kubelet分析-csi driver注册源码分析
kubelet注册csi driver分析
kubelet注册csi driver的相关功能代码与kubelet的pluginManager有关,所以接下来对pluginManager进行分析。分析将分为pluginManager的初始化分析以及pluginManager的运行(处理逻辑)分析。
基于tag v1.17.4
https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/releases/tag/v1.17.4
kubelet注册csi driver的原理
kubelet的pluginManager会监听某个特定目录,而负责向kubelet注册csi driver的组件Node Driver Registrar会创建暴露服务的socket在该目录下(每个plugin会对应一个Node Driver Registrar组件,也就是说,一个Node Driver Registrar只负责一个plugin的注册工作),pluginManager通过Node Driver Registrar组件暴露的socket获取plugin信息(包括plugin的socket地址、plugin名称等),从而最终做到根据该目录下socket文件的新增/删除来做相应的plugin注册/取消注册操作。
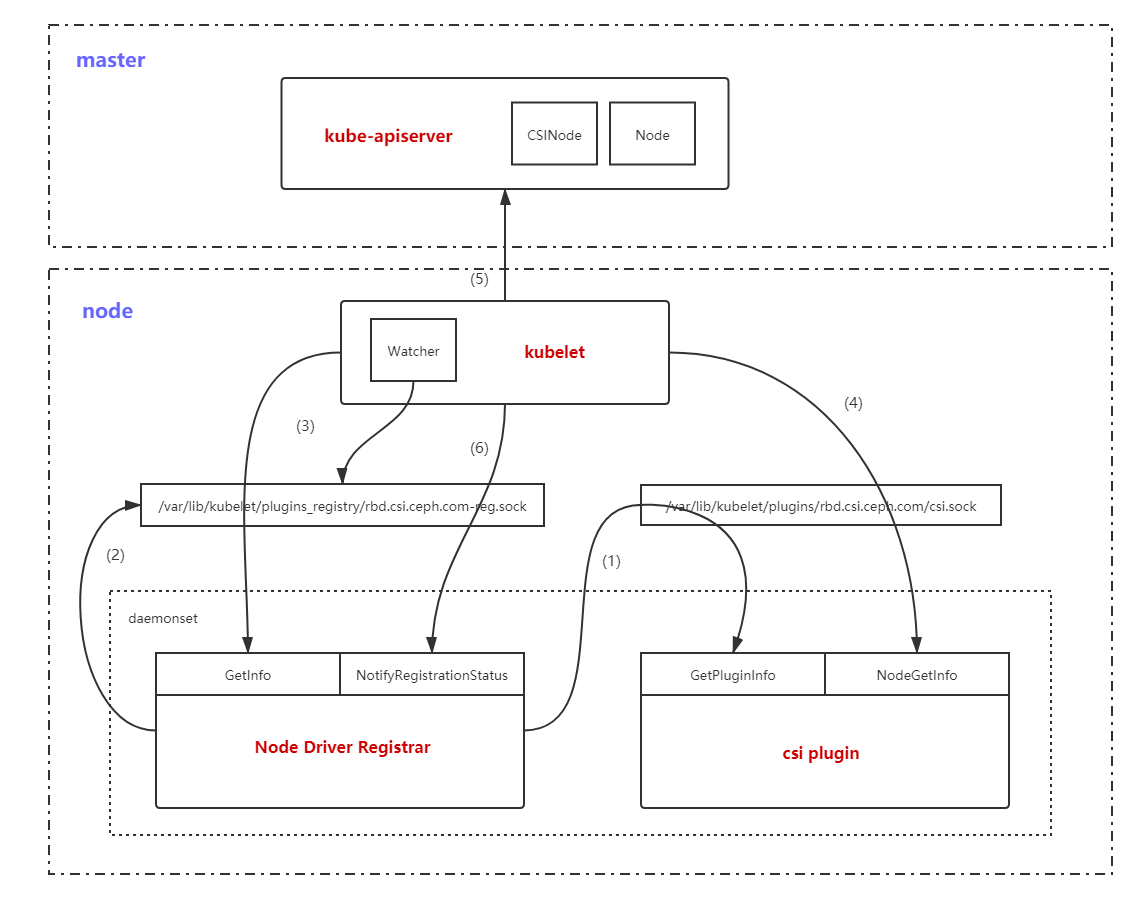
该图是Node Driver Registrar向kubelet注册csi driver的步骤流程图,这里大概看一下,具体请看这篇博客:Node Driver Registrar源码分析,结合本篇博客一起理解kubelet注册csi driver的整个过程。
plugin注册完成后,后续kubelet将通过plugin暴露的socket与plugin进行通信,做存储挂载/解除挂载等操作。
Node Driver Registrar
Node Driver Registrar在前面的文章中介绍过,它是一个sidecar容器,通过Kubelet的插件注册机制将CSI plugin(csi driver,两个名词意义一样)注册到Kubelet,让kubelet做volume的mount/umount操作时知道怎么调用相应的csi plugin。
kubelet pluginManager源码分析
1 pluginManager的初始化
调用NewMainKubelet()初始化kubelet的时候,会调用pluginmanager.NewPluginManager来初始化pluginManager,所以把NewMainKubelet()作为分析入口。
NewMainKubelet()
NewMainKubelet()中调用了pluginmanager.NewPluginManager来初始化pluginManager。
这里留意klet.getPluginsRegistrationDir(),调用该方法实际会返回plugins_registry,而该sockDir会传参进入pluginManager的desiredStateOfWorldPopulator结构体当中,相当于pluginManager会监听plugins_registry目录(负责向kubelet注册csi driver的组件Node Driver Registrar会创建暴露服务的socket在该目录下),pluginManager通过Node Driver Registrar组件暴露的socket获取plugin信息(包括plugin的socket地址、plugin名称等),从而最终做到根据该目录下socket文件的新增/删除来做相应的plugin注册/取消注册操作。
// pkg/kubelet/kubelet.go
// NewMainKubelet instantiates a new Kubelet object along with all the required internal modules.
// No initialization of Kubelet and its modules should happen here.
func NewMainKubelet(kubeCfg *kubeletconfiginternal.KubeletConfiguration,
...
nodeStatusMaxImages int32) (*Kubelet, error) {
...
klet.pluginManager = pluginmanager.NewPluginManager(
klet.getPluginsRegistrationDir(), /* sockDir */
kubeDeps.Recorder,
)
...
