Codeforces Round #464 (Div. 2)
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
As you could know there are no male planes nor female planes. However, each plane on Earth likes some other plane. There are nplanes on Earth, numbered from 1 to n, and the plane with number i likes the plane with number fi, where 1 ≤ fi ≤ n and fi ≠ i.
We call a love triangle a situation in which plane A likes plane B, plane B likes plane C and plane C likes plane A. Find out if there is any love triangle on Earth.
The first line contains a single integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 5000) — the number of planes.
The second line contains n integers f1, f2, ..., fn (1 ≤ fi ≤ n, fi ≠ i), meaning that the i-th plane likes the fi-th.
Output «YES» if there is a love triangle consisting of planes on Earth. Otherwise, output «NO».
You can output any letter in lower case or in upper case.
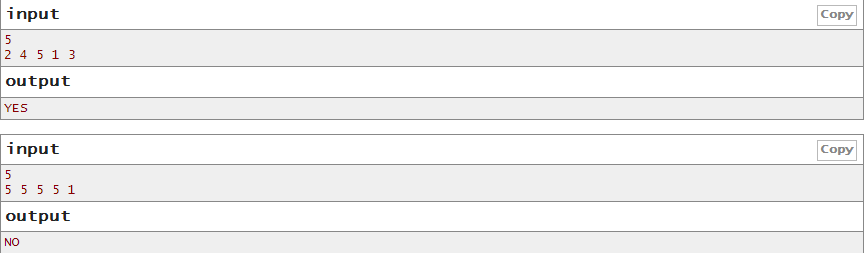
In first example plane 2 likes plane 4, plane 4 likes plane 1, plane 1 likes plane 2 and that is a love triangle.
In second example there are no love triangles.
思路:跑一边tarjin,判断其中是否有点数为3个的强连通分量。
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#define MAXN 5010
using namespace std;
int n,tot,tim,top,ans,sumcol;
int low[MAXN],dfn[MAXN],col[MAXN];
int to[MAXN],net[MAXN],head[MAXN];
int stack[MAXN],vis[MAXN],visstack[MAXN];
void add(int u,int v){
to[++tot]=v;net[tot]=head[u];head[u]=tot;
}
void tarjin(int now){
low[now]=dfn[now]=++tim;
stack[++top]=now;
vis[now]=;visstack[now]=;
for(int i=head[now];i;i=net[i])
if(!vis[to[i]]){
tarjin(to[i]);
low[now]=min(low[now],low[to[i]]);
}
else if(visstack[to[i]])
low[now]=min(low[now],dfn[to[i]]);
if(low[now]==dfn[now]){
sumcol++;
col[now]=sumcol;
while(stack[top]!=now){
col[stack[top]]=sumcol;
visstack[stack[top]]=;
top--;
}
top--;
visstack[now]=;
}
}
int main(){
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){
int x;
scanf("%d",&x);
add(i,x);
}
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
if(!vis[i]) tarjin(i);
memset(vis,,sizeof(vis));
for(int i=;i<=n;i++) vis[col[i]]++;
for(int i=;i<=sumcol;i++)
if(vis[i]==) ans++;
if(ans) cout<<"YES";
else cout<<"NO";
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Dima has a hamsters farm. Soon N hamsters will grow up on it and Dima will sell them in a city nearby.
Hamsters should be transported in boxes. If some box is not completely full, the hamsters in it are bored, that's why each box should be completely full with hamsters.
Dima can buy boxes at a factory. The factory produces boxes of K kinds, boxes of the i-th kind can contain in themselves ai hamsters. Dima can buy any amount of boxes, but he should buy boxes of only one kind to get a wholesale discount.
Of course, Dima would buy boxes in such a way that each box can be completely filled with hamsters and transported to the city. If there is no place for some hamsters, Dima will leave them on the farm.
Find out how many boxes and of which type should Dima buy to transport maximum number of hamsters.
The first line contains two integers N and K (0 ≤ N ≤ 1018, 1 ≤ K ≤ 105) — the number of hamsters that will grow up on Dima's farm and the number of types of boxes that the factory produces.
