五、C++运算符重载,使面向对象编程更方便
复数类CComplex
编译器做对象运算的时候,会调用对象的运算符重载函数(优先调用成员方法);如果没有成员方法,就砸全局作用域找合适的运算符重载函数
++和--运算符是单目运算符,在参数列表里放上一个int表示其在数的前面还是后面:operator++()表示前置,operator++(int)表示后置,括号里的int没有任何作用。
复数类的具体实现:
//// Created by 26685 on 2022-05-16 13:43.// Description:CComplex.h//#ifndef C___CCOMPLEX_H#define C___CCOMPLEX_H#include <iostream>using namespace std;class CComplex {friend CComplex operator+(const CComplex &l, const CComplex &r);friend iostream &operator<<(ostream &os, const CComplex &src);friend istream & operator>>(istream& is, CComplex &src);public:explicit CComplex(int r = 0, int i = 0) : _real(r), _image(i) {}// CComplex operator+(const CComplex& src) const{// return CComplex(this->_real+src._real,this->_image+src._image);// }void show() {cout << "real: " << _real << " image: " << _image << endl;}CComplex &operator++() {++_real;++_image;return *this;}CComplex operator++(int) {return CComplex(_real++, _image++);}private:int _real;int _image;};inline CComplex operator+(const CComplex &l, const CComplex &r) {return CComplex(l._real + r._real, l._image + r._image);}inline iostream &operator<<(ostream &os, const CComplex &src) {//重载输出操作os << "real: " << src._real << " image: " << src._image << endl;}inline istream & operator>>(istream& is,CComplex &src){//重载输入操作is>>src._real>>src._image;}#endif //C___CCOMPLEX_H
主函数:
int main(){CComplex cp1(10,15);CComplex cp2(20,30);CComplex cp3=cp2+cp1;cp3.show();CComplex cp4=cp3++;cp4.show();cp3.show();CComplex cp5= ++cp3;cp5.show();cp3.show();cout<<cp4;CComplex cp6;cin>>cp6;cout<<cp6;return 0;}
模拟实现string类的代码
//// Created by 26685 on 2022-05-16 14:30.// Description:String.h//#ifndef C___STRING_H#define C___STRING_H#include <iostream>#include <cstring>class String {friend std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const String &src);public:String(const char *src = nullptr) {if (src == nullptr) {_pstr = new char[1];*_pstr = '\0';} else {_pstr = new char[strlen(src) + 1];strcpy(_pstr, src);}}~String() {delete[] _pstr;_pstr = nullptr;}String(const String &src) {_pstr = new char[strlen(src._pstr) + 1];strcpy(_pstr, src._pstr);}bool operator>(const String &str) const {return strcmp(_pstr, str._pstr) > 0;}bool operator<(const String &str) const {return strcmp(_pstr, str._pstr) < 0;}bool operator==(const String &str) const {return strcmp(_pstr, str._pstr) == 0;}int length() const {return strlen(_pstr);}char &operator[](int index) {return _pstr[index];}char *c_str() const {return _pstr;}private:char *_pstr;};inline std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const String &src) {os << src._pstr;return os;}inline String operator+(const String& l,const String& r){char* ptmp=new char[strlen(l.c_str())+ strlen(r.c_str())+1];strcpy(ptmp,l.c_str());strcat(ptmp,r.c_str());String temp(ptmp);delete[] ptmp;return temp;}#endif //C___STRING_H
目前代码中的加法的重载运算效率不高,需要进一步改进。
上面代码的加法重载函数,会生成临时对象,影响性能。
暂时改进为:
inline String operator+(const String &l, const String &r) {// char *ptmp = new char[strlen(l.c_str()) + strlen(r.c_str()) + 1];String temp;temp._pstr=new char[strlen(l.c_str()) + strlen(r.c_str()) + 1];//避免了开辟两次内存空间strcpy(temp._pstr, l.c_str());strcat(temp._pstr, r.c_str());// String temp(ptmp);// delete[] ptmp;return temp;}
String对象的迭代器的实现
迭代器可以透明的访问容器内部元素的值
foreach遍历容器,其底层是用迭代器实现的
迭代器的功能:提供一种统一的方式,透明的遍历容器
在对迭代器加加时,一般用前置的++,因为不会生成新的对象,效率会高一些
/*** 迭代器的实现, 放在String类中*/class Iterator{public:Iterator(char* p= nullptr):_p(p){}bool operator!=(const String::Iterator&it){//判断两个迭代器是否相等return _p!=it._p;}void operator++(){++ _p;}char& operator*(){return *_p;}private:char* _p;};Iterator begin(){return {_pstr};}Iterator end(){return {_pstr+length()};}
实现vector容器中的迭代器
迭代器一般实现成容器的嵌套结构。
在VectorT类中添加以下代码:
class iterator {public:iterator(const T *p = nullptr): _ptr((int *) p) {}bool operator!=(const VectorT::iterator &it) {return _ptr != it._ptr;}void operator++() {++_ptr;}T &operator*() { return *_ptr; }private:T *_ptr;};iterator begin(){return {_first};}iterator end(){return {_last};}
迭代器的失效问题
1、调用erase后,当前位置到末尾元素的迭代器就会失效。
2、调用insert后,当前位置到末尾元素的迭代器就会失效
3、容器扩容后迭代器也会失效
首元素到插入点/删除点的迭代器依然有效
迭代器失效该怎么解决?要对迭代器进行更新操作!
不同容器的迭代器是不能进行比较运算的
vector中迭代器的实现(包含迭代器失效的判断)
//// Created by 26685 on 2022-05-15 20:33.// Description://#ifndef C___VECTORT_H#define C___VECTORT_H#include "AllocatorT.h"using namespace std;/*** 容器底层内存开辟,内存释放,对象构造和析构都通过allocator实现* @tparam T* @tparam Alloc*/template<typename T, typename Alloc=AllocatorT<T> >class VectorT {public:VectorT(int size = 10) {// _first=new T[size];_first = _alloctor.allocate(size);_last = _first;_end = _first + size;}~VectorT() {// delete[] _first;//使用allocator对vector逐个删除for (T *p = _first; p != _last; ++p) {_alloctor.destory(p);}_alloctor.deallocate(_first);_first = _last = _end = nullptr;}VectorT(const VectorT<T> &src) {int size = src._end - src._first;// _first = new T[size];_first = _alloctor.allocate(size);int len = src._last - src._first;for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {// _first[i] = src._first[i];_alloctor.contruct(_first + 1, src._first[i]);}_last = _first + len;_end = _first + size;}VectorT<T> &operator=(const VectorT<T> &src) {if (src == *this) {return *this;}//delete[] _first;for (T *p = _first; p != _last; p++) {_alloctor.destory(p);}_alloctor.deallocate(_first);int size = src._end - src._first;_first = new T[size];int len = src._last - src._first;for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {// _first[i] = src._first[i];_alloctor.contruct(_first + 1, src._first[i]);}_last = _first + len;_end = _first + size;return *this;}T &operator[](int index) {if (index < 0 || index >= size()) {throw "OutOfRangeException";}return _first[index];}void push_back(T val) {if (full()) {expend();}//*_last++ = val;_alloctor.construct(_last, val);_last++;}void pop_back() {if (empty()) { return; }verify(_last - 1, _last);--_last;_alloctor.destory(_last);}T back() const {return *(_last - 1);}bool full() const {return _last == _end;}bool empty() const {return _first == _last;}int size() const {return _last - _first;}/*** 