CNN卷积神经网络
import os # third-party library
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.utils.data as Data
import torchvision
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # torch.manual_seed(1) # reproducible # Hyper Parameters
EPOCH = 1 # train the training data n times, to save time, we just train 1 epoch
BATCH_SIZE = 50
LR = 0.001 # learning rate
DOWNLOAD_MNIST = False # Mnist digits dataset
if not(os.path.exists('./mnist/')) or not os.listdir('./mnist/'):
# not mnist dir or mnist is empyt dir
DOWNLOAD_MNIST = True train_data = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(
root='./mnist/',
train=True, # this is training data
transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(), # Converts a PIL.Image or numpy.ndarray to
# torch.FloatTensor of shape (C x H x W) and normalize in the range [0.0, 1.0]
download=DOWNLOAD_MNIST,
) # plot one example
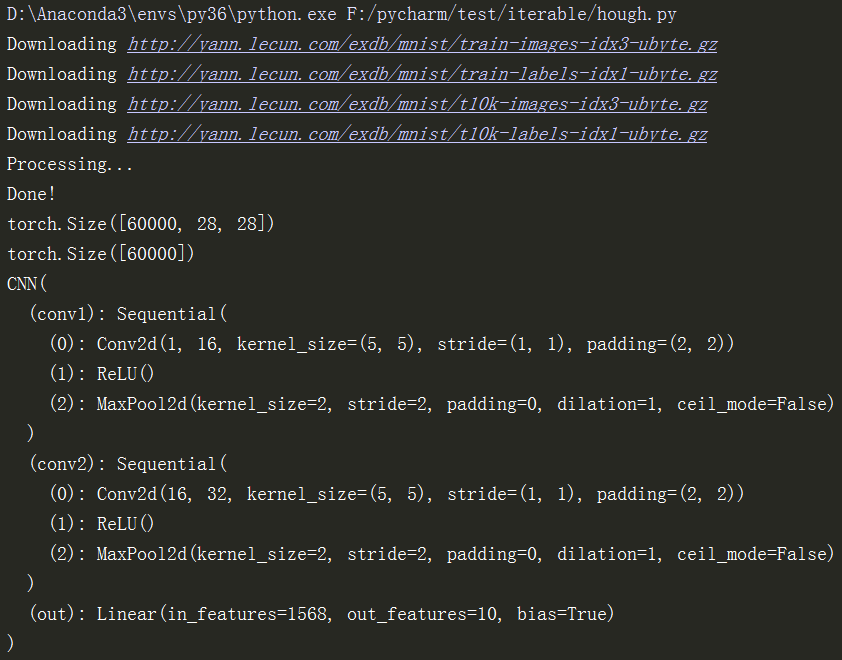
print(train_data.train_data.size()) # (60000, 28, 28)
print(train_data.train_labels.size()) # (60000)
plt.imshow(train_data.train_data[0].numpy(), cmap='gray')
plt.title('%i' % train_data.train_labels[0])
plt.show() # Data Loader for easy mini-batch return in training, the image batch shape will be (50, 1, 28, 28)
train_loader = Data.DataLoader(dataset=train_data, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True) # pick 2000 samples to speed up testing
test_data = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(root='./mnist/', train=False)
test_x = torch.unsqueeze(test_data.test_data, dim=1).type(torch.FloatTensor)[:2000]/255. # shape from (2000, 28, 28) to (2000, 1, 28, 28), value in range(0,1)
test_y = test_data.test_labels[:2000] class CNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(CNN, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential( # input shape (1, 28, 28)
nn.Conv2d(
in_channels=1, # input height
out_channels=16, # n_filters
kernel_size=5, # filter size
stride=1, # filter movement/step
padding=2, # if want same width and length of this image after Conv2d, padding=(kernel_size-1)/2 if stride=1
), # output shape (16, 28, 28)
nn.ReLU(), # activation
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2), # choose max value in 2x2 area, output shape (16, 14, 14)
)
self.conv2 = nn.Sequential( # input shape (16, 14, 14)
nn.Conv2d(16, 32, 5, 1, 2), # output shape (32, 14, 14)
nn.ReLU(), # activation
nn.MaxPool2d(2), # output shape (32, 7, 7)
)
self.out = nn.Linear(32 * 7 * 7, 10) # fully connected layer, output 10 classes def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1) # flatten the output of conv2 to (batch_size, 32 * 7 * 7)
output = self.out(x)
return output, x # return x for visualization cnn = CNN()
