SpringMVC处理方法的数据绑定
一、SpringMVC数据绑定流程
Spring MVC通过反射机制对目标处理方法的签名进行解析,将请求消息中的信息以一定的方式转换并绑定到处理方法的入参中。数据绑定的核心部件是DataBinder,运行机制如下:
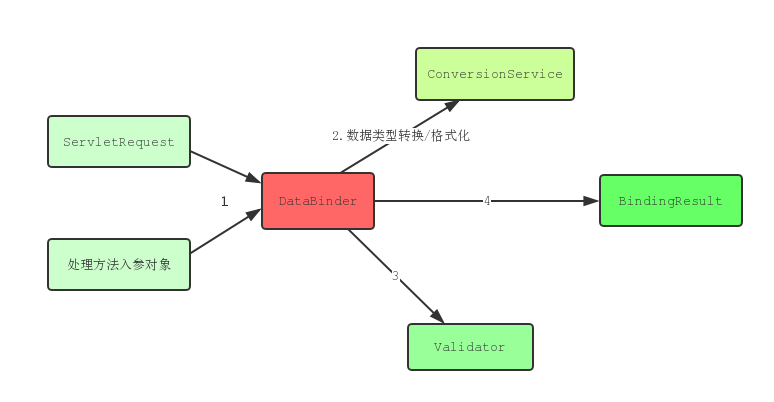
1.Spring MVC主框架将ServletRequest对象及处理方法的入参对象实例传递给DataBinder。
2.DataBinder调用装配在Spring MVC上下文中的ConversionService组件进行数据类型转换、数据格式化工作。将ServletRequest中的请求信息填充到入参对象中
3.调用Validator组件对已经绑定了请求消息数据的入参对象进行数据合法性校验,并最终生成数据绑定结果BindingResult对象,BindingResult包含了已经完成数据绑定的入参对象,还包含相应的校验错误对象!
4. Spring MVC抽取BindingResult中的入参对象和校验错误对象,将它们赋给处理方法的相应入参
二、数据转换
Java标准的PropertyEditor的核心功能是将一个字符串转换为一个Java对象,以便根据界面的输入或者跟会员配置文件中配置字符串构造出一个JVM内部的Java对象。
但是Javav原生的PropertyEditor存在以下不足:
(1)只能用于字符串到java对象的转换,不适用于任意两个java类型之间的转换。
(2)对源对象以及目标对象所在的上下文信息不敏感,在类型住哪换的时候不能使用这些上下文信息实施高级的转换逻辑。
所以Spring在核心模型中添加了一个通用的类型转换模块。
ConversionService是Spring类型转换体系的核心接口。
- public interface ConversionService {
- /**
- * Return {@code true} if objects of {@code sourceType} can be converted to the {@code targetType}.
- * <p>If this method returns {@code true}, it means {@link #convert(Object, Class)} is capable
- * of converting an instance of {@code sourceType} to {@code targetType}.
- * <p>Special note on collections, arrays, and maps types:
- * For conversion between collection, array, and map types, this method will return {@code true}
- * even though a convert invocation may still generate a {@link ConversionException} if the
- * underlying elements are not convertible. Callers are expected to handle this exceptional case
- * when working with collections and maps.
- * @param sourceType the source type to convert from (may be {@code null} if source is {@code null})
- * @param targetType the target type to convert to (required)
- * @return {@code true} if a conversion can be performed, {@code false} if not
- * @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code targetType} is {@code null}
- */
- boolean canConvert(Class<?> sourceType, Class<?> targetType);
- /**
- * Return {@code true} if objects of {@code sourceType} can be converted to the {@code targetType}.
- * The TypeDescriptors provide additional context about the source and target locations
- * where conversion would occur, often object fields or property locations.
- * <p>If this method returns {@code true}, it means {@link #convert(Object, TypeDescriptor, TypeDescriptor)}
- * is capable of converting an instance of {@code sourceType} to {@code targetType}.
- * <p>Special note on collections, arrays, and maps types:
- * For conversion between collection, array, and map types, this method will return {@code true}
- * even though a convert invocation may still generate a {@link ConversionException} if the
- * underlying elements are not convertible. Callers are expected to handle this exceptional case
- * when working with collections and maps.
