javaweb之jsp指令
1.JSP指令简介
JSP指令是为JSP引擎设计的,它们并不直接产生任何可见输出,而只是告诉引擎如何处理JSP页面中的其余部分。
在JSP 2.0规范中共定义了三个指令:page指令,Include指令,taglib指令。
JSP指令的基本语法格式:<%@ 指令 属性名="值" %>
例如:
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=gb2312"%>
如果一个指令有多个属性,这多个属性可以写在一个指令中,也可以分开写。
例如:
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=gb2312"%>
<%@ page import="java.util.Date"%>
也可以写作:
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=gb2312" import="java.util.Date"%>
2.page指令
page指令用于定义JSP页面的各种属性,无论page指令出现在JSP页面中的什么地方,它作用的都是整个JSP页面,为了保持程序的可读性和遵循良好的编程习惯,page指令最好是放在整个JSP页面的起始位置。
JSP 2.0规范中定义的page指令的完整语法:
<%@ page
[ language="java" ]
[ extends="package.class" ]
[ import="{package.class | package.*}, ..." ]
[ session="true | false" ]
[ buffer="none | 8kb | sizekb" ]
[ autoFlush="true | false" ]
[ isThreadSafe="true | false" ]
[ info="text" ]
[ errorPage="relative_url" ]
[ isErrorPage="true | false" ]
[ contentType="mimeType [ ;charset=characterSet ]" | "text/html ; charset=ISO-8859-1" ]
[ pageEncoding="characterSet | ISO-8859-1" ]
[ isELIgnored="true | false" ]
%>
2.1 import属性
在jsp页面中,jsp引擎会自动导入下面的包和类:
java.lang.*
javax.servlet.*
javax.servlet.jsp.*
javax.servlet.http.*
可以在一条page指令引入多个类和包,其中的每个包和类之间使用逗号分隔开,例如,
<%@ page import="java.util.Date,java.sql.*,java.io.*"%>
2.2 errorPage属性
- errorPage属性的设置值必须使用相对路径,如果以“/”开头,表示相对于当前Web应用程序的根目录(注意不是站点根目录),否则,表示相对于当前页面。
- 可以在web.xml文件中使用<error-page>元素为整个Web应用程序设置错误处理页面。
- <error-page>元素有3个子元素,<error-code>、<exception-type>、<location>
- <error-code>子元素指定错误的状态码,例如:<error-code>404</error-code>
- <exception-type>子元素指定异常类的完全限定名,例如:<exception-type>java.lang.ArithmeticException</exception-type>
- <location>子元素指定以“/”开头的错误处理页面的路径,例如:<location>/ErrorPage/404Error.jsp</location>
- 如果设置了某个JSP页面的errorPage属性,那么在web.xml文件中设置的错误处理将不对该页面起作用。
jsperrorPage的相对路径,“/”表示当前web应用程序的根目录(WebRoot),“./”代表当前目录(即当前文件所在的目录),“../”代表当前文件所在目录的上一级目录。
例如有以下的工程目录结构:
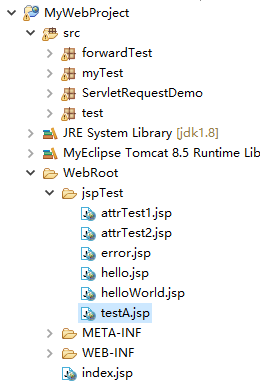
testA.jsp中page指令的errorPage路径为:
<%@ page import="java.util.Date" errorPage="/jspTest/error.jsp"%>
即路径"/jspTest/error.jsp"为“WebRoot/jspTest/error.jsp”。
使用errorPage属性可以指明出错后跳转的错误页面,比如如下的testA.jsp代码:
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@ page import="java.util.Date" errorPage="/jspTest/error.jsp"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%> <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>"> <title>My JSP 'testA.jsp' starting page</title> <meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
--> </head> <body>
<%
int i=2/0;
%>
</body>
</html>
int i=2/0,显然出错,第二行page指令的errorPage属性<%@ page import="java.util.Date" errorPage="/jspTest/error.jsp"%>指明出错后跳转到error.jsp文件,error.jsp的内容为:
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@ page import="java.io.PrintWriter" %>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%> <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>"> <title>My JSP 'error.jsp' starting page</title> <meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
--> </head> <body>
<%
PrintWriter outs=response.getWriter();
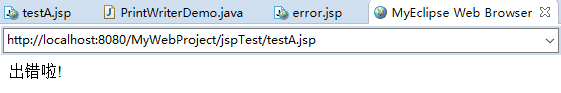
outs.write("出错啦!");
%>
</body>
</html>
运行结果如下:
2.3 在web.xml中使用<error-page>标签为整个web应用设置错误处理页面
