[ACM International Collegiate Programming Contest, Amman Collegiate Programming Contest (2018)]
2.5 s
256 MB
standard input
standard output
There are consecutive buildings numbered from 1 to 109 each of which has an amount of money in it. The money is given in the form of mnon-overlapping segments, in which each segment i has 3 values: li, ri, and vi, meaning that each building with number x (li ≤ x ≤ ri) has vi amount of money.
A thief came to rob the city, however, this thief does not want to get caught, so he can only rob at most k consecutive buildings, such that if he starts robbing buildings from building z, he can rob all buildings in the range 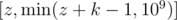 inclusive.
inclusive.
Your task is to find the maximum amount of money the thief can collect. Can you?
The first line contains an integer T (1 ≤ T ≤ 100) specifying the number of test cases.
The first line of each test case contains two integers m and k (1 ≤ m ≤ 1e5, 1 ≤ k ≤ 1e9), in which m is the number money segments, and k is the maximum number of consecutive buildings the thief can rob.
Then m lines follow, giving the description of money segments. Each segment i is represented by 3 integers li, ri and vi (1 ≤ li ≤ ri ≤ 1e9, 1 ≤ vi ≤ 1e9), in which li and ri are the boundaries of the segment, and vi is the amount of money in each building in that segment.
The sum of m overall test cases does not exceed 2 × 1e6.
For each test case, print a single line containing the maximum amount of money the thief can collect by robbing at most k consecutive buildings.
1
2 5
1 5 1
7 11 1
5
题意:数轴上有1e9个点,有n(1e5)个区间,每个区间内所有点有一个相同的值ai,你可以从任意一个点开始取连续的k个数,求最大总值。
题解:易知,总值最大时的取法一定是起点在某个区间的起点或者终点在某个区间的终点(因为如果不这样取,总可以通过向左或向右移动得到更优的解),而区间的个数是1e5的数量级,所以可以直接枚举区间起点利用二分找到相应终点求出一个最优解,再通过直接枚举区间终点利用二分找到相应起点来求出另一个最优解,取二者最小值即可。
注意一些细节即可。(使用lowerbound和upperbound时注意数组边界)
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
struct edge{
ll l;
ll r;
ll val;
}e[];
ll sum[];
ll id[],id2[];
bool cmp(struct edge aa,struct edge bb){
return aa.l<bb.l;
}
int main(){
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--){
ll m,k;
scanf("%lld%lld",&m,&k);
for(int i=;i<=m;i++)scanf("%lld%lld%lld",&e[i].l,&e[i].r,&e[i].val);
sort(e+,e++m,cmp);
for(int i=;i<=m;i++){
sum[i]=sum[i-]+e[i].val*(e[i].r-e[i].l+);
id[i]=e[i].r;
id2[m-i+]=-e[i].l;
}
/*
1
2 5
1 4 2
6 7 1
*/
ll ans=;
for(int i=;i<=m;i++){
int xx=lower_bound(id+,id++m,e[i].l+k-)-id;
//cout<<xx<<endl;
ll s=sum[xx-]-sum[i-];
if(xx<=m)s+=(max(0ll,min(e[i].l+k-,id[xx])-e[xx].l+))*e[xx].val;
ans=max(s,ans);
}
for(int i=m;i>=;i--){
int xx=lower_bound(id2+,id2++m,-e[i].r+k-)-id2;
ll s=sum[i]-sum[m-(xx-)];
if(xx<=m)s+=max(0ll,(min(-e[i].r+k-,id2[xx])-(-e[m-xx+].r)+))*e[m-xx+].val;
ans=max(s,ans);
}
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
return ;
}
1.0 s
256 MB
standard input
standard output
Abood's birthday has come, and his n friends are aligned in a single line from 1 to n, waiting for their cookies, Abood has x cookies to give to his friends.
Here is an example to understand how Abood gives away the cookies. Suppose Abood has 4 friends and x cookies, then Abood will do the following:
- Give a cookie to the 1st friend.
