基2时域抽取FFT、IFFT的C++实现代码,另附DFT与IDFT的原始实现--转1
介绍
网络上的原理介绍非常丰富,具体请自行搜索网络资源。
本算法依靠FFT流图进行布置。
算法 ##
进行完所有的原理推导后,我们可以得到如下的16点FFT流图:
通过上图可以看出整个流图输入序列的顺序已经被颠倒,这实际上是输入序列中元素的序号进行了比特位的逆序排列,即其二进制比特位发生了镜像,例如001变为了100。另外一共有三个镶嵌的循环。
为了实现输入序列的比特逆序排列,要使用雷德算法进行实现。
下面进行FFT算法的核心讲解:
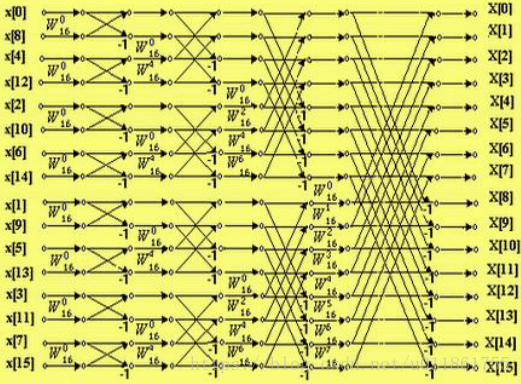
第一层循环: 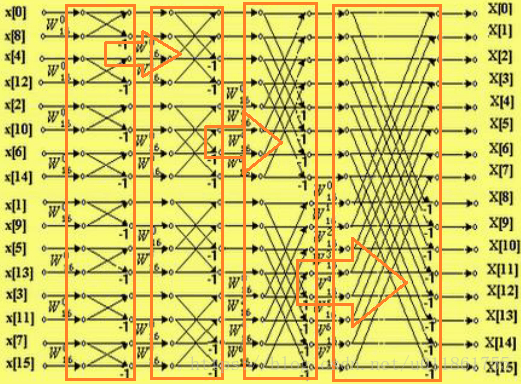
第二层循环:
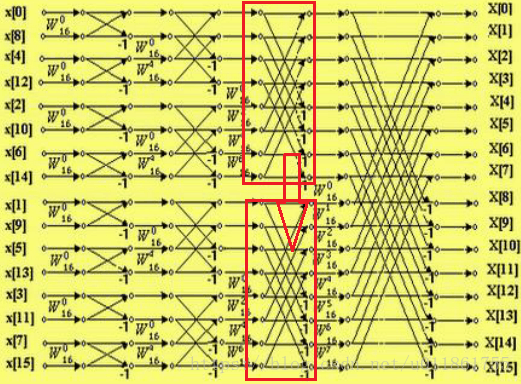
第三层循环:
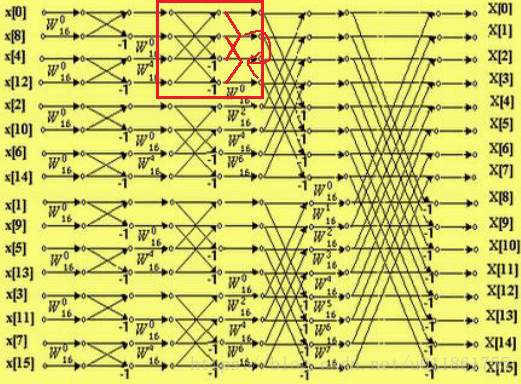
每一次循环中的蝴蝶运算操作请参阅网络资源。
FFT和IFFT的结果与DFT和IDFT的结果有一定的偏差,且由于计算机计算的精度关系,反变换结果与原始输入序列不一定完全相同。
下面给出代码:
- #include <iostream>
- #include <cmath>
- #include <iomanip>
- using namespace std;
- double PI = 3.1415926535897933;
- //定义复数结构体
- typedef struct complex_number
- {
- double real;
- double imagine;
- }complex_number;
- //定义旋转因子
- complex_number omega_num(int k, int n, int input_length);
- complex_number omega_num(int k, int n, int input_length)
- {
- //k是傅里叶变换结果的序号
- //n是求解DFT时的序号
- //input_length是输入序列的长度
- complex_number omega_num;
- omega_num.real = cos(- * PI * k * n / input_length);
- omega_num.imagine = sin(- * PI * k * n / input_length);
- return omega_num;
- }
- //定义复数乘法的函数
- complex_number complex_multiply(complex_number a, complex_number b);
- complex_number complex_multiply(complex_number a, complex_number b)
- {
- complex_number result;
- result.real = a.real*b.real - a.imagine*b.imagine;
- result.imagine = a.real*b.imagine + a.imagine*b.real;
- return result;
- }
- void main()
- {
- //FFT - 快速傅里叶变换!
