Java异常之try,catch,finally,throw,throws
Java异常之try,catch,finally,throw,throws
你能区分异常和错误吗?
我们每天上班,正常情况下可能30分钟就能到达。但是由于车多,人多,道路拥挤,致使我们要花费更多地时间,这就是生活中的异常!
程序和生活一样都会出现异常,先来看个异常:

上面出现的是算数错误的异常。
在java中,除去一些编译上的错误(语法)之外,就有异常和错误!
异常的定义是可自己进行处理后,程序依然可以正常运行下去!错误是Java虚拟机抛出的,终止程序的运行,这就是程序和异常的区别。
一:什么是异常处理?
异常处理机制就像我们对平时可能遇到的意外情况,预先想好了一些处理的办法。也就是说,在程序执行代码的时候,万一发生了异常,程序会按照预定的处理办法对异常进行处理,异常处理完毕后,程序继续运行。
java的异常处理是通过5个关键字来实现的:try、catch、finally、throw、throws。
二:java异常类的层次结构
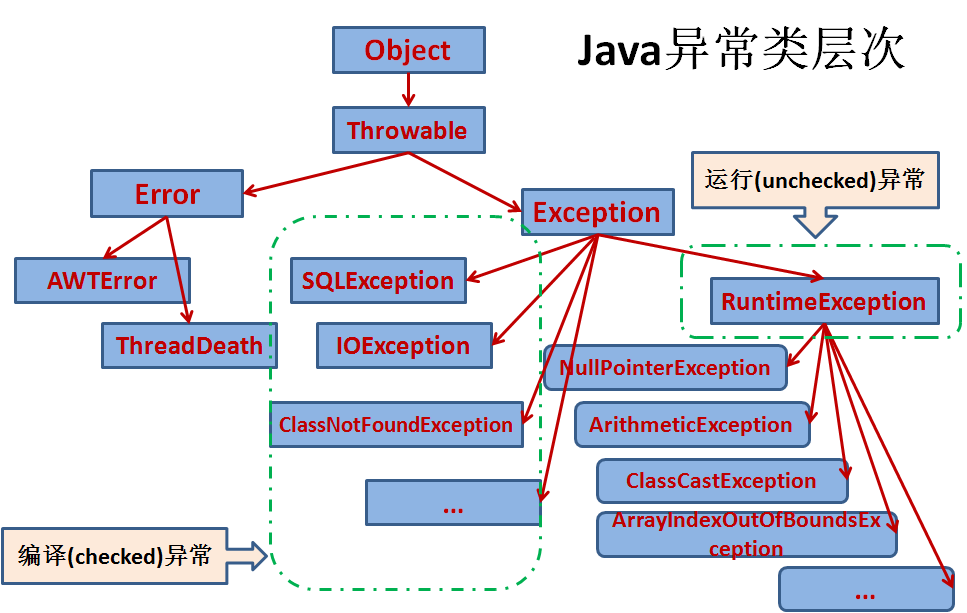
三.常见的异常类型
Exception 异常层次结构的根类
ArithmeticException 算数错误情形
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException 数组下标越界
NullPointerException 尝试访问null对象成员
ClassNotFoundException 不能加载所需的类
InputMismatchException 欲得到的数据类型与实际输入的类型不匹配
IllegalArgumentException 方法接受到非法参数
ClassCastException 对象强制类型转换出错
NumberFormatException 数字格式转换异常
四.具体实例
- try—catch
- package Test;
- import java.util.Scanner;
- public class Test_Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Scanner input =new Scanner(System.in);
- System.out.println("请输入被除数:");
- try {
- int num1=input.nextInt();
- System.out.println("请输入除数:");
- int num2=input.nextInt();
- System.out.println(String.format("%d / %d = %d",
- num1, num2, num1 / num2));
- }catch (Exception e) {
- System.err.println("出现错误:被除数和除数必须是整数,"+
- "除数不能为零。");
- System.out.println(e.getMessage());
- }
- }
运行结果如下:
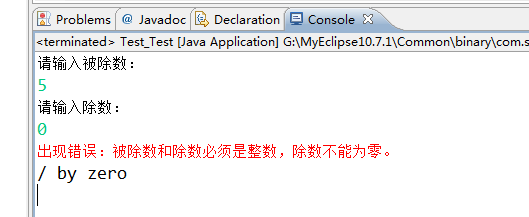
System.err.println();这种输出方式可以输出错误的消息,在控制台呈现红色。
System.out用于正常的输出,也就是程序真正想输出的内容。而System.err用于出错信息的输出,也就是你本来不期待看到的东西。
- System.out.println(e.getMessage());
这行的作用是——返回该错误的详细信息的字符串。
- try-catch-finally
- package Test;
- import java.util.Scanner;
- public class Test_Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Scanner input =new Scanner(System.in);
- System.out.println("请输入被除数:");
- try {
- int num1=input.nextInt();
- System.out.println("请输入除数:");
- int num2=input.nextInt();
- System.out.println(String.format("%d / %d = %d",
- num1, num2, num1 / num2));
- }catch (Exception e) {
- System.err.println("出现错误:被除数和除数必须是整数,"+
- "除数不能为零。");
- System.out.println(e.getMessage());
- }
- finally{
- System.out.println("Thanks");
- }
- }
- }
运行结果如下:
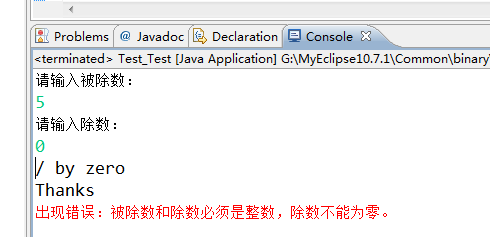
try-catch-finally 程序块的流程大致分为两种情况:
- 如果try块中所有语句正常执行完毕,那么finally块就会被执行。