}
// pkg/kubelet/pluginmanager/plugin_manager.go
// NewPluginManager returns a new concrete instance implementing the
// PluginManager interface.
func NewPluginManager(
sockDir string,
recorder record.EventRecorder) PluginManager {
asw := cache.NewActualStateOfWorld()
dsw := cache.NewDesiredStateOfWorld()
reconciler := reconciler.NewReconciler(
operationexecutor.NewOperationExecutor(
operationexecutor.NewOperationGenerator(
recorder,
),
),
loopSleepDuration,
dsw,
asw,
)
pm := &pluginManager{
desiredStateOfWorldPopulator: pluginwatcher.NewWatcher(
sockDir,
dsw,
),
reconciler: reconciler,
desiredStateOfWorld: dsw,
actualStateOfWorld: asw,
}
return pm
}
klet.getPluginsRegistrationDir()
调用klet.getPluginsRegistrationDir()会返回plugins_registry。
// pkg/kubelet/kubelet_getters.go
// getPluginsRegistrationDir returns the full path to the directory under which
// plugins socket should be placed to be registered.
// More information is available about plugin registration in the pluginwatcher
// module
func (kl *Kubelet) getPluginsRegistrationDir() string {
return filepath.Join(kl.getRootDir(), config.DefaultKubeletPluginsRegistrationDirName)
}
// pkg/kubelet/config/defaults.go
const (
...
DefaultKubeletPluginsRegistrationDirName = "plugins_registry"
...
)
2 pluginManager struct
再来看到pluginManager结构体,pluginManager结构体与volumeManager结构体类似,都有actualStateOfWorld与desiredStateOfWorld两个属性。
kubelet pluginManager监听的socket注册目录每增加/删除一个socket文件,都会写入desiredStateOfWorld中/从desiredStateOfWorld中删除。
// pkg/kubelet/pluginmanager/plugin_manager.go
// pluginManager implements the PluginManager interface
type pluginManager struct {
// desiredStateOfWorldPopulator (the plugin watcher) runs an asynchronous
// periodic loop to populate the desiredStateOfWorld.
desiredStateOfWorldPopulator *pluginwatcher.Watcher
// reconciler runs an asynchronous periodic loop to reconcile the
// desiredStateOfWorld with the actualStateOfWorld by triggering register
// and unregister operations using the operationExecutor.
reconciler reconciler.Reconciler
// actualStateOfWorld is a data structure containing the actual state of
// the world according to the manager: i.e. which plugins are registered.
// The data structure is populated upon successful completion of register
// and unregister actions triggered by the reconciler.
actualStateOfWorld cache.ActualStateOfWorld
// desiredStateOfWorld is a data structure containing the desired state of
// the world according to the plugin manager: i.e. what plugins are registered.
// The data structure is populated by the desired state of the world
// populator (plugin watcher).
desiredStateOfWorld cache.DesiredStateOfWorld
}
actualStateOfWorld
actualStateOfWorld结构体中存放的是已经完成了plugin注册操作的Node Driver Registrar组件暴露的socket相关信息。
// ActualStateOfWorld defines a set of thread-safe operations for the kubelet
// plugin manager's actual state of the world cache.
// This cache contains a map of socket file path to plugin information of
// all plugins attached to this node.
type ActualStateOfWorld interface {
// GetRegisteredPlugins generates and returns a list of plugins
// that are successfully registered plugins in the current actual state of world.
GetRegisteredPlugins() []PluginInfo
// AddPlugin add the given plugin in the cache.
// An error will be returned if socketPath of the PluginInfo object is empty.
// Note that this is different from desired world cache's AddOrUpdatePlugin
// because for the actual state of world cache, there won't be a scenario where
// we need to update an existing plugin if the timestamps don't match. This is
// because the plugin should have been unregistered in the reconciller and therefore
// removed from the actual state of world cache first before adding it back into
// the actual state of world cache again with the new timestamp
AddPlugin(pluginInfo PluginInfo) error
// RemovePlugin deletes the plugin with the given socket path from the actual
// state of world.
// If a plugin does not exist with the given socket path, this is a no-op.
RemovePlugin(socketPath string)
// PluginExists checks if the given plugin exists in the current actual
// state of world cache with the correct timestamp
PluginExistsWithCorrectTimestamp(pluginInfo PluginInfo) bool
}
// NewActualStateOfWorld returns a new instance of ActualStateOfWorld
func NewActualStateOfWorld() ActualStateOfWorld {
return &actualStateOfWorld{
socketFileToInfo: make(map[string]PluginInfo),
}
}
type actualStateOfWorld struct {
// socketFileToInfo is a map containing the set of successfully registered plugins
// The keys are plugin socket file paths. The values are PluginInfo objects
socketFileToInfo map[string]PluginInfo
sync.RWMutex
}
desiredStateOfWorld
desiredStateOfWorld结构体中存放的是在pluginManager监听目录下存在的,希望完成plugin注册操作的Node Driver Registrar组件暴露的socket相关信息。
// DesiredStateOfWorld defines a set of thread-safe operations for the kubelet
// plugin manager's desired state of the world cache.
// This cache contains a map of socket file path to plugin information of
// all plugins attached to this node.
type DesiredStateOfWorld interface {
// AddOrUpdatePlugin add the given plugin in the cache if it doesn't already exist.
// If it does exist in the cache, then the timestamp of the PluginInfo object in the cache will be updated.
// An error will be returned if socketPath is empty.
AddOrUpdatePlugin(socketPath string) error
// RemovePlugin deletes the plugin with the given socket path from the desired
// state of world.
// If a plugin does not exist with the given socket path, this is a no-op.
RemovePlugin(socketPath string)
// GetPluginsToRegister generates and returns a list of plugins
// in the current desired state of world.
GetPluginsToRegister() []PluginInfo
// PluginExists checks if the given socket path exists in the current desired
// state of world cache
PluginExists(socketPath string) bool
}
// NewDesiredStateOfWorld returns a new instance of DesiredStateOfWorld.
