加密算法--->对称加密与非对称加密算举例说明
对称加密例子:des对称加密
des对称加密,对称加密,是一种比较传统的加密方式,其加密运算、解密运算使用的是同样的密钥,信息的发送者和信息的接收者在进行信息的传输与处理时,必须共同持有该密码(称为对称密码),是一种对称加密方式。
package me.andpay.ac.common.srv.idtag.bypay.util; import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import javax.crypto.KeyGenerator;
import javax.crypto.SecretKey;
import javax.crypto.SecretKeyFactory;
import javax.crypto.spec.DESedeKeySpec;
import java.security.Key; /**
* @author wch
*/
public class DesUtil {
/**
* 密钥算法
* @version 1.0
* @author
*/
public static final String KEY_ALGORITHM = "DESede"; /**
* 加密/解密算法/工作模式/填充方式
* @version 1.0
* @author
*/
public static final String CIPHER_ALGORITHM = "DESede/ECB/PKCS5Padding"; /**
* 转换密钥
* @param key 二进制密钥
* @return key 密钥
*
*/
public static Key toKey(byte[] key) throws Exception{
//实例化DES密钥材料
DESedeKeySpec dks = new DESedeKeySpec(key);
//实例化秘密密钥工厂
SecretKeyFactory keyFactory = SecretKeyFactory.getInstance(KEY_ALGORITHM);
//生成秘密密钥
return keyFactory.generateSecret(dks);
} /**
* 解密
* @param data 待解密数据
* @param key 密钥
* @return byte[] 解密数据
*/
public static byte[] decrypt(byte[] data, byte[] key)throws Exception{
//还原密钥
Key k = toKey(key);
/**
* 实例化
* 使用PKCS7Padding填充方式,按如下代码实现
* Cipher.getInstance(CIPHER_ALGORITHM,"BC");
*/
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(CIPHER_ALGORITHM);
//初始化,设置为解密模式
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, k);
//执行操作
return cipher.doFinal(data);
} public static byte[] encrypt(byte[] data, byte[] key) throws Exception{
//还原密钥
Key k = toKey(key);
/**
* 实例化
* 使用PKCS7Padding填充方式,按如下代码实现
* Cipher.getInstance(CIPHER_ALGORITHM,"BC");
*/
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("DESede/ECB/PKCS5Padding");
//初始化,设置为解密模式
//cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, k);
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, k); //执行操作
return cipher.doFinal(data);
} /**
* 生成密钥
*
* @return byte[] 二进制密钥
*/
public static byte[] initKey() throws Exception{
/**
* 实例化
* 使用128位或192位长度密钥
* KeyGenerator.getInstance(KEY_ALGORITHM,"BC");
*/
KeyGenerator kg = KeyGenerator.getInstance(KEY_ALGORITHM);
/**
* 初始化
*使用128位或192位长度密钥,按如下代码实现
*kg.init(128);
*kg.init(192);
*/
kg.init(168);
//生成秘密密钥
SecretKey secretKey = kg.generateKey();
//获得密钥的二进制编码形式
return secretKey.getEncoded();
} //10进制数组转换16进制数组
public static String printbytes(String tip, byte[] b) {
String ret = "";
String str;
for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) { str = Integer.toHexString((int) (b[i] & 0xff)); if (str.length() == 1)
str = "0" + str;
ret = ret + str + " ";
} // 02 00 07 00 00 60 70 01 17 35 03 C8
return ret;
}
}
des对称加密工具栏
对称加密例子:aes对称加密
Aes加密解密方法使用Hex进行了编码解码 [java] view plain copy
package com.baidu.wallet.bdwallet.utils;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.security.InvalidKeyException;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import javax.crypto.BadPaddingException;
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import javax.crypto.IllegalBlockSizeException;
import javax.crypto.NoSuchPaddingException;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
import org.apache.commons.codec.DecoderException;
import org.apache.commons.codec.binary.Hex;
public class Test {
private static final String AES="AES";
private static final String UTF8="UTF-8"; /**
* AES加密
* @param content
* @param pkey
* @return
* @throws DecoderException
*/
private static byte[] encrypt(String content, String pkey) throws DecoderException {
try {
String private_key=pkey;
