【cs231n】图像分类-Nearest Neighbor Classifier(最近邻分类器)【python3实现】
【学习自CS231n课程】
转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/GraceSkyer/p/8735908.html
图像分类:
一张图像的表示:长度、宽度、通道(3个颜色通道,分别是红R、绿G、蓝B)。
对于计算机来说,图像是一个由数字组成的巨大的三维数组,数组元素是取值范围从0到255的整数,其中0表示全黑,255表示全白。
图像分类的任务:对于一个给定的图像,预测它属于的那个分类标签。
如何写图像分类算法呢?
数据驱动方法:
图像分类流程:
图像分类:输入一个元素为像素值的数组,然后给它分配一个分类标签。完整流程如下:
- 输入:输入是包含N个图像的集合,每个图像的标签是K种分类标签中的一种。这个集合称为训练集。
- 学习:这一步的任务是使用训练集来学习每个类到底长什么样。一般该步骤叫做训练分类器或者学习一个模型。
- 评价:让分类器来预测它未曾见过的图像的分类标签,并以此来评价分类器的质量。我们会把分类器预测的标签和图像真正的分类标签对比。毫无疑问,分类器预测的分类标签和图像真正的分类标签如果一致,那就是好事,这样的情况越多越好。
Nearest Neighbor Classifier
最简单的分类器......
最近邻算法:在训练机器的过程中,我们什么也不做,我们只是单纯记录所有的训练数据,在图片预测的步骤,我们会拿一些新的图片去在训练数据中寻找与新图片最相似的,然后基于此,来给出一个标签。
例:用最近邻算法用于这数据集中的图片,在训练集中找到最接近的样本:图像分类数据集:CIFAR-10
这个数据集包含了60000张32X32的小图像。每张图像都有10种分类标签中的一种。这60000张图像被分为包含50000张图像的训练集和包含10000张图像的测试集。
我们需要的是,输入一张测试图片,从训练集中找出与它L1距离最近的一张训练图,将其所对应的分类标签作为答案,也就是作为测试图片的分类标签。
下面,让我们看看如何用代码来实现这个分类器。首先,我们将CIFAR-10的数据加载到内存中,并分成4个数组:训练数据和标签,测试数据和标签。在下面的代码中,Xtr(大小是50000x32x32x3)存有训练集中所有的图像,Ytr是对应的长度为50000的1维数组,存有图像对应的分类标签(从0到9):
Xtr, Ytr, Xte, Yte = load_CIFAR10('data/cifar10/') # a magic function we provide
# flatten out all images to be one-dimensional
Xtr_rows = Xtr.reshape(Xtr.shape[0], 32 * 32 * 3) # Xtr_rows becomes 50000 x 3072
Xte_rows = Xte.reshape(Xte.shape[0], 32 * 32 * 3) # Xte_rows becomes 10000 x 3072
现在我们得到所有的图像数据,并且把他们拉长成为行向量了。接下来展示如何训练并评价一个分类器:
nn = NearestNeighbor() # create a Nearest Neighbor classifier class
nn.train(Xtr_rows, Ytr) # train the classifier on the training images and labels
Yte_predict = nn.predict(Xte_rows) # predict labels on the test images
# and now print the classification accuracy, which is the average number
# of examples that are correctly predicted (i.e. label matches)
print 'accuracy: %f' % ( np.mean(Yte_predict == Yte) )
作为评价标准,我们常常使用准确率,它描述了我们预测正确的得分。请注意以后我们实现的所有分类器都需要有这个API:train(X, y)函数。该函数使用训练集的数据和标签来进行训练。从其内部来看,类应该实现一些关于标签和标签如何被预测的模型。这里还有个predict(X)函数,它的作用是预测输入的新数据的分类标签。
L1距离(即两尺寸相同图对应位置间差异的和):
完整代码:
Python3 实现:【使用L1距离的Nearest Neighbor分类器】
【我是将cifar-10-batches-py数据放在代码同一目录下,代码中具体文件位置请根据情况自行设置】
import numpy as np
import pickle
import os class NearestNeighbor(object):
def __init__(self):
pass def train(self, X, y):
""" X is N x D where each row is an example. Y is 1-dimension of size N """
# the nearest neighbor classifier simply remembers all the training data
self.Xtr = X
self.ytr = y def predict(self, X):
""" X is N x D where each row is an example we wish to predict label for """
num_test = X.shape[0]
# lets make sure that the output type matches the input type
Ypred = np.zeros(num_test, dtype=self.ytr.dtype) # loop over all test rows
for i in range(num_test):