实现迭代器*/class iterator {friend void VectorT<T, Alloc>::verify(T *first, T *last);friend iterator VectorT<T, Alloc>::insert(iterator it,const T& val);friend iterator VectorT<T, Alloc>::erase(iterator it);public:/*iterator(const T *p = nullptr): _ptr((int *) p) {}*//*** 根据新的成员变量实现新的构造函数,使其能实现迭代器失效* @param pvec 容器指针* @param ptr 位置指针*/iterator(VectorT<T, Alloc> *pvec = nullptr, T *ptr = nullptr) : _ptr(ptr), _pVec(pvec) {Iterator_Base *itb = new Iterator_Base(this, _pVec->_head._next);//构造新节点_pVec->_head._next = itb;//将头结点连接新节点}//接下来就是在改变数组的过程中使迭代器失效bool operator!=(const VectorT<T, Alloc>::iterator &it) {/*** 判断迭代器是否失效*/if (_pVec == nullptr || _pVec != it._pVec) {throw "iterator incompatable!";}return _ptr != it._ptr;}void operator++() {if (_pVec == nullptr) {throw "iterator invalid!";}++_ptr;}T &operator*() {if (_pVec == nullptr) {throw "iterator invalid!";}return *_ptr;}private:T *_ptr;/*** 实现迭代器失效,首先要添加一个指向容器的指针*/VectorT<T, Alloc> *_pVec;};/*** 根据新的成员方法生成相应的begin和end方法* @return*/iterator begin() {return {this, _first};}iterator end() {return {this, _last};}/*** 最后一步:判断迭代器是否失效* @param first* @param last*/void verify(T *first, T *last) {Iterator_Base *pre = &this->_head;Iterator_Base *it = this->_head._next;while (it != nullptr) {if (it->_cur->_ptr > first && it->_cur->_ptr <= last) {//迭代器失效,把iterator持有的容器指针置nullit->_cur->_pVec = nullptr;//删除当前迭代器节点,继续判断后面的迭代器节点是否失效pre->_next = it->_next;delete it;it = pre->_next;}else{pre=it;it=it->_next;}}}/*** 插入操作* @param it 迭代器位置* @param val 插入的值* @return 迭代器*/iterator insert(iterator it,const T& val){/** 不考虑扩容,* 不考虑指针的合法性*/verify(it._ptr-1,_last);T* p=_last;while(p>it._ptr){_alloctor.construct(p,*(p-1));_alloctor.destory(p-1);p--;}_alloctor.construct(p,val);_last++;return {this,p};}iterator erase(iterator it){verify(it._ptr-1,_last);T* p=it._ptr;while(p<_last-1){//元素向前移_alloctor.destory(p);_alloctor.construct(p,*(p+1));p++;}_alloctor.destory(p);_last--;return {this,it._ptr-1};}private:T *_first;//表示vector起始位置T *_last;//表示vector定义元素的末尾T *_end;//表示vector的末尾Alloc _alloctor;//负责内存管理/*** 在链表的结构中保存每个迭代器*/struct Iterator_Base {Iterator_Base(iterator *c = nullptr, VectorT<T, Alloc>::Iterator_Base *n = nullptr) : _cur(c), _next(n) {}iterator *_cur;Iterator_Base *_next;};/*** 头结点*/Iterator_Base _head;void expend() {//size扩大两倍int size = _end - _first;// T *ptmp = new T[size * 2];T *ptmp = _alloctor.allocate(2 * size);for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {//ptmp[i] = _first[i];_alloctor.construct(ptmp + i, _first[i]);}//delete[] _first;for (T *p = _first; p != _last; p++) {_alloctor.destory(p);}_alloctor.deallocate(_first);_first = ptmp;_last = _first + size;_end = _first + (2 * size);}};#endif //C___VECTORT_H
深入理解new和delete的原理
1、malloc和new的区别:
- malloc按字节开辟内存,new开辟内存时需要指定类型,如
new int[10],所以malloc开辟内存返回的都是void* - malloc只负责开辟空间,new不仅有malloc的功能,还可以进行数据的初始化
- malloc开辟内存失败返回nullptr指针,new抛出的是bad_alloc类型的异常
2、free和delete的区别:
- delete调用析构函数,free是内存释放
检查内存泄漏要重写new和delete
new和delete能混用吗?C++为什么要区分单个元素和数组的内存分配和释放呢?
