CookieRememberMeManager());
setSessionManager(new ServletContainerSessionManager());
}最终的创建又回到:
public class DefaultWebSubjectFactory extends DefaultSubjectFactory {
public DefaultWebSubjectFactory() {
super();
}
public Subject createSubject(SubjectContext context) {
if (!(context instanceof WebSubjectContext)) {
return super.createSubject(context);
}
WebSubjectContext wsc = (WebSubjectContext) context;
SecurityManager securityManager = wsc.resolveSecurityManager();
Session session = wsc.resolveSession();
boolean sessionEnabled = wsc.isSessionCreationEnabled();
PrincipalCollection principals = wsc.resolvePrincipals();
boolean authenticated = wsc.resolveAuthenticated();
String host = wsc.resolveHost();
ServletRequest request = wsc.resolveServletRequest();
ServletResponse response = wsc.resolveServletResponse();
return new WebDelegatingSubject(principals, authenticated, host, session, sessionEnabled,
request, response, securityManager);
}
//......
}根据相关属性new出来一个WebDelegatingSubject。
shiro中很多都是这样的继承和组合关系:
DefaultSecurityManager -> DefaultSubjectFactory -> DelegatingSubject
DefaultWebSecurityManager -> DefaultWebSubjectFactory -> WebDelegatingSubject
再回到创建的方法:
final Subject subject = createSubject(request, response);
//noinspection unchecked
subject.execute(new Callable() {
public Object call() throws Exception {
updateSessionLastAccessTime(request, response);
executeChain(request, response, chain);
return null;
}
});这个execute方法是在DelegatingSubject中实现的:
public <V> V execute(Callable<V> callable) throws ExecutionException {
Callable<V> associated = associateWith(callable);
try {
return associated.call();
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new ExecutionException(t);
}
}
public <V> Callable<V> associateWith(Callable<V> callable) {
return new SubjectCallable<V>(this, callable);
}
SubjectCallable首先构造了一个ThreadState:
public SubjectCallable(Subject subject, Callable<V> delegate) {
this(new SubjectThreadState(subject), delegate);
}associated.call()调用ThreadState.bind():
public V call() throws Exception {
try {
threadState.bind();
return doCall(this.callable);
} finally {
threadState.restore();
}
}SubjectThreadState的bind方法:
public void bind() {
SecurityManager securityManager = this.securityManager;
if ( securityManager == null ) {
//try just in case the constructor didn't find one at the time:
securityManager = ThreadContext.getSecurityManager();
}
this.originalResources = ThreadContext.getResources();
ThreadContext.remove();
ThreadContext.bind(this.subject);
if (securityManager != null) {
ThreadContext.bind(securityManager);
}
}这样就妥妥地把当前subject和线程绑定到了一起(还有securityManager)。
在这里遇到一个问题,记录下:
https://www.oschina.net/question/2275855_2273492
其实这只是每次进入核心过滤器时默认为我们创建的一个Subject,当调用subject.login方法之后会再次创建一个Subject,后面登录部分会做详细介绍。
获取
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
public static Subject getSubject() {
Subject subject = ThreadContext.getSubject();
if (subject == null) {
subject = (new Subject.Builder()).buildSubject();
ThreadContext.bind(subject);
}
return subject;
}绑定是通过ThreadContext,获取当然也是从其取。
public abstract class ThreadContext {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ThreadContext.class);