- * @param sourceType context about the source type to convert from
- * (may be {@code null} if source is {@code null})
- * @param targetType context about the target type to convert to (required)
- * @return {@code true} if a conversion can be performed between the source and target types,
- * {@code false} if not
- * @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code targetType} is {@code null}
- */
- boolean canConvert(TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType);
- /**
- * Convert the given {@code source} to the specified {@code targetType}.
- * @param source the source object to convert (may be null)
- * @param targetType the target type to convert to (required)
- * @return the converted object, an instance of targetType
- * @throws ConversionException if a conversion exception occurred
- * @throws IllegalArgumentException if targetType is null
- */
- <T> T convert(Object source, Class<T> targetType);
- /**
- * Convert the given {@code source} to the specified {@code targetType}.
- * The TypeDescriptors provide additional context about the source and target locations
- * where conversion will occur, often object fields or property locations.
- * @param source the source object to convert (may be null)
- * @param sourceType context about the source type to convert from
- * (may be {@code null} if source is {@code null})
- * @param targetType context about the target type to convert to (required)
- * @return the converted object, an instance of {@link TypeDescriptor#getObjectType() targetType}
- * @throws ConversionException if a conversion exception occurred
- * @throws IllegalArgumentException if targetType is {@code null},
- * or {@code sourceType} is {@code null} but source is not {@code null}
- */
- Object convert(Object source, TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType);
- }
可以利用 ConversionServiceFactoryBean 在 Spring 的 IOC容器中定义一个 ConversionService. Spring 将自动识别出 IOC 容器中的 ConversionService,并在 Bean 属性配置及 Spring MVC处理方法入参绑定等场合使用它进行数据的转换。该FactoryBean创建ConversionService內建了很多转换器,可以完成大多数Java类型的转换工作,,除了包括将String对象转换成各种基础类型对象外,还包括String,Number,Array,Collection,Map及Object之间的转换器。可通过 ConversionServiceFactoryBean 的 converters 属性注册自定义的类型转换器。
Spring 定义了 3 种类型的转换器接口,实现任意一个转换器接口都可以作为自定义转换器注册到 ConversionServiceFactroyBean 中:
★ Converter<S,T>:将 S 类型对象转为 T 类型对象
★ ConverterFactory:将相同系列多个 “同质” Converter 封装在一 起。如果希望将一种类型的对象转换为另一种类型及其子类的对象(例如将 String 转换为 Number 及 Number子类(Integer、Long、Double 等)对象)可使用该转换器工厂类
★ GenericConverter:会根据源类对象及目标类对象所在的宿主类中的上下文信息进行类型转换
ConversionServiceFactoryBean 的converters属性可以接受这些接口的实现类,并把这些转换器的转换逻辑统一封装到一个 ConversionService实例对象中,Spring在Bean属性配置以及Spring MVC请求消息绑定时将利用这个ConversionService实例完成类型转换工作。
使用示例:
假设处理方法有一个User类型的入参,我们希望将一个格式化的请求参数字符串直接转换为User对象,字符串的格式为
<userName>:<password>:<realName>
这就要求我们定义一个负责将格式化的String转换为User对象的自定义转换器
首先创建一个自定义类型转换器
- public class StringToUserConverter implements Converter<String,User> {
- @Override
- public User convert(String source) {
- User user = new User();
- if (StringUtils.isNoneBlank(source)) {
- String[] items = source.split(":");
- user.setUserName(items[0]);
- user.setPassword(items[1]);
- user.setRealName(items[2]);
- }
- return user;
- }
- }
然后在SpringMVC中配置该自定义类型转换器
- <!-- 配置自定义类型转换器 -->
- <bean id="conversionService" class="org.springframework.context.support.ConversionServiceFactoryBean">
- <property name="converters">
- <list>
- <bean class="com.winner.converter.StringToUserConverter"></bean>
- </list>
- </property>
- </bean>
最后将 自定义的类型转换器注册到SpringMVC 中
- <mvc:annotation-driven conversion-service="conversionService"></mvc:annotation-driven>
- <mvc:annotation-driven>简化了Spring MVC的相关配置。
Controller 如下
- @RequestMapping(value="testConversion",method=RequestMethod.POST)
- public String testConversion(@RequestParam("user")User user){
- System.out.println(user);
- return "success";
- }
发送一个url请求:http://xx.xx.xx?user=tom:1234:tomson,
请求参数tom:1234:tomson将会被StringToUserConverter正式转换并绑定到方法的User入参中。
三、时间日期、数字的转换和格式化
SpringMVC 已经提供了 时间和数字格式的转换,但需要开启<mvc:annotation-driven>注解,该注解内部默认创建的ConversionService实例就是一个FormattingConversionServiceFactoryBean。示例如下
- @Component
- public class User {
- private Integer id;
- private String name;
- @DateTimeFormat(pattern="yyyy-MM-dd")
- private Date birthday;
- private String address;
- //get set 构造器等省略......