byte[] encodeFormat=null;
try {
//秘钥 Hex解码为什么秘钥要进行解码,因为秘钥是某个秘钥明文进行了Hex编码后的值,所以在使用的时候要进行解码
encodeFormat = Hex.decodeHex(private_key.toCharArray());
} catch (DecoderException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
SecretKeySpec key = new SecretKeySpec(encodeFormat, AES);
// Cipher对象实际完成加密操作
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("AES/ECB/PKCS5Padding");
// 加密内容进行编码
byte[] byteContent = content.getBytes(UTF8);
// 用密匙初始化Cipher对象
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, key);
// 正式执行加密操作
byte[] result = cipher.doFinal(byteContent);
return result;
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchPaddingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvalidKeyException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalBlockSizeException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (BadPaddingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
} /**
* AES解密
* @param contents
* @param password
* @return
* @throws DecoderException
*/
private static byte[] decrypt(String contents, String password) throws DecoderException {
try {
//密文使用Hex解码
byte[]content = Hex.decodeHex(contents.toCharArray());
//秘钥 Hex解码为什么秘钥要进行解码,因为秘钥是某个秘钥明文进行了Hex编码后的值,所以在使用的时候要进行解码
byte[] encodeFormat = Hex.decodeHex(password.toCharArray());
SecretKeySpec key = new SecretKeySpec(encodeFormat, AES);
// Cipher对象实际完成加密操作
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(AES);
// 用密匙初始化Cipher对象
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, key);
// 正式执行解密操作
byte[] result = cipher.doFinal(content);
return result;
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchPaddingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvalidKeyException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalBlockSizeException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (BadPaddingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
} /**
* Aes加密
* @param context 明文
* @param private_key 秘钥
* @return
* @throws DecoderException
*/
public static String encryption(String context,String private_key) throws DecoderException{
//加密后的明文也就变成了密文
byte[] encryptResult = encrypt(context, private_key);
//密码文Hex编码
String encryptResultStr = Hex.encodeHexString(encryptResult);
return encryptResultStr;
} /**
* Aes解密
* @param context 密文
* @param private_key 秘钥
* @return
* @throws DecoderException
* @throws UnsupportedEncodingException
*/
public static String decryption(String context,String private_key) throws DecoderException, UnsupportedEncodingException{
//这里的密文解密前先进行了Hex解码
byte[] decryptResult = decrypt(context, private_key);
String result = new String(decryptResult, UTF8);
return result;
} public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException, DecoderException {
//加密内容
String content = "123456787654321";
//AES加密解密秘钥
String password = "这个值一般都是给定的,双发都知道";
// 加密
System.out.println("加密前:" + content);
// 调用加密方法
String encryptResultStr = encryption(content, password);
System.out.println("加密后:" + encryptResultStr);
// 调用解密方法
String result = decryption(encryptResultStr, password);
// 解密内容进行解码
System.out.println("解密后:" + result);
}
}
这个方法在正式的项目中已经在使用木有问题,注意这里的AES加密解密你要要对哦……
上面使用的就是org.apache.commons.codec.binary.Hex这个类的方法,在maven中配置如下: [html] view plain copy
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-codec</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-codec</artifactId>
<version>1.4</version>
</dependency>
注意:这里要使用1.4以及以上版本,应为1.4以下的没有Hex.encodeHexString(byte[])这个方法!