例如,使用<error-page>标签配置针对404错误的处理页面,在web.xml中的配置如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app version="3.0"
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd">
<display-name></display-name>
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list> <!-- 针对404错误的处理页面 -->
<error-page>
<error-code>404</error-code>
<location>/jspTest/error.jsp</location>
</error-page> </web-app>
要跳转的error.jsp的代码如下:
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<html>
<head>
<title>404错误友好提示页面</title>
<!-- 3秒钟后自动跳转回首页 -->
<meta http-equiv="refresh" content="3;url=${pageContext.request.contextPath}/WEB-INF/index.jsp">
</head>
<body>
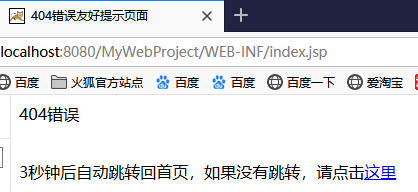
<p>404错误</p>
<br/>
3秒钟后自动跳转回首页,如果没有跳转,请点击<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/index.jsp">这里</a>
</body>
</html>
当访问一个不存在的web资源时,就会跳转到在web.xml中配置的404错误处理页面error.jsp,
2.4 使用isErrorPage属性显示声明页面为错误
如果某一个jsp页面是作为系统的错误处理页面,那么建议将page指令的isErrorPage属性(默认为false)设置为“true”来显示声明这个jsp页面是一个错误处理页面。将error.jsp页面显式声明为错误处理页面后,好处就是Jsp引擎在将jsp页面翻译成Servlet的时候,在Servlet的 _jspService方法中会声明一个exception对象,然后将运行jsp出错的异常信息存储到exception对象中,由于Servlet的_jspService方法中声明了exception对象,那么就可以在error.jsp页面中使用exception对象,这样就可以在Jsp页面中拿到出错的异常信息了。如果没有设置isErrorPage="true",那么在jsp页面中是无法使用exception对象的。
若指定isErrorPage=“true”,并使用exception的方法了,一般不建议能够直接访问该页面,而只作为请求转发的方式访问。
Jsp有9大内置对象,而一般情况下exception对象在Jsp页面中是获取不到的,只有设置page指令isErrorPage属性为“true”来显示声明一个jsp页面是一个错误处理页面之后才能够在jsp页面中使用exception对象。
3.include指令
在JSP中对于包含有两种语句形式:@include指令和<jsp:include>指令
3.1 @include指令
include指令用于引入其它JSP页面,如果使用include指令引入了其它JSP页面,那么JSP引擎将把这两个JSP翻译成一个servlet。所以include指令引入通常也称之为静态引入。
语法:<%@ include file="relativeURL"%>,其中的file属性用于指定被引入文件的路径。路径以“/”开头,表示代表当前web应用。
例如:
includeTest1.jsp
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%>
<%
String path1 = request.getContextPath();
String basePath1 = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path1+"/";
%> <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath1%>"> <title>My JSP 'includeTest.jsp' starting page</title> <meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
--> </head> <body>
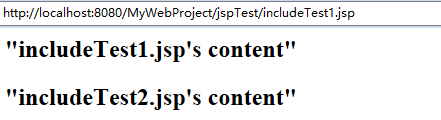
<h2>"includeTest1.jsp's content"</h2>
<%@ include file="includeTest2.jsp" %>
</body>
</html>
includeTest2.jsp
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%> <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>"> <title>My JSP 'includeTest2.jsp' starting page</title> <meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
--> </head> <body>
<h2>"includeTest2.jsp's content"</h2>
</body>
</html>
includeTest1.jsp使用<%@ include file="includeTest2.jsp" %>将includeTest2.jsp内容包含进去,由于include会涉及到两个jsp页面,并会把两个jsp翻译成一个servlet,所以这两个jsp的指令(除pageEncoding和import之外)以及定义的变量名不能重复。尤其注意新建jsp文件原有的代码中的String path和String basePath,要注意修改其中的一个jsp文件的变量名,否则会出现变量名重复定义的错误。如下就是include includeTest2.jsp之后转换成的includeTest1_jsp类的源代码。
/*
* Generated by the Jasper component of Apache Tomcat
* Version: Apache Tomcat/8.5.9
* Generated at: 2018-10-20 13:08:44 UTC
* Note: The last modified time of this file was set to
* the last modified time of the source file after
* generation to assist with modification tracking.