The second line contains K integers a1, a2, ..., aK (1 ≤ ai ≤ 1018 for all i) — the capacities of boxes.
Output two integers: the type of boxes that Dima should buy and the number of boxes of that type Dima should buy. Types of boxes are numbered from 1 to K in the order they are given in input.
If there are many correct answers, output any of them.
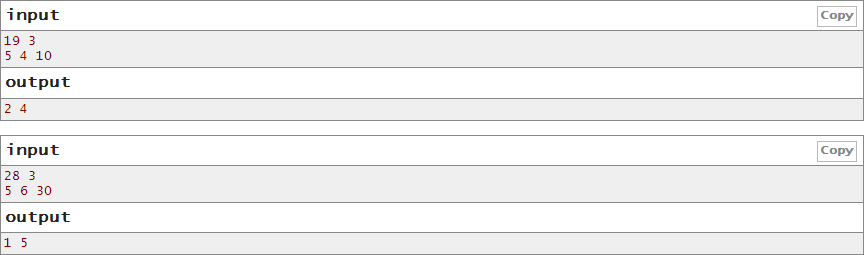
思路:o(k)扫一遍就好了。
错误:minn值取小了,3个变量名重复竟然没看见。
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
long long k,ans,bns,n,minn=;
int main(){
cin>>n>>k;
for(int i=;i<=k;i++){
long long x;cin>>x;
long long kkk=n%x;
if(kkk<minn){ minn=kkk;ans=i;bns=x; }
}
long long kk=n/bns;
cout<<ans<<" "<<kk;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
In distant future on Earth day lasts for n hours and that's why there are n timezones. Local times in adjacent timezones differ by one hour. For describing local time, hours numbers from 1 to n are used, i.e. there is no time "0 hours", instead of it "n hours" is used. When local time in the 1-st timezone is 1 hour, local time in the i-th timezone is i hours.
Some online programming contests platform wants to conduct a contest that lasts for an hour in such a way that its beginning coincides with beginning of some hour (in all time zones). The platform knows, that there are ai people from i-th timezone who want to participate in the contest. Each person will participate if and only if the contest starts no earlier than s hours 00 minutes local time and ends not later than f hours 00 minutes local time. Values s and f are equal for all time zones. If the contest starts at f hours 00 minutes local time, the person won't participate in it.
Help platform select such an hour, that the number of people who will participate in the contest is maximum.
The first line contains a single integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 100 000) — the number of hours in day.
The second line contains n space-separated integers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 10 000), where ai is the number of people in the i-th timezone who want to participate in the contest.
The third line contains two space-separated integers s and f (1 ≤ s < f ≤ n).
Output a single integer — the time of the beginning of the contest (in the first timezone local time), such that the number of participants will be maximum possible. If there are many answers, output the smallest among them.
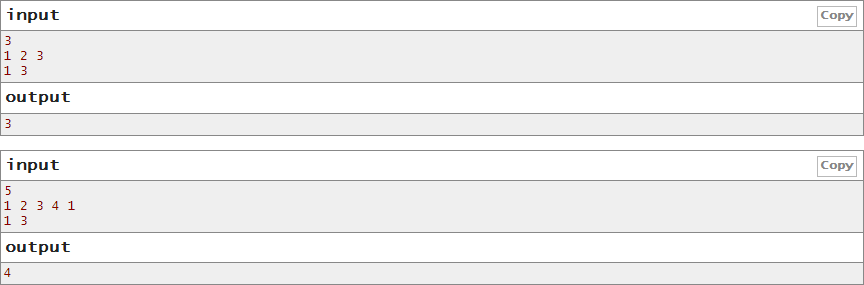
In the first example, it's optimal to start competition at 3 hours (in first timezone). In this case, it will be 1 hour in the second timezone and2 hours in the third timezone. Only one person from the first timezone won't participate.
In second example only people from the third and the fourth timezones will participate.
