UVA1103-Ancient Messages(脑洞+dfs)
Problem UVA1103-Ancient Messages
Accept: 1176 Submit: 6103
Time Limit: 3000 mSec
 Problem Description
Problem Description
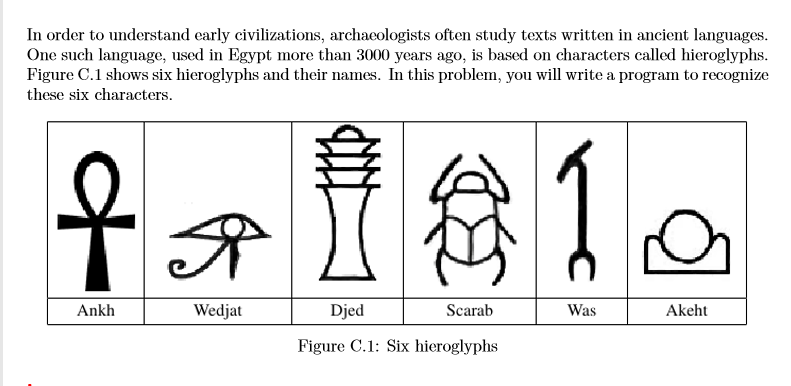
 Input
Input

 Output
Output

 Sample Input
Sample Input
100 25 0000000000000000000000000
0000000000000000000000000
...(50 lines omitted)...
00001fe0000000000007c0000
00003fe0000000000007c0000
...(44 lines omitted)...
0000000000000000000000000
0000000000000000000000000
150 38
00000000000000000000000000000000000000
00000000000000000000000000000000000000
...(75 lines omitted)...
0000000003fffffffffffffffff00000000000
0000000003fffffffffffffffff00000000000
...(69 lines omitted)...
00000000000000000000000000000000000000
00000000000000000000000000000000000000
0 0
 Sample output
Sample output
Case 1: AKW
Case 2: AAAAA
题解:这个题重在脑洞,看出来联通块的个数与字母之间的关系的确不容易(我是没看出来)。开了脑洞之后问题就简单多了,先对最外面的白色区域dfs一下,然后就是dfs各个黑色区域,先把他们包围的联通块的范围划出来,然后计数里面的联通块个数,说的时候这划区域与计数是分开的,其实实现的时候是在一起的,划区域的时候如果碰到了白格,就停下来先对这个白格所在的联通块进行dfs,顺便记个数,区域划完了,计数也就搞定了
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std; const int maxn = +,maxm = +;
const int converse[][] =
{
{,,,},{,,,},{,,,},{,,,},
{,,,},{,,,},{,,,},{,,,},
{,,,},{,,,},{,,,},{,,,},
{,,,},{,,,},{,,,},{,,,}
}; char gra[maxn][maxm];
int buf[maxn][maxm<<];
int n,m,cnt;
int dir[][] = {{,},{,},{-,},{,-}}; inline bool Judge(int x,int y){
if(<=x && <=y && x<n && y<m) return true;
else return false;
} void dfsw(int x,int y,int num){
buf[x][y] = num;
int xx,yy;
for(int i = ;i < ;i++){
xx = x+dir[i][],yy = y+dir[i][];
if(Judge(xx,yy) && buf[xx][yy] == ){
dfsw(xx,yy,num);
}
}
} void dfsn(int x,int y,int num){
buf[x][y] = num;
int xx,yy;
for(int i = ;i < ;i++){
xx = x+dir[i][],yy = y+dir[i][];
if(Judge(xx,yy)){
if(buf[xx][yy] == ) dfsn(xx,yy,num);
else if(buf[xx][yy] == ){
cnt++;
dfsw(xx,yy,-);
}
}
}
} void map_print(){
for(int i = ;i < n;i++){
for(int j = ;j < m;j++){
printf("%d ",buf[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
} int sum[];
char q[] = {'W','A','K','J','S','D'};
int iCase = ; int main()
{
//freopen("input.txt","r",stdin);
//freopen("output.txt","w",stdout);
while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m) && (n||m)){
memset(buf,,sizeof(buf));
for(int i = ;i <= n;i++){
scanf("%s",gra[i]+);
for(int j = ;j <= (int)strlen(gra[i]+);j++){
int y = (j-)<<;
if('a'<=gra[i][j] && gra[i][j]<='z'){
for(int k = ;k < ;k++){
buf[i][y+k+] = converse[gra[i][j]-'a'+][k];
}
}
else{
for(int k = ;k < ;k++){
buf[i][y+k+] = converse[gra[i][j]-''][k];
}
}
}
}
n = n+,m = *m+;
//map_print();
dfsw(,,-);
int flag = ;
memset(sum,,sizeof(sum));
for(int i = ;i < n;i++){
for(int j = ;j < m;j++){
if(buf[i][j] == ){
cnt = ;
dfsn(i,j,flag);
flag++;
sum[cnt]++;
}
}
}
//map_print();
printf("Case %d: ",iCase++);
if(sum[] != ) for(int i = ;i < sum[];i++) printf("%c",'A');
if(sum[] != ) for(int i = ;i < sum[];i++) printf("%c",'D');
if(sum[] != ) for(int i = ;i < sum[];i++) printf("%c",'J');
if(sum[] != ) for(int i = ;i < sum[];i++) printf("%c",'K');
if(sum[] != ) for(int i = ;i < sum[];i++) printf("%c",'S');
if(sum[] != ) for(int i = ;i < sum[];i++) printf("%c",'W');
printf("\n");
}
return ;
}
UVA1103-Ancient Messages(脑洞+dfs)的更多相关文章
- HDU 3839 Ancient Messages(DFS)
In order to understand early civilizations, archaeologists often study texts written in ancient lang ...