对于内置类型int等,可以混用。但是对于自定义的类,就不能混用,因为自定义的类类型有析构函数,为了正确的析构函数,在开辟对象数组的时候会在数组前多开辟4个字节,记录对象的个数。
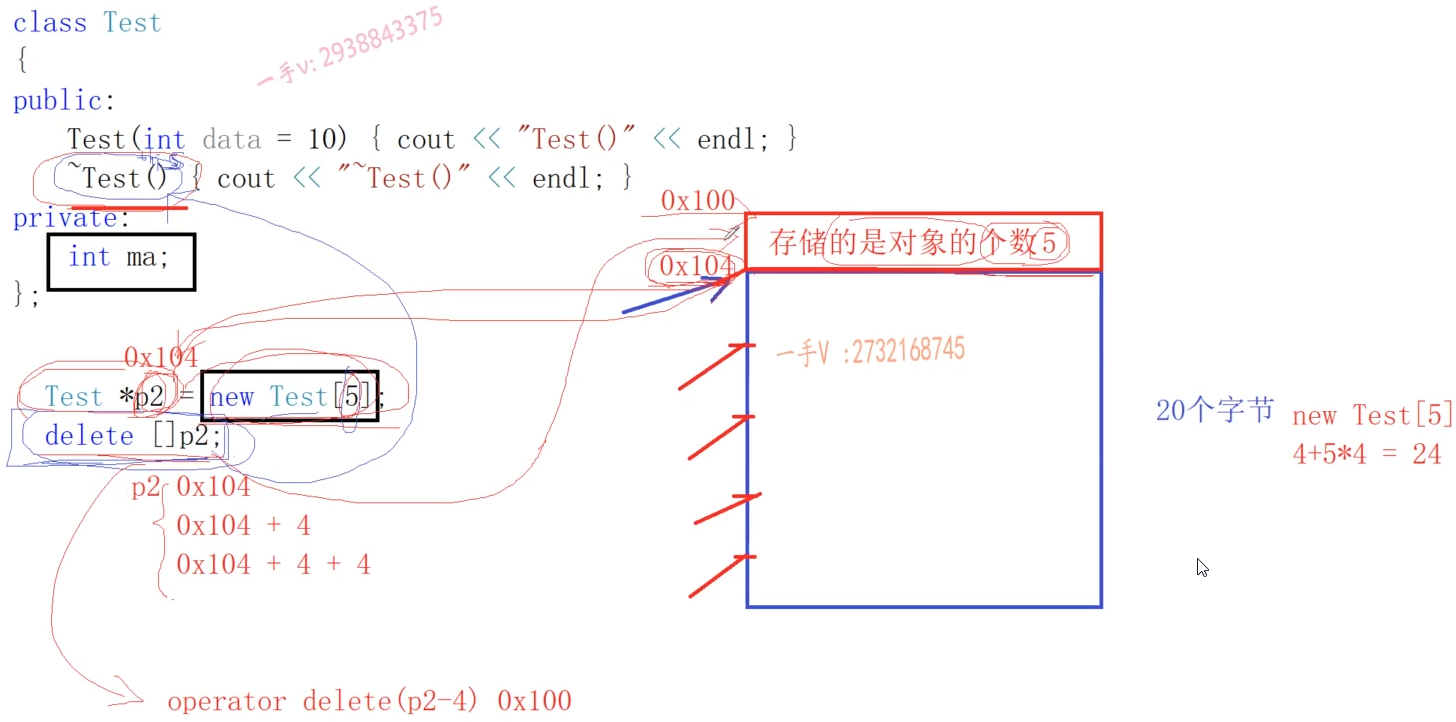
//两个操作符的重载void* operator new(size_t size){void* p=malloc(size);if(p== nullptr){throw bad_alloc();}cout<<"opeartor new addr:"<<p<<endl;return p;}void operator delete (void *ptr) noexcept{cout<<"opeartor delete addr:"<<ptr<<endl;free(ptr);}
new和delete重载实现对象池应用
对象池是在堆上开辟的静态链表
//// Created by 26685 on 2022-05-17 9:40.// Description://#ifndef C___QUEUEWITHITEMPOOL_H#define C___QUEUEWITHITEMPOOL_H#include <iostream>using namespace std;template<typename T>class Queue {public:Queue(){//默认构造_front=_rear=new QueueItem();}~Queue(){QueueItem* cur=_front;while(cur!= nullptr){//遍历链表,依次删除元素_front=_front->_next;delete cur;cur=_front;}}void push(const T& val){QueueItem* item=new QueueItem(val);_rear->_next=item;_rear=item;//尾部元素置为新值,与front区分开}void pop(){if(empty()){return;}QueueItem* first=_front->_next;_front->_next=first->_next;if(_front->_next== nullptr){//如果队列只有一个有效节点_rear=_front;}delete first;}bool empty() const{return _front==_rear;}T front()const {return _front->_next->_data;}private:/*** 实现一个链式的队列,带有头结点*/struct QueueItem {QueueItem(T data=T()):_data(data),_next(nullptr){}//重载new实现对象池void* operator new (size_t