Solution -「Gym 102798I」Sean the Cuber
\(\mathcal{Description}\)
Link.
给定两个可还原的二阶魔方,求从其中一个状态拧到另一个状态的最小步数。
数据组数 \(T\le2.5\times10^5\)。
\(\mathcal{Solution}\)
是这样的,我画了两面草稿纸,顺便手工了一个立体魔方,所以我可以拜访出题人吗?
先放一张展开图:
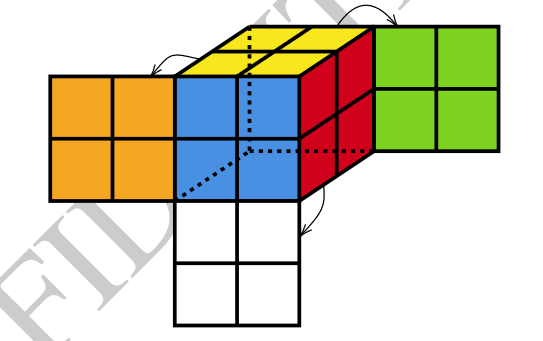
第一步,给魔方在整体转动的意义下定位。任取一个角块,例如 \((B,R,Y)\)(指由这三种颜色构成的角块,下同),钦定它必须在前方右上角,且蓝色必须朝前。此时能够计算魔方本质不同状态数:其余 \(7\) 个角块任意排列 \(7!\),每个角块三种状态 \(3^7\),但当算上 \((B,R,Y)\) 的其中七个角块确定时,剩下的角块只有一种状态能使魔方可还原,所以总状态数为 \(7!\times3^6=3674160\)。这亦提供了一种对已定位魔方的 hash 方法:对于角块排列 Cantor 展开,再算上块的三进制状态。
第二步,将每个面唯一编号(同色面可以通过所在角块颜色组合确定编号),以还原状态为零元 \(\iota\),所有可还原状态构成置换群 \((G,\cdot)\),那么对于两个魔方 \(p,q\),\(\operatorname{dist}(p,q)=\operatorname{dist}(\iota,p^{-1}q)\)。我们预处理 \(\iota\) 到每种魔方的最短步数就能快速查表求出答案。而由于 \((B,R,Y)\) 固定,可用的转动有 后侧左旋、后侧右旋、左侧左旋、左侧右旋、下侧左旋、下侧右旋六种,分别打出置换表即可。
好吧我来好心地讲一下实现。我对如上图还原魔方的编号方式为:
20 3
21 2
19 22 23 0 1 4 5 18
16 13 12 11 10 7 6 17
14 9
15 8
总之角块上三个面的编号得连续。设现在输入的魔方置换为 \(p\),第一步定位过程中,首先若 \(0\) 所在角块不在右侧面,则交换 \(p_i\) 与 \(p_{i+12}\)(整体右旋 \(180°\));此后不停整体上旋 \(180°\) 直到 \(0\) 所在角块在右侧上方;最后以右上-左下为轴整体旋转 \(120°\) 直到 \(p_0=0\),定位完成。
对于六种转动置换,打三个表,另外三个直接求逆就好√
其他细节貌似不吓人了,主要是表别打错。
我所实现的复杂度大概是 \(\mathcal O(3674160\times24\times6+T)\) 叭。
\(\mathcal{Code}\)
/*~Rainybunny~*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define rep( i, l, r ) for ( int i = l, rep##i = r; i <= rep##i; ++i )
#define per( i, r, l ) for ( int i = r, per##i = l; i >= per##i; --i )
const int MAXS = 3674160;
struct Cube {
int prm[24];
Cube() { rep ( i, 0, 23 ) prm[i] = i; }
Cube( const std::vector<int>& p ) { rep ( i, 0, 23 ) prm[i] = p[i]; }
Cube( const char* tmp ) {
static std::map<std::string, int> BLOCK = {
{ "BRY", 0 }, { "YRG", 1 }, { "GRW", 2 }, { "WRB", 3 },
{ "BOW", 4 }, { "WOG", 5 }, { "GOY", 6 }, { "YOB", 7 }
};
/* turn into permutation */
for ( int i = 0; i < 24; i += 3 ) {
rep ( j, 0, 2 ) {
std::string cor = { tmp[i + j], tmp[i + ( j + 1 ) % 3],
tmp[i + ( j + 2 ) % 3] };
if ( BLOCK.count( cor ) ) {
int v = BLOCK[cor];
prm[i + j] = v * 3;
prm[i + ( j + 1 ) % 3] = v * 3 + 1;
prm[i + ( j + 2 ) % 3] = v * 3 + 2;
}
}
}
/* adjust it till prm[0]=0 */
int zpos = 0; while ( prm[zpos] ) ++zpos;
if ( zpos >= 12 ) { // RR, turn to right side.
