1,Boost -> Bind
<1>auto ,initializer_list<T>,auto指向函数指针的简易,和typdef 定义的类型执行函数指针有多复杂。
- #include <iostream>
- #include <initializer_list>
- #include <string>
- using namespace std;
- template <typename T>
- T sum(initializer_list<T> rh)
- {
- T val;
- for(auto p= rh.begin();p!=rh.end();p++)
- {
- val+= *p;
- }
- return val;
- }
- int main()
- {
- // use init list
- cout << sum({,,,,}) <<endl;
- cout << sum({1.0,2.0,3.1,4.0,5.0}) <<endl;
- //
- cout << "use auto to point the function sum" <<endl;
- auto dadd_func = sum<double>;
- auto iadd_func = sum<int>;
- auto tadd_func = sum<string>;
- cout << dadd_func({,,,}) <<endl;
- cout << iadd_func({,,,,}) <<endl;
- cout << tadd_func({"houdini","maya","json"}) <<endl;
- cout << "\nuse the typedef to pointer\n";
- typedef int (*td_int_sum)(initializer_list<int> rh);
- typedef string (*td_str_sum)(initializer_list<string> rh);
- td_int_sum int_add = sum<int>;
- td_str_sum str_add = sum<string>;
- cout << int_add({,,,,,}) <<endl;
- cout << str_add({"s1","s2","s5"}) << endl;
- return ;
- }
<2>funcional,std::generate,std::count_if
- #include <iostream>
- #include <math.h>
- #include <vector>
- #include <algorithm>
- #include <functional>
- using namespace std;
- double square(double x){return x*x;}
- int main()
- {
- vector <int> vars();
- generate(vars.begin(),vars.end(),std::rand);
- for_each(vars.begin(),vars.end(),[](int v){cout << v <<endl;});
- // lambda can transfer local variable
- int sum = ;
- for_each(vars.begin(),vars.end(),[&sum](int v){sum+=v;});
- cout << "the sum is " << sum <<endl;
- // <100 num
- cout << "get <100 numbers" <<endl;
- cout << count_if(vars.begin(),vars.end(),[](int v){ return v<;}) <<endl;
- // functional
- function<double(double)> ef1 = square;
- cout << ef1() <<endl; //
- function<void(int var)> ef2 = [](int val){cout << val <<endl;};
- ef2(); //
- return ;
- }
<3> remove_if,vector,min_element,max_element
- include <iostream>
- #include <algorithm>
- #include <vector>
- #include <string>
- using namespace std;
- void cppRemove_if()
- {
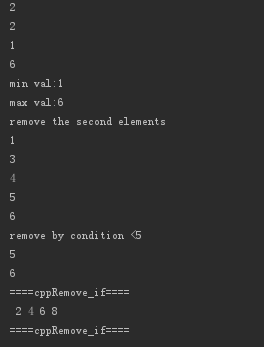
- cout << "====cppRemove_if====\n";
- int myInts[]{,,,,,,,}; // 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
- int *pbegin = myInts;
- int *pend = myInts + sizeof(myInts)/ sizeof(int);
- pend = remove_if(pbegin,pend,
- [](const int &val)->bool{return val% == ;});//2 4 5 8 ? ? ? ?
- for (int* p=pbegin; p!=pend; ++p)
- cout << ' ' << *p;
- cout << "\n";
- cout << "====cppRemove_if====\n";
- }
- int main()
- {
- vector<int> va{,,,,,};
- // find, if not find elements,will return last *iter;
- auto va_find2 = find(va.begin(),va.end(),);
- auto va_find2e = find_if(va.begin(),va.end(),[](const int &x){return x==;});
- cout << *va_find2 <<endl;
- cout << *va_find2e <<endl;
- cout << *min_element(va.begin(),va.end()) <<endl;
- cout << *max_element(va.begin(),va.end()) <<endl;
- auto min_max = minmax_element(va.begin(),va.end());
- cout << "min val:" <<*(min_max.first)<<endl;
- cout << "max val:" <<*(min_max.second)<<endl;
- cout << "remove the second elements \n";
- va.erase(va.begin()+,va.begin()+);
- for_each(va.begin(),va.end(),[](const int &x){cout << x <<endl;});
- cout << "remove by condition <5 \n";
- va.erase(remove_if(va.begin(),va.end(),[](int x){return x <;}),va.end());
- for_each(va.begin(),va.end(),[](const int &x){cout << x <<endl;});
- cppRemove_if();
- return ;
- }
<4>binary_search,sort更加详细的用法:
- #include <iostream>
- #include <algorithm>
- #include <vector>
- #include <functional>
- using namespace std;
- template <typename T1>
- void ShowIntArray(const T1 begin, const T1 end)
- {
- for_each(begin,end,[](const int &x){cout << x <<" "; });
- cout << "\n";
- }
- template <typename T>
- void ShowSTLArray(const T&cont)
- {
- auto iter = cont.begin();
- auto end = cont.end();