func NewDesiredStateOfWorld() DesiredStateOfWorld {
return &desiredStateOfWorld{
socketFileToInfo: make(map[string]PluginInfo),
}
}
type desiredStateOfWorld struct {
// socketFileToInfo is a map containing the set of successfully registered plugins
// The keys are plugin socket file paths. The values are PluginInfo objects
socketFileToInfo map[string]PluginInfo
sync.RWMutex
}
3 pluginManager的运行
上面介绍了pluginManager的初始化,接下来介绍pluginManager的运行也即Run方法进行分析,分析一下pluginManager的处理逻辑。
因为调用逻辑比较复杂,这里直接跳过了调用过程的分析,直接进入kl.pluginManager.Run()的分析,下面只给出该方法的一个调用链:
kubelet的Run()方法(pkg/kubelet/kubelet.go) --> kl.updateRuntimeUp()(pkg/kubelet/kubelet.go) --> kl.initializeRuntimeDependentModules()(pkg/kubelet/kubelet.go) --> kl.pluginManager.Run()
kl.pluginManager.Run
下面直接看到kl.pluginManager.Run的代码。
该方法主要逻辑有两个:
(1)pm.desiredStateOfWorldPopulator.Start():持续监听plugin的socket注册目录的变化事件,将Node Driver Registrar的socket信息写入desiredStateOfWorld中/从desiredStateOfWorld中删除;
(2)pm.reconciler.Run()。
// pkg/kubelet/pluginmanager/plugin_manager.go
func (pm *pluginManager) Run(sourcesReady config.SourcesReady, stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
defer runtime.HandleCrash()
pm.desiredStateOfWorldPopulator.Start(stopCh)
klog.V(2).Infof("The desired_state_of_world populator (plugin watcher) starts")
klog.Infof("Starting Kubelet Plugin Manager")
go pm.reconciler.Run(stopCh)
metrics.Register(pm.actualStateOfWorld, pm.desiredStateOfWorld)
<-stopCh
klog.Infof("Shutting down Kubelet Plugin Manager")
}
3.1 pm.desiredStateOfWorldPopulator.Start()
跑一个goroutine,持续监听plugin的socket注册目录的变化事件:
(1)当变化事件为新增事件时,即socket目录下多了文件,则调用w.handleCreateEvent,将该socket加入到desiredStateOfWorld中;
(2)当变化事件为删除事件时,即socket目录下删除了文件,则调用w.handleDeleteEvent,将该socket从desiredStateOfWorld中删除。
// pkg/kubelet/pluginmanager/pluginwatcher/plugin_watcher.go
// Start watches for the creation and deletion of plugin sockets at the path
func (w *Watcher) Start(stopCh <-chan struct{}) error {
klog.V(2).Infof("Plugin Watcher Start at %s", w.path)
w.stopped = make(chan struct{})
// Creating the directory to be watched if it doesn't exist yet,
// and walks through the directory to discover the existing plugins.
if err := w.init(); err != nil {
return err
}
fsWatcher, err := fsnotify.NewWatcher()
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to start plugin fsWatcher, err: %v", err)
}
w.fsWatcher = fsWatcher
// Traverse plugin dir and add filesystem watchers before starting the plugin processing goroutine.
if err := w.traversePluginDir(w.path); err != nil {
klog.Errorf("failed to traverse plugin socket path %q, err: %v", w.path, err)
}
go func(fsWatcher *fsnotify.Watcher) {
defer close(w.stopped)
for {
select {
case event := <-fsWatcher.Events:
//TODO: Handle errors by taking corrective measures
if event.Op&fsnotify.Create == fsnotify.Create {
err := w.handleCreateEvent(event)
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("error %v when handling create event: %s", err, event)
}
} else if event.Op&fsnotify.Remove == fsnotify.Remove {
w.handleDeleteEvent(event)
}
continue
case err := <-fsWatcher.Errors:
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("fsWatcher received error: %v", err)
}
continue
case <-stopCh:
// In case of plugin watcher being stopped by plugin manager, stop
// probing the creation/deletion of plugin sockets.
// Also give all pending go routines a chance to complete
select {
case <-w.stopped:
case <-time.After(11 * time.Second):
klog.Errorf("timeout on stopping watcher")
}
w.fsWatcher.Close()
return
}
}
}(fsWatcher)
return nil
}
w.handleCreateEvent()
w.handleCreateEvent()主要逻辑:
(1)判断新增事件是否为文件,且是否是socket文件;
(2)是socket文件,则调用w.handlePluginRegistration做处理,主要是将该socket加入到desiredStateOfWorld中。
// pkg/kubelet/pluginmanager/pluginwatcher/plugin_watcher.go
func (w *Watcher) handleCreateEvent(event fsnotify.Event) error {
klog.V(6).Infof("Handling create event: %v", event)
fi, err := os.Stat(event.Name)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("stat file %s failed: %v", event.Name, err)
}
if strings.HasPrefix(fi.Name(), ".") {
klog.V(5).Infof("Ignoring file (starts with '.'): %s", fi.Name())
return nil
}
if !fi.IsDir() {
isSocket, err := util.IsUnixDomainSocket(util.NormalizePath(event.Name))
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to determine if file: %s is a unix domain socket: %v", event.Name, err)
}
if !isSocket {
klog.V(5).Infof("Ignoring non socket file %s", fi.Name())
return nil
}
return w.handlePluginRegistration(event.Name)
}
return w.traversePluginDir(event.Name)
}
func (w *Watcher) handlePluginRegistration(socketPath string) error {
if runtime.GOOS == "windows" {
socketPath = util.NormalizePath(socketPath)
}
//TODO: Implement rate limiting to mitigate any DOS kind of attacks.
// Update desired state of world list of plugins
// If the socket path does exist in the desired world cache, there's still
// a possibility that it has been deleted and recreated again before it is
// removed from the desired world cache, so we still need to call AddOrUpdatePlugin
// in this case to update the timestamp
klog.V(2).Infof("Adding socket path or updating timestamp %s to desired state cache", socketPath)
err := w.desiredStateOfWorld.AddOrUpdatePlugin(socketPath)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("error adding socket path %s or updating timestamp to desired state cache: %v", socketPath, err)
}
return nil
}
w.handleDeleteEvent()
w.handleDeleteEvent()主要逻辑:
(1)将socket从desiredStateOfWorld中删除。
// pkg/kubelet/pluginmanager/pluginwatcher/plugin_watcher.go
func (w *Watcher) handleDeleteEvent(event fsnotify.Event) {
klog.V(6).Infof("Handling delete event: %v", event)
socketPath := event.Name
klog.V(2).Infof("Removing socket path %s from desired state cache", socketPath)
w.desiredStateOfWorld.RemovePlugin(socketPath)
}
3.2 pm.reconciler.Run()
pm.reconciler.Run()主要逻辑为对比desiredStateOfWorld与actualStateOfWorld做调谐,做plugin的注册操作/取消注册操作。具体逻辑如下:
(1)对比actualStateOfWorld,如果desiredStateOfWorld中没有该socket信息,或者desiredStateOfWorld中该socket的Timestamp值与actualStateOfWorld中的不相等(即plugin更新了),则说明该plugin需要取消注册(更新的plugin需先取消注册,然后再次注册),调用rc.operationExecutor.UnregisterPlugin做plugin取消注册操作;
(2)对比desiredStateOfWorld,如果actualStateOfWorld中没有该socket信息,则调用rc.operationExecutor.RegisterPlugin做plugin注册操作。
// pkg/kubelet/pluginmanager/reconciler/reconciler.go
func (rc *reconciler) Run(stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
wait.Until(func() {
rc.reconcile()
},
rc.loopSleepDuration,
stopCh)
}
func (rc *reconciler) reconcile() {
// Unregisterations are triggered before registrations
// Ensure plugins that should be unregistered are unregistered.
for _, registeredPlugin := range rc.actualStateOfWorld.GetRegisteredPlugins() {
unregisterPlugin := false
if !rc.desiredStateOfWorld.PluginExists(registeredPlugin.SocketPath) {
unregisterPlugin = true
} else {
// We also need to unregister the plugins that exist in both actual state of world
// and desired state of world cache, but the timestamps don't match.