- Give a cookie to the 2nd friend.
- Give a cookie to the 3rd friend.
- Give a cookie to the 4th friend.
- Give a cookie to the 3rd friend.
- Give a cookie to the 2nd friend.
- Give a cookie to the 1st friend.
- Give a cookie to the 2nd friend.
- And so on until all the x cookies are given away.
Your task is to find how many cookies each friend will get. Can you?
The first line contains an integer T (1 ≤ T ≤ 100) specifying the number of test cases.
Each test case consists of a single line containing two integers x and n (1 ≤ x ≤ 1e18, 1 ≤ n ≤ 1000), in which x is the number of cookies Abood has, and n is the number of his friends.
For each test case, print a single line containing n space-separated integers a1, ..., an, in which ai represents how many cookies the ithfriend got.
1
5 3
2 2 1
题意:按题目要求分饼干。
题解:按要求模拟即可
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
ll a[];
int main(){
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--){
ll x,n;
scanf("%lld%lld",&x,&n);
if(n==){
printf("%lld\n",x);
}
else{if(x<=n){
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){
int s=(i<=x);
printf("%d",s);
char cc=(i==n)?'\n':' ';
printf("%c",cc);
}
}
else{
x-=n;
ll q=x/(n-);
if(q%){
a[]=((q+)/)+;
a[n]=(q/)+;
for(int i=;i<=+x%(n-);i++){
a[i]=q+;
}
for(int i=+x%(n-);i<=n-;i++){
a[i]=q+;
}
}
else{
a[]=((q)/)+;
a[n]=(q/)+;
for(int i=n-;i>=n-x%(n-);i--){
a[i]=q+;
}
for(int i=n-x%(n-)-;i>=;i--){
a[i]=q+;
}
}
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){
printf("%lld",a[i]);
char cc=(i==n)?'\n':' ';
printf("%c",cc);
}
}
}
}
return ;
}
1.0 s
256 MB
standard input
standard output
You are given a positive integer n. Your task is to build a number m by flipping the minimum number of bits in the binary representation of nsuch that m is less than n (m < n) and it is as maximal as possible. Can you?
The first line contains an integer T (1 ≤ T ≤ 1e5) specifying the number of test cases.
Each test case consists of a single line containing one integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 1e9), as described in the statement above.
For each test case, print a single line containing the minimum number of bits you need to flip in the binary representation of n to build the number m.
2
5
10
1
2
题意:求x与x-1二进制下的不同数位的个数。
题解:异或之后直接求即可
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
ll a[];
int main(){
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--){
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
int k=(n-)^n;
int ans=;
while(k){
if(k&)ans++;
k/=;
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
return ;
}
1.0 s
256 MB
standard input
standard output
You are given a n × m grid, your goal is to find a group of lines such that the following conditions are met:
- No two lines are touching.
- Each cell in the grid has one of its sides covered by at least one line in the group.
A line is a border of a cell in the grid with length 1. Each cell has 4 lines covering every side of it. Every pair of neighboring cells shares a line. Two lines are touching if they meet at their ends.
The size of a group of lines is the number of lines it contains. Your task is to find the minimum size of a group of lines that meet all the conditions above. Can you?
The first line contains an integer T (1 ≤ T ≤ 128) specifying the number of test cases.
Each test case consists of a single line containing two integers n and m (1 ≤ n ≤ 1e9, 1 ≤ m ≤ 1024), giving a grid of size n × m.
For each test case, print a single line containing the minimum size of a group of lines that meet all the conditions in the statement above.
1
4 4
10
题意:一个n*m的矩形,里面一共有n*m个格子,要求每个格子至少一条边被标记,并且所有被标记的边不能相交,求最少要标记多少边。
题解:这个我完全是画出样例的情形图之后猜公式..
