python的基础类源码解析——collection类
1、计数器(counter)
Counter是对字典类型的补充,用于追踪值的出现次数。
ps:具备字典的所有功能 + 自己的功能
########################################################################
### Counter
######################################################################## class Counter(dict):
'''Dict subclass for counting hashable items. Sometimes called a bag
or multiset. Elements are stored as dictionary keys and their counts
are stored as dictionary values. >>> c = Counter('abcdeabcdabcaba') # count elements from a string >>> c.most_common(3) # three most common elements
[('a', 5), ('b', 4), ('c', 3)]
>>> sorted(c) # list all unique elements
['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e']
>>> ''.join(sorted(c.elements())) # list elements with repetitions
'aaaaabbbbcccdde'
>>> sum(c.values()) # total of all counts >>> c['a'] # count of letter 'a'
>>> for elem in 'shazam': # update counts from an iterable
... c[elem] += 1 # by adding 1 to each element's count
>>> c['a'] # now there are seven 'a'
>>> del c['b'] # remove all 'b'
>>> c['b'] # now there are zero 'b' >>> d = Counter('simsalabim') # make another counter
>>> c.update(d) # add in the second counter
>>> c['a'] # now there are nine 'a' >>> c.clear() # empty the counter
>>> c
Counter() Note: If a count is set to zero or reduced to zero, it will remain
in the counter until the entry is deleted or the counter is cleared: >>> c = Counter('aaabbc')
>>> c['b'] -= 2 # reduce the count of 'b' by two
>>> c.most_common() # 'b' is still in, but its count is zero
[('a', 3), ('c', 1), ('b', 0)] '''
# References:
# http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multiset
# http://www.gnu.org/software/smalltalk/manual-base/html_node/Bag.html
# http://www.demo2s.com/Tutorial/Cpp/0380__set-multiset/Catalog0380__set-multiset.htm
# http://code.activestate.com/recipes/259174/
# Knuth, TAOCP Vol. II section 4.6.3 def __init__(self, iterable=None, **kwds):
'''Create a new, empty Counter object. And if given, count elements
from an input iterable. Or, initialize the count from another mapping
of elements to their counts. >>> c = Counter() # a new, empty counter
>>> c = Counter('gallahad') # a new counter from an iterable
>>> c = Counter({'a': 4, 'b': 2}) # a new counter from a mapping
>>> c = Counter(a=4, b=2) # a new counter from keyword args '''
super(Counter, self).__init__()
self.update(iterable, **kwds) def __missing__(self, key):
""" 对于不存在的元素,返回计数器为0 """
'The count of elements not in the Counter is zero.'
# Needed so that self[missing_item] does not raise KeyError
return 0 def most_common(self, n=None):
""" 数量大于等n的所有元素和计数器 """
'''List the n most common elements and their counts from the most
common to the least. If n is None, then list all element counts. >>> Counter('abcdeabcdabcaba').most_common(3)
[('a', 5), ('b', 4), ('c', 3)] '''
# Emulate Bag.sortedByCount from Smalltalk
if n is None:
return sorted(self.iteritems(), key=_itemgetter(1), reverse=True)
return _heapq.nlargest(n, self.iteritems(), key=_itemgetter(1)) def elements(self):
""" 计数器中的所有元素,注:此处非所有元素集合,而是包含所有元素集合的迭代器 """
'''Iterator over elements repeating each as many times as its count. >>> c = Counter('ABCABC')
>>> sorted(c.elements())
['A', 'A', 'B', 'B', 'C', 'C'] # Knuth's example for prime factors of 1836: 2**2 * 3**3 * 17**1
>>> prime_factors = Counter({2: 2, 3: 3, 17: 1})
>>> product = 1
>>> for factor in prime_factors.elements(): # loop over factors
... product *= factor # and multiply them
>>> product Note, if an element's count has been set to zero or is a negative
number, elements() will ignore it. '''
