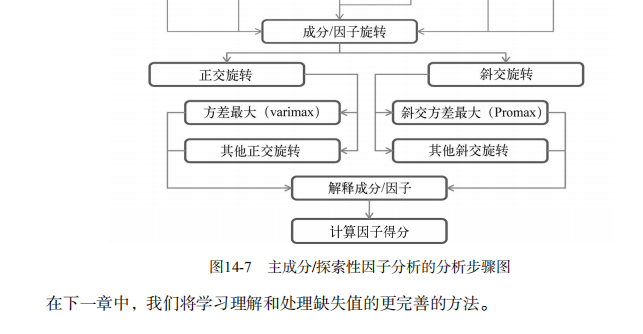
吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:主成分分析和因子分析(续一)














#--------------------------------------------#
# R in Action (2nd ed): Chapter 14 #
# Principal components and factor analysis #
# requires package psych #
# install.packages("psych") #
#--------------------------------------------# par(ask=TRUE)
set.seed(1234) # make results reproducible # Listing 14.1 - Principal components analysis of US Judge Ratings
library(psych)
pc <- principal(USJudgeRatings[,-1], nfactors=1)
pc # Principal components analysis Harman23.cor data
library(psych)
fa.parallel(Harman23.cor$cov, n.obs=302, fa="pc", n.iter=100,
show.legend=FALSE, main="Scree plot with parallel analysis") # Listing 14.2 - Principal components analysis of body measurements
library(psych)
PC <- principal(Harman23.cor$cov, nfactors=2, rotate="none")
PC # Listing 14.3 - Principal components analysis with varimax rotation
rc <- principal(Harman23.cor$cov, nfactors=2, rotate="varimax")
rc # Listing 14.4 - Obtaining componenet scores from raw data
library(psych)
pc <- principal(USJudgeRatings[,-1], nfactors=1, score=TRUE)
head(pc$scores)
cor(USJudgeRatings$CONT, pc$score) # Listing 14.5 - Obtaining principal component scoring coefficients
library(psych)
rc <- principal(Harman23.cor$cov, nfactors=2, rotate="varimax")
round(unclass(rc$weights), 2) ## Exploratory factor analysis of ability.cov data options(digits=2)
library(psych)
covariances <- ability.cov$cov
# convert covariances to correlations
correlations <- cov2cor(covariances)
correlations # determine number of factors to extract
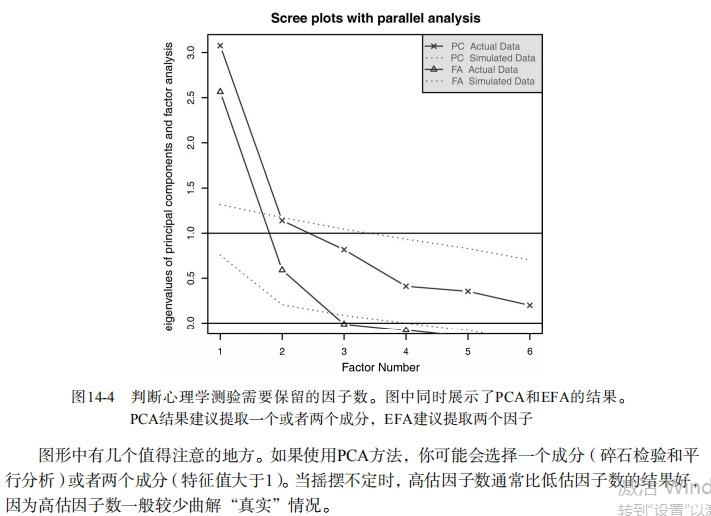
fa.parallel(correlations, n.obs=112, fa="both", n.iter=100,
main="Scree plots with parallel analysis") # Listing 14.6 - Principal axis factoring without rotation
fa <- fa(correlations, nfactors=2, rotate="none", fm="pa")
fa # Listing 14.7 - Factor extraction with orthogonal rotation
fa.varimax <- fa(correlations, nfactors=2, rotate="varimax", fm="pa")
fa.varimax # Listing 14.8 - Factor extraction with oblique rotation
fa.promax <- fa(correlations, nfactors=2, rotate="promax", fm="pa")
fa.promax # calculate factor loading matrix
fsm <- function(oblique) {
if (class(oblique)[2]=="fa" & is.null(oblique$Phi)) {
warning("Object doesn't look like oblique EFA")
} else {
P <- unclass(oblique$loading)
F <- P %*% oblique$Phi
colnames(F) <- c("PA1", "PA2")
return(F)
}
}
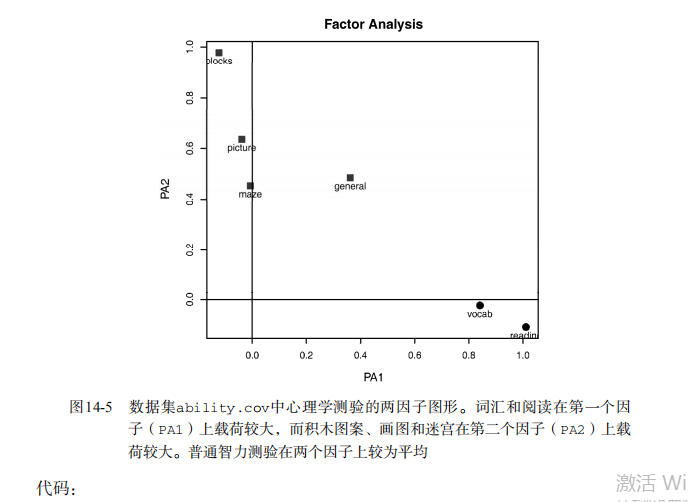
fsm(fa.promax) # plot factor solution
factor.plot(fa.promax, labels=rownames(fa.promax$loadings))
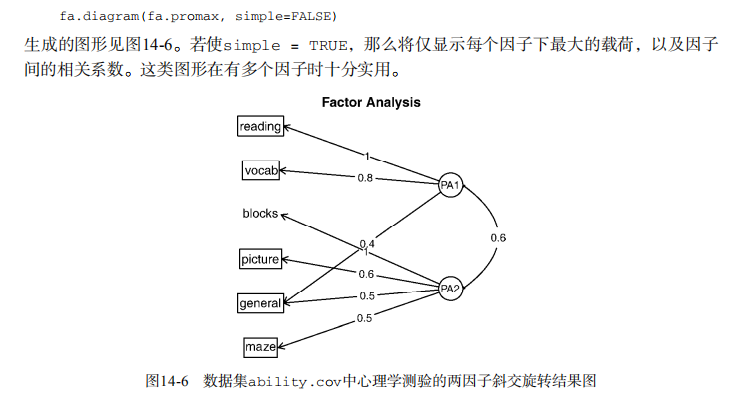
fa.diagram(fa.promax, simple=FALSE) # factor scores
fa.promax$weights
吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:主成分分析和因子分析(续一)的更多相关文章
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:聚类分析(续一)