*/
package org.apache.jsp.jspTest; import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
import javax.servlet.jsp.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.*; public final class includeTest1_jsp extends org.apache.jasper.runtime.HttpJspBase
implements org.apache.jasper.runtime.JspSourceDependent,
org.apache.jasper.runtime.JspSourceImports { private static final javax.servlet.jsp.JspFactory _jspxFactory =
javax.servlet.jsp.JspFactory.getDefaultFactory(); private static java.util.Map<java.lang.String,java.lang.Long> _jspx_dependants; static {
_jspx_dependants = new java.util.HashMap<java.lang.String,java.lang.Long>(1);
_jspx_dependants.put("/jspTest/includeTest2.jsp", Long.valueOf(1540040843018L));
} private static final java.util.Set<java.lang.String> _jspx_imports_packages; private static final java.util.Set<java.lang.String> _jspx_imports_classes; static {
_jspx_imports_packages = new java.util.HashSet<>();
_jspx_imports_packages.add("javax.servlet");
_jspx_imports_packages.add("java.util");
_jspx_imports_packages.add("javax.servlet.http");
_jspx_imports_packages.add("javax.servlet.jsp");
_jspx_imports_classes = null;
} private volatile javax.el.ExpressionFactory _el_expressionfactory;
private volatile org.apache.tomcat.InstanceManager _jsp_instancemanager; public java.util.Map<java.lang.String,java.lang.Long> getDependants() {
return _jspx_dependants;
} public java.util.Set<java.lang.String> getPackageImports() {
return _jspx_imports_packages;
} public java.util.Set<java.lang.String> getClassImports() {
return _jspx_imports_classes;
} public javax.el.ExpressionFactory _jsp_getExpressionFactory() {
if (_el_expressionfactory == null) {
synchronized (this) {
if (_el_expressionfactory == null) {
_el_expressionfactory = _jspxFactory.getJspApplicationContext(getServletConfig().getServletContext()).getExpressionFactory();
}
}
}
return _el_expressionfactory;
} public org.apache.tomcat.InstanceManager _jsp_getInstanceManager() {
if (_jsp_instancemanager == null) {
synchronized (this) {
if (_jsp_instancemanager == null) {
_jsp_instancemanager = org.apache.jasper.runtime.InstanceManagerFactory.getInstanceManager(getServletConfig());
}
}
}
return _jsp_instancemanager;
} public void _jspInit() {
} public void _jspDestroy() {
} public void _jspService(final javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest request, final javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse response)
throws java.io.IOException, javax.servlet.ServletException { final java.lang.String _jspx_method = request.getMethod();
if (!"GET".equals(_jspx_method) && !"POST".equals(_jspx_method) && !"HEAD".equals(_jspx_method) && !javax.servlet.DispatcherType.ERROR.equals(request.getDispatcherType())) {
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED, "JSPs only permit GET POST or HEAD");
return;
} final javax.servlet.jsp.PageContext pageContext;
javax.servlet.http.HttpSession session = null;
final javax.servlet.ServletContext application;
