我要手撕mybatis源码
传统的JDBC编程中的一般操作:
- 1、注册数据库驱动类,指定数据库的URL地址、数据库用户名、密码等连接信息
- 2、通过DriverManager打开数据库连接
- 3、通过数据库连接创建Statement对象。
- 4、通过State对象执行SQL语句,得到ResultSet对象。
- 5、通过ResultSet读取数据,将数据转换成JavaBean对象
- 6、关闭连接、释放资源
ORM(Object Relational Mapping) 对象—关系映射。用于实现面向对象编程语言里 不同类型系统的数据 之间的转换。


1、源码分析
1、先读取配置文件中的信息

经过多次追踪、找到这个getResourceAsStream核心方法,以下是该方法的源码

该方法的参数不仅有传入的文件路径还有类加载器。类加载的主要作用是将名称转化为文件名,读取外部资源。
作为debug的入口

跟踪到核心源码部分

这里完成两个操纵:
- 在这里生成了一个XMLConfigBuilder的对象,并且调用了其parse()方法。返回解析好的configuration对象信息。
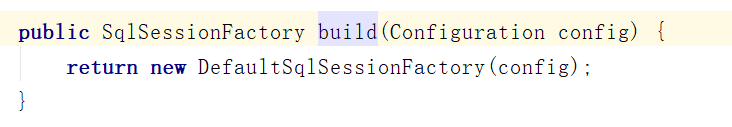
- 调用了SqlSessionFactoryBuilder自身的build()方法,传入的参数为上一步得到的Configuration对象。
先追踪XMLConfigBuilder对象的parse()方法

这里的parsed保证只加载一次,这里的/configuration是整个配置文件的根节点、是解析整个配置文件的入口。然后调用parseConfiguration方法,继续追踪

查看root的传入的值,实际上就是configuration下的各个节点
<configuration>
<typeAliases>
<package name="com.github.yeecode.mybatisdemo"/>
</typeAliases>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mybatis?serverTimezone=UTC"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/github/yeecode/mybatisdemo/UserMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
查看environment下的信息、继续追踪,到environmentsElement方法,

查看传入的context的值,这里就是解析的信息。也就是url、username、password 、驱动的信息。和上一个的信息是不一样的
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mybatis?serverTimezone=UTC"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>

通过进入每个子方法可以看出来,Configuration类中保存了配置文件的所有配置信息。
通过调用SqlSessionFactoryBuilder自身的build()方法,返回了SqlSessionFactory对象。

小结
初始化阶段、MyBatis主要完成以下几项工作
- 根据配值文件的位置,获取它的输入流InputStream
- 从配置文件的根节点开始,逐层解析配置问价,也包括相应的映射文件。解析过程不断将解析结果放入Configuration对象
- 以配置好的Configuration对象作为参数,获取一个SqlSessionFactory对象
2、数据读写阶段追踪
2.1 获得sqlsession

追踪openSession方法

进入openSessionFromDataSource方法内部,这里是生成SqlSession的核心源码

进入DefaultSqlSession类中,类里提供了查询、增加、更新、删除、提交、回滚等大量的方法



执行完new DefaultSqlSession(this.configuration, executor, autoCommit);后就返回了一个SqlSession对象

2.2 映射接口文件与映射文件的绑定


通过操作Configuration的getMapper方法最终进入MapperRegistry类的getMapper方法。

2.3 映射接口的代理
session.getMapper(UserMapper.class)得到的是mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession)返回的对象,追踪此方法得到

返回的是基于反射的动态代理对象,找到MapperProxy类的invoke方法,被代理对象的方法会被代理对象的invoke方法拦截、直接到 MapperProxy类的invoke方法拦截,

在invoke打上断点,当执行 userMapper.queryUserBySchoolName(userParam);会自动进入断点invoke内

然后会触发MapperMethod对象的execute方法

进入该方法
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
Object param;
switch(this.command.getType()) {
case INSERT:
param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = this.rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(this.command.getName(), param));
break;
case UPDATE:
param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = this.rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(this.command.getName(), param));
break;
case DELETE:
param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = this.rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(this.command.getName(), param));
break;
case SELECT:
if (this.method.returnsVoid() && this.method.hasResultHandler()) {
this.executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (this.method.returnsMany()) {
result = this.executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (this.method.returnsMap()) {
result = this.executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (this.method.returnsCursor()) {
result = this.executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(this.command.getName(), param);
if (this.method.returnsOptional() && (result == null || !this.method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {
result = Optional.ofNullable(result);
}
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + this.command.getName());
}
if (result == null && this.method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !this.method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + this.command.getName() + " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + this.method.getReturnType() + ").");
} else {
return result;
}
}
会根据不同的操作类型调用不同的处理方法、这里执行的是查询操作、所以就调用这个方法