# Emulate Bag.do from Smalltalk and Multiset.begin from C++.
return _chain.from_iterable(_starmap(_repeat, self.iteritems())) # Override dict methods where necessary @classmethod
def fromkeys(cls, iterable, v=None):
# There is no equivalent method for counters because setting v=1
# means that no element can have a count greater than one.
raise NotImplementedError(
'Counter.fromkeys() is undefined. Use Counter(iterable) instead.') def update(self, iterable=None, **kwds):
""" 更新计数器,其实就是增加;如果原来没有,则新建,如果有则加一 """
'''Like dict.update() but add counts instead of replacing them. Source can be an iterable, a dictionary, or another Counter instance. >>> c = Counter('which')
>>> c.update('witch') # add elements from another iterable
>>> d = Counter('watch')
>>> c.update(d) # add elements from another counter
>>> c['h'] # four 'h' in which, witch, and watch '''
# The regular dict.update() operation makes no sense here because the
# replace behavior results in the some of original untouched counts
# being mixed-in with all of the other counts for a mismash that
# doesn't have a straight-forward interpretation in most counting
# contexts. Instead, we implement straight-addition. Both the inputs
# and outputs are allowed to contain zero and negative counts. if iterable is not None:
if isinstance(iterable, Mapping):
if self:
self_get = self.get
for elem, count in iterable.iteritems():
self[elem] = self_get(elem, 0) + count
else:
super(Counter, self).update(iterable) # fast path when counter is empty
else:
self_get = self.get
for elem in iterable:
self[elem] = self_get(elem, 0) + 1
if kwds:
self.update(kwds) def subtract(self, iterable=None, **kwds):
""" 相减,原来的计数器中的每一个元素的数量减去后添加的元素的数量 """
'''Like dict.update() but subtracts counts instead of replacing them.
Counts can be reduced below zero. Both the inputs and outputs are
allowed to contain zero and negative counts. Source can be an iterable, a dictionary, or another Counter instance. >>> c = Counter('which')
>>> c.subtract('witch') # subtract elements from another iterable
>>> c.subtract(Counter('watch')) # subtract elements from another counter
>>> c['h'] # 2 in which, minus 1 in witch, minus 1 in watch
>>> c['w'] # 1 in which, minus 1 in witch, minus 1 in watch
-1 '''
if iterable is not None:
self_get = self.get
if isinstance(iterable, Mapping):
for elem, count in iterable.items():
self[elem] = self_get(elem, 0) - count
else:
for elem in iterable:
self[elem] = self_get(elem, 0) - 1
if kwds:
self.subtract(kwds) def copy(self):
""" 拷贝 """
'Return a shallow copy.'
return self.__class__(self) def __reduce__(self):
""" 返回一个元组(类型,元组) """
return self.__class__, (dict(self),) def __delitem__(self, elem):
""" 删除元素 """
'Like dict.__delitem__() but does not raise KeyError for missing values.'
if elem in self:
super(Counter, self).__delitem__(elem) def __repr__(self):
if not self:
return '%s()' % self.__class__.__name__
items = ', '.join(map('%r: %r'.__mod__, self.most_common()))
return '%s({%s})' % (self.__class__.__name__, items) # Multiset-style mathematical operations discussed in:
# Knuth TAOCP Volume II section 4.6.3 exercise 19
# and at http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multiset
#
# Outputs guaranteed to only include positive counts.
#
# To strip negative and zero counts, add-in an empty counter:
# c += Counter() def __add__(self, other):
'''Add counts from two counters. >>> Counter('abbb') + Counter('bcc')
Counter({'b': 4, 'c': 2, 'a': 1}) '''
if not isinstance(other, Counter):
return NotImplemented
result = Counter()
for elem, count in self.items():
newcount = count + other[elem]
if newcount > 0:
result[elem] = newcount
for elem, count in other.items():
if elem not in self and count > 0:
result[elem] = count
return result def __sub__(self, other):
''' Subtract count, but keep only results with positive counts. >>> Counter('abbbc') - Counter('bccd')
Counter({'b': 2, 'a': 1}) '''
if not isinstance(other, Counter):
return NotImplemented
result = Counter()
for elem, count in self.items():
newcount = count - other[elem]
if newcount > 0:
result[elem] = newcount
for elem, count in other.items():
if elem not in self and count < 0:
result[elem] = 0 - count
return result def __or__(self, other):
'''Union is the maximum of value in either of the input counters. >>> Counter('abbb') | Counter('bcc')
Counter({'b': 3, 'c': 2, 'a': 1}) '''
if not isinstance(other, Counter):
return NotImplemented
result = Counter()
for elem, count in self.items():
other_count = other[elem]
newcount = other_count if count < other_count else count
if newcount > 0:
result[elem] = newcount
for elem, count in other.items():
if elem not in self and count > 0:
result[elem] = count
return result def __and__(self, other):
''' Intersection is the minimum of corresponding counts. >>> Counter('abbb') & Counter('bcc')
Counter({'b': 1}) '''
if not isinstance(other, Counter):
return NotImplemented
result = Counter()
for elem, count in self.items():
other_count = other[elem]
newcount = count if count < other_count else other_count
if newcount > 0:
result[elem] = newcount
return result Counter
Counter Code
我们从中挑选一些相对常用的方法来举例:
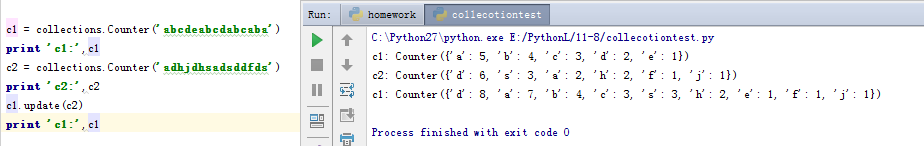
在上面的例子我们可以看出,counter方法返回的是一个字典,它将字符串中出现的所有字符都进行了统计。在这里再介绍一下update方法,这个update方法是将两次统计的结果相加,和字典的update略有不同。
2、有序字典(orderedDict )
orderdDict是对字典类型的补充,他记住了字典元素添加的顺序
class OrderedDict(dict):
'Dictionary that remembers insertion order'
# An inherited dict maps keys to values.
# The inherited dict provides __getitem__, __len__, __contains__, and get.
# The remaining methods are order-aware.
# Big-O running times for all methods are the same as regular dictionaries. # The internal self.__map dict maps keys to links in a doubly linked list.
# The circular doubly linked list starts and ends with a sentinel element.
# The sentinel element never gets deleted (this simplifies the algorithm).
# Each link is stored as a list of length three: [PREV, NEXT, KEY]. def __init__(self, *args, **kwds):
'''Initialize an ordered dictionary. The signature is the same as
regular dictionaries, but keyword arguments are not recommended because
their insertion order is arbitrary. '''
if len(args) > 1:
raise TypeError('expected at most 1 arguments, got %d' % len(args))
try:
self.__root
except AttributeError:
self.__root = root = [] # sentinel node
root[:] = [root, root, None]
self.__map = {}
self.__update(*args, **kwds) def __setitem__(self, key, value, dict_setitem=dict.__setitem__):
'od.__setitem__(i, y) <==> od[i]=y'
# Setting a new item creates a new link at the end of the linked list,
# and the inherited dictionary is updated with the new key/value pair.
if key not in self:
root = self.__root
last = root[0]
last[1] = root[0] = self.__map[key] = [last, root, key]
return dict_setitem(self, key, value) def __delitem__(self, key, dict_delitem=dict.__delitem__):
'od.__delitem__(y) <==> del od[y]'
# Deleting an existing item uses self.__map to find the link which gets
# removed by updating the links in the predecessor and successor nodes.
dict_delitem(self, key)
link_prev, link_next, _ = self.__map.pop(key)
link_prev[1] = link_next # update link_prev[NEXT]
link_next[0] = link_prev # update link_next[PREV] def __iter__(self):
'od.__iter__() <==> iter(od)'
# Traverse the linked list in order.
root = self.__root
curr = root[1] # start at the first node
while curr is not root:
yield curr[2] # yield the curr[KEY]
curr = curr[1] # move to next node def __reversed__(self):
'od.__reversed__() <==> reversed(od)'
# Traverse the linked list in reverse order.
root = self.__root
curr = root[0] # start at the last node
while curr is not root:
yield curr[2] # yield the curr[KEY]
curr = curr[0] # move to previous node def clear(self):
'od.clear() -> None. Remove all items from od.'