- hdu 3839 Ancient Messages (dfs )
题目大意:给出一幅画,找出里面的象形文字. 要你翻译这幅画,把象形文字按字典序输出. 思路:象形文字有一些特点,分别有0个圈.1个圈.2个圈...5个圈.然后dfs或者bfs,就像油井问题一样,找出在 ...
- Uva1103 Ancient Messages
题意:识别图中的象形文字.但是,图形可以任意的拉伸,但不能拉断. 分析:这种题如果图形没有特征是不可做类型的题,不过观察图形可以发现每个图形中的洞的数量是一定的,我们只需要数出每一个封闭图形的洞数就能 ...
- K - Ancient Messages(dfs求联通块)
K - Ancient Messages Time Limit:3000MS Memory Limit:0KB 64bit IO Format:%lld & %llu Subm ...
- UVA1103 古代象形符号 Ancient Messages 题解
题目链接: https://www.luogu.org/problemnew/show/UVA1103 题目分析: 我们可以先进行矩阵的还原 for(int k=1;k<=4;k++) { a[ ...
- UVA - 1103Ancient Messages(dfs)
UVA - 1103Ancient Messages In order to understand early civilizations, archaeologists often study te ...
- UVa 1103 Ancient Messages(二重深搜)
In order to understand early civilizations, archaeologists often study texts written in ancient lang ...
- Ancient Messages UVA - 1103
题目链接:https://vjudge.net/problem/UVA-1103 题目大意:每组数据包含H行W列的字符矩阵(H<=200,W<=50) 每个字符为为16进制 你需要把它转 ...
- UVa 1103 (利用连通块来判断字符) Ancient Messages
本题就是灵活运用DFS来求连通块来求解的. 题意: 给出一幅黑白图像,每行相邻的四个点压缩成一个十六进制的字符.然后还有题中图示的6中古老的字符,按字母表顺序输出这些字符的标号. 分析: 首先图像是被 ...
随机推荐
- [NOI 2017]整数
Description 题库链接 P 博士将他的计算任务抽象为对一个整数的操作. 具体来说,有一个整数 \(x\) ,一开始为 \(0\) . 接下来有 \(n\) 个操作,每个操作都是以下两种类型中 ...
- VPS杂谈(一)
1. VPS购买推荐 可参考:http://www.laozuo.org/myvps 2. VPS配置SSH端口号 购买的VPS的主机,一般情况下端口号不是22,被改成了其它的,这个时候为了方便自己的 ...
- Spring Boot 初始化运行特定方法
Spring Boot提供了两种 “开机自启动” 的方式,ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner 这两种方式的目的是为了满足,在容器启动时like执行某些方法.我们可以 ...
- 数据库部分(MySql)_1
SQL规范 以 “ ; ” 结尾:关键字之间要有空格(可以由多个空格):SQL语句中可以一个或多个换行:关键字不区分大小写. 数据库相关SQL 查询所有数库库: show databases; 创建数 ...
- 用JDOM解析XML文件时如何解决中文问题?如何解析?
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder; import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory; import ja ...
- c#实战开发:用.net core开发一个简单的Web以太坊钱包 (六)
今天就来开发一个C# 版的简易钱包 先回顾以前的内容 c#实战开发:以太坊Geth 命令发布智能合约 (五) c#实战开发:以太坊Geth 常用命令 (四) c#实战开发:以太坊钱包快速同步区块和钱包 ...
- callback.js
function writeCode(callback){ console.log("i am waiting....") callback(); console.log(&quo ...
- docker 部署 java 项目
Docker Docker官方网址: https://docs.docker.com/ 英文地址 Docker中文网址: http://www.docker.org.cn/ 中文地址 Docker是 ...
- vue和webpack打包 项目相对路径修改
一般vue使用webpack打包是整个工程的根目录,但是很多情况下都是把vue打包后的文件在某子目录下. 修改: 1,打开index.js assetsPublicPath:'/' 改为: asset ...
- Quill编辑器IOS下无法获取焦点的解决方法
造成Quill-Editor无法获取焦点的大部分原因是Css的问题,罪魁祸首: *{ -webkit-user-select:none; } ios下直接造成无法获取焦点. 解决方法,覆盖以上css设 ...