进入executeForMany方法,在这个方法中,MyBatis已经开始通过SqlSession对象的selectList方法开展后续的查询工作。

2.4 sql语句的查找
继续追踪到DefaultSqlSession中的selectList方法,源码如下

每个MappedStatement对象对应设置的一个数据库操作节点,主要定义了数据库操作语句、输入/输出参数等信息。this.configuration.getMappedStatement(statement)语句将要执行的MappedStatement对象从Configuration对象存储的映射文件信息中找了出来。
2.5 查询缓存
其中的query方法是Executor中的抽象方法,实现有两个、一个是查询数据库、一个是查询缓存

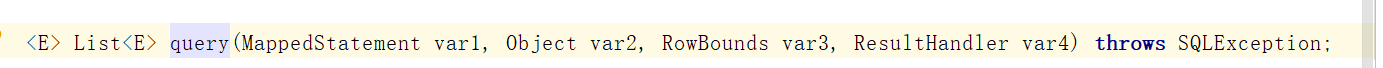

直接在抽象方法上打一个断点、查看执行哪边、这里执行的是CachingExecutor中的方法、源码如下

其中的BoundSql是经过层层转化后去掉if、where、等标签的sql语句,CacheKey是为该此次查询操作计算出来的缓存建。
继续追踪代码流程到这里

查看当前的查询操作是否名中缓存,如果是从缓存中获取数据值、如果不是则调用delegate调用query方法。随后将此次查询的结果放入缓存中。
2.6 数据库查询
再次调用了executor接口中的抽象方法

继续追踪代码流向

最终进入了BaseExecutor中的query方法上,源码如下
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
if (this.closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
} else {
if (this.queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
this.clearLocalCache();
}
List list;
try {
++this.queryStack;
list = resultHandler == null ? (List)this.localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
this.handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
list = this.queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
--this.queryStack;
}
if (this.queryStack == 0) {
Iterator var8 = this.deferredLoads.iterator();
while(var8.hasNext()) {
BaseExecutor.DeferredLoad deferredLoad = (BaseExecutor.DeferredLoad)var8.next();
deferredLoad.load();
}
this.deferredLoads.clear();
if (this.configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
this.clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
}
其中的关键部分、开始调用数据库展开查询操作

queryFromDatabase的源代码如下

首先在缓存中放置一个占位符,然后调用doQuery方法实际执行,最后,将缓存中的占位符替换成真正的查询结果。
doQuery方法是BaseExecutor中的抽象方法,实际运行的最终实现代码

生成了Statement对象,是java.sql包中的类,Statement类能够执行静态SQL语句并返回结果。

获得了一个StatementHandler对象handler,然后将查询操作交给StatementHandler执行,StatementHandler是一个语句处理器,其中封装了很多的语句操作方法。,继续追踪代码流向。
handler.query(stmt,resultHandler)调用的是StatementHandler接口中的抽象方法

接续追踪代码走向、进入PreparedStatementHandler中,调用方法、源码如下

这里,ps.execute()真正执行了SQL语句,然后把执行结果交给ResulHandler对象处理。
流程梳理
- 1、先查缓存,如果一定要查数据库、则查询数据库后需要将结果也放入缓存中
- 2、SQL语句经过多次转化,经过了MappedStatement对象、Statement对象和PreparedStatement对象,最后才执行
- 最后将查询的结果交给ResultHandler对象处理
2.7 处理结果集
查询到的结果集并没有直接返回,而是交给ResultHandler对象处理,ResultHandler是结果处理器,用来接受查询结果的方法是该接口中的抽象方法handleResultSets

继续代码追踪,最终的执行方法是DefaultResultSetHandler类中的handleResultSets方法
public List<Object> handleResultSets(Statement stmt) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("handling results").object(this.mappedStatement.getId());
List<Object> multipleResults = new ArrayList();
int resultSetCount = 0;
ResultSetWrapper rsw = this.getFirstResultSet(stmt);
List<ResultMap> resultMaps = this.mappedStatement.getResultMaps();
int resultMapCount = resultMaps.size();
this.validateResultMapsCount(rsw, resultMapCount);
while(rsw != null && resultMapCount > resultSetCount) {
ResultMap resultMap = (ResultMap)resultMaps.get(resultSetCount);
this.handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, multipleResults, (ResultMapping)null);
rsw = this.getNextResultSet(stmt);
this.cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
++resultSetCount;
}
String[] resultSets = this.mappedStatement.getResultSets();
if (resultSets != null) {
while(rsw != null && resultSetCount < resultSets.length) {
ResultMapping parentMapping = (ResultMapping)this.nextResultMaps.get(resultSets[resultSetCount]);
if (parentMapping != null) {
String nestedResultMapId = parentMapping.getNestedResultMapId();
ResultMap resultMap = this.configuration.getResultMap(nestedResultMapId);
this.handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, (List)null, parentMapping);
}
rsw = this.getNextResultSet(stmt);
this.cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
++resultSetCount;
}
}
return this.collapseSingleResultList(multipleResults);
}
查询出来的结果被遍历后放入list列表multipleResults中并返回。
继续代码追踪