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#define MAXN 100010
using namespace std;
int a[MAXN];
int n,s,f,ans,sum,maxn;
int main(){
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
scanf("%d%d",&s,&f);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){
int x=i;
if(x>=s&&x<=f-) sum+=a[];
for(int j=;j<n;j++){
x++;if(x>n) x=;
if(x>=s&&x<=f-) sum+=a[j+];
}
if(sum>maxn){ ans=i;maxn=sum; }sum=;
}
cout<<ans;
}
暴力
Codeforces Round #464 (Div. 2)的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #464 (Div. 2) E. Maximize!
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/939/problem/E E. Maximize! time limit per test3 seconds memory li ...
- Codeforces Round #464 (Div. 2) D. Love Rescue
D. Love Rescue time limit per test2 seconds memory limit per test256 megabytes Problem Description V ...
- Codeforces Round #464 (Div. 2) C. Convenient For Everybody
C. Convenient For Everybody time limit per test2 seconds memory limit per test256 megabytes Problem ...
- Codeforces Round #464 (Div. 2) B. Hamster Farm
B. Hamster Farm time limit per test2 seconds memory limit per test256 megabytes Problem Description ...
- Codeforces Round #464 (Div. 2) A Determined Cleanup
A. Love Triangle time limit per test1 second memory limit per test256 megabytes Problem Description ...
- Codeforces Round #464 (Div. 2) B. Hamster Farm[盒子装仓鼠/余数]
B. Hamster Farm time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard inp ...
- Codeforces Round #464 (Div. 2) A. Love Triangle[判断是否存在三角恋]
A. Love Triangle time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard inp ...
- Codeforces Round #464 (Div. 2) D题【最小生成树】
Valya and Tolya are an ideal pair, but they quarrel sometimes. Recently, Valya took offense at her b ...
- Codeforces Round #366 (Div. 2) ABC
Codeforces Round #366 (Div. 2) A I hate that I love that I hate it水题 #I hate that I love that I hate ...
随机推荐
- iOS 隐藏NavigationBar的方法
使用下面方法: - (void)viewWillAppear:(BOOL)animated { [super viewWillAppear:animated]; [self.navigationCon ...
- 在ubuntu中安装与配置zsh与oh-my-zsh
先补充点东西 1.ubuntu中默认安装了那些shell jiang@Linux:~$ cat /etc/shells # /etc/shells: valid login shells/bin/sh ...
- Android系统之Recovery移植教程 【转】
本文转载自:http://luckytcl.blog.163.com/blog/static/14258648320130165626644/ recovery的移植,这方面的资料真实少之又少啊,谷歌 ...
- 0x59 单调队列优化DP
倍增DP太难啦心情好再回去做 poj1821 先让工匠按s排序,f[i][j]表示枚举到第i个工匠涂了j个木板(注意第j个木板不一定要涂) 那么f[i][j]可以直接继承f[i-1][j]和f[i][ ...
- php中全局变量global和超全局变量$GLOBALS
php中全局变量global和超全局变量$GLOBALS 1.global Global的作用是定义全局变量,但是这个全局变量不是应用于整个网站,而是应用于当前页面,包括include或require ...
- JavaScript:DOM对象
ylbtech-JavaScript:DOM对象 1. HTML DOM Document 对象返回顶部 1. HTML DOM Document 对象 HTML DOM 节点 在 HTML DOM ...
- Mysql慢查询和慢查询日志分析利器–mysqlsla
1.安装mysqlsla Source code wget http://hackmysql.com/scripts/mysqlsla-2.03.tar.gz tar zvxf mysqlsl ...
- [Plugin] WEB版一次选择多个文件进行批量上传(swfupload)的解决方案
URL:http://www.cnblogs.com/chillsrc/archive/2010/02/21/1670594.html 说明:功能完全支持ie和firefox浏览器! 一般的WEB方式 ...
- docker(三):Harbor 1.8.0 仓库的安装和使用
回顾: docker(一):docker是什么? docker(二):CentOS安装docker docker(部署常见应用):docker部署mysql 安装的先决条件 硬件环境 1.CPU ...
- ps -aux ,ps aux ,ps -ef 的区别
Linux中的ps命令是Process Status的缩写.ps命令用来列出系统中当前运行的那些进程.ps命令列出的是当前那些进程的快照,就是执行ps命令的那个时刻的那些进程,如果想要动态的显示进程信 ...