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int mod=1e9+;
ll n,m;
ll sol(ll n,ll m){
return n*((m+)/)+((m+)%)*((n)/);
}
int main(){
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--){
scanf("%lld%lld",&n,&m); ll xx=min(sol(n,m),sol(m,n));
printf("%lld\n",xx); }
return ;
}
2.5 s
256 MB
standard input
standard output
You are given an n-dimensional grid in which the dimensions of the grid are a1 × a2 × ... × an. Each cell in the grid is represented as an n-tuple (x1, x2, ..., xn) (1 ≤ xi ≤ ai).
Two cells are considered to be adjacent if the Manhattan Distance between them is equal to 1. The Manhattan Distancebetween two cells X(x1, x2, ..., xn) and Y(y1, y2, ..., yn) is equal to: |x1 - y1| + |x2 - y2| + ... + |xn - yn|.
Your task is to count how many pairs of cells are adjacents. Can you? Two pairs of cells are considered the same if they include the same cells, i.e the pair (c1, c2) is the same as (c2, c1).
The first line contains an integer T (1 ≤ T ≤ 100) specifying the number of test cases.
The first line of each test case contains an integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 1e5), in which n is the number of dimensions of the grid. Then a line follows containing n integers a1, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 1e5), in which ai is the size of the ith dimension.
The sum of n overall test cases does not exceed 6 × 1e6.
For each test case, print a single line containing the number of pairs of adjacent cells modulo 1e9 + 7.
1
3
1 2 3
7
The absolute value |x| of a real number x is the non-negative value of x without regard to its sign. Namely, |x| = x for a positive x, |x| = - xfor a negative x (in which case - x is positive), and |0| = 0. For example, the absolute value of 3 is 3, and the absolute value of - 3 is also 3. The absolute value of a number may be thought of as its distance from zero.
题意:一共n个数列,每个数列中都有ai个值,分别为1,2,3...ai,在每个数列中选两个值分别放到两个队列中,则最后两个队列中各有n个值,要求最后两个队列的对应元素相减的绝对值之和=1,求总情况数%1e9+7.
题解:由于绝对值之和的最后结果需要=1,所以只能是两个队列某个位置的差值为1(每个数列有ai-1种情况),其他对应元素值为0(每个数列有ai种情况),所以共有$\sum_{i=1}^n$(($\sum_{j=1}^n$aj)/ai*(ai-1))种方案,求解过程可以先计算出($\sum_{j=1}^n$aj)%mod,然后*mypow(aj,mod-2)求出结果,注意这题会卡常..用long long会超时,改成int就过了
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int mod=1e9+;
int a[],in[];
ll mypow(ll x,int y){
ll ans=;
while(y){
if(y&)ans=ans*x%mod;
x=x*x%mod;
y/=;
}
return ans;
}
int main(){
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--){
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
ll ak=;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
in[a[i]]++;
ak=ak*a[i]%mod;
}
ll ans=;
sort(a+,a++n);
int k=unique(a+,a++n)-a-;
for(int i=;i<=k;i++){
ans=(ans+in[a[i]]*(ak*mypow((long long)a[i],mod-)%mod*(a[i]-)%mod)%mod)%mod;
in[a[i]]=;
}
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
return ;
}
2.5 s
256 MB
standard input
standard output
You are given an array a consisting of n integers a1, ..., an. In one operation, you can choose 2 elements ai and aj in which ai is divisible by aj and transform ai to aj.
A number x is said to be divisible by a number y if x can be divided by y and the result is an exact whole number. For example, 15 is divisible by 3, because 15÷ 3 = 5 exactly, but 9 is not divisible by 2 because 9÷ 2 is 4 with 1 left over.
Your task is to find the minimum sum of the array a that can be obtained by making as many transform operations as you want. Can you?
The first line contains an integer T (1 ≤ T ≤ 100) specifying the number of test cases.
The first line of each test case contains an integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 1e5), in which n is the size of array a. Then a line follows containing nintegers a1, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 1e6), giving array a.
The sum of n overall test cases does not exceed 3 × 1e6.
For each test case, print a single line containing the minimum sum of the array a that can be obtained after making as many transform operations as you want.