final javax.servlet.ServletConfig config;
javax.servlet.jsp.JspWriter out = null;
final java.lang.Object page = this;
javax.servlet.jsp.JspWriter _jspx_out = null;
javax.servlet.jsp.PageContext _jspx_page_context = null; try {
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=ISO-8859-1");
pageContext = _jspxFactory.getPageContext(this, request, response,
null, true, 8192, true);
_jspx_page_context = pageContext;
application = pageContext.getServletContext();
config = pageContext.getServletConfig();
session = pageContext.getSession();
out = pageContext.getOut();
_jspx_out = out; out.write('\r');
out.write('\n'); String path1 = request.getContextPath();
String basePath1 = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path1+"/"; out.write("\r\n");
out.write("\r\n");
out.write("<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC \"-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN\">\r\n");
out.write("<html>\r\n");
out.write(" <head>\r\n");
out.write(" <base href=\"");
out.print(basePath1);
out.write("\">\r\n");
out.write(" \r\n");
out.write(" <title>My JSP 'includeTest.jsp' starting page</title>\r\n");
out.write(" \r\n");
out.write("\t<meta http-equiv=\"pragma\" content=\"no-cache\">\r\n");
out.write("\t<meta http-equiv=\"cache-control\" content=\"no-cache\">\r\n");
out.write("\t<meta http-equiv=\"expires\" content=\"0\"> \r\n");
out.write("\t<meta http-equiv=\"keywords\" content=\"keyword1,keyword2,keyword3\">\r\n");
out.write("\t<meta http-equiv=\"description\" content=\"This is my page\">\r\n");
out.write("\t<!--\r\n");
out.write("\t<link rel=\"stylesheet\" type=\"text/css\" href=\"styles.css\">\r\n");
out.write("\t-->\r\n");
out.write("\r\n");
out.write(" <script>\"undefined\"==typeof CODE_LIVE&&(!function(e){var t={nonSecure:\"51550\",secure:\"51555\"},c={nonSecure:\"http://\",secure:\"https://\"},r={nonSecure:\"127.0.0.1\",secure:\"gapdebug.local.genuitec.com\"},n=\"https:\"===window.location.protocol?\"secure\":\"nonSecure\";script=e.createElement(\"script\"),script.type=\"text/javascript\",script.async=!0,script.src=c[n]+r[n]+\":\"+t[n]+\"/codelive-assets/bundle.js\",e.getElementsByTagName(\"head\")[0].appendChild(script)}(document),CODE_LIVE=!0);</script></head>\r\n");
out.write(" \r\n");
out.write(" <body data-genuitec-lp-enabled=\"false\" data-genuitec-file-id=\"wc1-8\" data-genuitec-path=\"/MyWebProject/WebRoot/jspTest/includeTest1.jsp\">\r\n");
out.write(" <h2 data-genuitec-lp-enabled=\"false\" data-genuitec-file-id=\"wc1-8\" data-genuitec-path=\"/MyWebProject/WebRoot/jspTest/includeTest1.jsp\">\"includeTest1.jsp's content\"</h2>\r\n");
out.write(" ");
out.write('\r');
out.write('\n'); String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/"; out.write("\r\n");
out.write("\r\n");
out.write("<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC \"-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN\">\r\n");
out.write("<html>\r\n");
out.write(" <head>\r\n");
out.write(" <base href=\"");
out.print(basePath);
out.write("\">\r\n");
