springboot学习笔记-3 整合redis&mongodb
一.整合redis
1.1 建立实体类
@Entity
@Table(name="user")
public class User implements Serializable {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.AUTO)
private Long id;
private String name;
@DateTimeFormat(pattern="yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")
private Date createDate; @JsonBackReference //防止json的重复引用问题
private Department department;
private Set<Role> roles;
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Date getCreateDate() {
return createDate;
}
public void setCreateDate(Date createDate) {
this.createDate = createDate;
}
public Department getDepartment() {
return department;
}
public void setDepartment(Department department) {
this.department = department;
}
public Set<Role> getRoles() {
return roles;
}
public void setRoles(Set<Role> roles) {
this.roles = roles;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", createDate=" + createDate + ", department=" + department
+ ", roles=" + roles + "]";
} }
1.2 建立Redis的配置类
首先导入pom.xml相应的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
在springboot中,没有去提供直接操作Redis的Repository,但是我们可以使用RedisTemplate去访问Redis.想要去使用RedisTemplate,首先需要完成一些必要的配置.这里使用配置类去完成.
在application.properties中建立Redis的相关配置:
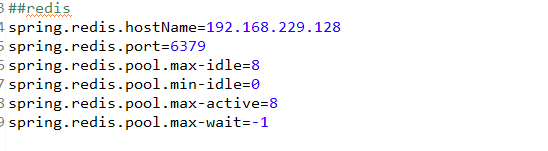
建立配置类,配置RedisTemplate,而要使用RedisTemplate还需要配置RedisConnectionFactory:
@ConfigurationProperties("application.properties")
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Value("${spring.redis.hostName}")
private String hostName;
@Value("${spring.redis.port}")
private Integer port;
@Bean
public RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory() {
JedisConnectionFactory cf = new JedisConnectionFactory();
cf.setHostName(hostName);
cf.setPort(port);
cf.afterPropertiesSet();
return cf;
}
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
StringRedisTemplate template=new StringRedisTemplate(factory);
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer=new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
ObjectMapper om=new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL,JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
template.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
template.afterPropertiesSet();
return template;
}
}
1.3 建立UserRedis类,它实现了与Redis的交互
注意,在UserRedis中,使用了Redis的数据结构中最常用的key-value都是字符串的形式,采用Gson将对象转化为字符串然后存放到redis中.
@Repository
public class UserRedis {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate; public void add(String key,User user) {
Gson gson=new Gson();
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key,gson.toJson(user));
}
public void add(String key,List<User> users) {
Gson gson=new Gson();
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key,gson.toJson(users));
}
public User get(String key ) {
Gson gson=new Gson();
User user=null;
String userStr=redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(userStr))
user=gson.fromJson(userStr, User.class);
return user;
}
public List<User> getList(String key) {
Gson gson=new Gson();
List<User> users=null;
String listJson=redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(listJson)) {
users=gson.fromJson(listJson,new TypeToken<List<User>>(){}.getType());
}
return users;
}
public void delete(String key) {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().getOperations().delete(key);
}
}
1.4 建立UserController类
它自动注入了UserRedis类,通过不同的url实现了向redis存储数据,获取数据的功能.
@Controller
public class UserController {
@Autowired
UserRedis userRedis; @RequestMapping("/user/testRedisSave")
public String testRedis() {
Department department=new Department();
department.setName("开发部");
Role role=new Role();
role.setName("admin");
User user=new User();
user.setName("hlhdidi");
user.setCreateDate(new Date());
user.setDepartment(department);
Set<Role> roles=new HashSet<>();
roles.add(role);
user.setRoles(roles);
userRedis.delete(this.getClass().getName()+":username:"+user.getName());
userRedis.add(this.getClass().getName()+":username:"+user.getName(), user);
return null;
}
@RequestMapping("/user/testRedisGet")
public String testRedis2() {
User user=userRedis.get(this.getClass().getName()+":username:hlhdidi");
System.out.println(user);
return null;
}
}
先访问localhost:8080/user/testRedisSave,再访问localhost:8080/user/testRedisGet,即可测试成功!