// Iterate through desired state of world plugins and see if there's any plugin
// with the same socket path but different timestamp.
for _, dswPlugin := range rc.desiredStateOfWorld.GetPluginsToRegister() {
if dswPlugin.SocketPath == registeredPlugin.SocketPath && dswPlugin.Timestamp != registeredPlugin.Timestamp {
klog.V(5).Infof(registeredPlugin.GenerateMsgDetailed("An updated version of plugin has been found, unregistering the plugin first before reregistering", ""))
unregisterPlugin = true
break
}
}
}
if unregisterPlugin {
klog.V(5).Infof(registeredPlugin.GenerateMsgDetailed("Starting operationExecutor.UnregisterPlugin", ""))
err := rc.operationExecutor.UnregisterPlugin(registeredPlugin.SocketPath, rc.getHandlers(), rc.actualStateOfWorld)
if err != nil &&
!goroutinemap.IsAlreadyExists(err) &&
!exponentialbackoff.IsExponentialBackoff(err) {
// Ignore goroutinemap.IsAlreadyExists and exponentialbackoff.IsExponentialBackoff errors, they are expected.
// Log all other errors.
klog.Errorf(registeredPlugin.GenerateErrorDetailed("operationExecutor.UnregisterPlugin failed", err).Error())
}
if err == nil {
klog.V(1).Infof(registeredPlugin.GenerateMsgDetailed("operationExecutor.UnregisterPlugin started", ""))
}
}
}
// Ensure plugins that should be registered are registered
for _, pluginToRegister := range rc.desiredStateOfWorld.GetPluginsToRegister() {
if !rc.actualStateOfWorld.PluginExistsWithCorrectTimestamp(pluginToRegister) {
klog.V(5).Infof(pluginToRegister.GenerateMsgDetailed("Starting operationExecutor.RegisterPlugin", ""))
err := rc.operationExecutor.RegisterPlugin(pluginToRegister.SocketPath, pluginToRegister.Timestamp, rc.getHandlers(), rc.actualStateOfWorld)
if err != nil &&
!goroutinemap.IsAlreadyExists(err) &&
!exponentialbackoff.IsExponentialBackoff(err) {
// Ignore goroutinemap.IsAlreadyExists and exponentialbackoff.IsExponentialBackoff errors, they are expected.
klog.Errorf(pluginToRegister.GenerateErrorDetailed("operationExecutor.RegisterPlugin failed", err).Error())
}
if err == nil {
klog.V(1).Infof(pluginToRegister.GenerateMsgDetailed("operationExecutor.RegisterPlugin started", ""))
}
}
}
}
3.2.1 rc.operationExecutor.UnregisterPlugin()
rc.operationExecutor.UnregisterPlugin()主要逻辑:做plugin取消注册操作。
那plugin取消注册操作具体做了什么呢?继续往下分析。
plugin取消注册操作方法调用链
kl.pluginManager.Run --> pm.desiredStateOfWorldPopulator.Start() --> pm.reconciler.Run() --> rc.reconcile() --> rc.operationExecutor.UnregisterPlugin() --> oe.operationGenerator.GenerateUnregisterPluginFunc() --> handler.DeRegisterPlugin() --> nim.UninstallCSIDriver() --> nim.updateNode()
下面来对plugin取消注册操作的部分关键方法进行分析。
GenerateUnregisterPluginFunc
下面来分析下GenerateUnregisterPluginFunc的逻辑,主要是定义并实现一个plugin取消注册的方法,然后返回。plugin取消注册方法主要逻辑如下:
(1)检测Node Driver Registrar组件socket的连通性;
(2)通过Node Driver Registrar组件socket获取plugin信息;
(3)从actualStateOfWorld中删除该Node Driver Registrar组件的socket信息;
(4)调用handler.DeRegisterPlugin做进一步的plugin取消注册操作。
所以接下来会对handler.DeRegisterPlugin方法进行分析。
// pkg/kubelet/pluginmanager/operationexecutor/operation_executor.go
func (oe *operationExecutor) UnregisterPlugin(
socketPath string,
pluginHandlers map[string]cache.PluginHandler,
actualStateOfWorld ActualStateOfWorldUpdater) error {
generatedOperation :=
oe.operationGenerator.GenerateUnregisterPluginFunc(socketPath, pluginHandlers, actualStateOfWorld)
return oe.pendingOperations.Run(
socketPath, generatedOperation)
}
// pkg/kubelet/pluginmanager/operationexecutor/operation_generator.go
func (og *operationGenerator) GenerateUnregisterPluginFunc(
socketPath string,
pluginHandlers map[string]cache.PluginHandler,
actualStateOfWorldUpdater ActualStateOfWorldUpdater) func() error {
unregisterPluginFunc := func() error {
client, conn, err := dial(socketPath, dialTimeoutDuration)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("UnregisterPlugin error -- dial failed at socket %s, err: %v", socketPath, err)
}
defer conn.Close()
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), time.Second)
defer cancel()
infoResp, err := client.GetInfo(ctx, ®isterapi.InfoRequest{})
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("UnregisterPlugin error -- failed to get plugin info using RPC GetInfo at socket %s, err: %v", socketPath, err)
}
handler, ok := pluginHandlers[infoResp.Type]
if !ok {
return fmt.Errorf("UnregisterPlugin error -- no handler registered for plugin type: %s at socket %s", infoResp.Type, socketPath)
}
// We remove the plugin to the actual state of world cache before calling a plugin consumer's Unregister handle
// so that if we receive a register event during Register Plugin, we can process it as a Register call.