aes对称加密
Java使用AES加解密 目录 1.1生成密钥 1.2密钥的存储 1.3获取存储的密钥 1.4加解密 1.5使用存储的密钥进行加解密示例 AES是一种对称的加密算法,可基于相同的密钥进行加密和解密。Java采用AES算法进行加解密的逻辑大致如下: 1、生成/获取密钥 2、加/解密 1.1生成密钥
密钥的生成是通过KeyGenerator来生成的。通过获取一个KeyGenerator实例,然后调用其generateKey()方法即可生成一个SecretKey对象。大致逻辑一般如下: private SecretKey geneKey() throws Exception {
//获取一个密钥生成器实例
KeyGenerator keyGenerator = KeyGenerator.getInstance(ALGORITHM);
SecureRandom random = new SecureRandom();
random.setSeed("123456".getBytes());//设置加密用的种子,密钥
keyGenerator.init(random);
SecretKey secretKey = keyGenerator.generateKey();
return secretKey;
} 上述生成密钥的过程中指定了固定的种子,每次生成出来的密钥都是一样的。还有一种形式,我们可以通过不指定SecureRandom对象的种子,即不调用其setSeed方法,这样每次生成出来的密钥都可能是不一样的。 private SecretKey geneKey() throws Exception {
//获取一个密钥生成器实例
KeyGenerator keyGenerator = KeyGenerator.getInstance(ALGORITHM);
SecureRandom random = new SecureRandom();
keyGenerator.init(random);
SecretKey secretKey = keyGenerator.generateKey();
return secretKey;
} 通过KeyGenerator的init(keySize)方法进行初始化,而不是通过传递SecureRandom对象进行初始化也可以达到上面的效果,每次生成的密钥都可能是不一样的。但是对应的keySize的指定一定要正确,AES算法的keySize是128。 private SecretKey geneKey() throws Exception {
//获取一个密钥生成器实例
KeyGenerator keyGenerator = KeyGenerator.getInstance(ALGORITHM);
keyGenerator.init(128);
SecretKey secretKey = keyGenerator.generateKey();
return secretKey;
} 但是这种每次生成出来的密钥都是不同的情况下,我们需要把加密用的密钥存储起来,以供解密的时候使用,不然就没法进行解密了。 1.2密钥的存储
密钥SecretKey里面最核心的内容就是其中的密钥对应的字节数组,可以通过SecretKey的getEncoded()方法获取。然后把它存储起来即可。最简单的方式就是直接写入一个文件中。 //把上面的密钥存起来
Path keyPath = Paths.get("D:/aes.key");
Files.write(keyPath, secretKey.getEncoded()); 1.3获取存储的密钥
获取存储的密钥的核心是把密钥的字节数组转换为对应的SecretKey。这可以通过SecretKeySpec来获取,其实现了SecretKey接口,然后构造参数里面将接收密钥的字节数组。 private SecretKey readKey(Path keyPath) throws Exception {
//读取存起来的密钥
byte[] keyBytes = Files.readAllBytes(keyPath);
SecretKeySpec keySpec = new SecretKeySpec(keyBytes, ALGORITHM);
return keySpec;
} 1.4加解密
Java采用AES算法进行加解密的过程是类似的,具体如下: 1、指定算法,获取一个Cipher实例对象 Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ALGORITHM);//算法是AES 2、生成/读取用于加解密的密钥 SecretKey secretKey = this.geneKey(); 3、用指定的密钥初始化Cipher对象,同时指定加解密模式,是加密模式还是解密模式。 cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, secretKey); 4、通过update指定需要加密的内容,不可多次调用。 cipher.update(content.getBytes()); 5、通过Cipher的dofinal()进行最终的加解密操作。 byte[] result = cipher.doFinal();//加密后的字节数组 通过以上几步就完成了使用AES算法进行加解密的操作了。其实第4、5步是可以合在一起的,即在进行doFinal的时候传递需要进行加解密的内容。但是如果update指定了加密的内容,而doFinal的时候也指定了加密的内容,那最终加密出来的结果将是两次指定的加密内容的和对应的加密结果。 byte[] result = cipher.doFinal(content.getBytes()); 以下是一次加解密操作的完整示例。 public class AESTest { private static final String ALGORITHM = "AES"; /**
* 生成密钥
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
private SecretKey geneKey() throws Exception {
//获取一个密钥生成器实例
KeyGenerator keyGenerator = KeyGenerator.getInstance(ALGORITHM);
SecureRandom random = new SecureRandom();
random.setSeed("123456".getBytes());//设置加密用的种子,密钥
keyGenerator.init(random);
SecretKey secretKey = keyGenerator.generateKey();
//把上面的密钥存起来
Path keyPath = Paths.get("D:/aes.key");
Files.write(keyPath, secretKey.getEncoded());
return secretKey;
} /**
* 读取存储的密钥
* @param keyPath
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
private SecretKey readKey(Path keyPath) throws Exception {
//读取存起来的密钥
byte[] keyBytes = Files.readAllBytes(keyPath);
SecretKeySpec keySpec = new SecretKeySpec(keyBytes, ALGORITHM);
return keySpec;
} /**
* 加密测试
*/
@Test
public void testEncrypt() throws Exception {
//1、指定算法、获取Cipher对象
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ALGORITHM);//算法是AES
//2、生成/读取用于加解密的密钥