- //初始化 - 常量、变量的定义。
- const int input_length = ;//输入数组的长度
- double input[input_length] = { ,,, };
- //将输入数组进行比特倒位排列 - 雷德算法
- for (int j = , i = ; i < input_length - ; i++)//这里实现了奇偶前后分开排序
- {
- int k;
- if (i < j)//如果i<j,即进行变址
- {
- double temp;
- temp = input[j];
- input[j] = input[i];
- input[i] = temp;
- }
- k = input_length / ;//求j的下一个倒位序
- while (j >= k)//如果k<=j,表示j的最高位为1
- {
- j = j - k;//把最高位变成0
- k = k / ;//k/2,比较次高位,依次类推,逐个比较,直到某个位为0
- }
- j = j + k;
- }
- ////显示比特逆排序的结果
- //比特逆序数结束后,原输入序列已经发生改变~~~,如果要用原始DFT公式进行FFT的验算,则需要将原始输入序列重新定义。
- //核心部分:FFT迭代-------------------------------------------------------------------
- int EachLayer_length;//蝶形运算数量。每执行一次外循环时,每个区域的蝶形运算器的数量的2倍
- complex_number FFT_Output[input_length];
- //由于最底层的输入是实数,而输出也是实数,所以单独拿出来进行循环
- //最底层
- for (int a = ; a < input_length; a += )
- {
- double temp;
- temp = input[a];
- input[a] = input[a] + input[a + ];//注意这一步完成以后input[a]的值将改变,必须将原始input[a]的值放在临时变量中保存。
- input[a + ] = temp - input[a + ];
- }
- //显示最底层的计算结果
- //for (int i = 0; i < input_length; i++)
- //{
- // cout << input[i] << endl;
- //}
- //将最底层计算出的结果全部赋值给FFT输出变量,即FFT_Output
- for (int b = ; b < input_length; b++)
- {
- FFT_Output[b].real = input[b];
- FFT_Output[b].imagine = ;
- }
- //从倒数第二层开始循环,保证所有的输入与输出都是复数
- for (int s = ; s <= log(input_length) / log(); s++)
- {
- EachLayer_length = (int)pow(, s);//每一次最外层循环时,每层的蝶形运算数量,是蝶形运算器数量的2倍。
- for (int m = ; m < input_length; m = m + EachLayer_length)
- {
- for (int n = ; n < EachLayer_length / ; n++)
- {
- complex_number temp;//定义临时复数变量。
- //蝶形运算
- temp.real = FFT_Output[m + n].real;
- temp.imagine = FFT_Output[m + n].imagine;
- FFT_Output[m + n].real = FFT_Output[m + n].real + complex_multiply(FFT_Output[m + n + EachLayer_length / ], omega_num(, n*input_length/( << s), input_length)).real;
- FFT_Output[m + n].imagine = FFT_Output[m + n].imagine + complex_multiply(FFT_Output[m + n + EachLayer_length / ], omega_num(, n*input_length / ( << s), input_length)).imagine;
- FFT_Output[m + n + EachLayer_length / ].real = temp.real - complex_multiply(FFT_Output[m + n + EachLayer_length / ], omega_num(, n*input_length / ( << s), input_length)).real;
- FFT_Output[m + n + EachLayer_length / ].imagine = temp.imagine - complex_multiply(FFT_Output[m + n + EachLayer_length / ], omega_num(, n*input_length / ( << s), input_length)).imagine;
- }
- }
- }
- EachLayer_length = ;//为后面的IFFT使用而将该变量置零。
- cout << "FFT变换结果为:\n";
- for (int q = ; q < input_length; q++)
- {
- if (FFT_Output[q].imagine < )
- cout << FFT_Output[q].real << FFT_Output[q].imagine << "i" << endl;
- else if (FFT_Output[q].imagine == )
- cout << FFT_Output[q].real << endl;
- else
- cout << FFT_Output[q].real << "+" << FFT_Output[q].imagine << "i" << endl;
- }
- cout << endl;
- //IFFT - 快速傅里叶逆变换!具体的循环原理请参照IFFT流图。
- //直接将FFT的输出结果作为输入,输入到FFT算法中,输出结果的实部就是IFFT的实序列。
- //定义需要使用的变量
- complex_number IFFT_Input[input_length];//IFFT的输入序列
- complex_number IFFT_Output[input_length];//IFFT的输出序列
- //将上文中FFT的计算结果全部赋给IFFT_Input,并对IFFT_Input的虚部取共轭;
- for (int a = ; a < input_length; a++)
- {
- IFFT_Input[a].real = FFT_Output[a].real;
- IFFT_Input[a].imagine = -FFT_Output[a].imagine;
- }
- //对输入的复数序列进行比特逆序排序 - 雷德算法
- //首先对输入序列的实数部分进行排序
- for (int j = , i = ; i < input_length - ; i++)
