Pandas 索引和切片
Series和Datafram索引的原理一样,我们以Dataframe的索引为主来学习
- 列索引:df['列名'] (Series不存在列索引)
- 行索引:df.loc[]、df.iloc[]
选择列 / 选择行 / 切片 / 布尔判断
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
# 导入numpy、pandas模块 # 选择行与列 df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(12).reshape(3,4)*100,
index = ['one','two','three'],
columns = ['a','b','c','d'])
print(df) data1 = df['a'] # 列的索引
data2 = df[['a','c']] # 注意:选择多列的时候要用两个中括号 ['列1','列2','列3',····’列n'····]
print(data1,type(data1))
print(data2,type(data2))
print('-----')
# 按照列名选择列,只选择一列输出Series,选择多列输出Dataframe data3 = df.loc['one'] #行的索引
data4 = df.loc[['one','two']]
print(data2,type(data3))
print(data3,type(data4))
# 按照index选择行,只选择一行输出Series,选择多行输出Dataframe
输出结果:
a b c d
one 5.191896 33.756807 55.531059 48.271119
two 73.611065 25.943409 63.896590 10.736052
three 82.450101 45.914238 37.840761 64.896341
one 5.191896
two 73.611065
three 82.450101
Name: a, dtype: float64 <class 'pandas.core.series.Series'>
a c
one 5.191896 55.531059
two 73.611065 63.896590
three 82.450101 37.840761 <class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
-----
a c
one 5.191896 55.531059
two 73.611065 63.896590
three 82.450101 37.840761 <class 'pandas.core.series.Series'>
a 5.191896
b 33.756807
c 55.531059
d 48.271119
Name: one, dtype: float64 <class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
2. 选择/索引 列
# df[] - 选择列
# 一般用于选择列,也可以选择行,但不推荐,行索引用.loc与.iloc df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(12).reshape(3,4)*100,
index = ['one','two','three'],
columns = ['a','b','c','d'])
print(df)
print('-----') data1 = df['a']
data2 = df[['b','c']] # 尝试输入 data2 = df[['b','c','e']]
print(data1)
print(data2)
# df[]默认选择列,[]中写列名(所以一般数据colunms都会单独制定,不会用默认数字列名,以免和index冲突)
# 单选列为Series,print结果为Series格式
# 多选列为Dataframe,print结果为Dataframe格式 # 核心笔记:df[col]一般用于选择列,[]中写列名
输出结果:
a b c d
one 32.302368 89.444542 70.904647 3.899547
two 71.309217 63.006986 73.751675 34.063717
three 13.534943 84.102451 48.329891 33.537992
-----
one 32.302368
two 71.309217
three 13.534943
Name: a, dtype: float64
b c
one 89.444542 70.904647
two 63.006986 73.751675
three 84.102451 48.329891
3. 选择/索引 行
# df.loc[] - 按index选择行 df1 = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(16).reshape(4,4)*100,
index = ['one','two','three','four'],
columns = ['a','b','c','d'])
df2 = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(16).reshape(4,4)*100,
columns = ['a','b','c','d'])
print(df1)
print(df2)
print('-----') data1 = df1.loc['one']
data2 = df2.loc[1]
print(data1)
print(data2)
print('单标签索引\n-----')
# 单个标签索引,返回Series data3 = df1.loc[['two','three','five']] #多了个标签,明明没有'five',会出现警告。
data4 = df2.loc[[3,2,1]]
print(data3)
print(data4)
print('多标签索引\n-----')
# 多个标签索引,如果标签不存在,则返回NaN
# 顺序可变
# 这里‘five’标签不存在,所以有警告 data5 = df1.loc['one':'three'] #从初始到结束,末端也包含
data6 = df2.loc[1:3]
print(data5)
print(data6)
print('切片索引')
# 可以做切片对象
# 末端包含 # 核心笔记:df.loc[label]主要针对index选择行,同时支持指定index
输出结果:
a b c d
one 41.473536 36.036192 61.836041 13.373447
two 83.709165 96.248540 31.266231 84.736594
three 48.617461 82.627569 68.185809 71.803329
four 38.772901 89.275885 84.279757 78.687116
a b c d
0 1.387796 39.795388 12.439624 20.428982
1 88.289011 47.849035 50.188306 77.745736
2 20.914579 13.127105 28.333499 73.411151
3 27.545903 89.901712 14.438023 81.676334