size){if(_itemPool== nullptr){//如果未开辟空间;如果当前内存池使用完,最后一个元素指向的也是nullptr,会分配新的内存池_itemPool=(QueueItem*)new char[POOL_ITEM_SIZE*sizeof(QueueItem)];//开辟对象池//我们用char,按字节开辟,因为如果用new QueueItem,//就又会调用到当前这个方法了,//我们现在就是在给QueueItem自定义new运算符重载QueueItem* p=_itemPool;for(;p<_itemPool+POOL_ITEM_SIZE-1;++p){p->_next=p+1;//初始化连续链表}p->_next= nullptr;}//新建queueItem的时候会使用对象池中未使用的节点,然后指向下一个未使用的节点QueueItem* p=_itemPool;_itemPool=_itemPool->_next;return p;}void operator delete (void* ptr){QueueItem* p=(QueueItem*)ptr;p->_next=_itemPool;_itemPool=p;}T _data;QueueItem *_next;static const int POOL_ITEM_SIZE=100000;static QueueItem *_itemPool;};QueueItem* _front;//指向头结点QueueItem* _rear;//指向队尾,};template<typename T>typename Queue<T>::QueueItem* Queue<T>::QueueItem::_itemPool= nullptr;#endif //C___QUEUEWITHITEMPOOL_H
五、C++运算符重载,使面向对象编程更方便的更多相关文章
- 四、C# 5.0 新特性——Async和Await使异步编程更简单
一.引言 .NET 4.5 的推出,对于C#又有了新特性的增加--就是C#5.0中async和await两个关键字,这两个关键字简化了异步编程,之所以简化了,还是因为编译器给我们做了更多的工作,下面就 ...
- 【转】【C#】C# 5.0 新特性——Async和Await使异步编程更简单
一.引言 在之前的C#基础知识系列文章中只介绍了从C#1.0到C#4.0中主要的特性,然而.NET 4.5 的推出,对于C#又有了新特性的增加--就是C#5.0中async和await两个关键字,这两 ...
- 转:[你必须知道的异步编程]C# 5.0 新特性——Async和Await使异步编程更简单
本专题概要: 引言 同步代码存在的问题 传统的异步编程改善程序的响应 C# 5.0 提供的async和await使异步编程更简单 async和await关键字剖析 小结 一.引言 在之前的C#基础知 ...