createResultObject(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, List<Class<?>> constructorArgTypes, List<Object> constructorArgs, String columnPrefix)方法:在自动属性映射功能开启的情况下,该方法将数据记录的值赋给输出结果对象。

追踪代码进入applyAutomaticMappings方法
private boolean applyAutomaticMappings(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, MetaObject metaObject, String columnPrefix) throws SQLException {
List<DefaultResultSetHandler.UnMappedColumnAutoMapping> autoMapping = this.createAutomaticMappings(rsw, resultMap, metaObject, columnPrefix);
boolean foundValues = false;
if (!autoMapping.isEmpty()) {
Iterator var7 = autoMapping.iterator();
while(true) {
DefaultResultSetHandler.UnMappedColumnAutoMapping mapping;
Object value;
do {
if (!var7.hasNext()) {
return foundValues;
}
mapping = (DefaultResultSetHandler.UnMappedColumnAutoMapping)var7.next();
value = mapping.typeHandler.getResult(rsw.getResultSet(), mapping.column);
if (value != null) {
foundValues = true;
}
} while(value == null && (!this.configuration.isCallSettersOnNulls() || mapping.primitive));
metaObject.setValue(mapping.property, value);
}
} else {
return foundValues;
}
}
applyAutomaticMappings方法:该方法将按照用户的映射设置,给输出结果对象的属性赋值
继续追踪代码、进入applyPropertyMappings方法