SecretKey secretKey = this.geneKey();
//3、用指定的密钥初始化Cipher对象,指定是加密模式,还是解密模式
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, secretKey);
String content = "Hello AES";//需要加密的内容
//4、更新需要加密的内容
cipher.update(content.getBytes());
//5、进行最终的加解密操作
byte[] result = cipher.doFinal();//加密后的字节数组
//也可以把4、5步组合到一起,但是如果保留了4步,同时又是如下这样使用的话,加密的内容将是之前update传递的内容和doFinal传递的内容的和。
// byte[] result = cipher.doFinal(content.getBytes());
String base64Result = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(result);//对加密后的字节数组进行Base64编码
System.out.println("Result: " + base64Result);
} /**
* 解密测试
*/
@Test
public void testDecrpyt() throws Exception {
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ALGORITHM);
SecretKey secretKey = this.geneKey();
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, secretKey);
String content = "pK9Xw4zqTMXYraDadSGJE3x/ftrDxIg2AM/acq0uixA=";//经过Base64加密的待解密的内容
byte[] encodedBytes = Base64.getDecoder().decode(content.getBytes());
byte[] result = cipher.doFinal(encodedBytes);//对加密后的字节数组进行解密
System.out.println("Result: " + new String(result));
} } 1.5使用存储的密钥进行加解密示例 @Test
public void test() throws Exception {
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ALGORITHM);
KeyGenerator keyGenerator = KeyGenerator.getInstance(ALGORITHM);
keyGenerator.init(128);
SecretKey secretKey = keyGenerator.generateKey();
//把上面的密钥存起来
Path keyPath = Paths.get("D:/aes.key");
Files.write(keyPath, secretKey.getEncoded()); //读取存起来的密钥
SecretKey key = this.readKey(keyPath);
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, key);
cipher.update("Hello World".getBytes());
//密文
byte[] encryptBytes = cipher.doFinal();
System.out.println(Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(encryptBytes)); //用取出来的密钥进行解密
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, key);
//明文
byte[] decryptBytes = cipher.doFinal(encryptBytes);
System.out.println(new String(decryptBytes));
} 在上面的示例中,我们先生成了一个密钥,然后把它保存到本地文件中,然后再把它读出来,分别用以加密和解密。而且我们加密和解密都是用的同一个Cipher对象,但是在使用前需要重新通过init方法初始化加解密模式。
aes的总结
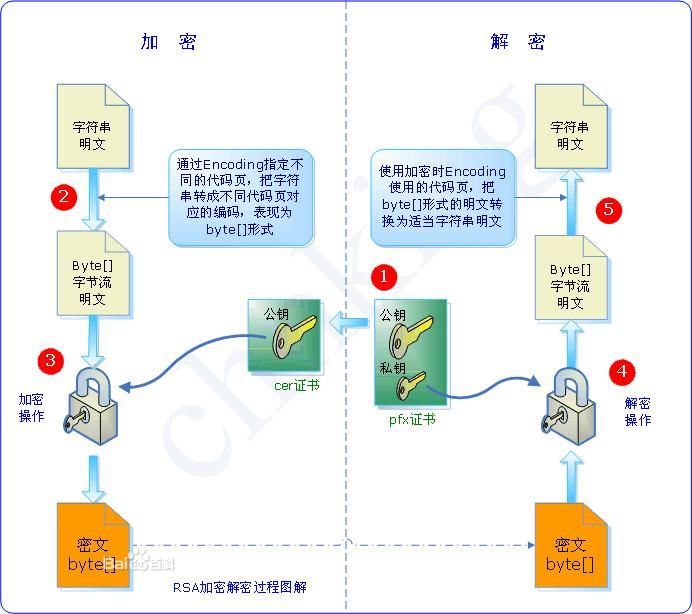
非对称加密例子:RSA非对称加密
流程如下:
秘钥生成工具类
package com.test; import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.security.Key;
import java.security.KeyPair;
import java.security.KeyPairGenerator;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import java.security.SecureRandom; import sun.misc.BASE64Encoder; public class RSAKEYUtil { /** 指定加密算法为RSA */
private static final String ALGORITHM = "RSA";
/** 密钥长度,用来初始化 */
private static final int KEYSIZE = 1024;
/** 指定公钥存放文件 */
private static String PUBLIC_KEY_FILE = "PublicKey";
/** 指定私钥存放文件 */
private static String PRIVATE_KEY_FILE = "PrivateKey"; public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
generateKeyPair();
genKeyPair();
} /**
* 生成密钥对
* @throws Exception
*/
private static void generateKeyPair() throws Exception { // /** RSA算法要求有一个可信任的随机数源 */
// SecureRandom secureRandom = new SecureRandom();
/** 为RSA算法创建一个KeyPairGenerator对象 */
KeyPairGenerator keyPairGenerator = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance(ALGORITHM); /** 利用上面的随机数据源初始化这个KeyPairGenerator对象 */
// keyPairGenerator.initialize(KEYSIZE, secureRandom);
keyPairGenerator.initialize(KEYSIZE); /** 生成密匙对 */
KeyPair keyPair = keyPairGenerator.generateKeyPair(); /** 得到公钥 */
Key publicKey = keyPair.getPublic(); /** 得到私钥 */
Key privateKey = keyPair.getPrivate(); ObjectOutputStream oos1 = null;
ObjectOutputStream oos2 = null;
try {
/** 用对象流将生成的密钥写入文件 */
oos1 = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(PUBLIC_KEY_FILE));