root = self.__root
root[:] = [root, root, None]
self.__map.clear()
dict.clear(self) # -- the following methods do not depend on the internal structure -- def keys(self):
'od.keys() -> list of keys in od'
return list(self) def values(self):
'od.values() -> list of values in od'
return [self[key] for key in self] def items(self):
'od.items() -> list of (key, value) pairs in od'
return [(key, self[key]) for key in self] def iterkeys(self):
'od.iterkeys() -> an iterator over the keys in od'
return iter(self) def itervalues(self):
'od.itervalues -> an iterator over the values in od'
for k in self:
yield self[k] def iteritems(self):
'od.iteritems -> an iterator over the (key, value) pairs in od'
for k in self:
yield (k, self[k]) update = MutableMapping.update __update = update # let subclasses override update without breaking __init__ __marker = object() def pop(self, key, default=__marker):
'''od.pop(k[,d]) -> v, remove specified key and return the corresponding
value. If key is not found, d is returned if given, otherwise KeyError
is raised. '''
if key in self:
result = self[key]
del self[key]
return result
if default is self.__marker:
raise KeyError(key)
return default def setdefault(self, key, default=None):
'od.setdefault(k[,d]) -> od.get(k,d), also set od[k]=d if k not in od'
if key in self:
return self[key]
self[key] = default
return default def popitem(self, last=True):
'''od.popitem() -> (k, v), return and remove a (key, value) pair.
Pairs are returned in LIFO order if last is true or FIFO order if false. '''
if not self:
raise KeyError('dictionary is empty')
key = next(reversed(self) if last else iter(self))
value = self.pop(key)
return key, value def __repr__(self, _repr_running={}):
'od.__repr__() <==> repr(od)'
call_key = id(self), _get_ident()
if call_key in _repr_running:
return '...'
_repr_running[call_key] = 1
try:
if not self:
return '%s()' % (self.__class__.__name__,)
return '%s(%r)' % (self.__class__.__name__, self.items())
finally:
del _repr_running[call_key] def __reduce__(self):
'Return state information for pickling'
items = [[k, self[k]] for k in self]
inst_dict = vars(self).copy()
for k in vars(OrderedDict()):
inst_dict.pop(k, None)
if inst_dict:
return (self.__class__, (items,), inst_dict)
return self.__class__, (items,) def copy(self):
'od.copy() -> a shallow copy of od'
return self.__class__(self) @classmethod
def fromkeys(cls, iterable, value=None):
'''OD.fromkeys(S[, v]) -> New ordered dictionary with keys from S.