private boolean applyPropertyMappings(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, MetaObject metaObject, ResultLoaderMap lazyLoader, String columnPrefix) throws SQLException {
List<String> mappedColumnNames = rsw.getMappedColumnNames(resultMap, columnPrefix);
boolean foundValues = false;
List<ResultMapping> propertyMappings = resultMap.getPropertyResultMappings();
Iterator var9 = propertyMappings.iterator();
while(true) {
while(true) {
Object value;
String property;
do {
ResultMapping propertyMapping;
String column;
do {
if (!var9.hasNext()) {
return foundValues;
}
propertyMapping = (ResultMapping)var9.next();
column = this.prependPrefix(propertyMapping.getColumn(), columnPrefix);
if (propertyMapping.getNestedResultMapId() != null) {
column = null;
}
} while(!propertyMapping.isCompositeResult() && (column == null || !mappedColumnNames.contains(column.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH))) && propertyMapping.getResultSet() == null);
value = this.getPropertyMappingValue(rsw.getResultSet(), metaObject, propertyMapping, lazyLoader, columnPrefix);
property = propertyMapping.getProperty();
} while(property == null);
if (value == DEFERRED) {
foundValues = true;
} else {
if (value != null) {
foundValues = true;
}
if (value != null || this.configuration.isCallSettersOnNulls() && !metaObject.getSetterType(property).isPrimitive()) {
metaObject.setValue(property, value);
}
}
}
}
}
- applyPropertyMappings 方法:该方法按照用户的映射设置,给输出结果对象的属性赋值
执行完之后,装载着multipleResults被返回给List<User> userList 变量
小结
- 1、建立连接数据库的sqlsession
- 2、查找当前映射接口中抽象方法对应的数据库操作节点,根据该节点生成接口的实现
- 3、接口的实现拦截对映射接口中抽象方法的调用,并将其转化为数据查询操作
- 4、对数据库操作节点中的数据库操作语句进行多次处理、最终得到标准的sql语句。
- 5、尝试从缓存查询、找到返回;找不到继续找数据库
- 6、从数据库中查询结果
- 7、处理结果集(建立输出对象,根据输出结果对输出对象的属性赋值)
- 在缓存中记录查询结果
- 返回查询结果
我要手撕mybatis源码的更多相关文章
- 竟然还有人说ArrayList是2倍扩容,今天带你手撕ArrayList源码
ArrayList是我们开发中最常用到的集合,但是很多人对它的源码并不了解,导致面试时,面试官问的稍微深入的问题,就无法作答,今天我们一起来探究一下ArrayList源码. 1. 简介 ArrayLi ...
- 从Mybatis源码理解jdk动态代理默认调用invoke方法
一.背景最近在工作之余,把开mybatis的源码看了下,决定自己手写个简单版的.实现核心的功能即可.写完之后,执行了一下,正巧在mybatis对Mapper接口的动态代理这个核心代码这边发现一个问题. ...
- MyBatis 源码分析 - 插件机制
1.简介 一般情况下,开源框架都会提供插件或其他形式的拓展点,供开发者自行拓展.这样的好处是显而易见的,一是增加了框架的灵活性.二是开发者可以结合实际需求,对框架进行拓展,使其能够更好的工作.以 My ...
- MyBatis 源码分析系列文章导读
1.本文速览 本篇文章是我为接下来的 MyBatis 源码分析系列文章写的一个导读文章.本篇文章从 MyBatis 是什么(what),为什么要使用(why),以及如何使用(how)等三个角度进行了说 ...
- Eclipse里导入Mybatis源码工程
打开Eclipse,在前两天的记录里我已经把Maven什么的都配置好了,还有Mybatis的源码也下载下来了,不相信的话可以去看一下我之前的记录:) OK. Mybatis源码解压之后是一个标准的Ma ...
- myBatis源码解析-缓存篇(2)
上一章分析了mybatis的源码的日志模块,像我们经常说的mybatis一级缓存,二级缓存,缓存究竟在底层是怎样实现的.此次开始分析缓存模块 1. 源码位置,mybatis源码包位于org.apach ...
- myBatis源码解析-二级缓存的实现方式
1. 前言 前面近一个月去写自己的mybatis框架了,对mybatis源码分析止步不前,此文继续前面的文章.开始分析mybatis一,二级缓存的实现.附上自己的项目github地址:https:// ...
- Mybatis源码解析3——核心类SqlSessionFactory,看完我悟了
这是昨晚的武汉,晚上九点钟拍的,疫情又一次来袭,曾经熙熙攘攘的夜市也变得冷冷清清,但比前几周要好很多了.希望大家都能保护好自己,保护好身边的人,生活不可能像你想象的那么好,但也不会像你想象的那么糟. ...
- MyBatis源码分析(一)开篇
源码学习的好处不用多说,Mybatis源码量少.逻辑简单,将写个系列文章来学习. SqlSession Mybatis的使用入口位于org.apache.ibatis.session包中的SqlSes ...
随机推荐
- Python怎么打印彩色字符串
print 也许是我们在使用 Python 的时候用的最多的一种操作,但是经常发现很多人可以打印彩色文本,这种操作是怎么得到的呢? 一行代码突出重点内容 现在我们通过一个例子,说明彩色文本怎么打印.先 ...
- 我在Apache DolphinScheduler的心路历练
摘要:Apache DolphinScheduler 目前是 Apache 孵化项目,目前正在快速发展中.加入Apache DolphinScheduler社区已一年多,已有 400+ 公司在生产上使 ...
- POJ2201 Cartesian Tree (cartesian tree)
#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> ...
- Mysql 实现数据库读写分离
Amoeba+Mysql实现数据库读写分离 一.Amoeba 是什么 Amoeba(变形虫)项目,专注 分布式数据库 proxy 开发.座落与Client.DB Server(s)之间.对客户端透明. ...
- HTTP 的 Content-Type 及其媒体类型(MIME)
Content-Type Content-Type 代表 HTTP 携带的文件类型,决定文件接收方或发送方将以什么形式.什么编码读取这个文件.下图,load.gif 的媒体类型就是 image/gif ...
- JavaScript 基础知识(二):闭包
首先来思考一下下面的案例: function unclosure() { let count = 0 return count++ } for (let index = 0; index < 1 ...
- JZM 的印象笔记 (卷积,分块)
题面 题目背景 大名鼎鼎的 OI 天花板选手 JZM 对自己的好伙伴--印象笔记有些生疏了 题目描述 作为一名 OI 选手,他的笔记中的字母只包含数字0和1. JZM 在印象笔记中找到了一行 N N ...
- python 二分法查找字典中指定项第一次出现的索引
import time #引入time库,后续计算时间. inform_m = {} #创建母字典 inform_s = {} #母字典下嵌套的子字典 #给母字典添加键-值 for i in rang ...
- 【设计模式】Java设计模式 - 适配器模式
[设计模式]Java设计模式 - 适配器模式 不断学习才是王道 继续踏上学习之路,学之分享笔记 总有一天我也能像各位大佬一样 原创作品,更多关注我CSDN: 一个有梦有戏的人 准备将博客园.CSDN一 ...
- yum install lrzsz
yum install lrzsz rz:从本地上传文件至服务器 sz filename:从服务器下载文件至本地