oos2 = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(PRIVATE_KEY_FILE));
oos1.writeObject(publicKey);
oos2.writeObject(privateKey);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw e;
} finally {
/** 清空缓存,关闭文件输出流 */
oos1.close();
oos2.close();
}
} private static void genKeyPair() throws NoSuchAlgorithmException { /** RSA算法要求有一个可信任的随机数源 */
SecureRandom secureRandom = new SecureRandom(); /** 为RSA算法创建一个KeyPairGenerator对象 */
KeyPairGenerator keyPairGenerator = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance(ALGORITHM); /** 利用上面的随机数据源初始化这个KeyPairGenerator对象 */
keyPairGenerator.initialize(KEYSIZE, secureRandom);
//keyPairGenerator.initialize(KEYSIZE); /** 生成密匙对 */
KeyPair keyPair = keyPairGenerator.generateKeyPair(); /** 得到公钥 */
Key publicKey = keyPair.getPublic(); /** 得到私钥 */
Key privateKey = keyPair.getPrivate(); byte[] publicKeyBytes = publicKey.getEncoded();
byte[] privateKeyBytes = privateKey.getEncoded(); String publicKeyBase64 = new BASE64Encoder().encode(publicKeyBytes);
String privateKeyBase64 = new BASE64Encoder().encode(privateKeyBytes); System.out.println("publicKeyBase64.length():" + publicKeyBase64.length());
System.out.println("publicKeyBase64:" + publicKeyBase64); System.out.println("privateKeyBase64.length():" + privateKeyBase64.length());
System.out.println("privateKeyBase64:" + privateKeyBase64);
}
}
公钥和私钥生成
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.security.Key;
import java.security.KeyFactory;
import java.security.PrivateKey;
import java.security.spec.PKCS8EncodedKeySpec; import javax.crypto.Cipher; import sun.misc.BASE64Decoder;
import sun.misc.BASE64Encoder; public class RSAUtil { /** 指定加密算法为RSA */
private static final String ALGORITHM = "RSA";
/** 指定公钥存放文件 */
private static String PUBLIC_KEY_FILE = "PublicKey";
/** 指定私钥存放文件 */
private static String PRIVATE_KEY_FILE = "PrivateKey"; public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { String source = "你好nihao";// 要加密的字符串
System.out.println("准备用公钥加密的字符串为:" + source); String cryptograph = encrypt(source);// 生成的密文
System.out.print("用公钥加密后的结果为:" + cryptograph);
System.out.println(); String target = decrypt(cryptograph);// 解密密文
System.out.println("用私钥解密后的字符串为:" + target);
System.out.println();
} /**
* 加密方法
* @param source 源数据
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public static String encrypt(String source) throws Exception { Key publicKey = getKey(PUBLIC_KEY_FILE); /** 得到Cipher对象来实现对源数据的RSA加密 */
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ALGORITHM);
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, publicKey);
byte[] b = source.getBytes();
/** 执行加密操作 */
byte[] b1 = cipher.doFinal(b);
BASE64Encoder encoder = new BASE64Encoder();
return encoder.encode(b1);
} /**
* 解密算法
* @param cryptograph 密文
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public static String decrypt(String cryptograph) throws Exception { Key privateKey = getKey(PRIVATE_KEY_FILE); /** 得到Cipher对象对已用公钥加密的数据进行RSA解密 */
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ALGORITHM);
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, privateKey);
BASE64Decoder decoder = new BASE64Decoder();
byte[] b1 = decoder.decodeBuffer(cryptograph); /** 执行解密操作 */
byte[] b = cipher.doFinal(b1);
return new String(b);
} /**
* 读取文件转化成key
* @param fileName
* @return
* @throws Exception
* @throws IOException
*/
private static Key getKey(String fileName) throws Exception, IOException {
Key key;
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
try {