If not specified, the value defaults to None. '''
self = cls()
for key in iterable:
self[key] = value
return self def __eq__(self, other):
'''od.__eq__(y) <==> od==y. Comparison to another OD is order-sensitive
while comparison to a regular mapping is order-insensitive. '''
if isinstance(other, OrderedDict):
return dict.__eq__(self, other) and all(_imap(_eq, self, other))
return dict.__eq__(self, other) def __ne__(self, other):
'od.__ne__(y) <==> od!=y'
return not self == other # -- the following methods support python 3.x style dictionary views -- def viewkeys(self):
"od.viewkeys() -> a set-like object providing a view on od's keys"
return KeysView(self) def viewvalues(self):
"od.viewvalues() -> an object providing a view on od's values"
return ValuesView(self) def viewitems(self):
"od.viewitems() -> a set-like object providing a view on od's items"
return ItemsView(self)
OrderdDict Code
我们都知道字典本来是无序的,它依靠key,value之间的索引进行匹配,那么有序字典的原理是什么呢? 原理: dic = {'k2':1,'k1':2},li = ['k1','k2'],这个字典在内部维护了一个key列表。
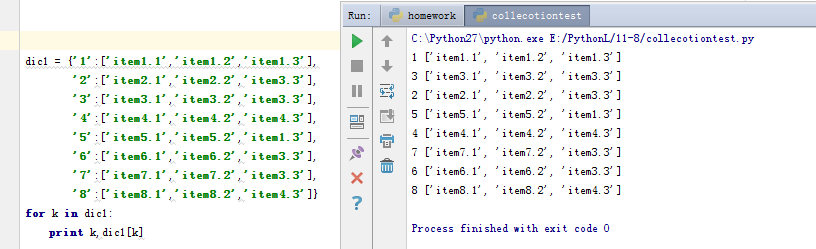
从上面的图中我们就知道,尽管我们定义的字典是从1到8按顺序写的,但是在打印的过程当中并没有按到我们希望的顺序打印。这个时候有序字典的优势就出来了:
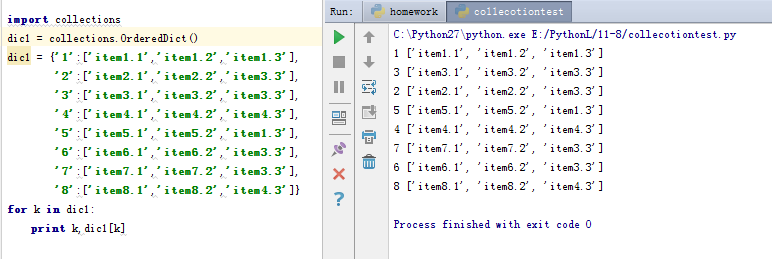
3、默认字典(defaultdict)
defaultdict是对字典的类型的补充,他默认给字典的值设置了一个类型。
class defaultdict(dict):
"""
defaultdict(default_factory[, ...]) --> dict with default factory The default factory is called without arguments to produce
a new value when a key is not present, in __getitem__ only.
A defaultdict compares equal to a dict with the same items.
All remaining arguments are treated the same as if they were
passed to the dict constructor, including keyword arguments.
"""
def copy(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" D.copy() -> a shallow copy of D. """
pass def __copy__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" D.copy() -> a shallow copy of D. """
pass def __getattribute__(self, name): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """
pass def __init__(self, default_factory=None, **kwargs): # known case of _collections.defaultdict.__init__
"""
defaultdict(default_factory[, ...]) --> dict with default factory The default factory is called without arguments to produce
a new value when a key is not present, in __getitem__ only.
A defaultdict compares equal to a dict with the same items.
All remaining arguments are treated the same as if they were
passed to the dict constructor, including keyword arguments. # (copied from class doc)
"""
pass def __missing__(self, key): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
__missing__(key) # Called by __getitem__ for missing key; pseudo-code:
if self.default_factory is None: raise KeyError((key,))
self[key] = value = self.default_factory()
return value
"""
pass def __reduce__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return state information for pickling. """
pass def __repr__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """
pass default_factory = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
"""Factory for default value called by __missing__().""" defaultdict
defaultdict Code
用代码实现了下述功能
有如下值集合 [11,22,33,44,55,66,77,88,99,90...],将所有大于 66 的值保存至字典的第一个key中,将小于 66 的值保存至第二个key的值中。即: {'k1': 大于66 , 'k2': 小于66}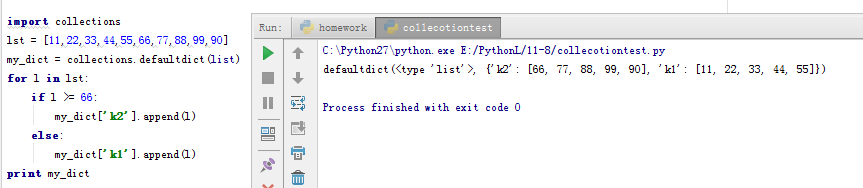
看出神奇的地方了么?我们可以不需要在空字典中指定value的值,直接执行append,就可以向字典中插入值了,就是因为我们使用defauldict(list)方式定义了一个value值默认为list的字典。
否则我们就要这么写才行:
lst = [11,22,33,44,55,66,77,88,99,90]
dic = {}
for l in lst:
if l >= 66:
if 'k2'in dic.keys():
dic['k2'].append(l)
else:
dic['k2'] = [l,]
else:
if 'k1'in dic.keys():
dic['k1'].append(l)
else:
dic['k1'] = [l,]
print dic
普通字典的实现方式
4、可命名元组(namedtuple)
根据nametuple可以创建一个包含tuple所有功能以及其他功能的类型。
class Mytuple(__builtin__.tuple)
| Mytuple(x, y)
|
| Method resolution order:
| Mytuple
| __builtin__.tuple
| __builtin__.object
|
| Methods defined here:
|
| __getnewargs__(self)
| Return self as a plain tuple. Used by copy and pickle.