# find the nearest training image to the i'th test image
# using the L1 distance (sum of absolute value differences)
distances = np.sum(np.abs(self.Xtr - X[i, :]), axis=1)
min_index = np.argmin(distances) # get the index with smallest distance
Ypred[i] = self.ytr[min_index] # predict the label of the nearest example return Ypred def load_CIFAR_batch(file):
""" load single batch of cifar """
with open(file, 'rb') as f:
datadict = pickle.load(f, encoding='latin1')
X = datadict['data']
Y = datadict['labels']
X = X.reshape(10000, 3, 32, 32).transpose(0, 2, 3, 1).astype("float")
Y = np.array(Y)
return X, Y def load_CIFAR10(ROOT):
""" load all of cifar """
xs = []
ys = []
for b in range(1,6):
f = os.path.join(ROOT, 'data_batch_%d' % (b, ))
X, Y = load_CIFAR_batch(f)
xs.append(X)
ys.append(Y)
Xtr = np.concatenate(xs) # 使变成行向量
Ytr = np.concatenate(ys)
del X, Y
Xte, Yte = load_CIFAR_batch(os.path.join(ROOT, 'test_batch'))
return Xtr, Ytr, Xte, Yte Xtr, Ytr, Xte, Yte = load_CIFAR10('data/cifar-10-batches-py/') # a magic function we provide
# flatten out all images to be one-dimensional
Xtr_rows = Xtr.reshape(Xtr.shape[0], 32 * 32 * 3) # Xtr_rows becomes 50000 x 3072
Xte_rows = Xte.reshape(Xte.shape[0], 32 * 32 * 3) # Xte_rows becomes 10000 x 3072 nn = NearestNeighbor() # create a Nearest Neighbor classifier class
nn.train(Xtr_rows, Ytr) # train the classifier on the training images and labels
Yte_predict = nn.predict(Xte_rows) # predict labels on the test images
# and now print the classification accuracy, which is the average number
# of examples that are correctly predicted (i.e. label matches)
print('accuracy: %f' % (np.mean(Yte_predict == Yte)))
然后我运行了很久......几个小时?
运行结果:accuracy: 0.385900
若用L2距离(欧式距离):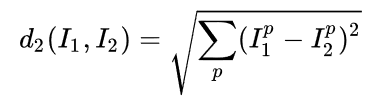
修改上面代码1行就可以:
distances = np.sqrt(np.sum(np.square(self.Xtr - X[i,:]), axis = 1))
关于简单分类器的问题:
- 如果我们有N个实例,训练和测试的过程可以有多快?
- Train:O(1),predict:O(n)
这是糟糕的。训练是连续的过程,因为我们并不需要做任何事情, 我们只需存储数据。但在测试时,我们需要停下来,将数据集中N个训练实例 与我们的测试图像进行比较,这是个很慢的过程。
但是在实际使用中,我们希望训练过程比较慢,而测试过程快。因为,训练过程是在数据中心中完成的,它可以负担起非常大的运算量,从而训练出一个优秀的分类器。 然而,当你在测试过程部署分类器时,你希望它运行在手机上、浏览器、或其他低功耗设备,但你又希望分类器能够快速地运行,由此看来,最近邻算法有点落后了。。。
参考:
https://www.bilibili.com/video/av17204303/?from=search&seid=6625954842411789830
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/20894041?refer=intelligentunit
https://blog.csdn.net/dawningblue/article/details/75119639
https://www.cnblogs.com/hans209/p/6919851.html
【cs231n】图像分类-Nearest Neighbor Classifier(最近邻分类器)【python3实现】的更多相关文章
- 【cs231n】图像分类 k-Nearest Neighbor Classifier(K最近邻分类器)【python3实现】
[学习自CS231n课程] 转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/GraceSkyer/p/8763616.html k-Nearest Neighbor(KNN)分类器 与其 ...