public static final String SECURITY_MANAGER_KEY = ThreadContext.class.getName() + "_SECURITY_MANAGER_KEY";
public static final String SUBJECT_KEY = ThreadContext.class.getName() + "_SUBJECT_KEY";
private static final ThreadLocal<Map<Object, Object>> resources = new InheritableThreadLocalMap<Map<Object, Object>>();
private static Object getValue(Object key) {
return resources.get().get(key);
}
public static Object get(Object key) {
Object value = getValue(key);
return value;
}
public static Subject getSubject() {
return (Subject) get(SUBJECT_KEY);
}
}最终是到ThreadLocal中拿,不过这个ThreadLocal是 InheritableThreadLocalMap 类型的(继承自InheritableThreadLocal)。
每个线程都有一个Map
SecurityManager
<!-- 安全管理器 -->
<bean id="securityManager" class="org.apache.shiro.web.mgt.DefaultWebSecurityManager">
<property name="realm" ref="casRealm" />
<property name="sessionManager" ref="sessionManager" />
<property name="cacheManager" ref="shiroCacheManager" />
<!-- <property name="rememberMeManager" ref="rememberMeManager" /> -->
</bean>
<bean id="sessionManager" class="org.apache.shiro.web.session.mgt.ServletContainerSessionManager"/>public interface SecurityManager extends Authenticator, Authorizer, SessionManager {
Subject login(Subject subject, AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException;
void logout(Subject subject);
Subject createSubject(SubjectContext context);
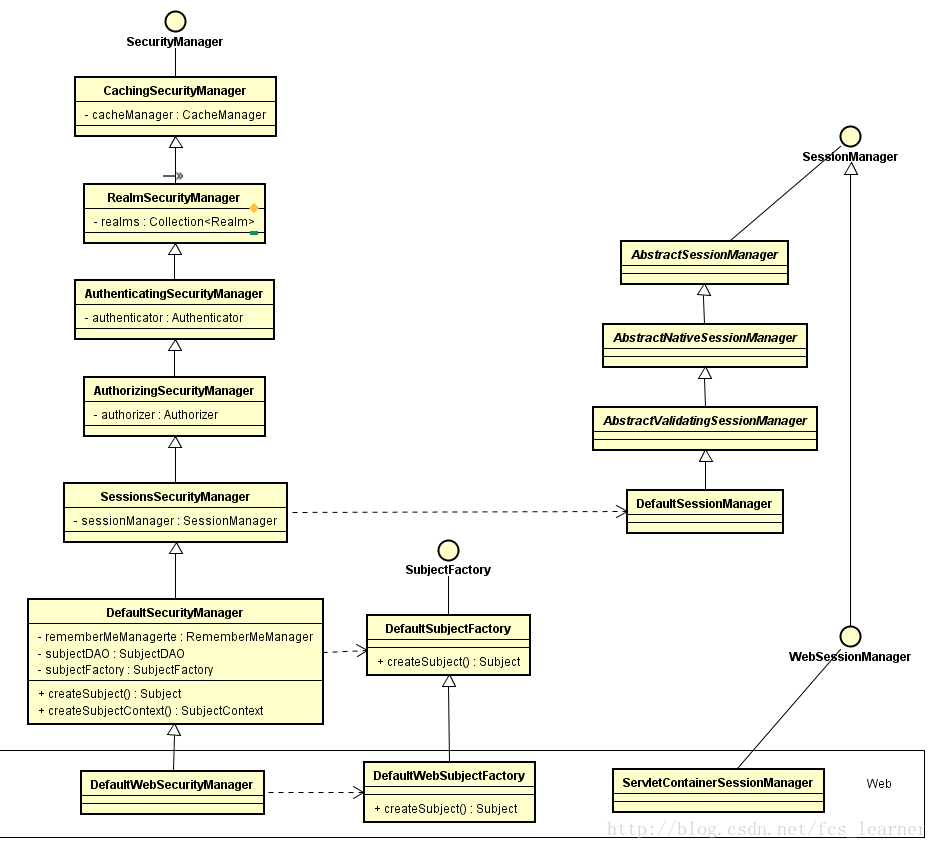
}安全管理器继承了Authenticator, Authorizer, SessionManager三个接口。自顶向下第一个抽象类是CachingSecurityManager,接着是RealmSecurityManager,后面是AuthenticatingSecurityManager,AuthorizingSecurityManager,SessionsSecurityManager。
然后才是DefaultSecurityManager,DefaultWebSecurityManager。
由于是web项目,我们指定了DefaultWebSecurityManager,在构造器中会为我们设置相匹配的属性(都是和web相关的):
public DefaultWebSecurityManager() {
super();
((DefaultSubjectDAO) this.subjectDAO).setSessionStorageEvaluator(new DefaultWebSessionStorageEvaluator());
this.sessionMode = HTTP_SESSION_MODE;
setSubjectFactory(new DefaultWebSubjectFactory());
setRememberMeManager(new CookieRememberMeManager());
setSessionManager(new ServletContainerSessionManager());
}SessionsSecurityManager持有一个sessionManager对象,对sessionManager接口的实现是转移到这个对象上来的:
public abstract class SessionsSecurityManager extends AuthorizingSecurityManager {
private SessionManager sessionManager;
public SessionsSecurityManager() {
super();
this.sessionManager = new DefaultSessionManager();
applyCacheManagerToSessionManager();
}
}AuthenticatingSecurityManager,AuthorizingSecurityManager类似,这两个抽象管理器在无参构造函数中创建了默认的对象:
public abstract class AuthorizingSecurityManager extends AuthenticatingSecurityManager {
private Authorizer authorizer;
public AuthorizingSecurityManager() {
super();
this.authorizer = new ModularRealmAuthorizer();
}
}
public abstract class AuthenticatingSecurityManager extends RealmSecurityManager {
private Authenticator authenticator;
public AuthenticatingSecurityManager() {
super();
this.authenticator = new ModularRealmAuthenticator();
}
}
所以这个安全管理器几乎承担了所有的操作,然后转移到具体的对象。它的层次结构非常清晰,职责分明。对Subject所有操作最终都会转移到SecurityManager。
Shiro源码分析之Subject和SecurityManager的更多相关文章
- Shiro源码分析之SecurityManager对象获取
目录 SecurityManager获取过程 1.SecurityManager接口介绍 2.SecurityManager实例化时序图 3.源码分析 4.总结 @ 上篇文章Shiro源码分析之获 ...