- 如果try语句在执行过程中碰到异常,无论这种异常能否被catch块捕获到,都将执行finally块中的代码。
try-catch-finally结构中try块是必须有的,catch和finally块为可选,但两者至少必须出现其中之一。
- try—catch-catch-finally(多重catch块)
- package Test;
- import java.util.InputMismatchException;
- import java.util.Scanner;
- public class Test_Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Scanner input =new Scanner(System.in);
- System.out.println("请输入被除数:");
- try {
- int num1=input.nextInt();
- System.out.println("请输入除数:");
- int num2=input.nextInt();
- System.out.println(String.format("%d / %d = %d",
- num1, num2, num1 / num2));
- }catch (InputMismatchException e) {
- System.err.println("被除数和除数必须是整数。");
- }
- catch (ArithmeticException e) {
- System.err.println("除数不能为零。");
- }
- catch (Exception e) {
- System.err.println("其他未知异常。");
- System.out.println(e.getMessage());
- }
- finally{
- System.out.println("Thanks");
- }
- }
- }
运行结果如下:
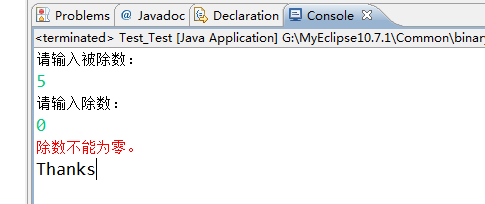
所以,在写异常处理的时候,一定要把异常范围小的放在前面,范围大的放在后面,Exception这个异常的根类一定要刚在最后一个catch里面,如果放在前面或者中间,任何异常都会和Exception匹配的,就会报已捕获到...异常的错误。
下面是try-catch-finally中包含return的情况:
- 情况一:try{} catch(){}finally{} return;
正常按程序顺序执行即可。
- package Test;
- public class Test_Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Test1();
- }
- public static int Test1(){
- int x = 1;
- try
- {
- x++;
- System.out.println("我有用!");
- }
- catch (Exception e) {
- System.out.println("我没用!");
- }
- finally
- {
- ++x;
- System.out.println("我也有用!");
- }
- return 2;
- }
- }
运行结果如下:
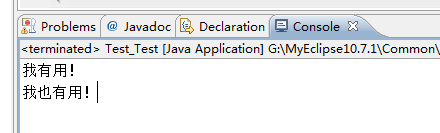
- 情况2:try{ return; }catch(){} finally{} return;
程序执行try块中return之前(包括return语句中的表达式运算)代码;
再执行finally块,最后执行try中return;
finally块之后的语句return,因为程序在try中已经return所以不再执行。
- package Test;
- public class Test_Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Test1();
- }
- public static int Test1(){
- int x = 1;
- try
- {
- x++;
- System.out.println("我有用!");
- return 6;
- }
- catch (Exception e) {
- System.out.println("我没用!");
- }
- finally
- {
- ++x;
- System.out.println("我也有用!");
- }
- return 2;
- }
- }
运行结果如下:
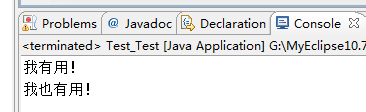
- 情况3:try{} catch(){return;} finally{} return;
程序先执行try,如果遇到异常执行catch块,
有异常:则执行catch中return之前(包括return语句中的表达式运算)代码,再执行finally语句中全部代码,
最后执行catch块中return. finally之后也就是4处的代码不再执行。
无异常:执行完try再finally再return.