- CS231n——图像分类(KNN实现)
图像分类 目标:已有固定的分类标签集合,然后对于输入的图像,从分类标签集合中找出一个分类标签,最后把分类标签分配给该输入图像. 图像分类流程 输入:输入是包含N个图像的集合,每个图像的标签是K ...
- cs231n笔记 (一) 线性分类器
Liner classifier 线性分类器用作图像分类主要有两部分组成:一个是假设函数, 它是原始图像数据到类别的映射.另一个是损失函数,该方法可转化为一个最优化问题,在最优化过程中,将通过更新假设 ...
- Nearest neighbor graph | 近邻图
最近在开发一套自己的单细胞分析方法,所以copy paste事业有所停顿. 实例: R eNetIt v0.1-1 data(ralu.site) # Saturated spatial graph ...
- Approximate Nearest Neighbors.接近最近邻搜索
(一):次优最近邻:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nearest_neighbor_search 有少量修改:如有疑问,请看链接原文.....1.Survey:Neares ...
- K Nearest Neighbor 算法
文章出处:http://coolshell.cn/articles/8052.html K Nearest Neighbor算法又叫KNN算法,这个算法是机器学习里面一个比较经典的算法, 总体来说KN ...
- Visualizing MNIST with t-SNE, MDS, Sammon’s Mapping and Nearest neighbor graph
MNIST 可视化 Visualizing MNIST: An Exploration of Dimensionality Reduction At some fundamental level, n ...
- Nearest Neighbor Search
## Nearest Neighbor Search ## Input file: standard input Output file: standard output Time limit: 1 ...
- K NEAREST NEIGHBOR 算法(knn)
K Nearest Neighbor算法又叫KNN算法,这个算法是机器学习里面一个比较经典的算法, 总体来说KNN算法是相对比较容易理解的算法.其中的K表示最接近自己的K个数据样本.KNN算法和K-M ...
随机推荐
- ES6新特性:var与let区别
1.let的用法类似于var,但是所声明的变量,只在let命令所在的代码块内有效.var定义的变量为全局变量. 2.var在同一块可以重复定义,let不能 //正常 function () { var ...
- .net core 2.2 部署CentOS7(1)安装虚拟机
目录: .net core 2.2 部署CentOS7(1)安装虚拟机 .net core 2.2 部署CentOS7(2)给虚拟机安装CentOS7 .net core 2.2 部署CentOS7( ...
- hdu 4090
GemAnd Prince Time Limit: 10000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)To ...
- zookeeper 典型应用
一.发布/订阅 配置文件的集中管理. 问题:当分布式系统变多后,每个系统保存相应的配置文件,会造成同个文件有多份,修改起来非常麻烦. 解决方法:使用zk的发布/订阅功能,配合Watcher机制,在应用 ...
- java设计模式-----13、组合模式
Composite模式也叫组合模式,是构造型的设计模式之一.通过递归手段来构造树形的对象结构,并可以通过一个对象来访问整个对象树. 组合(Composite)模式的其它翻译名称也很多,比如合成模式.树 ...
- 无法正常下载Nuget 包的问题
引用Nuget 是遇到的问题,再次记录一下. 问题描述:Install-Package : 无法安装程序包“Quartz 3.0.2”.您正在尝试将此程序包安装到某个将“.NETFramework,V ...
- 利用c#自带的类对文件进行压缩和解压处理
在做网络传输文件的小例子的时候,当传输的文件比较大的时候,我们通常都是将文件经过压缩之后才进行传输,以前都是利用第三方插件来对文件进行压缩的,但是现在我发现了c#自带的类库也能够实现文件的压缩,实际上 ...
- HTML5 MutationObserver检测页面劫持
好久没写博客了,业务一直在变化,陆陆续续的做了很多web app,被业务流淹没就很少有机会去反思,前端技术发展如此之快,常常有种不学则退的恐慌,一种技术还没吃透就涌出新的技术,然后一波人又打着各种旗帜 ...
- css过渡笔记
3D http://fangyexu.com/tool-CSS3Inspector.html <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" ...
- p2p手机绑定
本文工具类 http://www.cnblogs.com/jokerq/p/8590498.html 1.需求分析 2.设计分析 3.前台页面(freemarker) <script t ...