/** 将文件中的私钥对象读出 */
ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(fileName));
key = (Key) ois.readObject();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw e;
} finally {
ois.close();
}
return key;
} /**
* 转化器 String 转 PrivateKey实体
* @param key
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public static PrivateKey getPrivateKey(String key) throws Exception {
byte[] keyBytes = (new BASE64Decoder()).decodeBuffer(key);;
PKCS8EncodedKeySpec keySpec = new PKCS8EncodedKeySpec(keyBytes);
KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance("RSA");
PrivateKey privateKey = keyFactory.generatePrivate(keySpec);
return privateKey;
} /**
* Rsa解密
* 解密算法
* @param cryptograph 密文
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public static String decryptByPrivateKey(byte[] cryptograph,String key) throws Exception {
Key privateKey = getPrivateKey(key);
/** 得到Cipher对象对已用公钥加密的数据进行RSA解密 */
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("RSA");
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, privateKey);
return new String(cipher.doFinal(cryptograph));
} }
加密解密过程
package me.andpay.ac.common.srv.idtag.bypay.util; import sun.misc.BASE64Decoder;
import sun.misc.BASE64Encoder; import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import java.security.*;
import java.security.interfaces.RSAPrivateKey;
import java.security.interfaces.RSAPublicKey;
import java.security.spec.PKCS8EncodedKeySpec;
import java.security.spec.X509EncodedKeySpec;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map; /**
* @author xiao bin
*/
public class RSACoder {
public static final String KEY_ALGORITHM = "RSA";
public static final String PUBLIC_KEY = "RSAPublicKey";
public static final String PRIVATE_KEY = "RSAPrivateKey"; private static final int KEY_SIZE = 512; // 私钥解密
public static byte[] decryptByPrivateKey(byte[] data, byte[] key)
throws Exception {
PKCS8EncodedKeySpec pkcs8KeySpec = new PKCS8EncodedKeySpec(key);
KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance(KEY_ALGORITHM);
PrivateKey privateKey = keyFactory.generatePrivate(pkcs8KeySpec);
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(keyFactory.getAlgorithm());
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, privateKey);
return cipher.doFinal(data);
}
// 私钥解密2
public static String decryptByPrivateKey(String data, String key)
throws Exception {
BASE64Decoder dec=new BASE64Decoder();
byte[] dataByte=decryptByPrivateKey(dec.decodeBuffer(data),dec.decodeBuffer(key));
return new String(dataByte);
}
// 公钥解密
public static byte[] decryptByPublicKey(byte[] data, byte[] key)
throws Exception {
X509EncodedKeySpec x509KeySpec = new X509EncodedKeySpec(key);
KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance(KEY_ALGORITHM);
PublicKey publicKey = keyFactory.generatePublic(x509KeySpec); Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(keyFactory.getAlgorithm());
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, publicKey); return cipher.doFinal(data);
}
// 公钥解密2
public static String decryptByPublicKey(String data, String key)
throws Exception {
BASE64Decoder dec=new BASE64Decoder();
byte[] dataByte=decryptByPublicKey(dec.decodeBuffer(data),dec.decodeBuffer(key));
return new String(dataByte);
}
// 公钥加密
public static byte[] encryptByPublicKey(byte[] data, byte[] key)
throws Exception {
X509EncodedKeySpec x509KeySpec = new X509EncodedKeySpec(key);
KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance(KEY_ALGORITHM);
PublicKey publicKey = keyFactory.generatePublic(x509KeySpec);