actualStateOfWorldUpdater.RemovePlugin(socketPath)
handler.DeRegisterPlugin(infoResp.Name)
return nil
}
return unregisterPluginFunc
}
handler.DeRegisterPlugin()
handler.DeRegisterPlugin()方法里逻辑比较简单,主要是调用了unregisterDriver()方法。
unregisterDriver()方法主要逻辑:
(1)从csiDrivers变量中删除该plugin信息(后续kubelet调用csi plugin进行存储的挂载/解除挂载操作,将通过plugin名称从csiDrivers变量中拿到socket地址并进行通信,所以取消注册plugin时,需要从csiDrivers变量中把该plugin信息去除);
(2)调用nim.UninstallCSIDriver()做进一步处理。
// pkg/volume/csi/csi_plugin.go
// DeRegisterPlugin is called when a plugin removed its socket, signaling
// it is no longer available
func (h *RegistrationHandler) DeRegisterPlugin(pluginName string) {
klog.Info(log("registrationHandler.DeRegisterPlugin request for plugin %s", pluginName))
if err := unregisterDriver(pluginName); err != nil {
klog.Error(log("registrationHandler.DeRegisterPlugin failed: %v", err))
}
}
func unregisterDriver(driverName string) error {
csiDrivers.Delete(driverName)
if err := nim.UninstallCSIDriver(driverName); err != nil {
return errors.New(log("Error uninstalling CSI driver: %v", err))
}
return nil
}
nim.UninstallCSIDriver()
接下来看到nim.UninstallCSIDriver()方法的分析。
nim.UninstallCSIDriver()中主要看到nim.uninstallDriverFromCSINode()、removeMaxAttachLimit()与removeNodeIDFromNode()3个方法,主要逻辑都在其中:
(1)nim.uninstallDriverFromCSINode():更新CSINode对象,从中去除取消注册的plugin的相关信息。
(2)removeMaxAttachLimit():更新node对象,从node.Status.Capacity及node.Status.Allocatable中去除取消注册的plugin的相关信息。
(3)removeNodeIDFromNode():更新node对象,从node对象的annotation中key为csi.volume.kubernetes.io/nodeid的值中去除取消注册的plugin信息。
node对象的annotation示例:
csi.volume.kubernetes.io/nodeid: '{"cephfs.csi.ceph.com":"192.168.1.10","rbd.csi.ceph.com":"192.168.1.10"}'
CSIDriver对象示例:
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: CSINode
metadata:
name: 192.168.1.10
spec:
drivers:
- name: cephfs.csi.ceph.com
nodeID: 192.168.1.10
topologyKeys: null
- name: rbd.csi.ceph.com
nodeID: 192.168.1.10
topologyKeys: null
nim.UninstallCSIDriver()源码:
// pkg/volume/csi/nodeinfomanager/nodeinfomanager.go
// UninstallCSIDriver removes the node ID annotation from the Node object and CSIDrivers field from the
// CSINode object. If the CSINOdeInfo object contains no CSIDrivers, it will be deleted.
// If multiple calls to UninstallCSIDriver() are made in parallel, some calls might receive Node or
// CSINode update conflicts, which causes the function to retry the corresponding update.
func (nim *nodeInfoManager) UninstallCSIDriver(driverName string) error {
if utilfeature.DefaultFeatureGate.Enabled(features.CSINodeInfo) {
err := nim.uninstallDriverFromCSINode(driverName)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("error uninstalling CSI driver from CSINode object %v", err)
}
}
err := nim.updateNode(
removeMaxAttachLimit(driverName),
removeNodeIDFromNode(driverName),
)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("error removing CSI driver node info from Node object %v", err)
}
return nil
}
func (nim *nodeInfoManager) updateNode(updateFuncs ...nodeUpdateFunc) error {
var updateErrs []error
err := wait.ExponentialBackoff(updateBackoff, func() (bool, error) {
if err := nim.tryUpdateNode(updateFuncs...); err != nil {
updateErrs = append(updateErrs, err)
return false, nil
}
return true, nil
})
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("error updating node: %v; caused by: %v", err, utilerrors.NewAggregate(updateErrs))
}
return nil
}
(1)nim.uninstallDriverFromCSINode():更新CSINode对象,从中去除取消注册的plugin的相关信息。
// pkg/volume/csi/nodeinfomanager/nodeinfomanager.go
func (nim *nodeInfoManager) uninstallDriverFromCSINode(
csiDriverName string) error {
csiKubeClient := nim.volumeHost.GetKubeClient()
if csiKubeClient == nil {
return fmt.Errorf("error getting CSI client")
}
var updateErrs []error
err := wait.ExponentialBackoff(updateBackoff, func() (bool, error) {
if err := nim.tryUninstallDriverFromCSINode(csiKubeClient, csiDriverName); err != nil {
updateErrs = append(updateErrs, err)
return false, nil
}
return true, nil
})
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("error updating CSINode: %v; caused by: %v", err, utilerrors.NewAggregate(updateErrs))
}
return nil
}
func (nim *nodeInfoManager) tryUninstallDriverFromCSINode(
csiKubeClient clientset.Interface,
csiDriverName string) error {
nodeInfoClient := csiKubeClient.StorageV1().CSINodes()
nodeInfo, err := nodeInfoClient.Get(string(nim.nodeName), metav1.GetOptions{})
if err != nil && errors.IsNotFound(err) {
return nil
} else if err != nil {
return err
}
hasModified := false
// Uninstall CSINodeDriver with name csiDriverName
drivers := nodeInfo.Spec.Drivers[:0]
for _, driver := range nodeInfo.Spec.Drivers {
if driver.Name != csiDriverName {
drivers = append(drivers, driver)
} else {
// Found a driver with name csiDriverName
// Set hasModified to true because it will be removed
hasModified = true
}
}
if !hasModified {
// No changes, don't update
return nil
}
nodeInfo.Spec.Drivers = drivers
_, err = nodeInfoClient.Update(nodeInfo)
return err // do not wrap error
}
(2)removeMaxAttachLimit():更新node对象,从node.Status.Capacity及node.Status.Allocatable中去除取消注册的plugin的相关信息。
// pkg/volume/csi/nodeinfomanager/nodeinfomanager.go
func removeMaxAttachLimit(driverName string) nodeUpdateFunc {
return func(node *v1.Node) (*v1.Node, bool, error) {
limitKey := v1.ResourceName(util.GetCSIAttachLimitKey(driverName))
capacityExists := false
if node.Status.Capacity != nil {
_, capacityExists = node.Status.Capacity[limitKey]
}
allocatableExists := false
if node.Status.Allocatable != nil {
_, allocatableExists = node.Status.Allocatable[limitKey]
}
if !capacityExists && !allocatableExists {
return node, false, nil
}
delete(node.Status.Capacity, limitKey)
if len(node.Status.Capacity) == 0 {
node.Status.Capacity = nil
}
delete(node.Status.Allocatable, limitKey)
if len(node.Status.Allocatable) == 0 {
node.Status.Allocatable = nil
}
return node, true, nil
}
}
(3)removeNodeIDFromNode():更新node对象,从node对象的annotation中key为csi.volume.kubernetes.io/nodeid的值中去除取消注册的plugin信息。
// pkg/volume/csi/nodeinfomanager/nodeinfomanager.go
// removeNodeIDFromNode returns a function that removes node ID information matching the given
// driver name from a Node object.