|
| __getstate__(self)
| Exclude the OrderedDict from pickling
|
| __repr__(self)
| Return a nicely formatted representation string
|
| _asdict(self)
| Return a new OrderedDict which maps field names to their values
|
| _replace(_self, **kwds)
| Return a new Mytuple object replacing specified fields with new values
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Class methods defined here:
|
| _make(cls, iterable, new=<built-in method __new__ of type object>, len=<built-in function len>) from __builtin__.type
| Make a new Mytuple object from a sequence or iterable
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Static methods defined here:
|
| __new__(_cls, x, y)
| Create new instance of Mytuple(x, y)
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Data descriptors defined here:
|
| __dict__
| Return a new OrderedDict which maps field names to their values
|
| x
| Alias for field number 0
|
| y
| Alias for field number 1
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Data and other attributes defined here:
|
| _fields = ('x', 'y')
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Methods inherited from __builtin__.tuple:
|
| __add__(...)
| x.__add__(y) <==> x+y
|
| __contains__(...)
| x.__contains__(y) <==> y in x
|
| __eq__(...)
| x.__eq__(y) <==> x==y
|
| __ge__(...)
| x.__ge__(y) <==> x>=y
|
| __getattribute__(...)
| x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name
|
| __getitem__(...)
| x.__getitem__(y) <==> x[y]
|
| __getslice__(...)
| x.__getslice__(i, j) <==> x[i:j]
|
| Use of negative indices is not supported.
|
| __gt__(...)
| x.__gt__(y) <==> x>y
|
| __hash__(...)
| x.__hash__() <==> hash(x)
|
| __iter__(...)
| x.__iter__() <==> iter(x)
|
| __le__(...)
| x.__le__(y) <==> x<=y
|
| __len__(...)
| x.__len__() <==> len(x)
|
| __lt__(...)
| x.__lt__(y) <==> x<y
|
| __mul__(...)
| x.__mul__(n) <==> x*n
|
| __ne__(...)
| x.__ne__(y) <==> x!=y
|
| __rmul__(...)
| x.__rmul__(n) <==> n*x
|
| __sizeof__(...)
| T.__sizeof__() -- size of T in memory, in bytes
|
| count(...)
| T.count(value) -> integer -- return number of occurrences of value
|
| index(...)
| T.index(value, [start, [stop]]) -> integer -- return first index of value.
| Raises ValueError if the value is not present. Mytuple Mytuple
namedtuple Code
主要用于‘坐标’的表示。用法如下:
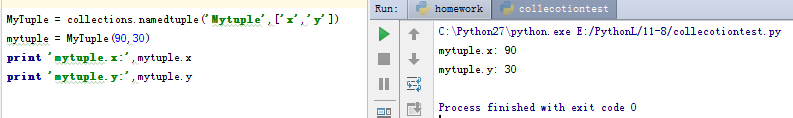
5、双向队列(deque)
一个线程安全的双向队列:双向队列我们可以理解为两个栈底相连的栈,和队列的先进先出不同,元素可以从这个队列的两端分别加入或者删除值。尽管list其实完全可以实现这个功能,但是python的collections类还是很贴心的把这些方法都归纳了出来,歪果仁就是有意思啊~~~
class deque(object):
"""
deque([iterable[, maxlen]]) --> deque object Build an ordered collection with optimized access from its endpoints.