#-------------------------------------------------------# # R in Action (2nd ed): Chapter 16 # # Clu ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:时间序列(续三)
#-----------------------------------------# # R in Action (2nd ed): Chapter 15 # # Time series # # r ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:时间序列(续二)
#-----------------------------------------# # R in Action (2nd ed): Chapter 15 # # Time series # # r ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:时间序列(续一)
#-----------------------------------------# # R in Action (2nd ed): Chapter 15 # # Time series # # r ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:方差分析(续二)
#-------------------------------------------------------------------# # R in Action (2nd ed): Chapte ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:方差分析(续一)
#-------------------------------------------------------------------# # R in Action (2nd ed): Chapte ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:回归(续四)
#------------------------------------------------------------# # R in Action (2nd ed): Chapter 8 # # ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:回归(续三)
#------------------------------------------------------------# # R in Action (2nd ed): Chapter 8 # # ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:回归(续二)
#------------------------------------------------------------# # R in Action (2nd ed): Chapter 8 # # ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:回归(续一)
#------------------------------------------------------------# # R in Action (2nd ed): Chapter 8 # # ...
随机推荐
- 201509-2 日期计算 Java
思路: 每月有多少天是固定的,放到数组中,2月单独判断一下. import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main ...
- Powershell 中的管道
管道 上个命令中的输出,通过管道作为下个命令的输入.Linux中的管道传递的是text,但ps中传递的是object.但是命令究竟返回的是什么类型呢?以下命令回答了这个问题: get-service ...
- windows下CreateDirectory创建路径失败的解决办法
第一: 权限不够: SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES sa;SECURITY_DESCRIPTOR sd; InitializeSecurityDescriptor(&sd,SECURI ...
- Graph & Tree2
续https://www.cnblogs.com/tyqtyq/p/9769817.html 0x65 负环 SPFA 当一个节点入队次数到达N的时候,就说明有负环 或者记录最短路包含的路径条数 还有 ...
- yum的repo文件详解、以及epel简介、yum源的更换、常用yum命令
https://www.cnblogs.com/nineep/p/6795692.html yum的repo文件详解.以及epel简介.yum源的更换 常用命令如下: yum list ...
- 二十七、rsync同步工具
1.什么是rsync? Rsync是一款开源的.快速的,多功能的,可实现全量及增量的本地或者远程数据同步备份的优秀工具.windows和linux都可以. 官网:http:www.samba.org/ ...
- jenkins_2
1.jenkins pipline:一些列jenkins插件将整个CD(持续交付过程)用解释性代码Jenkinsfile来描述(之前的都是通过配置设置的,这次是通过file) 2.创建一个流水线任务 ...
- JAVA并发思维导图
原博客:https://blog.csdn.net/oqkdws/article/details/82145389
- 如何将jar包打包到本地maven仓库
--例如下载jar到本地(例如经常用到的oracle数据库驱动) --前提本地已将安装maven并配置好环境,cmd并切换到jar包的文件夹下,执行以下命令,注意DgroupId.DartifactI ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然python学习笔记:python 用 Open CV 进行人脸识别
要对特定图像进行识别,最关键的是要有识别对象的特征文件, OpenCV 己内置 了人脸识别特征文件,我们只需使用 OpenCV 的 CascadeClassifier 类即可进行识别 . 创建 Cas ...