func removeNodeIDFromNode(csiDriverName string) nodeUpdateFunc {
return func(node *v1.Node) (*v1.Node, bool, error) {
var previousAnnotationValue string
if node.ObjectMeta.Annotations != nil {
previousAnnotationValue =
node.ObjectMeta.Annotations[annotationKeyNodeID]
}
if previousAnnotationValue == "" {
return node, false, nil
}
// Parse previousAnnotationValue as JSON
existingDriverMap := map[string]string{}
if err := json.Unmarshal([]byte(previousAnnotationValue), &existingDriverMap); err != nil {
return nil, false, fmt.Errorf(
"failed to parse node's %q annotation value (%q) err=%v",
annotationKeyNodeID,
previousAnnotationValue,
err)
}
if _, ok := existingDriverMap[csiDriverName]; !ok {
// Value is already missing in node annotation, nothing more to do
return node, false, nil
}
// Delete annotation value
delete(existingDriverMap, csiDriverName)
if len(existingDriverMap) == 0 {
delete(node.ObjectMeta.Annotations, annotationKeyNodeID)
} else {
jsonObj, err := json.Marshal(existingDriverMap)
if err != nil {
return nil, false, fmt.Errorf(
"failed while trying to remove key %q from node %q annotation. Existing data: %v",
csiDriverName,
annotationKeyNodeID,
previousAnnotationValue)
}
node.ObjectMeta.Annotations[annotationKeyNodeID] = string(jsonObj)
}
return node, true, nil
}
}
3.2.2 rc.operationExecutor.RegisterPlugin()
rc.operationExecutor.RegisterPlugin()主要逻辑:做plugin注册操作。
那plugin注册操作具体做了什么呢?继续往下分析。
plugin注册操作方法调用链
kl.pluginManager.Run --> pm.desiredStateOfWorldPopulator.Start() --> pm.reconciler.Run() --> rc.reconcile() --> rc.operationExecutor.RegisterPlugin() --> oe.operationGenerator.GenerateRegisterPluginFunc() --> handler.RegisterPlugin() --> nim.InstallCSIDriver() --> nim.updateNode()
下面来对plugin注册操作的部分关键方法进行分析。
GenerateRegisterPluginFunc
下面来分析下GenerateRegisterPluginFunc的逻辑,主要是定义并实现一个plugin注册的方法,然后返回。plugin注册方法主要逻辑如下:
(1)检测Node Driver Registrar组件socket的连通性;
(2)通过Node Driver Registrar组件socket获取plugin信息(包括plugin的socket地址、plugin名称等);
(3)调用handler.ValidatePlugin(),检查已注册的plugin中是否有比该需要注册的plugin同名的的更高的版本,如有,则返回注册失败,并通知plugin注册失败;
(4)向actualStateOfWorld中增加该Node Driver Registrar组件的socket信息;
(5)调用handler.RegisterPlugin()做进一步的plugin注册操作;
(6)调用og.notifyPlugin,通知plugin,已经向kubelet注册成功/注册失败。
所以接下来会对handler.RegisterPlugin()方法进行分析。
// pkg/kubelet/pluginmanager/operationexecutor/operation_executor.go
func (oe *operationExecutor) RegisterPlugin(
socketPath string,
timestamp time.Time,
pluginHandlers map[string]cache.PluginHandler,
actualStateOfWorld ActualStateOfWorldUpdater) error {
generatedOperation :=
oe.operationGenerator.GenerateRegisterPluginFunc(socketPath, timestamp, pluginHandlers, actualStateOfWorld)
return oe.pendingOperations.Run(
socketPath, generatedOperation)
}
// pkg/kubelet/pluginmanager/operationexecutor/operation_generator.go
func (og *operationGenerator) GenerateRegisterPluginFunc(
socketPath string,
timestamp time.Time,
pluginHandlers map[string]cache.PluginHandler,
actualStateOfWorldUpdater ActualStateOfWorldUpdater) func() error {
registerPluginFunc := func() error {
client, conn, err := dial(socketPath, dialTimeoutDuration)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("RegisterPlugin error -- dial failed at socket %s, err: %v", socketPath, err)
}
defer conn.Close()
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), time.Second)
defer cancel()
infoResp, err := client.GetInfo(ctx, ®isterapi.InfoRequest{})
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("RegisterPlugin error -- failed to get plugin info using RPC GetInfo at socket %s, err: %v", socketPath, err)
}
handler, ok := pluginHandlers[infoResp.Type]
if !ok {
if err := og.notifyPlugin(client, false, fmt.Sprintf("RegisterPlugin error -- no handler registered for plugin type: %s at socket %s", infoResp.Type, socketPath)); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("RegisterPlugin error -- failed to send error at socket %s, err: %v", socketPath, err)
}
return fmt.Errorf("RegisterPlugin error -- no handler registered for plugin type: %s at socket %s", infoResp.Type, socketPath)
}
if infoResp.Endpoint == "" {
infoResp.Endpoint = socketPath
}
if err := handler.ValidatePlugin(infoResp.Name, infoResp.Endpoint, infoResp.SupportedVersions); err != nil {
if err = og.notifyPlugin(client, false, fmt.Sprintf("RegisterPlugin error -- plugin validation failed with err: %v", err)); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("RegisterPlugin error -- failed to send error at socket %s, err: %v", socketPath, err)
}
return fmt.Errorf("RegisterPlugin error -- pluginHandler.ValidatePluginFunc failed")
}
// We add the plugin to the actual state of world cache before calling a plugin consumer's Register handle
// so that if we receive a delete event during Register Plugin, we can process it as a DeRegister call.