-----
a 41.473536
b 36.036192
c 61.836041
d 13.373447
Name: one, dtype: float64
a 88.289011
b 47.849035
c 50.188306
d 77.745736
Name: 1, dtype: float64
单标签索引
-----
a b c d
two 83.709165 96.248540 31.266231 84.736594
three 48.617461 82.627569 68.185809 71.803329
five NaN NaN NaN NaN
a b c d
3 27.545903 89.901712 14.438023 81.676334
2 20.914579 13.127105 28.333499 73.411151
1 88.289011 47.849035 50.188306 77.745736
多标签索引
-----
a b c d
one 41.473536 36.036192 61.836041 13.373447
two 83.709165 96.248540 31.266231 84.736594
three 48.617461 82.627569 68.185809 71.803329
a b c d
1 88.289011 47.849035 50.188306 77.745736
2 20.914579 13.127105 28.333499 73.411151
3 27.545903 89.901712 14.438023 81.676334
切片索引
C:\Users\iHJX_Alienware\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\ipykernel\__main__.py:19: FutureWarning:
Passing list-likes to .loc or [] with any missing label will raise
KeyError in the future, you can use .reindex() as an alternative. See the documentation here:
https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#deprecate-loc-reindex-listlike
4. 行的另一种索引方式:
# df.iloc[] - 按照整数位置(从轴的0到length-1)选择行 ,按位置进行索引
# 类似list的索引,其顺序就是dataframe的整数位置,从0开始计 df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(16).reshape(4,4)*100,
index = ['one','two','three','four'],
columns = ['a','b','c','d'])
print(df)
print('------') print(df.iloc[0]) #直接写位置,0就是第一行
print(df.iloc[-1])
#print(df.iloc[4])
print('单位置索引\n-----')
# 单位置索引
# 和loc索引不同,不能索引超出数据行数的整数位置 print(df.iloc[[0,2]])
print(df.iloc[[3,2,1]])
print('多位置索引\n-----')
# 多位置索引
# 顺序可变 print(df.iloc[1:3])
print(df.iloc[:2]) #类似于列表里面的索引,不包括第三列 这一点区别于loc
print(df.iloc[::2])
print('切片索引')
# 切片索引
# 末端不包含
输出结果:
a b c d
one 40.344453 97.884228 24.426729 12.624394
two 76.042829 86.362548 2.393513 92.894224
three 57.122758 45.150241 95.613046 63.914110
four 89.905096 63.079797 85.669807 0.008500
------
a 40.344453
b 97.884228
c 24.426729
d 12.624394
Name: one, dtype: float64
a 89.905096
b 63.079797
c 85.669807
d 0.008500
Name: four, dtype: float64
单位置索引
-----
a b c d
one 40.344453 97.884228 24.426729 12.624394
three 57.122758 45.150241 95.613046 63.914110
a b c d
four 89.905096 63.079797 85.669807 0.008500
three 57.122758 45.150241 95.613046 63.914110
two 76.042829 86.362548 2.393513 92.894224
多位置索引
-----
a b c d
two 76.042829 86.362548 2.393513 92.894224
three 57.122758 45.150241 95.613046 63.914110
a b c d
one 40.344453 97.884228 24.426729 12.624394
two 76.042829 86.362548 2.393513 92.894224
a b c d
one 40.344453 97.884228 24.426729 12.624394
three 57.122758 45.150241 95.613046 63.914110
切片索引
5. 布尔型索引
# 布尔型索引 与numpy里面的布尔型索引一个意思
# 多用于索引行
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(16).reshape(4,4)*100,
index = ['one','two','three','four'],
columns = ['a','b','c','d'])
print(df)
print('------') b1 = df < 20
print(b1,type(b1))
print(df[b1]) # 也可以书写为 df[df < 20] 只保留符合条件的值,不符合条件的返回空值
print('------')
# 不做索引则会对数据每个值进行判断
# 索引结果保留 所有数据:True返回原数据,False返回值为NaN b2 = df['a'] > 50 #只保留列a的索引里面大于50的值,按行索引。
print(b2,type(b2))
print(df[b2]) # 也可以书写为 df[df['a'] > 50]
#如果想筛选,a这一列大于50,并且我只需要b和c两列的值
print(df[df['a']>50][['b','c']],'哈哈哈哈')
print('------')
# 单列做判断
# 索引结果保留 单列判断为True的行数据,包括其他列 #这里区别于数组,看看数组的吧
ar = np.random.randn(20,2)*50
print(ar[ar>5],'数组数组数组!!!') #数组只会保留元素中大于5的值,而不大于5的值删除。也不会返回空值 b3 = df[['a','b']] > 50