- Shiro 源码分析
http://my.oschina.net/huangyong/blog/215153 Shiro 是一个非常优秀的开源项目,源码非常值得学习与研究. 我想尝试做一次 不一样 的源码分析:源码分析不再 ...
- Shiro源码分析
1.入口类:AbstractAuthenticator 用户输入的登录信息经过其authenticate方法: public final AuthenticationInfo authenticate ...
- Shiro源码分析-初始化-Realm
在上一篇介绍SecurityManager的初始化过程中,也有realm的粗略介绍. realm的概念在安全领域随处可见: 各种中间件的realm.spring security的realm.shir ...
- Shiro入门学习之shi.ini实现认证及源码分析(二)
一.Shiro.ini文件 1.文件说明 ①ini(InitializationFile)初始文件:Window系统文件扩展名 ②Shiro使用时可以连接数据库,也可以不连接数据库(可以使用shiro ...
- 源码分析shiro认证授权流程
1. shiro介绍 Apache Shiro是一个强大易用的Java安全框架,提供了认证.授权.加密和会话管理等功能: 认证 - 用户身份识别,常被称为用户“登录”: 授权 - 访问控制: 密码加密 ...
- shiro实现无状态的会话,带源码分析
转载请在页首明显处注明作者与出处 朱小杰 http://www.cnblogs.com/zhuxiaojie/p/7809767.html 一:说明 在网上都找不到相关的信息,还是翻了大半天 ...
- Shiro源码解析-Session篇
上一篇Shiro源码解析-登录篇中提到了在登录验证成功后有对session的处理,但未详细分析,本文对此部分源码详细分析下. 1. 分析切入点:DefaultSecurityManger的login方 ...
- spark源码分析以及优化
第一章.spark源码分析之RDD四种依赖关系 一.RDD四种依赖关系 RDD四种依赖关系,分别是 ShuffleDependency.PrunDependency.RangeDependency和O ...
随机推荐
- c# 事实证明,abstract类除了不能用new实例化和类没什么区别
abstract类是抽象类,不能够实例化,大家都知道,abstract类往往和接口interface一块儿使用,针对接口中一些公共的方法进行实现,然后实体类去继承抽象类和接口.虽然abstract类不 ...
- PHP系统编程--03.PHP进程信号处理
PHP的pcntl扩展提供了信号处理的功能,利用它可以让PHP来接管信号的处理,在开发服务器端守护进程方面,信号处理至关重要. 函数原型 bool pcntl_signal(int $signo ,c ...
- WCF 同一个解决方案中控制台应用添加服务引用报错
错误提示: “Unable to check out the current file. The file may be read-only or locked, or you may need to ...
- HDU 1422 重温世界杯 (dp)
题目链接 Problem Description 世界杯结束了,意大利人连本带利的收回了法国人6年前欠他们的债,捧起了大力神杯,成就了4星意大利. 世界杯虽然结束了,但是这界世界杯给我们还是留下许多值 ...
- python初步学习-python数据类型之number(数值)
数据类型之 Number python number 数据类型用于存储数值. 数据类型是不容许改变的. 这就意味着如果改变 number 数据类型的值,将重新分配内存空间. python支持四种不同数 ...
- Python模块学习 - Argparse
argparse模块 在Python中,argparse模块是标准库中用来解析命令行参数的模块,用来替代已经过时的optparse模块.argparse模块能够根据程序中的定义从sys.argv中解析 ...
- java基础 运算符
算数运算符 加号:在操作数值.字符.字符串时其结果是不同的,当两个字符相加得到的是ASCII码表值, 当两个字符串相加时表示将两个字符串连接在一起,从而组成新的字符串. 除号:整数在使用除号操作时,得 ...
- rhel-server srpms iso
http://ftp.redhat.com/pub/redhat/linux/enterprise/7Server/en/ ftp://ftp.pslib.cz/pub/linux/redhat-cz ...
- C高级 跨平台协程库
1.0 协程库引言 协程对于上层语言还是比较常见的. 例如C# 中 yield retrun, lua 中 coroutine.yield 等来构建同步并发的程序. 本文就是探讨如何从底层实现开发级别 ...
- git subtree:无缝管理通用子项目
移动互联网的爆发以及响应式页面的尴尬症,开发web和mobile项目成为了标配,当然实际情况下,会有更多的项目. 多项目开发对于前端来说是个很大的挑战✦ 重复,重复的前端架构,重复的前端依赖,重复的工 ...