// 取摸和指数
// System.out.println("publicKey:"+publicKey);
// RSAPublicKey rsaPublicKey = (RSAPublicKey) publicKey;
// System.out.println(rsaPublicKey.getModulus().toString());
// System.out.println(rsaPublicKey.getPublicExponent().toString());
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(keyFactory.getAlgorithm());
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, publicKey);
return cipher.doFinal(data);
}
// 公钥加密2
public static String encryptByPublicKey(String data, String key)throws Exception {
BASE64Decoder dec=new BASE64Decoder();
BASE64Encoder enc=new BASE64Encoder();
byte[] signByte=encryptByPublicKey(data.getBytes("utf-8"),dec.decodeBuffer(key));
return enc.encode(signByte);
}
// 私钥加密
public static byte[] encryptByPrivateKey(byte[] data, byte[] key)
throws Exception {
PKCS8EncodedKeySpec pkcs8KeySpec = new PKCS8EncodedKeySpec(key);
KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance(KEY_ALGORITHM);
PrivateKey privateKey = keyFactory.generatePrivate(pkcs8KeySpec);
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(keyFactory.getAlgorithm());
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, privateKey);
return cipher.doFinal(data);
}
// 私钥加密2
public static String encryptByPrivateKey(String data, String key)
throws Exception {
BASE64Decoder dec=new BASE64Decoder();
BASE64Encoder enc=new BASE64Encoder();
byte[] signByte=encryptByPrivateKey(data.getBytes(),dec.decodeBuffer(key));
return enc.encode(signByte);
} //私钥验证公钥密文
public static boolean checkPublicEncrypt(String data,String sign,String pvKey)
throws Exception{
return data.equals(decryptByPrivateKey(sign,pvKey));
}
public static boolean checkPrivateEncrypt(String data,String sign,String pbKey)
throws Exception{
return data.equals(decryptByPublicKey(sign,pbKey));
}
//取得私钥
public static byte[]getPrivateKey(Map<String,Object> keyMap) throws Exception{
Key key=(Key)keyMap.get(PRIVATE_KEY);
return key.getEncoded();
}
//取得公钥
public static byte[]getPublicKey(Map<String,Object> keyMap) throws Exception{
Key key=(Key)keyMap.get(PUBLIC_KEY);
return key.getEncoded();
}
//初始化密钥
public static Map<String,Object> initKey() throws Exception{
KeyPairGenerator keyPairGen =KeyPairGenerator.getInstance(KEY_ALGORITHM); keyPairGen.initialize(KEY_SIZE); KeyPair keyPair=keyPairGen.generateKeyPair(); RSAPublicKey publicKey=(RSAPublicKey)keyPair.getPublic();
RSAPrivateKey privateKey=(RSAPrivateKey)keyPair.getPrivate(); Map<String,Object> keyMap =new HashMap<String,Object>(2);
keyMap.put(PUBLIC_KEY,publicKey);
keyMap.put(PRIVATE_KEY,privateKey);
return keyMap;
}
}
别人提供的工具类
加密数据结构实体
// 加密报文体格式:BASE64(商户号)| BASE64(RSA(报文加密密钥))| BASE64(3DES(报文原文))
/**
* 生成秘钥
* @return
*/
public byte[] genTDesKey(){
byte[] key = UUID.randomUUID().toString().getBytes();
return key;
}
加密算法--->对称加密与非对称加密算举例说明的更多相关文章
- https原理及其中所包含的对称加密、非对称加密、数字证书、数字签名
声明:本文章已授权公众号Hollis转载,如需转载请标明转载自https://www.cnblogs.com/wutianqi/p/10654245.html(安静的boy) 一.为什么要使用http ...
- android 对称加密,非对称加密 android 常见的加密
韩梦飞沙 韩亚飞 313134555@qq.com yue31313 han_meng_fei_sha android 常见的加密 ======== 不可逆加密:md5,sha1 可逆的加密中 ...
- 数字签名中公钥和私钥是什么?对称加密与非对称加密,以及RSA的原理
http://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1581684919791448393&wfr=spider&for=pc https://blog.csdn.net/ ...
- (转)对称加密与非对称加密,以及RSA的原理
一 概述 二对称加密和非对称加密 对称加密 非对称加密 区别 三RSA原理 整数运算 同余运算 当模数为合数n时 当模数为质数p的时候 离散对数问题 RSA原理 一 , 概述 在现代密码学诞生以前,就 ...
- 对称加密,非对称加密,数字签名,https
对称加密和非对称加密 对称加密 概念:加密秘钥和解密秘钥使用相同的秘钥(即加密和解密都必须使用同一个秘钥) 特点:一对一的双向保密通信(每一方既可用该秘钥加密,也可用该秘钥解密,非对称加密是多对一的单 ...