二.整合MongoDB
MongoDB是一种文档类型的NoSql数据库.它内部有三个层次的概念,分别为数据库,集合,文档.使用springboot可以非常方便的整合MongoDB
2.1 建立mongo.properties配置文件
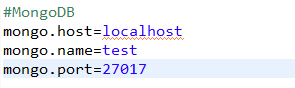
导入依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.pegdown</groupId>
<artifactId>pegdown</artifactId>
<version>1.4.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-hateoas</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.data</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-data-mongodb</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-annotations</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.2 建立MongoConfig配置类,完成对于MongoDB的配置
@Configuration
@EnableMongoRepositories(basePackages={"com.hlhdidi.springboot.mongo"})//MongoRepository的扫描包
@PropertySource("classpath:mongo.properties")//注入配置文件属性
public class MongoConfig extends AbstractMongoConfiguration{ @Autowired
private Environment env; @Override
protected String getDatabaseName() {
return env.getRequiredProperty("mongo.name");
} @Override
@Bean
public Mongo mongo() throws Exception {
ServerAddress serverAddress=new ServerAddress(env.getRequiredProperty("mongo.host"));
List<MongoCredential> credentials=new ArrayList<>();
return new MongoClient(serverAddress, credentials);
} }
2.3 建立SysUser实体类.
该实体类需要被存储到MongoDB数据库中.
@Document(collection="user")//配置collection的名称,如果没有将会自动建立对应的Collection
public class SysUser {
@Id
private String userId;
@NotNull @Indexed(unique=true)
private String username;
@NotNull
private String password;
@NotNull
private String name;
@NotNull
private String email;
@NotNull
private Date registrationDate=new Date();
private Set<String> roles=new HashSet<>();
public SysUser(){}
@PersistenceConstructor
public SysUser(String userId, String username, String password, String name, String email, Date registrationDate,
Set<String> roles) {
super();
this.userId = userId;
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
this.registrationDate = registrationDate;
this.roles = roles;
}
public String getUserId() {
return userId;
}
public void setUserId(String userId) {
this.userId = userId;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public Date getRegistrationDate() {
return registrationDate;
}
public void setRegistrationDate(Date registrationDate) {
this.registrationDate = registrationDate;
}
public Set<String> getRoles() {
return roles;
}
public void setRoles(Set<String> roles) {
this.roles = roles;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "SysUser [userId=" + userId + ", username=" + username + ", password=" + password + ", name=" + name
+ ", email=" + email + ", registrationDate=" + registrationDate + ", roles=" + roles + "]";
} }
2.4 建立SysUserRepository
由于springboot已经帮我们提供了操作MongoDB数据库的API,因此直接继承对应的类即可(和JPA一致)
@Repository
public interface SysUserRepository extends MongoRepository<SysUser, String>{ }
2.5 测试
测试类先向MongoDB中存储了一个实体类对象,随后获取指定对象的指定Collections下面的所有文档
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes={MongoConfig.class})
@FixMethodOrder
public class MongoTest {
@Autowired
SysUserRepository repository; @Before
public void setup() {
Set<String> roles=new HashSet<>();
roles.add("manage");
SysUser sysUser=new SysUser("1", "hlhdidi", "123", "xiaohulong", "email@com.cn", new Date(), roles);
repository.save(sysUser);
}
@Test
public void findAll() {
List<SysUser> users=repository.findAll();
for(SysUser user:users) {
System.out.println(user);
}
}
}
springboot学习笔记-3 整合redis&mongodb的更多相关文章
- SpringBoot学习- 5、整合Redis
SpringBoot学习足迹 SpringBoot项目中访问Redis主要有两种方式:JedisPool和RedisTemplate,本文使用JedisPool 1.pom.xml添加dependen ...
- springboot学习笔记-4 整合Druid数据源和使用@Cache简化redis配置
一.整合Druid数据源 Druid是一个关系型数据库连接池,是阿里巴巴的一个开源项目,Druid在监控,可扩展性,稳定性和性能方面具有比较明显的优势.通过Druid提供的监控功能,可以实时观察数据库 ...
- Spring Boot 学习笔记(六) 整合 RESTful 参数传递
Spring Boot 学习笔记 源码地址 Spring Boot 学习笔记(一) hello world Spring Boot 学习笔记(二) 整合 log4j2 Spring Boot 学习笔记 ...