print(cnn) # net architecture optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(cnn.parameters(), lr=LR) # optimize all cnn parameters
loss_func = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # the target label is not one-hotted # following function (plot_with_labels) is for visualization, can be ignored if not interested
from matplotlib import cm
try: from sklearn.manifold import TSNE; HAS_SK = True
except: HAS_SK = False; print('Please install sklearn for layer visualization')
def plot_with_labels(lowDWeights, labels):
plt.cla()
X, Y = lowDWeights[:, 0], lowDWeights[:, 1]
for x, y, s in zip(X, Y, labels):
c = cm.rainbow(int(255 * s / 9)); plt.text(x, y, s, backgroundcolor=c, fontsize=9)
plt.xlim(X.min(), X.max()); plt.ylim(Y.min(), Y.max()); plt.title('Visualize last layer'); plt.show(); plt.pause(0.01) plt.ion()
# training and testing
for epoch in range(EPOCH):
for step, (b_x, b_y) in enumerate(train_loader): # gives batch data, normalize x when iterate train_loader output = cnn(b_x)[0] # cnn output
loss = loss_func(output, b_y) # cross entropy loss
optimizer.zero_grad() # clear gradients for this training step
loss.backward() # backpropagation, compute gradients
optimizer.step() # apply gradients if step % 50 == 0:
test_output, last_layer = cnn(test_x)
pred_y = torch.max(test_output, 1)[1].data.numpy()
accuracy = float((pred_y == test_y.data.numpy()).astype(int).sum()) / float(test_y.size(0))
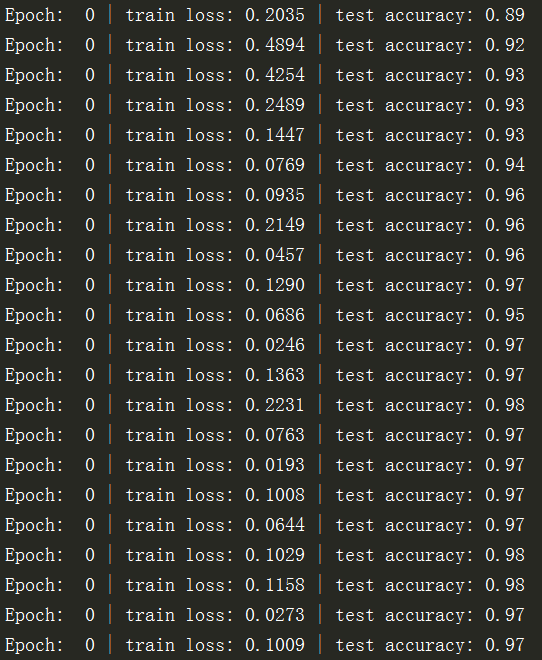
print('Epoch: ', epoch, '| train loss: %.4f' % loss.data.numpy(), '| test accuracy: %.2f' % accuracy)
if HAS_SK:
# Visualization of trained flatten layer (T-SNE)
tsne = TSNE(perplexity=30, n_components=2, init='pca', n_iter=5000)
plot_only = 500
low_dim_embs = tsne.fit_transform(last_layer.data.numpy()[:plot_only, :])
labels = test_y.numpy()[:plot_only]
plot_with_labels(low_dim_embs, labels)
plt.ioff() # print 10 predictions from test data
test_output, _ = cnn(test_x[:10])
pred_y = torch.max(test_output, 1)[1].data.numpy()
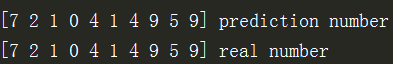
print(pred_y, 'prediction number')
print(test_y[:10].numpy(), 'real number')
运行效果:
CNN卷积神经网络的更多相关文章
- Deep Learning模型之:CNN卷积神经网络(一)深度解析CNN
http://m.blog.csdn.net/blog/wu010555688/24487301 本文整理了网上几位大牛的博客,详细地讲解了CNN的基础结构与核心思想,欢迎交流. [1]Deep le ...
- [转]Theano下用CNN(卷积神经网络)做车牌中文字符OCR
Theano下用CNN(卷积神经网络)做车牌中文字符OCR 原文地址:http://m.blog.csdn.net/article/details?id=50989742 之前时间一直在看 Micha ...
- Deep Learning论文笔记之(四)CNN卷积神经网络推导和实现(转)
Deep Learning论文笔记之(四)CNN卷积神经网络推导和实现 zouxy09@qq.com http://blog.csdn.net/zouxy09 自己平时看了一些论文, ...
- CNN(卷积神经网络)、RNN(循环神经网络)、DNN(深度神经网络)的内部网络结构有什么区别?
https://www.zhihu.com/question/34681168 CNN(卷积神经网络).RNN(循环神经网络).DNN(深度神经网络)的内部网络结构有什么区别?修改 CNN(卷积神经网 ...