err = actualStateOfWorldUpdater.AddPlugin(cache.PluginInfo{
SocketPath: socketPath,
Timestamp: timestamp,
})
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("RegisterPlugin error -- failed to add plugin at socket %s, err: %v", socketPath, err)
}
if err := handler.RegisterPlugin(infoResp.Name, infoResp.Endpoint, infoResp.SupportedVersions); err != nil {
return og.notifyPlugin(client, false, fmt.Sprintf("RegisterPlugin error -- plugin registration failed with err: %v", err))
}
// Notify is called after register to guarantee that even if notify throws an error Register will always be called after validate
if err := og.notifyPlugin(client, true, ""); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("RegisterPlugin error -- failed to send registration status at socket %s, err: %v", socketPath, err)
}
return nil
}
return registerPluginFunc
}
handler.RegisterPlugin()
handler.DeRegisterPlugin()方法主要逻辑:
(1)存储该plugin信息(主要是plugin名称与plugin的socket地址)到csiDrivers变量中(后续kubelet调用csi plugin进行存储的挂载/解除挂载操作,将通过plugin名称从此变量中拿到socket地址并进行通信);
(2)检测Node Driver Registrar组件socket的连通性;
(3)通过plugin的socket获取plugin信息(包括plugin的NodeId、最大挂载数量限制、拓扑信息等);
(4)调用nim.InstallCSIDriver,做进一步的plugin注册操作。
// pkg/volume/csi/csi_plugin.go
// TODO (verult) consider using a struct instead of global variables
// csiDrivers map keep track of all registered CSI drivers on the node and their
// corresponding sockets
var csiDrivers = &DriversStore{}
// RegisterPlugin is called when a plugin can be registered
func (h *RegistrationHandler) RegisterPlugin(pluginName string, endpoint string, versions []string) error {
klog.Infof(log("Register new plugin with name: %s at endpoint: %s", pluginName, endpoint))
highestSupportedVersion, err := h.validateVersions("RegisterPlugin", pluginName, endpoint, versions)
if err != nil {
return err
}
// Storing endpoint of newly registered CSI driver into the map, where CSI driver name will be the key
// all other CSI components will be able to get the actual socket of CSI drivers by its name.
csiDrivers.Set(pluginName, Driver{
endpoint: endpoint,
highestSupportedVersion: highestSupportedVersion,
})
// Get node info from the driver.
csi, err := newCsiDriverClient(csiDriverName(pluginName))
if err != nil {
return err
}
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), csiTimeout)
defer cancel()
driverNodeID, maxVolumePerNode, accessibleTopology, err := csi.NodeGetInfo(ctx)
if err != nil {
if unregErr := unregisterDriver(pluginName); unregErr != nil {
klog.Error(log("registrationHandler.RegisterPlugin failed to unregister plugin due to previous error: %v", unregErr))
}
return err
}
err = nim.InstallCSIDriver(pluginName, driverNodeID, maxVolumePerNode, accessibleTopology)
if err != nil {
if unregErr := unregisterDriver(pluginName); unregErr != nil {
klog.Error(log("registrationHandler.RegisterPlugin failed to unregister plugin due to previous error: %v", unregErr))
}
return err
}
return nil
}
nim.InstallCSIDriver()
nim.InstallCSIDriver()中主要看到updateNodeIDInNode()与nim.updateCSINode()两个方法,主要逻辑都在其中:
(1)updateNodeIDInNode():更新node对象,向node对象的annotation中key为csi.volume.kubernetes.io/nodeid的值中去增加注册的plugin信息。
(2)nim.updateCSINode():创建或更新CSINode对象。
// pkg/volume/csi/nodeinfomanager/nodeinfomanager.go
// InstallCSIDriver updates the node ID annotation in the Node object and CSIDrivers field in the
// CSINode object. If the CSINode object doesn't yet exist, it will be created.
// If multiple calls to InstallCSIDriver() are made in parallel, some calls might receive Node or
// CSINode update conflicts, which causes the function to retry the corresponding update.
func (nim *nodeInfoManager) InstallCSIDriver(driverName string, driverNodeID string, maxAttachLimit int64, topology map[string]string) error {
if driverNodeID == "" {
return fmt.Errorf("error adding CSI driver node info: driverNodeID must not be empty")
}
nodeUpdateFuncs := []nodeUpdateFunc{
updateNodeIDInNode(driverName, driverNodeID),
}
if utilfeature.DefaultFeatureGate.Enabled(features.CSINodeInfo) {
nodeUpdateFuncs = append(nodeUpdateFuncs, updateTopologyLabels(topology))
}
err := nim.updateNode(nodeUpdateFuncs...)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("error updating Node object with CSI driver node info: %v", err)
}
if utilfeature.DefaultFeatureGate.Enabled(features.CSINodeInfo) {
err = nim.updateCSINode(driverName, driverNodeID, maxAttachLimit, topology)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("error updating CSINode object with CSI driver node info: %v", err)
}
}
return nil
}
// pkg/volume/csi/nodeinfomanager/nodeinfomanager.go
// updateNodeIDInNode returns a function that updates a Node object with the given
// Node ID information.
func updateNodeIDInNode(
csiDriverName string,
csiDriverNodeID string) nodeUpdateFunc {
return func(node *v1.Node) (*v1.Node, bool, error) {
existingDriverMap, err := buildNodeIDMapFromAnnotation(node)
if err != nil {
return nil, false, err
}
if val, ok := existingDriverMap[csiDriverName]; ok {
if val == csiDriverNodeID {
// Value already exists in node annotation, nothing more to do
return node, false, nil
}
}
// Add/update annotation value
existingDriverMap[csiDriverName] = csiDriverNodeID