"""
def append(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Add an element to the right side of the deque. """
pass def appendleft(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Add an element to the left side of the deque. """
pass def clear(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Remove all elements from the deque. """
pass def count(self, value): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" D.count(value) -> integer -- return number of occurrences of value """
return 0 def extend(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Extend the right side of the deque with elements from the iterable """
pass def extendleft(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Extend the left side of the deque with elements from the iterable """
pass def pop(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Remove and return the rightmost element. """
pass def popleft(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Remove and return the leftmost element. """
pass def remove(self, value): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" D.remove(value) -- remove first occurrence of value. """
pass def reverse(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" D.reverse() -- reverse *IN PLACE* """
pass def rotate(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Rotate the deque n steps to the right (default n=1). If n is negative, rotates left. """
pass def __copy__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return a shallow copy of a deque. """
pass def __delitem__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__delitem__(y) <==> del x[y] """
pass def __eq__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__eq__(y) <==> x==y """
pass def __getattribute__(self, name): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """
pass def __getitem__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__getitem__(y) <==> x[y] """
pass def __ge__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__ge__(y) <==> x>=y """
pass def __gt__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__gt__(y) <==> x>y """
pass def __iadd__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__iadd__(y) <==> x+=y """
pass def __init__(self, iterable=(), maxlen=None): # known case of _collections.deque.__init__
"""
deque([iterable[, maxlen]]) --> deque object Build an ordered collection with optimized access from its endpoints.
# (copied from class doc)
"""
pass def __iter__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__iter__() <==> iter(x) """
pass def __len__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__len__() <==> len(x) """
pass def __le__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__le__(y) <==> x<=y """
pass def __lt__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__lt__(y) <==> x<y """
pass @staticmethod # known case of __new__
def __new__(S, *more): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """
pass def __ne__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__ne__(y) <==> x!=y """
pass def __reduce__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return state information for pickling. """
pass def __repr__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """
pass def __reversed__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" D.__reversed__() -- return a reverse iterator over the deque """
pass def __setitem__(self, i, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__setitem__(i, y) <==> x[i]=y """
pass def __sizeof__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" D.__sizeof__() -- size of D in memory, in bytes """
pass maxlen = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
"""maximum size of a deque or None if unbounded""" __hash__ = None deque
deque Code
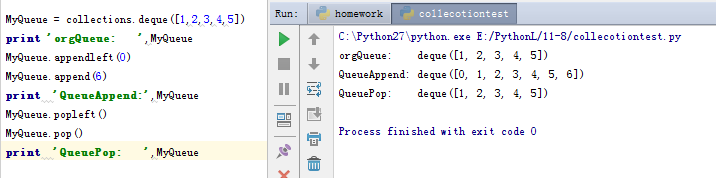
python的基础类源码解析——collection类的更多相关文章
- day3-python的基础类源码解析——collection类
1.计数器(counter) Counter是对字典类型的补充,用于追踪值的出现次数. ps:具备字典的所有功能 + 自己的功能 我们从中挑选一些相对常用的方法来举例: 在上面的例子我们可以看出,co ...
- [Java源码解析] -- String类的compareTo(String otherString)方法的源码解析
String类下的compareTo(String otherString)方法的源码解析 一. 前言 近日研究了一下String类的一些方法, 通过查看源码, 对一些常用的方法也有了更透彻的认识, ...
- lucene原理及源码解析--核心类
马云说:大家还没搞清PC时代的时候,移动互联网来了,还没搞清移动互联网的时候,大数据时代来了. 然而,我看到的是:在PC时代搞PC的,移动互联网时代搞移动互联网的,大数据时代搞大数据的,都是同一伙儿人 ...
- Log4j源码解析--Layout类解析
本文转载上善若水的博客,原文出处:http://www.blogjava.net/DLevin/archive/2012/07/04/382131.html.感谢作者的分享. Layout负责将Log ...