- SpringBoot学习笔记(10):使用MongoDB来访问数据
SpringBoot学习笔记(10):使用MongoDB来访问数据 快速开始 本指南将引导您完成使用Spring Data MongoDB构建应用程序的过程,该应用程序将数据存储在MongoDB(基于 ...
- SpringBoot学习笔记:Redis缓存
SpringBoot学习笔记:Redis缓存 关于Redis Redis是一个使用ANSI C语言编写的免费开源.支持网络.可基于内存亦可以持久化的日志型.键值数据库.其支持多种存储类型,包括Stri ...
- SpringBoot学习笔记
SpringBoot个人感觉比SpringMVC还要好用的一个框架,很多注解配置可以非常灵活的在代码中运用起来: springBoot学习笔记: .一.aop: 新建一个类HttpAspect,类上添 ...
- Springboot学习笔记(六)-配置化注入
前言 前面写过一个Springboot学习笔记(一)-线程池的简化及使用,发现有个缺陷,打个比方,我这个线程池写在一个公用服务中,各项参数都定死了,现在有两个服务要调用它,一个服务的线程数通常很多,而 ...
- SpringBoot学习笔记(14):使用SpringBootAdmin管理监控你的应用
SpringBoot学习笔记(14):使用SpringBootAdmin管理监控你的应用 Spring Boot Admin是一个管理和监控Spring Boot应用程序的应用程序.本文参考文档: 官 ...
- SpringMVC:学习笔记(10)——整合Ckeditor且实现图片上传
SpringMVC:学习笔记(10)——整合Ckeditor且实现图片上传 配置CKEDITOR 精简文件 解压之后可以看到ckeditor/lang下面有很多语言的js,如果不需要那么多种语言的,可 ...
随机推荐
- [BZOJ2742][HEOI2012]Akai的数学作业[推导]
题意 给定各项系数,求一元 \(n\) 次方程的有理数解. \(n\leq 100\). 分析 设答案为 \(\frac{p}{q}\) ,那么多项式可以写成 \(a_0\frac{p}{q}+a_1 ...
- 微信小程序如何检测接收iBeacon信号
前话 微信小程序开发带着许多坑,最近就遇到了个需求,检测iBeacon来进行地点签到. (╯▔皿▔)╯ 微信小程序对于iBeacon的文档也写的十分精简,只简单介绍了每个接口的作用,这就导致我以为简单 ...
- CobarClient源码分析
CobarClient是阿里巴巴公司开发一个的开源的.基于iBatis和Spring的分布式数据库访问层.为了支持iBatis,Spring框架提供了一个SqlMapClientTemplate,通过 ...
- electron快速开始
初学electron 接触了两周的electron,感觉还不错,以后pc端基本上可以用electron加壳写pc端应用了,可以用nodejs的模块,也可以用es6.7,还可以直接操作系统文件.基本上可 ...
- 二、Unity Editor模式下,操作选中对象
使用Unity提供的工具类 UnityEditor.Selection public static GameObject activeGameObject public static UnityEng ...
- 自动分配ip的方法- 【Linux】
1. 查看本机无线网络使用的网卡 2. 设置vbox的网络连接为桥接,并选择本机无线网络对应的网卡 3. 进入系统,输入ifconfig命令,记录下系统的HWaddr 4. 修改系统ip配置文 ...
- Netty源码分析第5章(ByteBuf)---->第1节: AbstractByteBuf
Netty源码分析第五章: ByteBuf 概述: 熟悉Nio的小伙伴应该对jdk底层byteBuffer不会陌生, 也就是字节缓冲区, 主要用于对网络底层io进行读写, 当channel中有数据时, ...
- day16 类
初识面向对象 1. 面向过程: 一切以事物的流程为核心. 核心是"过程"二字, 过程是指解决问题的步骤, 即, 先干什么, 后⼲什么. 基于该思想编写程序就好比在编写一套流 ...
- Codeforces1101 | EducationalRound58 | 瞎讲报告
目录 Educational Codeforces Round 58 (Rated for Div. 2) A. Minimum Integer B. Accordion C. Division an ...
- java web 3.1-web.xml文件配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <web-app xmlns:xsi="http:/ ...