print(b3,type(b3))
print(df[b3]) # 也可以书写为 df[df[['a','b']] > 50]
print('------')
# 多列做判断
# 索引结果保留 所有数据:True返回原数据,False返回值为NaN
# 注意这里报错的话,更新一下pandas → conda update pandas b4 = df.loc[['one','three']] < 50
print(b4,type(b4))
print(df[b4]) # 也可以书写为 df[df.loc[['one','three']] < 50]
print('------')
# 多行做判断
# 索引结果保留 所有数据:True返回原数据,False返回值为NaN
输出结果:
a b c d
one 42.182880 16.944943 97.143421 16.715137
two 3.894318 1.655007 62.291734 73.600681
three 96.052714 3.845297 43.290603 36.172796
four 8.988430 38.483679 51.538006 60.855976
------
a b c d
one False True False True
two True True False False
three False True False False
four True False False False <class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
a b c d
one NaN 16.944943 NaN 16.715137
two 3.894318 1.655007 NaN NaN
three NaN 3.845297 NaN NaN
four 8.988430 NaN NaN NaN
------
one False
two False
three True
four False
Name: a, dtype: bool <class 'pandas.core.series.Series'>
a b c d
three 96.052714 3.845297 43.290603 36.172796
b c
three 3.845297 43.290603 哈哈哈哈
------
[126.5305168 76.76672929 67.54122606 46.95383418 108.70865373
77.67833227 17.48275006 19.85031457 25.70929928 28.68636573
44.54084001 35.11082135 64.24927152 37.96842756 16.79771495
16.35297097 29.9591603 36.49625972 7.3347084 24.82526937
36.31873796 21.64895926 36.75066597] 数组数组数组!!!
a b
one False False
two False False
three True False
four False False <class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
a b c d
one NaN NaN NaN NaN
two NaN NaN NaN NaN
three 96.052714 NaN NaN NaN
four NaN NaN NaN NaN
------
a b c d
one True True False True
three False True True True <class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
a b c d
one 42.18288 16.944943 NaN 16.715137
two NaN NaN NaN NaN
three NaN 3.845297 43.290603 36.172796
four NaN NaN NaN NaN
------
5. 多重索引
# 多重索引:比如同时索引行和列
# 先选择列再选择行 —— 相当于对于一个数据,先筛选字段,再选择数据量 df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(16).reshape(4,4)*100,
index = ['one','two','three','four'],
columns = ['a','b','c','d'])
print(df)
print('------') print(df['a'].loc[['one','three']]) # 选择a列的one,three行
print(df[['b','c','d']].iloc[::2]) # 选择b,c,d列的one,three行
print(df[df['a'] < 50].iloc[:2]) # 选择满足判断索引的前两行数据
输出结果:
a b c d
one 48.981007 79.206804 43.775695 5.205462
two 43.786019 15.436499 85.919123 84.083483
three 94.546433 59.227961 97.579354 37.942078
four 11.292684 8.417224 38.782994 17.420902
------
one 48.981007
three 94.546433
Name: a, dtype: float64
b c d
one 79.206804 43.775695 5.205462
three 59.227961 97.579354 37.942078
a b c d
one 48.981007 79.206804 43.775695 5.205462
two 43.786019 15.436499 85.919123 84.083483
课后练习:
作业1:如图创建Dataframe(4*4,值为0-100的随机数),通过索引得到以下值
① 索引得到b,c列的所有值
② 索引得到第三第四行的数据
③ 按顺序索引得到two,one行的值
④ 索引得到大于50的值
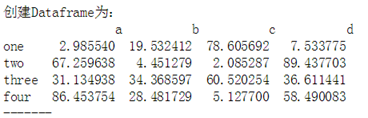
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
#练习1
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(16).reshape(4,4)*100,
index=['one','two','three','four'],
columns=['a','b','c','d'])
print(df) print(df[['b','c']])
print(df.loc[['three','four']])
print(df.iloc[2:4]) #或者print(df.iloc[[2,3]]) // print(df.iloc[[2:]]) print(df.loc[['two','one']]) b = df[df>50]
print(b)
作业2:创建一个Series,包含10个元素,且每个值为0-100的均匀分布随机值,index为a-j,请分别筛选出:
① 标签为b,c的值为多少
② Series中第4到6个值是哪些?
③ Series中大于50的值有哪些?