- CNN(卷积神经网络)、RNN(循环神经网络)、DNN,LSTM
http://cs231n.github.io/neural-networks-1 https://arxiv.org/pdf/1603.07285.pdf https://adeshpande3.g ...
- day-16 CNN卷积神经网络算法之Max pooling池化操作学习
利用CNN卷积神经网络进行训练时,进行完卷积运算,还需要接着进行Max pooling池化操作,目的是在尽量不丢失图像特征前期下,对图像进行downsampling. 首先看下max pooling的 ...
- cnn(卷积神经网络)比较系统的讲解
本文整理了网上几位大牛的博客,详细地讲解了CNN的基础结构与核心思想,欢迎交流. [1]Deep learning简介 [2]Deep Learning训练过程 [3]Deep Learning模型之 ...
- Keras(四)CNN 卷积神经网络 RNN 循环神经网络 原理及实例
CNN 卷积神经网络 卷积 池化 https://www.cnblogs.com/peng8098/p/nlp_16.html 中有介绍 以数据集MNIST构建一个卷积神经网路 from keras. ...
- TensorFlow——CNN卷积神经网络处理Mnist数据集
CNN卷积神经网络处理Mnist数据集 CNN模型结构: 输入层:Mnist数据集(28*28) 第一层卷积:感受视野5*5,步长为1,卷积核:32个 第一层池化:池化视野2*2,步长为2 第二层卷积 ...
- tensorflow CNN 卷积神经网络中的卷积层和池化层的代码和效果图
tensorflow CNN 卷积神经网络中的卷积层和池化层的代码和效果图 因为很多 demo 都比较复杂,专门抽出这两个函数,写的 demo. 更多教程:http://www.tensorflown ...
随机推荐
- MySQL函数--(1)
/*函数与存储过程的区别1.存储过程:可以有0个返回值,可以有多个返回值函数:有且仅有一个返回值*/ #创建语法create FUNCTION 函数名(参数列表) return 返回类型BEGIN函数 ...
- Django(七)缓存、信号、Form
大纲 一.缓存 1.1.五种缓存配置 1.2配置 2.1.三种应用(全局.视图函数.模板) 2.2 应用多个缓存时生效的优先级 二.信号 1.Django内置信号 2.自定义信号 三.Form 1.初 ...
- 回忆曾经的SSM框架实现文件上传
近期在使用springboot实现文件上传的功能,想到曾经用SSM做过这个功能,在这里记录一下过去实现的方式 maven添加文件上传所需的依赖 springMVC的配置文件配置一下文件上传 我实现的是 ...
- 洛谷P3469[POI2008]BLO-Blockade
题目 割点模板题. 可以将图中的所有点分成两部分,一部分是去掉之后不影响图的连通性的点,一部分是去掉之后影响连通性的点,称其为割点. 然后分两种情况讨论,如果该点不是割点,则最终结果直接加上2*(n- ...
- <TCP/IP原理> (一)
1.协议和标准 2.标准化组织 3.Internet标准:RFC 4.Internet的管理机构 一.协议和标准 1.协议(Protocol) 一组控制数据通信的规则 三要素:语法(syntax).语 ...
- Linux中查看TCP连接数
一.查看哪些IP连接本机 netstat -an 二.查看TCP连接数 1)统计80端口连接数netstat -nat|grep -i "80"|wc -l 2)统计httpd协议 ...
- Hackers' Crackdown UVA - 11825 (状压dp)
给出n个电脑,每个电脑连着n个服务,然后每个电脑都连着m个邻电脑,如果当前的电脑某个服务被断开了,相邻的电脑的服务也会被断开,每个电脑都只能操作一次,问你最多可以让多少种服务被断开.一种服务被断开的条 ...
- Flask框架(1)--基础
Flask是一个基于Python开发并且依赖jinja2模板和Werkzeug WSGI服务的一个微型框架,对于Werkzeug本质是Socket服务端,其用于接收http请求并对请求进行预处理,然后 ...
- React 16 加载性能优化指南
关于 React 应用加载的优化,其实网上类似的文章已经有太多太多了,随便一搜就是一堆,已经成为了一个老生常谈的问题. 但随着 React 16 和 Webpack 4.0 的发布,很多过去的优化手段 ...
- 《Exception团队》第一次作业:团队亮相
一.项目基本介绍 项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 任课教师博客主页链接 这个作业的要求在哪里 作业链接地址 团队名称 Exception 作业学习目标 深入了解软件思想,强化编程技术 二.正文 1. ...