- junit源码解析--核心类
JUnit 的概念及用途 JUnit 是由 Erich Gamma 和 Kent Beck 编写的一个开源的单元测试框架.它属于白盒测试,只要将待测类继承 TestCase 类,就可以利用 JUnit ...
- java源码解析——Stack类
在java中,Stack类继承了Vector类.Vector类和我们经常使用的ArrayList是类似的,底层也是使用了数组来实现,只不过Vector是线程安全的.因此可以知道Stack也是线程安全的 ...
- python Threading模块源码解析
查看源码: 这是一个线程控制的类,这个类可以被子类化(继承)在一定的条件限制下,这里有两种方式去明确活动:第一通过传入一个callable 对象也就是调用对象,一种是通过重写这个Thread类的run ...
- Spring源码解析——核心类介绍
前言: Spring用了这么久,虽然Spring的两大核心:IOC和AOP一直在用,但是始终没有搞懂Spring内部是怎么去实现的,于是决定撸一把Spring源码,前前后后也看了有两边,很多东西看了就 ...
- muduo源码解析11-logger类
logger: class logger { }; 在说这个logger类之前,先看1个关键的内部类 Impl private: //logger内部数据实现类Impl,内部含有以下成员变量 //时间 ...
随机推荐
- python file模块 替换输入内容脚本
root@python-10:/home/liujianzuo/python/test# ls passwd rc.local test1 root@python-10:/home/liujianzu ...
- JQuery执行DOM批量克隆并插入的提效方法
JQuery clone方法可以实现对指定DOM对象的快速复制,并插入文档中. 对于同一类型的对象往往需要按照同一样式模板(HTML标签代码)复制N份并插入文档中,然后再将内容填入模板中,这就需要批量 ...
- Oracle常用操作-----(二)
Oracle主要类型函数: 单行函数:只能输入一行结果,返回一个结果.常见的单行函数有: 字符函数 数字函数 转换函数 日期函数 2.聚合函数:同时可以对多行数据进行操作,并返回一个结果.(AVG.S ...
- C++之路进阶——bzoj3876(支线剧情)
F.A.Qs Home Discuss ProblemSet Status Ranklist Contest ModifyUser hyxzc Logout 捐赠本站 Notice:由于本OJ建立在 ...
- SpringMvc处理JSON
步骤如下: 1.加入jar包 2.编写目标方法,使其返回JSON对应的对象或集合 3.在方法上添加@ResponseBody注解 DispatcheServlet默认装配RequestMappingH ...
- linux下svn服务器安装配置与启动
1. 采用源文件编译安装.源文件共两个,为: subversion-1.6.1.tar.gz (subversion 源文件) subversion-deps-1.6.1.tar.gz (subv ...
- jquery-mobile的页面跳转和iscroll之间的兼容解决方法
有一项目需要用到滚动效果,最后选择了iscroll插件,代码写好后chrome测试一切正常(直接查看用到滚动效果的页面以下统称当前页面),运行APP应用一步步跳转到当前页面的时候,滚动效果和滚动条等死 ...
- 剑指offer——变态跳台阶
题目描述 一只青蛙一次可以跳上1级台阶,也可以跳上2级……它也可以跳上n级.求该青蛙跳上一个n级的台阶总共有多少种跳法. 问题分析 由于每次跳的阶数不确定,没有一个固定的规律,但是可以了解的是后一次跳 ...
- JSP页面嵌套
项目中审批过程需要将业务表单嵌套在审批的页面中.由于业务表单很多,前台已经axjx到了本次选择的表单的地址.本来做的就是把这个链接放在审批页面上,但现在需求的就是直接把这个biz表单嵌套在审批的页面中 ...
- Java基础 静态块、非静态块、构造函数的执行顺序
Java中经常有一些静态块,这是用来在生成类之前进行的初始化,无论java还C++语言中的static,都是最先初始化好的.结构如下: static { 静态语句代码块 } { 非静态语句代码块 } ...