rep ( i, 0, 11 ) prm[i] ^= prm[i + 12] ^= prm[i] ^= prm[i + 12];
zpos -= 12;
}
zpos /= 3; // block id.
while ( zpos ) { // U till 0 get block 0.
static int tp[24];
rep ( i, 0, 11 ) tp[( i + 3 ) % 12] = prm[i];
rep ( i, 12, 23 ) tp[( i + 9 ) % 12 + 12] = prm[i];
rep ( i, 0, 23 ) prm[i] = tp[i];
zpos = ( zpos + 1 ) & 3;
}
static const Cube ROT = std::vector<int>{ 1, 2, 0, 23, 21, 22,
19, 20, 18, 5, 3, 4,
7, 8, 6, 17, 15, 16,
13, 14, 12, 11, 9, 10 };
while ( prm[0] )
*this = *this * ROT;
}
inline int& operator [] ( const int k ) { return prm[k]; }
inline Cube inv() const {
static Cube ret;
rep ( i, 0, 23 ) ret[prm[i]] = i;
return ret;
}
inline Cube operator * ( const Cube& t ) const {
static Cube ret;
rep ( i, 0, 23 ) ret[i] = prm[t.prm[i]];
return ret;
}
inline int hash() const {
static const int fac[7] = { 1, 1, 2, 6, 24, 120, 720 };
int apr = 127, ret = 0;
rep ( i, 0, 6 ) { // cantor
int v = prm[( i + 1 ) * 3] / 3 - 1;
ret += fac[6 - i] * __builtin_popcount( apr & ( ( 1 << v ) - 1 ) );
apr ^= 1 << v;
}
rep ( i, 1, 6 ) ret = ret * 3 + prm[i * 3] % 3;
assert( 0 <= ret && ret < MAXS );
return ret;
}
};
const Cube TWIST[6] = {
std::vector<int>{ 0, 1, 2, 7, 8, 6, 17, 15, 16, 9, 10, 11,
12, 13, 14, 19, 20, 18, 5, 3, 4, 21, 22, 23 }, // BL
std::vector<int>{ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11,
21, 22, 23, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20 }, // LD
std::vector<int>{ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 10, 11, 9, 14, 12, 13,
16, 17, 15, 8, 6, 7, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23 }, // DR
TWIST[0].inv(),
TWIST[1].inv(),
TWIST[2].inv()
};
int dist[MAXS + 5];
inline void init() {
static std::queue<Cube> que; que.push( Cube() );
memset( dist, 0xff, sizeof dist ), dist[Cube().hash()] = 0;
while ( !que.empty() ) {
Cube u( que.front() ); int hu = u.hash();
que.pop();
rep ( i, 0, 5 ) {
Cube v( u * TWIST[i] ); int hv = v.hash();
if ( !~dist[hv] ) dist[hv] = dist[hu] + 1, que.push( v );
}
}
}
inline void readCubes( Cube& A, Cube& B ) {
char a[24], b[24], t;
std::cin >> a[20] >> a[3] >> t >> b[20] >> b[3];
std::cin >> a[21] >> a[2] >> t >> b[21] >> b[2];
std::cin >> a[19] >> a[22] >> a[23] >> a[0]
>> a[1] >> a[4] >> a[5] >> a[18] >> t
>> b[19] >> b[22] >> b[23] >> b[0]
>> b[1] >> b[4] >> b[5] >> b[18];
std::cin >> a[16] >> a[13] >> a[12] >> a[11]
>> a[10] >> a[7] >> a[6] >> a[17] >> t
>> b[16] >> b[13] >> b[12] >> b[11]
>> b[10] >> b[7] >> b[6] >> b[17];
std::cin >> a[14] >> a[9] >> t >> b[14] >> b[9];
std::cin >> a[15] >> a[8] >> t >> b[15] >> b[8];
A = a, B = b;
}
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio( false ), std::cin.tie( 0 );
init();
std::cerr << "init finished in "
<< double( clock() ) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC << "s\n";
int T; std::cin >> T;
while ( T-- ) {
static Cube u, v; readCubes( u, v );
std::cout << dist[( u.inv() * v ).hash()] << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
Solution -「Gym 102798I」Sean the Cuber的更多相关文章
- Solution -「Gym 102979E」Expected Distance
\(\mathcal{Description}\) Link. 用给定的 \(\{a_{n-1}\},\{c_n\}\) 生成一棵含有 \(n\) 个点的树,其中 \(u\) 连向 \([1, ...