- }
四、数据校验
应用程序在执行业务逻辑前,必须通过数据校验保证接收到的输入数据是正确合法的,如代表生日的日期应该是一个过去的时间,工资的数值必须是一个正数。很多时候同样的数据校验会出现在不同的层中,违反了DRY原则,为了避免数据的冗余校验,将验证逻辑和相应的域模型进行绑定,将代码验证的逻辑集中起来管理。
JSR 303是Java为Bean数据合法性校验提供的标准框架,它已经包含在JavaEE 6.0中 ,JSR 303通过在Bean属性上标注类似于@NotNull、@Max等标准的注解指定校验规则,并通过标准的验证接口对Bean进行验证,SpringMVC可通过Hibernate Validator(JSR303的参考实现)进行JSR303校验
Spring拥有自己独立的数据校验框架,同时支持JSR-303标准的校验框架。Spring的DataBinder在进行数据绑定时,可同时调用校验框架完成数据校验工作。在SpringMVC中,可直接通过注解驱动的方式进行数据校验。
Spring的org.springframework.validation是校验框架所在的包,Validator接口拥有以下两个方法:
boolean supports(Class<?> clazz):该校验器能够对clazz类型的对象进行校验
void validate(Object target,Errors erros):对目标类target进行校验,并将校验错误记录在errors中
LocalValidatorFactoryBean既实现了Spring的Validator接口,也实现了JSR-303的Validator接口,只要再Spring容器中定义一个LocalValidatorFactoryBean,即可将其注入需要数据校验的Bean中。定义一个LocalValidatorFactoryBean非常简单
- <bean id="validator" class="org.springframework.validation.beanvalidation.LocalValidatorFactoryBean"/>
注意:Spring本身没有提供JSR-303的实现,所以必须将JSR-303的实现者(如Hibernate Validator)的jar文件放到类路径下,Spring将自动加载并装配好JSR 303的实现者。
- <dependency>
- <groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
- <artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId>
- <version>5.2.0.Final</version>
- </dependency>
<mvc:annotaion-driver/>会默认装配好一个LocalValidatorFactoryBean,通过在处理方法的入参上标注@Valid注解即可让SpringMVC在完成数据绑定后执行数据校验工作。
- public class User {
- //加入 JSR303 验证注解
- @NotNull
- private Integer id;
- private String name;
- @DateTimeFormat(pattern="yyyy-MM-dd")
- private Date birthday;
- private String address;
- //省略 setter getter......
- }
- @RequestMapping(value="testConversion",method=RequestMethod.POST)
- //此处注意 :@Valid 注解表示其后面的java bean注入需要JSR303验证,如果其验证错误
- //那么必须在其后面紧跟一个BindingResult(或Error)类型参数,不可打乱顺序,验证bean和BindingResult间不能有其他参数
- public String testConversion(@Valid User user,BindingResult result){
- if(result.hasErrors()){
- for (FieldError error : result.getFieldErrors()) {
- System.out.println(error.getField()+"--"+error.getDefaultMessage());
- }
- }
- System.out.println(user);
- return SUCCESS;
- }
在已经标注了JSR-303注解的入参对象前添加@Valid注解,Spring MVC框架在将请求数据绑定到该入参对象之后,就会调用校验框架根据注解声明的校验规则实施校验。
BindingResult紧随校验入参对象之后,成对出现,它们之间不允许有其他入参。
SpringMVC处理方法的数据绑定的更多相关文章
- SpringMVC(5)数据绑定-2
在SpringMVC(4)数据绑定-1中我们介绍了如何用@RequestParam来绑定数据,下面我们来看一下其它几个数据绑定注解的使用方法. 1.@PathVariable 用来绑定URL模板变量值 ...
- DataBind()方法实现数据绑定
在为.aspx页上的对象设置了特定数据源之后,必须将数据绑定到这些数据源上.可以使用“Page.DataBind()”或“控件.DataBind()”方法将数据绑定到数据源上. 主要差别在于:调用Pa ...