jsonObj, err := json.Marshal(existingDriverMap)
if err != nil {
return nil, false, fmt.Errorf(
"error while marshalling node ID map updated with driverName=%q, nodeID=%q: %v",
csiDriverName,
csiDriverNodeID,
err)
}
if node.ObjectMeta.Annotations == nil {
node.ObjectMeta.Annotations = make(map[string]string)
}
node.ObjectMeta.Annotations[annotationKeyNodeID] = string(jsonObj)
return node, true, nil
}
}
// pkg/volume/csi/nodeinfomanager/nodeinfomanager.go
func (nim *nodeInfoManager) updateCSINode(
driverName string,
driverNodeID string,
maxAttachLimit int64,
topology map[string]string) error {
csiKubeClient := nim.volumeHost.GetKubeClient()
if csiKubeClient == nil {
return fmt.Errorf("error getting CSI client")
}
var updateErrs []error
err := wait.ExponentialBackoff(updateBackoff, func() (bool, error) {
if err := nim.tryUpdateCSINode(csiKubeClient, driverName, driverNodeID, maxAttachLimit, topology); err != nil {
updateErrs = append(updateErrs, err)
return false, nil
}
return true, nil
})
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("error updating CSINode: %v; caused by: %v", err, utilerrors.NewAggregate(updateErrs))
}
return nil
}
总结
本节主要讲解了kubelet注册csi driver的原理,以及其代码的分析,也顺带提了一下Node Driver Registrar组件,下面来做个总结。
Node Driver Registrar
Node Driver Registrar在后面的文章中会介绍,Node Driver Registrar源码分析,它是一个sidecar容器,通过Kubelet的插件注册机制将CSI plugin(csi driver,两个名词意义一样)注册到Kubelet,让kubelet做volume的mount/umount操作时知道怎么调用相应的csi plugin。
kubelet注册csi driver的原理
kubelet的pluginManager会监听某个特定目录,而负责向kubelet注册csi driver的组件Node Driver Registrar会创建暴露服务的socket在该目录下(每个plugin会对应一个Node Driver Registrar组件,也就是说,一个Node Driver Registrar只负责一个plugin的注册工作),pluginManager通过Node Driver Registrar组件暴露的socket获取plugin信息(包括plugin的socket地址、plugin名称等),从而最终做到根据该目录下socket文件的新增/删除来做相应的plugin注册/取消注册操作。
plugin注册完成后,后续kubelet将通过plugin暴露的socket与plugin进行通信,做存储挂载/解除挂载等操作。
下面再来总结一下在kubelet的pluginManager中,plugin的注册/取消注册操作分别做了什么动作。
plugin注册操作
(1)存储该plugin信息(主要是plugin名称与plugin的socket地址)到csiDrivers变量中(后续kubelet调用csi plugin进行存储的挂载/解除挂载操作,将通过plugin名称从此变量中拿到socket地址并进行通信;csiDriver变量代码位置-pkg/volume/csi/csi_plugin.go);
(2)更新node对象,向node对象的annotation中key为csi.volume.kubernetes.io/nodeid的值中去增加注册的plugin信息。
(3)创建或更新CSINode对象。
plugin取消注册操作
(1)从csiDrivers变量中删除该plugin信息(后续kubelet调用csi plugin进行存储的挂载/解除挂载操作,将通过plugin名称从csiDrivers变量(csiDriver变量代码位置-pkg/volume/csi/csi_plugin.go)中拿到socket地址并进行通信,所以取消注册plugin时,需要从csiDrivers变量中把该plugin信息去除);
(2)更新CSINode对象,从中去除取消注册的plugin的相关信息。
(3)更新node对象,从node.Status.Capacity及node.Status.Allocatable中去除取消注册的plugin的相关信息。
(4)更新node对象,从node对象的annotation中key为csi.volume.kubernetes.io/nodeid的值中去除取消注册的plugin信息。
kubelet分析-csi driver注册源码分析的更多相关文章
- kubelet分析-csi driver注册分析-Node Driver Registrar源码分析
kubernetes ceph-csi分析目录导航 Node Driver Registrar分析 node-driver-registrar是一个sidecar容器,通过Kubelet的插件注册机制 ...
- Spring Cloud Eureka服务注册源码分析
Eureka是怎么work的 那eureka client如何将本地服务的注册信息发送到远端的注册服务器eureka server上.通过下面的源码分析,看出Eureka Client的定时任务调用E ...
- [转] jQuery源码分析-如何做jQuery源码分析
jQuery源码分析系列(持续更新) jQuery的源码有些晦涩难懂,本文分享一些我看源码的方法,每一个模块我基本按照这样的顺序去学习. 当我读到难度的书或者源码时,会和<如何阅读一本书> ...
- 序列化器中钩子函数源码分析、many关键字源码分析
局部钩子和全局钩子源码分析(2星) # 入口是 ser.is_valid(),是BaseSerializer的方法 # 最核心的代码 self._validated_data = self.run_v ...
- k8s client-go源码分析 informer源码分析(5)-Controller&Processor源码分析
client-go之Controller&Processor源码分析 1.controller与Processor概述 Controller Controller从DeltaFIFO中pop ...
- 使用canal分析binlog(二) canal源码分析
在能够跑通example后有几个疑问 1. canal的server端对于已经读取的binlog,client已经ack的position,是否持久化,保存在哪里 2. 即使不启动zookeeper, ...
- Java源码分析系列之HttpServletRequest源码分析
从源码当中 我们可以 得知,HttpServletRequest其实 实际上 并 不是一个类,它只是一个标准,一个 接口而已,它的 父类是ServletRequest. 认证方式 public int ...
- 【Java】NIO中Channel的注册源码分析
Channel的注册是在SelectableChannel中定义的: public abstract SelectionKey register(Selector sel, int ops, Obje ...
- Flink的Job启动Driver端(源码分析)
整个Flink的Job启动是通过在Driver端通过用户的Envirement的execute()方法将用户的算子转化成StreamGraph,然后得到JobGraph通过远程RPC将这个JobGra ...
随机推荐
- 浅尝js垃圾回收机制
局部作用域内的变量,在函数执行结束之后就会被js的垃圾回收机制销毁 为什么要销毁局部变量? => 为了释放内存 js垃圾回收机制何时会销毁局部变量 : 如果局部变量无法再得到访问,就会被 ...
- 认识 Spring Cloud Alibaba
个人理解 Spring Cloud Alibaba 就是 Spring Cloud 的微服务规范的一种实现,外加一些阿里云的商业组件 Spring Cloud 是什么 Spring Cloud 为开发 ...
- 登陆框select绕过
0x00 原理 思路来自美团杯2021,本来说出题人已经把select通过正则过滤了,就不该总是往用select进行查询那方面想-> select id from users where u ...
- [Qt]《开发指南》3.1源码分析
界面: ButterflyGraph: 可以看出,本工程在主程序main里调用窗口界面qmywidget,窗口界面继承了QWidget,并调用自定义类qperson,推测是qmywidget类中的一个 ...
- gdb调试多线程多进程
多进程调试 我们使用gdb调试程序,gdb的调试默认是调试父进程的,如果要做到对父进程和子进程都做到调试,所以附加了调试子进程的功能. 设置条件 如果让gdb可以同时调试多个程序,只需要设置follo ...
- Ubuntu 20.04 版本安装
Ubuntu 20.04 版本安装 安装步骤 首先创建好Ubuntu 20.04虚拟机 等待系统检查完整性 选择语言 选择不更新,回车确定 键盘语言默认即可 网卡IP配置 设置代理服务器 设置源 自定 ...
- 源码安装Python3
源码安装Python3 一.安装Python3需要的依赖包 [root@localhost ~]# yum install -y gcc make wget openssl openssl-devel ...
- linux中级之netfilter防火墙(firewalld)
一.firewalld主要概念 dynamic firewall daemon.支持ipv4和ipv6.Centos7中默认将防火墙从iptables升级为了firewalld.firewalld相对 ...
- Kubernetes-3.3:ETCD集群搭建及使用(https认证+数据备份恢复)
etcd集群搭建 环境介绍 基于CentOS Linux release 7.9.2009 (Core) ip hostname role 172.17.0.4 cd782d0a790b etcd1 ...
- Python保留指定位数的小数
Python保留指定位数的小数 1 '%.2f' %f 方法(推荐) f = 1.23456 print('%.4f' % f) print('%.3f' % f) print('%.2f' % f) ...