- Solution -「Gym 102979L」 Lights On The Road
\(\mathcal{Description}\) Link. 给定序列 \(\{w_n\}\),选择 \(i\) 位置的代价为 \(w_i\),要求每个位置要不被选择,要不左右两个位置至少被 ...
- Solution -「Gym 102956F」Find the XOR
\(\mathcal{Description}\) Link. 给定 \(n\) 个点 \(m\) 条边的连通无向图 \(G\),边有边权.其中 \(u,v\) 的距离 \(d(u,v)\) ...
- Solution -「Gym 102956B」Beautiful Sequence Unraveling
\(\mathcal{Description}\) Link. 求长度为 \(n\),值域为 \([1,m]\) 的整数序列 \(\lang a_n\rang\) 的个数,满足 \(\not\ ...
- Solution -「Gym 102956F」Border Similarity Undertaking
\(\mathcal{Description}\) Link. 给定一张 \(n\times m\) 的表格,每个格子上写有一个小写字母.求其中长宽至少为 \(2\),且边界格子上字母相同的矩 ...
- Solution -「Gym 102956A」Belarusian State University
\(\mathcal{Description}\) Link. 给定两个不超过 \(2^n-1\) 次的多项式 \(A,B\),对于第 \(i\in[0,n)\) 个二进制位,定义任意一个二元 ...
- Solution -「Gym 102798K」Tree Tweaking
\(\mathcal{Description}\) Link. 给定排列 \(\{p_n\}\),求任意重排 \(p_{l..r}\) 的元素后,将 \(\{p_n\}\) 依次插入二叉搜索树 ...
- Solution -「Gym 102798E」So Many Possibilities...
\(\mathcal{Description}\) Link. 给定非负整数序列 \(\{a_n\}\) 和 \(m\),每次随机在 \(\{a\}\) 中取一个非零的 \(a_i\)(保证存 ...
- Solution -「Gym 102759I」Query On A Tree 17
\(\mathcal{Description}\) Link. 给定一棵含 \(n\) 个结点的树,结点 \(1\) 为根,点 \(u\) 初始有点权 \(a_u=0\),维护 \(q\) 次 ...
随机推荐
- react中Fragment组件
什么是Fragment?在我们定义组件的时候return里最外层包裹的div往往不想渲染到页面,那么就要用到我们的Fragment组件了,具体使用如下: import React, { Compone ...
- C/C++避免头文件重复包含的方法
C/C++避免头文件重复包含的方法 1. #ifndef 2. #pragma once 3. 混合使用 在实际的编程过程中,因为会使用多个文件,所以在文件中不可避免的要引入一些头文件,这样就可能会出 ...
- Spark-2.0.2源码编译
注:图片如果损坏,点击文章链接:https://www.toutiao.com/i6813925210731840013/ Spark官网下载地址: http://spark.apache.org/d ...
- jsencrypt vue相关的rsa加密
vue组件引入 import { JSEncrypt } from 'jsencrypt' 方法内使用 let publicKey = asdfsafdadfafasjdhfasfd // 从后台获取 ...
- 通过springBoot集成搭建webScoket服务器
前言: 最近工作中有一个需求,就是服务端要主动推送消息给客户端,而我们平常的Http请求只能一请求一响应,为此学习了webScokset通讯技术,以下介绍的是java 通过SpringBoot集成we ...
- CAS基础
有锁机制存在以下问题: (1)在多线程竞争下,加锁.释放锁会导致比较多的上下文切换和调度延时,引起性能问题. (2)一个线程持有锁会导致其它所有需要此锁的线程挂起. (3)如果一个优先级高的线程等待一 ...
- gin中在中间件或handler中使用goroutine
package main import ( "fmt" "github.com/gin-gonic/gin" "log" "tim ...
- javaweb登陆界面实现不同角色进入不同界面
目录结构 类包: AccountBean.java AccountDao.java JudgeServlet.java 登陆界面: index.jsp 代码实现 AccountBean.java pa ...
- 微服务架构 | 4.2 基于 Feign 与 OpenFeign 的服务接口调用
目录 前言 1. OpenFeign 基本知识 1.1 Feign 是什么 1.2 Feign 的出现解决了什么问题 1.3 Feign 与 OpenFeign 的区别与对比 2. 在服务消费者端开启 ...
- Python 调用 Shell