- https处理的一个过程,对称加密和非对称加密
一,对称加密 所谓对称加密,就是它们在编码时使用的密钥e和解码时一样d(e=d),我们就将其统称为密钥k. 对称加解密的过程如下: 发送端和接收端首先要共享相同的密钥k(即通信前双方都需要知道对应的密 ...
- Nginx系列6:对称加密与非对称加密各自的应用场景
强推:推荐一篇通俗易懂的对称加密和非对称加密的文章:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000004461428 推荐一篇文章:对称加密算法与非对称加密算法的优缺点:http ...
- 理解SSL、HTTPS原理中的对称加密与非对称加密
1.对称性加密 双方使用的同一个密钥,既可以加密又可以解密,这种加密方法称为对称加密,也称为单密钥加密. 简单来说就是:加密与解密都是同一个秘钥. 优点:通常在消息发送方需要加密大量数据时使用,算 ...
- 大话https演化过程(对称加密、非对称加密、公钥、私钥、数字签名、数字证书)
大话https演化过程(包括概念:对称加密.非对称加密.公钥.私钥.数字签名.数字证书.https访问全过程) 在网络上发送数据是非常不安全的,非常容易被劫持或是被篡改,所以每次定向发送数据你都可 ...
- 对称加密与非对称加密,以及RSA的原理
一 , 概述 在现代密码学诞生以前,就已经有很多的加密方法了.例如,最古老的斯巴达加密棒,广泛应用于公元前7世纪的古希腊.16世纪意大利数学家卡尔达诺发明的栅格密码,基于单表代换的凯撒密码.猪圈密码, ...
随机推荐
- catch异常
int ret = -1; try { ret = tBuyerCodeApplyInfoService.insertTBuyerCodeApplyInfoBySelective(buyerCode) ...
- MySql社区版和企业版的区别
1.社区版的免费,出问题MySql公司概不负责,是企业版的测试版,功能却没有企业版功能完善. 2.企业版的收费,并且价格不便宜,标准版2000美元,企业版5000美元,高级集群版10000美元(6万人 ...
- Open JDk 源码下载地址
OpenJDK 和Oracle JDK 共用了大量相同的代码,在性能.功能和执行逻辑上都和Oracle JDK非常一致,由于 现在Oracle JDK是闭源的,我们可以下载Open JDK的源码来研究 ...
- 【读】为什么BIO效率低下
原因: 假如有10000个连接,4核CPU ,那么bio 就需要一万个线程,而nio大概就需要5个线程(一个接收请求,四个处理请求).如果这10000个连接同时请求,那么bio就有10000个线程抢四 ...
- Eclipse发布的Dynamical web项目在Tomacat文件夹下显示
Eclipse设置了Tomacat后,项目信息会在你的workspace上,在Tomacat文件夹上是没有的.但是通过设置是可以在Tomacat文件夹上存在的. 配置好服务器后,先关闭服务器,然后在E ...
- MYSQL与MSSQL对比学习
最近在将公司的一个产品里面相关的MSSQL语句修改为可以在MYSQL上执行的语句 l 优点分析: MYSQL短小精悍,容易上手,操作简单,免费供用的.相对其它数据库有特色又实用的语法多一些.SQL怎 ...
- java设计模式-----18、职责链模式
概念: Chain of Responsibility(CoR)模式也叫职责链模式.责任链模式或者职责连锁模式,是行为模式之一,该模式构造一系列分别担当不同的职责的类的对象来共同完成一个任务,这些类的 ...
- Csv读写类
<?php /** * CSV 文件读写类 * * 示例: $header = array('name' => '名字', 'age' =>'年龄', 'idcard' => ...
- nginx的MainLine version、Stable version、Legacy versions
Nginx的版本说明Mainline version:在线版本,正处于开发状态Stable version :稳定版本(一般下载使用)Legacy version :遗留版本,遗留的老的版本 Linu ...
- 为样式找到应用目标-CSS选择器
1,常用选择器:元素(标签/简单)选择器.ID选择器.类选择器.后代选择器(可以将类或者ID应用于它们的祖先,然后使用后代选择器来定位) 2,伪类:有时候,我们需要根据文档结构之外的其他条件对元素应用 ...