- {
- int k;
- if (i < j)
- {
- complex_number temp;
- temp = IFFT_Input[j];
- IFFT_Input[j] = IFFT_Input[i];
- IFFT_Input[i] = temp;
- }
- k = input_length / ;
- while (j >= k)
- {
- j = j - k;
- k = k / ;
- }
- j = j + k;
- }
- //核心部分:IFFT迭代,与FFT迭代一模一样-------------------------------------------------
- //从倒数第一层开始循环
- for (int s = ; s <= log(input_length) / log(); s++)
- {
- EachLayer_length = (int)pow(, s);//每一次最外层循环时,每层的蝶形运算数量,是蝶形运算器数量的2倍。
- for (int m = ; m < input_length; m = m + EachLayer_length)
- {
- for (int n = ; n < EachLayer_length / ; n++)
- {
- complex_number temp;//定义临时复数变量。
- //蝶形运算
- temp.real = IFFT_Input[m + n].real;
- temp.imagine = IFFT_Input[m + n].imagine;
- IFFT_Input[m + n].real = IFFT_Input[m + n].real + complex_multiply(IFFT_Input[m + n + EachLayer_length / ], omega_num(, n*input_length / ( << s), input_length)).real;
- IFFT_Input[m + n].imagine = IFFT_Input[m + n].imagine + complex_multiply(IFFT_Input[m + n + EachLayer_length / ], omega_num(, n*input_length / ( << s), input_length)).imagine;
- IFFT_Input[m + n + EachLayer_length / ].real = temp.real - complex_multiply(IFFT_Input[m + n + EachLayer_length / ], omega_num(, n*input_length / ( << s), input_length)).real;
- IFFT_Input[m + n + EachLayer_length / ].imagine = temp.imagine - complex_multiply(IFFT_Input[m + n + EachLayer_length / ], omega_num(, n*input_length / ( << s), input_length)).imagine;
- }
- }
- }
- //将计算完成的结果赋给输出序列IFFT_Output并显示结果
- cout << "IFFT结果:\n";
- for (int c = ; c < input_length; c++)
- {
- IFFT_Output[c].real = IFFT_Input[c].real / input_length;
- cout << IFFT_Output[c].real << endl;
- }
- cout << endl;
- //应用原始DFT公式对FFT算法进行验算
- const int input_length1 = ;
- double input1[input_length1] = { ,,, };
- complex_number DFT_sum, DFT_Output[input_length1];
- for (int k = ; k < input_length1; k++)
- {
- DFT_sum.real = DFT_sum.imagine = ;
- for (int n = ; n < input_length1; n++)
- {
- DFT_sum.real += input1[n] * omega_num(k, n, input_length1).real;
- DFT_sum.imagine += input1[n] * omega_num(k, n, input_length1).imagine;
- }
- DFT_Output[k].real = DFT_sum.real;
- DFT_Output[k].imagine = DFT_sum.imagine;
- }
- cout << "DFT变换结果为:\n";
- for (int q = ; q < input_length1; q++)
- {
- if (DFT_Output[q].imagine < )
- cout << DFT_Output[q].real << DFT_Output[q].imagine << "i" << endl;
- else if (DFT_Output[q].imagine == )
- cout << DFT_Output[q].real << endl;
- else
- cout << DFT_Output[q].real << "+" << DFT_Output[q].imagine << "i" << endl;
- }
- cout << endl;
- //下面进行IDFT
- double output_IDFT[input_length1], IDFT_sum;
- for (int n = ; n < input_length1; n++)
- {
- IDFT_sum = ;
- for (int k = ; k < input_length1; k++)
- {
- //这里一定注意复数与复数相乘的法则,不仅要将实数部分相乘,由于i*i=-1,所以还要减去虚数部分相乘的结果!
- IDFT_sum += DFT_Output[k].real*omega_num(k, -n, input_length1).real - DFT_Output[k].imagine*omega_num(k, -n, input_length1).imagine;
- }
- output_IDFT[n] = IDFT_sum / input_length1;
- }
- cout << "IDFT变换结果为:\n";
- for (int q = ; q < input_length1; q++)
- cout << output_IDFT[q] << endl;
- cout << endl;
- }
---------------------
作者:WilliamS1995
来源:CSDN
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/u011861755/article/details/82666649
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请附上博文链接!