1
5
2 2 3 6 6
11
题意:给一个数组,规定如果ai%aj==0,那么可以将ai变成aj,求最后得到的数组的总和最小值
题解:用类似于筛素数的方法,可以在($\sum_{i=1}^n$(1/i))*n的复杂度内完成,而($\sum_{i=1}^n$(1/i))*n,近似等于nlogn
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
ll a[],b[],c[];
int main(){
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--){
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){
scanf("%lld",&a[i]);
b[a[i]]=a[i];
c[i]=a[i];
}
sort(a+,a++n);
int k=unique(a+,a++n)-(a+);
for(int i=;i<=k;i++){
for(int j=a[i];j<=a[k];j+=a[i]){
if(b[j]==j)b[j]=b[a[i]];
}
}
ll ans=;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){
ans+=b[c[i]];
//cout<<a[i]<<endl;
}
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
return ;
}
1.0 s
256 MB
standard input
standard output
Ali is trying to make his friends happier by matching them into pairs together. In the beginning, Ali has 2 × n friends standing in a row and numbered from 1 to 2 × n. Each friend i will be matched with the friend numbered (2 × n - i + 1).
Each friend i has a happiness level equal to hi. The happiness level of a matched pair of friends i and (2 × n - i + 1) is equal to hi + h2 × n - i + 1.
Your task is to find the maximum happiness level of a pair among all matched pairs. Can you?
The first line contains an integer T (1 ≤ T ≤ 50) specifying the number of test cases.
The first line of each test case contains an integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 1000), giving that Ali has 2 × n friends. Then a line follows containing 2 × nintegers h1, ..., h2 × n (1 ≤ hi ≤ 1000), in which hi represents the happiness level of the ith friend.
For each test case, print a single line containing the maximum happiness level of a pair among all matched pairs.
1
3
2 4 5 6 7 8
11
题解:签到
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int a[];
int main(){
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--){
int n;
int ans=;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=;i<=*n;i++){
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
if(i>n){
ans=max(a[i]+a[*n-i+],ans);
}
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
return ;
}
1.0 s
256 MB
standard input
standard output
You are given an integer x. Your task is to split the number x into exactly n strictly positive integers such that the difference between the largest and smallest integer among them is as minimal as possible. Can you?
The first line contains an integer T (1 ≤ T ≤ 100) specifying the number of test cases.
Each test case consists of a single line containing two integers x and n (1 ≤ x ≤ 109, 1 ≤ n ≤ 1000), as described in the statement above.
For each test case, print a single line containing n space-separated integers sorted in a non-decreasing order. If there is no answer, print - 1.
1
5 3
1 2 2
题解:签到
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int a[];
int main(){
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--){
int n,x;
scanf("%d%d",&x,&n);
if(x<n){
printf("-1\n");
}
else{
int s=x/n;
int m=x%n;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){
int ss=s+(n-i+<=m);
printf("%d",ss);
char cc=(i==n)?'\n':' ';
printf("%c",cc); }
}
}
return ;
}
4.0 s
256 MB
standard input
standard output
You are given n islands numbered from 1 to n and connected using n - 1 magical bridges. A greedy pirate wants to collect as many coins as possible by traveling through the bridges. Each bridge is a two-way bridge, but the pirate can only use the bridge at most twice. If a bridge connects islands u and v, then going from u to v gives c1 coins, and going from v to u gives c2.
Help the pirate to collect as many coins as he can knowing that he will start from some island x and finish at some island y.
The first line contains an integer T (1 ≤ T ≤ 100) specifying the number of test cases.
The first line of each test case contains one integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 105), in which n is the number of islands. The n - 1 lines follow, giving the bridges. Each line contains four integers u, v, c1, and c2 (1 ≤ u, v ≤ n, 1 ≤ c1, c2 ≤ 104), as describing in the statement above.
The next line contains an integer q (1 ≤ q ≤ 105), in which q is the number of queries. Then q lines follow, giving queries. Each query consists of two integers x and y (1 ≤ x, y ≤ n), in which x and y are the starting and finish islands, respectively.