- [你必须知道的异步编程]C# 5.0 新特性——Async和Await使异步编程更简单
本专题概要: 引言 同步代码存在的问题 传统的异步编程改善程序的响应 C# 5.0 提供的async和await使异步编程更简单 async和await关键字剖析 小结 一.引言 在之前的C#基础知 ...
- C++(三十五) — 运算符重载
运算符重载的实质:函数重载.除了增加一个关键字 operator 外,与函数重载没有区别,都是通过该类的某个对象来访问重载运算符. (1)重载运算符时,运算符运算顺序和优先级不变,操作数个数不变: ( ...
- Python之路【第五篇续】:面向对象编程二
aaarticlea/png;base64,iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAABgQAAALaCAIAAABxja8cAAAgAElEQVR4nOzd6X9Tdd74/+uv+f5uzF
- C# 5.0 新特性——Async和Await使异步编程更简单
http://www.cnblogs.com/zhili/archive/2013/05/15/csharp5asyncandawait.html http://blog.zhaojie.me/201 ...
- C++ 关于运算符重载
转载来源:http://c.biancheng.net/cpp/biancheng/view/216.html 重载运算符的函数一般格式如下: 函数类型 operator 运算符名称 (形参表列 ...
- C++ 运算符重载三(链式编程)
//运算符重载之链式编程 #include<iostream> using namespace std; //对于友元函数重载运算符只适用于左操作数是系统变量的场景 //因为成员无法在系统 ...
随机推荐
- 路径规划—BUG算法
- Spring Security OAuth 笔记
1 单点登录 关于单点登录的原理,我觉得下面这位老哥讲的比较清楚,有兴趣可以看一下,下面我把其中的重点在此做个笔记总结 https://juejin.cn/post/6844904079274197 ...
- 【转载】10个Web3D可视化精彩案例
1.化学元素周期表 六种排列方式,炫酷动画效果,TWaver 3D轻松实现. 演示地址:http://demo.servasoft.com/che... 2.DNA螺旋图 DNA3D模型,包含几千个球 ...
- javaweb图书管理系统之账号密码验证登录
验证账号与密码是否正确功能 一.注册功能 首先,在验证账号与密码是否正确的前提下的,需要先注册一个账号,如果没有账号,就会进不去,也无法验证. 其实,注册功能就是一个添加的功能,仿照我的第一篇文章,往 ...
- mysql在cmd中查询到的汉字乱码问题解决 方法一
只要执行如上两个 set character_set_connection = gbk; set character_set_results= gbk; 将编码格式转换成gbk即可
- jdbc连接MySQL数据库+简单实例(普通JDBC方法实现和连接池方式实现)
jdbc连接数据库 总结内容 1. 基本概念 jdbc的概念 2. 数据库连接 数据库的连接 DAO层思想 重构设计 3. 事务 概念 事务的ACID属性 事务的操作 4. 连接池 为什么要使用连接池 ...
- C++---变量、数据类型和运算符
内存 计算机使用内存来记忆或存储计算时所使用的的数据. 计算机执行程序时, 组成程序的指令和程序所操作的数据都必须存放在某个地方, 而这个地方就是计算机的内存, 也称为主存, 或随机访问存储器(RAM ...
- Go语言 映射(map)
Go语言 映射(map) 1. 什么是 map2. 创建 map3. 访问 map4. nil map和空map5. map中元素的返回值6. len()和delete()7. 测试map中元素是否 ...
- linux中查看端口号使用情况
百度一圈,以下是整理来的操作命令. 1.netstat -anp |grep (端口号) 这个方法可以直观看到对应端口号是否被使用. 2.netstat -nultp 这个方法可以看到该机上所有以用的 ...
- SSM实现个人博客-day04
项目源码免费下载:SSM实现个人博客 有问题询问vx:kht808 3.项目搭建(SSM整合) (1)创建maven工程,导入相应的依赖 <properties> <project. ...