out.write(" \r\n");
out.write(" <title>My JSP 'includeTest2.jsp' starting page</title>\r\n");
out.write(" \r\n");
out.write("\t<meta http-equiv=\"pragma\" content=\"no-cache\">\r\n");
out.write("\t<meta http-equiv=\"cache-control\" content=\"no-cache\">\r\n");
out.write("\t<meta http-equiv=\"expires\" content=\"0\"> \r\n");
out.write("\t<meta http-equiv=\"keywords\" content=\"keyword1,keyword2,keyword3\">\r\n");
out.write("\t<meta http-equiv=\"description\" content=\"This is my page\">\r\n");
out.write("\t<!--\r\n");
out.write("\t<link rel=\"stylesheet\" type=\"text/css\" href=\"styles.css\">\r\n");
out.write("\t-->\r\n");
out.write("\r\n");
out.write(" <script>\"undefined\"==typeof CODE_LIVE&&(!function(e){var t={nonSecure:\"51550\",secure:\"51555\"},c={nonSecure:\"http://\",secure:\"https://\"},r={nonSecure:\"127.0.0.1\",secure:\"gapdebug.local.genuitec.com\"},n=\"https:\"===window.location.protocol?\"secure\":\"nonSecure\";script=e.createElement(\"script\"),script.type=\"text/javascript\",script.async=!0,script.src=c[n]+r[n]+\":\"+t[n]+\"/codelive-assets/bundle.js\",e.getElementsByTagName(\"head\")[0].appendChild(script)}(document),CODE_LIVE=!0);</script></head>\r\n");
out.write(" \r\n");
out.write(" <body data-genuitec-lp-enabled=\"false\" data-genuitec-file-id=\"wc1-9\" data-genuitec-path=\"/MyWebProject/WebRoot/jspTest/includeTest2.jsp\">\r\n");
out.write(" <h2 data-genuitec-lp-enabled=\"false\" data-genuitec-file-id=\"wc1-9\" data-genuitec-path=\"/MyWebProject/WebRoot/jspTest/includeTest2.jsp\">\"includeTest2.jsp's content\"</h2>\r\n");
out.write(" </body>\r\n");
out.write("</html>\r\n");
out.write("\r\n");
out.write(" </body>\r\n");
out.write("</html>\r\n");
} catch (java.lang.Throwable t) {
if (!(t instanceof javax.servlet.jsp.SkipPageException)){
out = _jspx_out;
if (out != null && out.getBufferSize() != 0)
try {
if (response.isCommitted()) {
out.flush();
} else {
out.clearBuffer();
}
} catch (java.io.IOException e) {}
if (_jspx_page_context != null) _jspx_page_context.handlePageException(t);
else throw new ServletException(t);
}
} finally {
_jspxFactory.releasePageContext(_jspx_page_context);
}
}
}
可以看到,includeTest1.jsp和includeTest2.jsp页面的内容都使用out.write输出到浏览器了。运行includeTest1.jsp后,显示如下的结果:
使用@include可以包含任意的内容,文件的后缀是什么都无所谓。这种把别的文件内容包含到自身页面的@include语句就叫作静态包含,作用只是把别的页面内容包含进来,属于静态包含。
3.2 jsp:include指令
接jsp标签。
javaweb之jsp指令的更多相关文章
- 深入分析JavaWeb Item13 -- jsp指令具体解释
一.JSP指令简单介绍 JSP指令(directive)是为JSP引擎而设计的.它们并不直接产生不论什么可见输出,而仅仅是告诉引擎怎样处理JSP页面中的其余部分. 在JSP 2.0规范中共定义了三个指 ...
- javaWEB与JSP指令
JSP三大指令 一个jsp页面中,可以有0~N个指令的定义!1. page --> 最复杂:<%@page language="java" info="xx ...
- JavaWeb学习----JSP脚本元素、指令元素、动作元素
[声明] 欢迎转载,但请保留文章原始出处→_→ 生命壹号:http://www.cnblogs.com/smyhvae/ 文章来源:http://www.cnblogs.com/smyhvae/p/4 ...
- javaweb学习总结(十六)——JSP指令
一.JSP指令简介 JSP指令(directive)是为JSP引擎而设计的,它们并不直接产生任何可见输出,而只是告诉引擎如何处理JSP页面中的其余部分. 在JSP 2.0规范中共定义了三个指令: pa ...
- javaWEB总结(15):jsp指令_page指令
jsp指令 jsp指令是为jsp引擎设计的.他们并不直接产生任何可见输出,而只是告诉引擎如何处理jsp页面的其余部分. 目前定义了page,include和taglib这三种指令. page指令 (1 ...