The sum of n and q overall test cases does not exceed 25 × 105 for each.
For each query, print a single line containing the maximum amount of money the greedy pirate can collect by traveling through the bridges starting from island x and finishing at island y.
1
5
1 2 5 10
3 5 25 3
4 2 15 12
3 2 6 7
2
1 5
4 3
64
65
题意:给一棵树,树边u->v和v->u的权值不一样,每条边最多经过两次,有q次询问,求从u到v走过的权值和的最大值
题解:树上两点的距离关系,可以想到使用LCA求解,因为每条边最多走两次,所以从u到v的路径只能向前移动,而不能后退,所以也就是从u到v的路径只能走一次,所以结果就=所有边的权值和-从v到u的路径权值和,用LCA很容易得到结果
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int mod=1e9+;
const int maxn=1e5+;
struct edge{
int x;
int y;
int nex;
int v1;
int v2;
}e[maxn<<];
int cnt,head[maxn],dis1[maxn],dis2[maxn];
void adde(int x1,int y1,int z1,int c1){
e[cnt].x=x1;
e[cnt].y=y1;
e[cnt].v1=z1;
e[cnt].v2=c1;
e[cnt].nex=head[x1];
head[x1]=cnt++;
}
struct pot{
int xzc;
int aq;
};
vector<struct pot>query[maxn];
vector<int>num[maxn];
int vis[maxn],ans[maxn],fa[maxn];
void init(int n)
{
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){dis1[i]=dis2[i]=;fa[i]=i;vis[i]=;num[i].clear();query[i].clear();}
}
int finds(int x)
{
int xx=x;
while(fa[x]!=x)
{
x=fa[x];
}
while(fa[xx]!=x)
{
int t=fa[xx];
fa[xx]=x;
xx=t;
}
return x;
}
void Union(int x,int y)
{
int xx=finds(x);
int yy=finds(y);
if(xx!=yy);
fa[yy]=xx;//在完成子节点的Tarjan遍历之后,把子节点纳入父节点名下
}
void Tarjan(int u,int a1,int a2)
{
vis[u]=;
dis1[u]=a1;
dis2[u]=a2;
for(int i=head[u] ; i != - ;i=e[i].nex)
{
int v=e[i].y;
if(vis[v])continue;
Tarjan(v,e[i].v1+a1,e[i].v2+a2);
Union(u,v);
}
for(int i = ; i < query[u].size() ; i++)
{
if(vis[query[u][i].aq])
{
if(query[u][i].xzc)
ans[num[u][i]]=dis2[query[u][i].aq]+dis1[u]-dis1[finds(query[u][i].aq)]-dis2[finds(query[u][i].aq)];
else
ans[num[u][i]]=dis1[query[u][i].aq]+dis2[u]-dis1[finds(query[u][i].aq)]-dis2[finds(query[u][i].aq)];
// cout<<ans[num[u][i]]<<query[u][i].aq<<" "<<dis2[query[u][i].aq]<<dis1[u]<<"####"<<endl;
}
}
}
int main(){
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--){
int n;
cnt=;
int sum=;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)head[i]=-;
for(int i=;i<=n-;i++){
int a,b,c,d;
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c,&d);
adde(a,b,d,c);
adde(b,a,c,d);
sum+=c+d;
}
init(n);
int q;
scanf("%d",&q);
for(int i=;i<=q;i++){
int a,b;
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
struct pot aa;
aa.aq=b;
aa.xzc=;
query[a].push_back(aa);
struct pot bb;
bb.aq=a;
bb.xzc=;
query[b].push_back(bb);
num[a].push_back(i);
num[b].push_back(i);
}
Tarjan(,,);
for(int i=;i<=q;i++){
printf("%d\n",sum-ans[i]);
} }
return ;
}
[ACM International Collegiate Programming Contest, Amman Collegiate Programming Contest (2018)]的更多相关文章
- GYM101810 ACM International Collegiate Programming Contest, Amman Collegiate Programming Contest (2018) M. Greedy Pirate (LCA)
题意:有\(n\)个点,\(n-1\)条边,每条边正向和反向有两个权值,且每条边最多只能走两次,有\(m\)次询问,问你从\(u\)走到\(v\)的最大权值是多少. 题解:可以先在纸上画一画,不难发现 ...