- SpringMVC:学习笔记(5)——数据绑定及表单标签
SpringMVC——数据绑定及表单标签 理解数据绑定 为什么要使用数据绑定 基于HTTP特性,所有的用户输入的请求参数类型都是String,比如下面表单: 按照我们以往所学,如果要获取请求的所有参数 ...
- springMVC中 request请求数据绑定到Controller入参 过程剖析
前言:Controller方法的参数类型可以是基本类型,也可以是封装后的普通Java类型.若这个普通Java类型没有声明任何注解,则意味着它的每一个属性都需要到Request中去查找对应的请求参数.众 ...
- springMVC 多方法controller
1. 新建web project 2. 加入jar包 3. 写web.xml <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?& ...
- Android(或者Java)通过HttpUrlConnection向SpringMVC请求数据(数据绑定)
问题描写叙述 当我们使用SpringMVC作为服务端的框架时,有时不仅仅要应对web前端(jsp.javascript.Jquery等)的訪问请求,有时还可能须要响应Android和JavaSE(桌面 ...
- 【JavaEE】Springmvc搭建方法及example
现在介绍SSH的文章很多,但是适合自己需求的却经常找不到,这些东西呢,会了之后总会感觉别人的程序哪里哪里别扭,会之前呢就感觉很混乱,而且SSH的官方文档,至少在我看来是“会者勉强能看.不会者一片迷茫” ...
- springmvc请求方法那些事
@RequestMapping 用法详解之地址映射 (2013-08-11 16:06:58) 转载▼ 标签: it 前段时间项目中用到了RESTful模式来开发程序,但是当用POST.PUT模式 ...
- SpringMVC学习笔记之---数据绑定
SpringMVC数据绑定 一.基础配置 (1)pom.xml <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>junit</gro ...
随机推荐
- 调整linux系统时区
cp /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai /etc/localtime 好吧,使用tzselect又靠谱些,使用前把/etc/localtime删除了. 执行上 ...
- Hadoop CapacitySchedule配置
下面是Hadoop中CapacitySchedule配置,包含了新建队列和子队列 <configuration> <property> <name>yarn.sch ...
- 《Android源码设计模式》--状态模式--责任链模式--解释器模式--命令模式--观察者模式--备忘录模式--迭代器模式
[状态模式] No1: Wifi设置界面是一个叫做WifiSetting的Fragment实现的 No2: 在不同的状态下对于扫描Wifi这个请求的处理是完全不一样的.在初始状态下扫描请求被直接忽略, ...
- 关于table边框,设置了border-collapse:collapse之后,设置border-radius没效果
做项目遇到边框需要设置圆角,然后发现在设置了border-collapse:collapse之后,border-radius:10px不起作用了,发现这个是css本身的问题,两者不能混在一起使用. 代 ...
- 层级目录结构的Makefile递归编译方法
层级目录结构的Makefile编写方法. 层级目录结构的Makefile编写方法. 0.前言 1.如何编译整个工程 2.过滤每层不需要编译的目录 3将所有输出文件定向输出. 0.前言 假如现在有这样一 ...
- 快递鸟电子面单打印功能基于java
之前的后天管理系统的电子面单打印使用的是灵通打单. 使用相对比较麻烦,需要到处Excel之后再导入,麻烦. 快递鸟有电子面单api,后台系统直接对接很是方便,不过也遇到了好些问题. 不难是不难,但是遇 ...
- 如何快速分析出现性能问题的Linux服务器
Brendan Gregg曾经分享过当遇到一个系统性能问题时,如何利用登录的前60秒对系统的性能情况做一个快速浏览和分析,主要包括如下10个工具,这是一个非常有用且有效的工具列表.本文将详细介绍这些命 ...
- android Handler机制 消息机制
韩梦飞沙 韩亚飞 313134555@qq.com yue31313 han_meng_fei_sha 循环器Looper 管理该线程内对象之间的消息交换 messageExchange 循 ...
- BZOJ 4419: [Shoi2013]发微博 set模拟
4419: [Shoi2013]发微博 题目连接: http://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=4419 Description 刚开通的SH微博共 ...
- hdoj 5113 Black And White DFS+剪枝
Black And White Time Limit: 2000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 512000/512000 K (Java/Others) T ...