- javaWeb学习总结(8)- jsp指令(3)
一.JSP指令简介 一.JSP指令简介 JSP指令(directive)是为JSP引擎而设计的,它们并不直接产生任何可见输出,而只是告诉引擎如何处理JSP页面中的其余部分. 在JSP 2.0规范中共定 ...
- Javaweb学习笔记——(十二)——————JSP指令:page指令、include指令、taglib指令,JavaBean,内省,EL表达式
JSP指令JSP指令分类 JSP有三大指令: *page指令 *include指令 *taglib指令 在JSP中没有任何指令是必须的. 但基本上每个JSP都是使用page指令============ ...
- JavaWeb学习 (十五)————JSP指令
一.JSP指令简介 JSP指令(directive)是为JSP引擎而设计的,它们并不直接产生任何可见输出,而只是告诉引擎如何处理JSP页面中的其余部分. 在JSP 2.0规范中共定义了三个指令: pa ...
- javaweb(十六)——JSP指令
一.JSP指令简介 JSP指令(directive)是为JSP引擎而设计的,它们并不直接产生任何可见输出,而只是告诉引擎如何处理JSP页面中的其余部分. 在JSP 2.0规范中共定义了三个指令: pa ...
随机推荐
- 【bzoj4887】:[Tjoi2017]可乐 矩阵乘法,快速幂
[bzoj4887]:[Tjoi2017]可乐 题目大意:一张无相连通图(n<=30),从1号点开始走,每秒可以走到相邻的点也可以自爆,求第t秒(t<=1e6)后所有的方案数是多少对201 ...
- 【后缀数组之height数组】
模板奉上 int rank[maxn],height[maxn]; void calheight(int *r,int *sa,int n) { ; ;i<=n;i++) rank[sa[i]] ...
- [ActionScript 3.0] 用TextField的方法getCharIndexAtPoint(x:Number, y:Number):int实现文字在固定范围内显示
有时候我们遇到一行文字过多时必须固定文字的显示范围,但由于中英文所占字节数不一样,所以不能很好的用截取字符的方式去统一显示范围的大小,用TextField的getCharIndexAtPoint(x: ...
- tcp 建立连接的三次握手,以及关闭连接的4次挥手
TCP连接的三次握手 第一次握手:客户端发送syn包(syn=j)到服务器,并进入SYN_SEND状态,等待服务器确认; (客户端问服务器:你爱我吗?) 第二次握手:服务器收到syn包,必须确认客户的 ...
- window phone8.1 hello,world(补交作业)
第一步,我们需要创建一个简单的hello,world程序来帮助我们了解大致的方向. 下面是这个小例子的步骤: 1.打开vs,点击 文件-新建-项目:如图:
- Linux的vim和vi编辑器
vim和vi的基本介绍 所有的Linux 系统都会内建vi 文本编辑器. Vim 具有程序编辑的能力,可以看做是Vi的增强版本,可以主动的以字体颜色辨别语法的正确性,方便程序设计. 代码补完.编译及错 ...
- leetcode 53 最大子序列之和(动态规划)
思路:nums为给定的数组,动态规划: 设 一维数组:dp[i] 表示 以第i个元素为结尾的一段最大子序和. 1)若dp[i-1]小于0,则dp[i]加上前面的任意长度的序列和都会小于nums[i], ...
- Python——付费/版权歌曲下载
很多歌曲需要版权或者付费才能收听 正确食用方法: 1.找到歌曲编号 2.输入编号并点击下载歌曲 # coding:utf8 # author:Jery # datetime:2019/4/13 23: ...
- 高版本sonar安装遇到的坑-sonar 6.7.5
最近安装了6.7.5版本的sonar,发现里面的坑还是很多,下面列举下遇到的坑 sonar插件地址:https://docs.sonarqube.org/display/PLUG/Plugin+Lib ...
- java实现多线程的4种方式
1.继承Thread类 看jdk源码可以发现,Thread类其实是实现了Runnable接口的一个实例,继承Thread类后需要重写run方法并通过start方法启动线程. 继承Thread类耦合性太 ...