- ACM International Collegiate Programming Contest World Finals 2014
ACM International Collegiate Programming Contest World Finals 2014 A - Baggage 题目描述:有\(2n\)个字符摆在编号为\ ...
- ACM International Collegiate Programming Contest World Finals 2013
ACM International Collegiate Programming Contest World Finals 2013 A - Self-Assembly 题目描述:给出\(n\)个正方 ...
- ACM International Collegiate Programming Contest, Tishreen Collegiate Programming Contest (2018) Syria, Lattakia, Tishreen University, April, 30, 2018
ACM International Collegiate Programming Contest, Tishreen Collegiate Programming Contest (2018) Syr ...
- ACM International Collegiate Programming Contest, Tishreen Collegiate Programming Contest (2017)- K. Poor Ramzi -dp+记忆化搜索
ACM International Collegiate Programming Contest, Tishreen Collegiate Programming Contest (2017)- K. ...
- 18春季训练01-3/11 2015 ACM Amman Collegiate Programming Contest
Solved A Gym 100712A Who Is The Winner Solved B Gym 100712B Rock-Paper-Scissors Solved C Gym 100712C ...
- Call for Papers IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Network Analysis and Mining (ASONAM)
IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Network Analysis and Mining (ASONAM) 2014 In ...
- IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Network Analysis and Mining (ASONAM) 2014 Industry Track Call for Papers
IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Network Analysis and Mining (ASONAM) 2014 In ...
- 2017 ACM - ICPC Asia Ho Chi Minh City Regional Contest
2017 ACM - ICPC Asia Ho Chi Minh City Regional Contest A - Arranging Wine 题目描述:有\(R\)个红箱和\(W\)个白箱,将这 ...
随机推荐
- Learning-MySQL【2】:MySQL存储引擎及数据库的操作管理
一.存储引擎 存储引擎实际上就是如何存储数据.如何为存储的数据建立索引和如何更新.查询数据.存储引擎也可以称为表类型. MySQL提供了插件式(pluggable)的存储引擎,存储引擎是基于表的.同一 ...
- 个人爱好:idea 项目结构呈现风格
- 03.v-cloak、v-v-text、v-html、v-bind、v-on
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8&quo ...
- PHP冒泡排序-手写
<?php $a = [1,3,5,2,9,6]; for ($i = 0 ;$i < count($a) ;$i++) { for ($j = $i + 1;$j < count( ...
- 使用python内置库matplotlib,实现折线图的绘制
环境准备: 需要安装matplotlib,安装方式: pip install matplotlib 直接贴代码喽: #引入模块 from matplotlib import pyplot,font_m ...
- Python自学:第三章 索引从0开始而不是从1
#返回最后一个,和倒数第二个元素 bicycles = ['trek','cannondale','redline','specialized'] print(bicycles[-1]) print( ...
- VSCode汉化
1.打开VSCode 点击箭头指示地方 在搜索框中输入chinese 然后安装中文简体 2.按住 Ctrl+shift+p 选择配置显示语言 然后会看见下面的样子 添加 "locale&q ...
- JavaScript的DOM对象
HTML DOM (文档对象模型) 当网页被加载时,浏览器会创建页面的文档对象模型(Document Object Model). HTML DOM 模型被构造为对象的树. HTML DOM 树 通过 ...
- 『Argparse』命令行解析
一.基本用法 Python标准库推荐使用的命令行解析模块argparse 还有其他两个模块实现这一功能,getopt(等同于C语言中的getopt())和弃用的optparse.因为argparse是 ...
- js获取当前时间:封装js的日期时间
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content ...