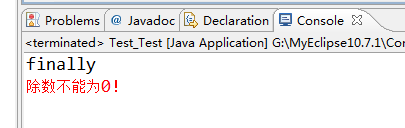
1.有异常的情况:
- package Test;
- public class Test_Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Test1();
- }
- public static int Test1(){
- int x = 5;
- try
- {
- int num=x / 0;
- System.out.println(num);
- }
- catch (ArithmeticException e) {
- System.err.println("除数不能为0!");
- return 6;
- }
- finally
- {
- ++x;
- System.out.println("finally");
- }
- return 2;
- }
- }
运行结果如下:
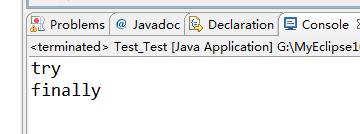
2.无异常的情况:
- package Test;
- public class Test_Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Test1();
- }
- public static int Test1(){
- int x = 5;
- try
- {
- System.out.println("try");
- }
- catch (ArithmeticException e) {
- System.err.println("除数不能为0!");
- return 6;
- }
- finally
- {
- ++x;
- System.out.println("finally");
- }
- return 2;
- }
- }
运行结果如下:
- 情况4:try{ return; }catch(){} finally{return;}
程序执行try块中return之前(包括return语句中的表达式运算)代码;
再执行finally块,因为finally块中有return所以提前退出。
- package Test;
- public class Test_Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Test1();
- }
- public static int Test1(){
- int x = 5;
- try
- {
- int num = x / 0;
- System.out.println("try");
- return 3;
- }
- catch (ArithmeticException e) {
- System.err.println("除数不能为0!");
- }
- finally
- {
- ++x;
- System.out.println("finally");
- return 2;
- }
- }
- }
运行结果如下:
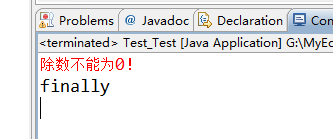
- 情况5:try{} catch(){return;}finally{return;}
程序执行catch块中return之前(包括return语句中的表达式运算)代码;
再执行finally块,因为finally块中有return所以提前退出。
- package Test;
- public class Test_Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Test1();
- }
- public static int Test1(){
- int x = 5;
- try
- {
- int num = x / 0;
- System.out.println("try");
- }
- catch (ArithmeticException e) {
- System.err.println("除数不能为0!");
- return 4;
- }
- finally
- {
- ++x;
- System.out.println("finally");
- return 2;
- }
- }
- }
运行结果如下:
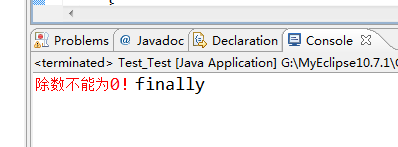
- 情况6:try{ return;}catch(){return;} finally{return;}
程序执行try块中return之前(包括return语句中的表达式运算)代码;
有异常:执行catch块中return之前(包括return语句中的表达式运算)代码;
则再执行finally块,因为finally块中有return所以提前退出。
无异常:则再执行finally块,因为finally块中有return所以提前退出。
1.有异常
- package Test;
- public class Test_Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Test1();
- }
- public static int Test1(){
- int x = 5;
- try
- {
- int num = x / 0;
- System.out.println("try");
- return 4;