#练习2
df1 = pd.Series(np.random.rand(10)*100,index=['a','b','c','d','e','f','g','h','i','j'])
print(df1)
print(df1.loc[['b','c']])
print(df1.iloc[4:7]) print(df1[df1>50])
Pandas 索引和切片的更多相关文章
- pandas中层次化索引与切片
Pandas层次化索引 1. 创建多层索引 隐式索引: 常见的方式是给dataframe构造函数的index参数传递两个或是多个数组 Series也可以创建多层索引 Series多层索引 B =Ser ...
- 金融量化分析【day110】:Pandas-DataFrame索引和切片
一.实验文档准备 1.安装 tushare pip install tushare 2.启动ipython C:\Users\Administrator>ipython Python 3.7.0 ...
- Pandas索引和选择数据
在本章中,我们将讨论如何切割和丢弃日期,并获取Pandas中大对象的子集. Python和NumPy索引运算符"[]"和属性运算符".". 可以在广泛的用例中快 ...
- pandas索引操作
Pandas的索引操作 索引对象Index 1. Series和DataFrame中的索引都是Index对象 示例代码: print(type(ser_obj.index)) print(type(d ...
- Numpy 索引及切片
1.一维数组的索引及切片 ar = np.arange(20) print(ar) print(ar[4]) print(ar[3:6]) print(ar[:4:2]) #索引到4 按2的步长 pr ...
- numpy之索引和切片
索引和切片 一维数组 一维数组很简单,基本和列表一致. 它们的区别在于数组切片是原始数组视图(这就意味着,如果做任何修改,原始都会跟着更改). 这也意味着,如果不想更改原始数组,我们需要进行显式的复制 ...
- Numpy系列(四)- 索引和切片
Python 中原生的数组就支持使用方括号([])进行索引和切片操作,Numpy 自然不会放过这个强大的特性. 单个元素索引 1-D数组的单元素索引是人们期望的.它的工作原理与其他标准Python序 ...
- Numpy学习二:数组的索引与切片
1.一维数组索引与切片#创建一维数组arr1d = np.arange(10)print(arr1d) 结果:[0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9] #数组的索引从0开始,通过索引获取第三个元素a ...
- 数据类型&字符串得索引及切片
一:数据类型 1):int 1,2,3用于计算 2):bool ture false 用于判断,也可做为if的条件 3):str 用引号引起来的都是str 存储少量数据,进行 ...
随机推荐
- Django实战-用户注册和登陆系统
1.环境搭建和创建项目 1.环境搭建 每当我们开始一个新项目的时候,通常都会搭建一个全新.独立.隔离的项目环境,这样做的好处自然不必多说.有很多种建立项目虚拟环境的工具,使用比较普遍的是Python中 ...
- 五分钟急速搭建wordpress(博主亲测有效)
第一步:下载WordPress安装包并解压 从此处下载WordPress压缩包并解压缩 http://wordpress.org/download/ 如果你想将WordPress上传至一个远程服务器, ...
- DOMNodeInserted,DOMNodeRemoved 和监听内容变化插件
元素的增加 删除 及事件监听 <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset= ...
- MyEclipse快捷键大全,很实用
Eclipse本身很快的,但是加上了myeclipse后,就狂占内存,而且速度狂慢,那如何让Eclipse拖着myeclipse狂飚呢?这里提供一个: 技巧:取消自动validation valid ...
- 【Android 界面效果47】RecyclerView详解
RecylerView作为 support-library发布出来,这对开发者来说绝对是个好消息.因为可以在更低的Android版本上使用这个新视图.下面我们看如何获取 RecylerView.首先打 ...
- Java—字符串
字符串 在java中,字符串被作为String类型的对象处理.String类位于java.lang包中,默认情况下,该包被自动导入所有的程序. 创建String对象的方法: String s1 = & ...
- ASP.NET 页面之间传递参数方法
1.通过URL链接地址传递 (1) send.aspx代码 protected void Button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { Request.Red ...
- 关于使用Encoding转码的问题,以及StreamWriter的小应用
StreamWriter write = new StreamWriter("../../test2.txt"); write.WriteLine("中国123巴西red ...
- Uva 11997 多路归并
题目链接:https://uva.onlinejudge.org/external/119/11997.pdf 题意: k*k的矩阵,从每一行中选一个元素加起来,可以得到 kk个和,求前 k 个最小值 ...
- 广搜,智能拼图(ZOJ1079)
题目链接:http://acm.zju.edu.cn/onlinejudge/showProblem.do?problemId=79 解题报告: 思路简单,写法太难. #include <std ...