基2时域抽取FFT、IFFT的C++实现代码,另附DFT与IDFT的原始实现--转1的更多相关文章
- 15 FFT及其框图实现
FFT及其框图实现 \(FFT\)的全称为快速傅里叶变换,但是\(FFT\)并不是一种变换,而是实现\(DFT\)的一种快速算法.当\(N\)比较大时,使用\(FFT\)可大大减少进行\(DFT\)变 ...
- FFT快速傅里叶变换算法
1.FFT算法概要: FFT(Fast Fourier Transformation)是离散傅氏变换(DFT)的快速算法.即为快速傅氏变换.它是根据离散傅氏变换的奇.偶.虚.实等特性,对离散傅立叶变换 ...
- 基于C++任意点数的FFT/IFFT(时域和频域)实现
函数说明:更改主函数体中的N和length(=log2(N))既可以实现任意点数(2的幂次)的FFT/ IFFT的实现,fft函数中flag标志位控制是正变换还是逆变换. 1.复数操作类 定 ...
- FFT通过傅里叶级数图解频域补零时域内插
在时域频域的信号分析的过程中,一个常见的说法叫:频域数据补零会让时域数据内插. 意思是在频域数据中多补几个零,再做ifft(逆傅里叶变换)后的时域数据,会变得更加"细腻",分辨率会 ...
- Xilinx FFT IP v9.0 使用(一)
reference:https://blog.csdn.net/shichaog/article/details/51189711 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_36375505/ ...
- Xilinx FFT IP v9.0 使用
该ip用于实现N=2**m(m=3~16)点FFT的变换, 实现的数学类型包含: A) 定点全精度 B) 定点缩减位宽 C) 块浮点 每一级蝶型运算后舍入或者取整.对于N ...
- FFT原理及C++与MATLAB混合编程详细介绍
一:FFT原理 1.1 DFT计算 在一个周期内的离散傅里叶级数(DFS)变换定义为离散傅里叶变换(DFT). \[\begin{cases} X(k) = \sum_{n=0}^{N-1}x(n)W ...
- 数字信号处理专题(3)——FFT运算初探
一.前言 FFT运算是目前最常用的信号频谱分析算法.在本科学习数字信号处理这门课时一直在想:学这些东西有啥用?公式推来推去的,有实用价值么?到了研究生后期才知道,广义上的数字信号处理无处不在:手机等各 ...
- hdu 4609 FFT
题意:给出一堆数,问从这些数中取3个能组成三角形的概率? sol:其实就是问从这些数里取3个组成三角形有多少种取法 脑洞大开的解法:用FFT 设一开始的数是1 3 3 4 作一个向量x,其中x[i]= ...
随机推荐
- js 星星效果思路
//星星的效果思路 1.获取需要修改的元素 ul li 跟p 布局 2.给li 加移入事件 更改提示框显示, 3.给li 加移出事件 更改提示框隐藏 4.给li加索引值代表自己的序号 5.在li移入时 ...
- "Login failed for user 'NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM'. 原因: 无法打开明确指定的数据库。"异常处理
公司一台SQL Server服务器一直报 "Login failed for user 'NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM'. 原因: 无法打开明确指定的数据库."错误,按网 ...
- LeetCode #001# Two Sum(js描述)
索引 思路1:暴力搜索 思路2:聪明一点的搜索 思路3:利用HashMap巧解 问题描述:https://leetcode.com/problems/two-sum/ 思路1:暴力搜索 一个很自然的想 ...
- 配置cron定时任务
题:配置一个 cron 任务用户 natasha 必须配置一个定时执行任务,每天在本地时间 14:23 时执行命令* /bin/echo hiya 答: # 方法1 # su - natasha # ...
- 剑指offer(52)正则表达式的匹配
题目描述 请实现一个函数用来匹配包括'.'和'*'的正则表达式.模式中的字符'.'表示任意一个字符,而'*'表示它前面的字符可以出现任意次(包含0次). 在本题中,匹配是指字符串的所有字符匹配整个模式 ...
- NPOI解决由于excel删除数据导致空行读取问题
1.解决问题思路一:申明判断是否空行变量用于判断是否空行,声明变量数组用于临时非空行数据,最后存于datatable中. /// <summary>读取excel, /// 默认第一行为表 ...
- Ansible在Ubuntu上的安装
#apt安装 apt-get install software-properties-common apt-add-repository ppa:ansible/ansible apt-get upd ...
- UVA1329 Corporative Network
思路 用带权并查集维护到根的距离即可 代码 #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> #i ...
- scala 入门Eclipse环境搭建
scala 入门Eclipse环境搭建及第一个入门经典程序HelloWorld IDE选择并下载: scala for eclipse 下载: http://scala-ide.org/downloa ...
- 阿里技术专家详解Dubbo实践,演进及未来规划
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/9rVGHYfeE8yM2qkSVd2yEQ