- }
- catch (ArithmeticException e) {
- System.err.println("除数不能为0!");
- return 4;
- }
- finally
- {
- ++x;
- System.out.println("finally");
- return 2;
- }
- }
- }
运行结果如下:

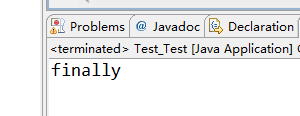
2.无异常
- package Test;
- public class Test_Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Test1();
- }
- public static int Test1(){
- int x = 5;
- try
- {
- // int num = x / 0;
- // System.out.println("try");
- return 4;
- }
- catch (ArithmeticException e) {
- System.err.println("除数不能为0!");
- return 4;
- }
- finally
- {
- ++x;
- System.out.println("finally");
- return 2;
- }
- }
- }
运行结果如下:
最终结论:任何执行try 或者catch中的return语句之前,都会先执行finally语句,如果finally存在的话。
如果finally中有return语句,那么程序就return了,所以finally中的return是一定会被return的,
编译器把finally中的return实现为一个warning。
- throw——抛出异常
抛出异常有三种形式,一是throw,一个throws,还有一种系统自动抛异常。
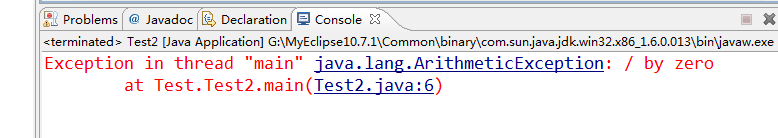
系统抛出异常:
- package Test;
- public class Test2 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int a = 5, b =0;
- System.out.println(5/b);
- }
- }
运行结果如下:
throw抛出异常:
throw是语句抛出一个异常。
语法:throw (异常对象);
- package Test;
- public class Test2 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s = "abc";
- if(s.equals("abc")) {
- throw new NumberFormatException();
- } else {
- System.out.println(s);
- }
- }
- }
运行结果如下:
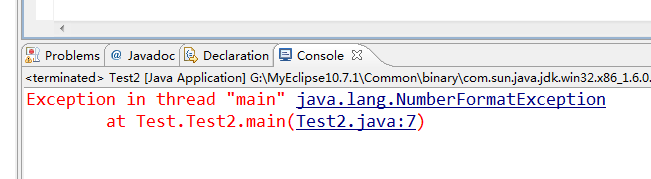
- throws——声明异常
throws是方法可能抛出异常的声明。(用在声明方法时,表示该方法可能要抛出异常)
语法:[(修饰符)](返回值类型)(方法名)([参数列表])[throws(异常类)]{......}
- package Test;
- public class Test2 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- try {
- Test3();
- } catch (NumberFormatException e) {
- System.err.println("非数据类型不能转换。");
- }
- }
- public static void Test3() throws NumberFormatException{
- String s = "abc";
- System.out.println(Double.parseDouble(s));
- }
- }
运行结果如下:
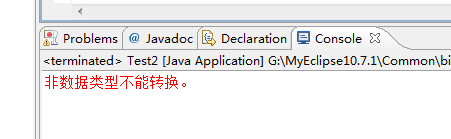
如果在一个方法体中抛出了异常,那么我们就可以通过throws——声明异常来通知调用者,非常方便。
throws表示出现异常的一种可能性,并不一定会发生这些异常;throw则是抛出了异常,执行throw则一定抛出了某种异常对象。
最后说一句,try-catch-finally虽好用,但是如果是滥用,这样只是会让程序的可读性变的很糟糕,当程序报错,就无法快速准确的定位了,物尽其用 人尽其才嘛!
Java异常之try,catch,finally,throw,throws的更多相关文章
- 顺平讲try catch finally throw throws(精华)
try catch finally 有点像if else语句 还有像javascript的服务器执行成功后的回调函数,success:function(){ 进行处理 }; throws的意思是将异 ...
- 基础知识《十》java 异常捕捉 ( try catch finally ) 你真的掌握了吗?
本文转载自 java 异常捕捉 ( try catch finally ) 你真的掌握了吗? 前言:java 中的异常处理机制你真的理解了吗?掌握了吗?catch 体里遇到 return 是怎么处理 ...
- java:异常机制(try,catch,finally,throw,throws,自定义异常)
* String类中的格式化字符串的方法: * public static String format(String format, Object... args):使用指定的格式字符串和参数返回一个 ...
- Java异常机制关键字总结,及throws 和 throw 的区别
在Java的异常机制中,时常出现五个关键字:try , catch , throw , throws , finally. 下面将总结各个关键字的用法,以及throw和throws的区别: (1) t ...
- Java基础-异常处理机制 及异常处理的五个关键字:try/catch/finally/throw /throws
笔记: /** 异常处理机制: 抓抛模型 * 1."抛", 一旦抛出,程序终止! printStackTrace()显示异常路径! * 2."抓", 抓住异常 ...
- java 异常捕捉 ( try catch finally ) 你真的掌握了吗?
掌握下面几条原则就可以完全解决“当try.catch.finally遭遇return”的问题. 原则:1.finally语句块中的代码是一定会执行的,而catch块中的代码只有发生异常时才会执行. 2 ...
- Java异常01——捕获和抛出异常
捕获和抛出异常 异常处理五个关键字 try , catch , finally , throw , throws try catch finally(快捷键:选中要要监控的代码语句 快捷键: ctrl ...
- 菜鸡的Java笔记 第三十 - java 异常的捕获及处理
异常的捕获及处理 1.异常的产生分析以及所带来的影响 2.异常的处理的基本格式 3.异常的处理流程 4.异常的处理模式 5.自定义 ...
- java异常——Exception、RuntimException
一.Exception和RuntimeException的区别 Exception是RuntimeException的父类,使用了 Exception 的类都必须对异常进行处理(try / throw ...
随机推荐
- Java IO学习总结
Java IO流学习总结 Io流的内容比较多 ,大致可以分为字节流和字符流,其中为了提高效率又用到了缓冲区. Java流操作有关的类或接口: 流的概念和作用 流是一组有顺序的,有起点和终点的字节集合, ...
- “未能加载文件或程序集file:///E:/MoneySet.dll或它的某一个依赖项,试图加载格式不正确的程序,行203,位置5. 文件:MReportSet.resx”,
http://bbs.csdn.net/topics/390334265 1.右键卸载项目2.右键选择编辑工程文件,在打开的文件的最后一行</project>之前加以下内容: <Pr ...
- [MVC] WebSecurity在VS2013中不识别
使用VS2013创建了MVC4项目以后,在filters中添加了类InitializeSimpleMembershipAttribute ,不能识别UserContext和WebSecurity,发现 ...
- Alternating Current
Codeforces Round #200 (Div. 1) B:http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/343/B 题意:这一题看懂题意是关键,题目的意思就 ...
- UIImageView之我的动画为什么停了?UIImageView, highLighted,animationImages
如果你的动画总是停了!停了!停了!不管你想不想都停,这里有个参考,你可以看看!这只是一种可能性!!! 受最近看到段子影响,画风略诡异,不喜勿喷. 最近在“刻”动画!!! 为什么是“刻”,动画写了3周啊 ...
- Ubuntu 12安装Virtualbox
用aptitude或者apt-get安装Virtualbox,安装过程中会报:”No suitable module for running kernel found [fail]“,安装未成功. 在 ...
- cron表达式详解(Spring定时任务配置时间间隔)
Cron表达式是一个字符串,字符串以5或6个空格隔开,分为6或7个域,每一个域代表一个含义,Cron有如下两种语法格式: Seconds Minutes Hours DayofMonth Month ...
- NSUserDefaults(数据存储)
NSUserDefaults(数据存储) NSUserDefaults适合存储轻量级的本地数据,比如要保存一个登陆界面的数据,用户名.密码之类的,个人觉得使用NSUserDefaults是首选.下 ...
- 【HDOJ】3183 A Magic Lamp
RMQ. /* 3183 */ #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <cstdlib> #define MA ...
- java学习面向对象之父子构造函数初始化
在之前讲到java面向对象继承的时候,我们只讲到了两个比较重要的知识点,一个是父子类当中有同名的成员变量,这个时候,我们引入了super这个关键字来区分这两个同名成员变量,除此之外,我们还讲到了父子同 ...