- for(;iter!=end;iter++)
- {
- cout << *iter <<" ";
- }
- cout <<endl;
- };
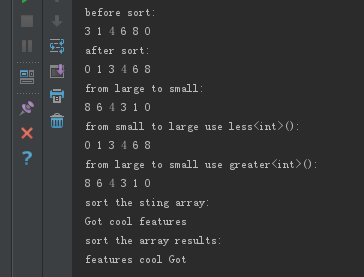
- void cpp_sort()
- {
- int a[]= {,,,,,};
- int *begin = a;
- int *end = a + ;
- cout << "before sort:\n";
- ShowIntArray(begin, end);
- sort(begin,end);
- cout << "after sort:\n";
- ShowIntArray(begin, end);
- cout << "from large to small:\n";
- sort(begin,end,[](const int &x,const int &y){return x>y;});
- ShowIntArray(begin, end);
- cout << "from small to large use less<int>():\n";
- sort(begin,end,less<int>());
- ShowIntArray(begin, end);
- cout << "from large to small use greater<int>():\n";
- sort(begin,end,greater<int>());
- ShowIntArray(begin, end);
- vector<string> vecStr{"Got","cool","features"};
- cout << "sort the sting array:\n";
- ShowSTLArray(vecStr);
- auto strCmp = [](string &a,string &b)
- {
- return a.length() > b.length();
- };
- cout << "sort the array results:\n";
- sort(vecStr.begin(),vecStr.end(),strCmp);
- ShowSTLArray(vecStr);
- }
- void cpp_binary_search()
- {
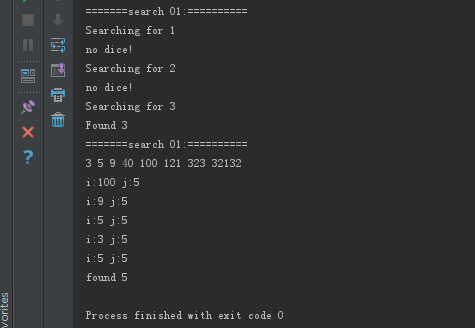
- cout << "=======search 01:==========\n";
- std::vector<int> haystack {, , , , };
- std::vector<int> needles {, , };
- sort(haystack.begin(),haystack.end());
- for (auto needle : needles)
- {
- cout << "Searching for " << needle << '\n';
- if (binary_search(haystack.begin(), haystack.end(), needle))
- {
- cout << "Found " << needle << '\n';
- }
- else
- {
- cout << "no dice!\n";
- }
- }
- cout << "=======search 01:==========\n";
- std::vector<int> haystack2 {, , , , ,,,};
- sort(haystack2.begin(),haystack2.end(),[](int &x,int &y){return x<y;});
- ShowSTLArray(haystack2);
- auto func =[](int i,int j)->bool{cout<< "i:" << i; cout << " j:"<<j;cout<<"\n";return (i<j);};
- if (binary_search(haystack2.begin(),haystack2.end(),,func))
- {
- cout << "found 5" <<endl;
- }
- }
- int main()
- {
- //cpp_sort();
- cpp_binary_search();
- return ;
- }
binarySearch结果:
Sort结果:
<5> 线程大法
(1) hello world thread:
- #include <iostream>
- #include <thread>
- #include <memory>
- using namespace std;
- void thread_task()
- {
- cout << "thread hello world\n";
- }
- int main()
- {
- shared_ptr<thread> t(new thread(thread_task));
- t->join();
- return ;
- }
(2)带参数的函数(bind方法,直接使用thread构造也可以)
- void thread_parm(const int &n,const string& name)
- {
- for(int i=;i<n;i++)
- {
- cout << name <<":thread loop in " << i <<endl;
- }
- }
- void withParam()
- {
- thread t0(thread_parm,,"houdini");
- thread t1(bind(thread_parm,,"maya"));
- t0.join();
- t1.join();
- }
- int main()
- {
- withParam();
- return ;
- }
(3)成员对象函数执行在线程中(也可以作用到智能指针对象)
- class HelloObject
- {
- public:
- void sayHello(const string& name,int n)
- {
- for(int i=;i<n;i++)
- {
- cout << name << " thread: " << i <<endl;
- }
- }
- };
- void objectFunction()
- {
- HelloObject obj;
- thread t(&HelloObject::sayHello,&obj,"Json",);
- t.join();
- // work with shared_ptr
- shared_ptr<HelloObject> objPtr(new HelloObject());
- thread tptr(&HelloObject::sayHello,objPtr,"Houdini",);
- tptr.join();
- }
- int main()
- {
- objectFunction();
- return ;
- }
(4)传递引用,头文件functional,std::ref()
- class FuncObj
- {
- public:
- void operator()()const
- {
- cout << this <<endl;
- }
- };
- void passRef()
- {
- auto obj = FuncObj();
- obj();
- //pass by value
- cout << "thread will pass by value\n";
- thread t1(obj);
- t1.join();
- //pass by ref
- cout << "thread will pass by ref\n";
- thread t2(ref(obj));
- t2.join();
- }
- int main()
- {
- passRef();
- return ;
- }
结果:
0x22fdff
thread will pass by value
0x7c6150
thread will pass by ref
0x22fdff
普通的函数也可以
- void increment(int &value)
- {
- value++ ;
- cout << "value :" << value <<endl;
- }
- void passRef2()
- {
- int a = ;
- thread t(increment,ref(a));
- t.join();
- }
- int main()
- {
- passRef2();
- return ;
- }
(5)基本功能:
匿名函数:get_id() 区分线程
- void lambdaTest()
- {
- vector <thread> threads;
- for(int i=;i<;i++)
- {
- threads.emplace_back(thread([](){cout << "thread id " << this_thread::get_id() << endl;}));
- }
- for(auto &t : threads)
- {
- t.join();
- }
- }
- int main()
- {
- lambdaTest();
- return ;
- }
总线程数:
- cout << thread::hardware_concurrency() <<endl;
(6)异常与线程
标准处理方法
- struct Counter2
- {
- int value;
- Counter2():value(){}
- void increment()
- {
- ++value;
- }
- void decrement()
- {
- if(value == )
- {
- throw string("value cannot be less than 0");
- }
- --value;
- }
- };
- struct Wrapper
- {
- Counter2 ct;
- mutex m;
- void increment()
- {
- }
- void decrement()
- {
- m.lock();
- try
- {
- ct.decrement();
- }
- catch (const string &e)
- {
- m.unlock();
- cout << e <<endl;
- throw e;
- }
- m.unlock();
- }
- };
- void exceptionLock()
- {
- Wrapper wap;
- wap.ct.value = ;
- vector<thread> threads;
- for(int i=;i<;i++)
- {
- threads.emplace_back(thread([&wap](){
- wap.decrement();
- }));
- }
- for(auto &t:threads)
- {
- t.join();
- }
- cout << wap.ct.value << endl;
- }
(7)模仿Inter TBB parallel_for
串行时间:87
并行时间:19
- struct BlockRange
- {
- BlockRange():begin(),end()
- {
- }
- int begin;
- int end;
- };
- class ApplyFoo
- {
- public:
- ApplyFoo(vector<int> *data):mData(data)
- {
- }
- void operator()(const BlockRange &range)const
- {
- for(int i=range.begin;i<range.end;i++)
- {
- (*mData)[i] += ;
- }
- }
- private:
- vector<int> *mData;
- };
- template <typename T>
- void parallel_for(const T &body,int size,int begin)
- {
- auto nThreads = thread::hardware_concurrency();
- auto nValuesSize = size;
- auto perBlockSize =nValuesSize / nThreads;
- if(nValuesSize < nThreads)
- {
- BlockRange range;
- range.begin = begin;
- range.end = nValuesSize;
- body(range);
- return;
- }
- // building blocks
- vector<BlockRange> blocks;
- int index = begin;
- while(index <= nValuesSize)
- {
- BlockRange range;
- range.begin = index;
- range.end = index+ perBlockSize;
- blocks.push_back(range);
- index += (perBlockSize) ;
- }
- // fix last block end size;
- blocks[blocks.size()-].end = nValuesSize;
- // thread pool to run
- typedef shared_ptr<thread> thread_ptr;
- vector<thread_ptr> pools;
- for(BlockRange&r:blocks)
- {
- pools.emplace_back(new thread(body,r));
- }
- for(auto &t:pools)
- {
- t->join();
- }
- }
- void parallel()
- {
- vector<int> values();
- fill(values.begin(),values.end(),);
- double start,end,cost;
- start=clock();
- parallel_for(ApplyFoo(&values),values.size(),);
- end= clock();
- cost = end -start;
- cout << "parallel for cost time:" << cost <<endl;
- }
- void serial()
- {
- vector<int> values();
- fill(values.begin(),values.end(),);
- double start,end,cost;
- start=clock();
- for(int i=;i<values.size();i++)
- {
- values[i] += ;
- }
- end= clock();
- cost = end -start;
- cout << "serial for cost time:" << cost <<endl;
- }
- int main()
- {
- parallel();
- serial();
- return ;
- }
并行accumulation:
10亿个元素相加:简直他妈的快飞起来了。
串行时间:13063
并行时间:1023
- #include <vector>
- #include <time.h>
- #include <iostream>
- #include <thread>
- #include <algorithm>
- using namespace std;
- struct BlockRange
- {
- BlockRange():begin(),end(),id()
- {
- }
- int begin;
- int end;
- int id;
- };
- class ApplyFoo
- {
- public:
- ApplyFoo(vector<int> *data):mData(data)
- {
- }
- void operator()(const BlockRange &range,vector<int> *des)const
- {
- auto value = int();
- for(int i=range.begin;i<range.end;i++)
- {
- value +=(*mData)[i];
- }
- (*des)[range.id] = value;
- }
- private:
- vector<int> *mData;
- };
- template <typename retType,typename T>
- retType parallel_add(const T &body,int size,int begin)
- {
- vector<retType> partial_accum;
- auto nThreads = thread::hardware_concurrency();
- auto nValuesSize = size;
- auto perBlockSize =nValuesSize / nThreads;
- if(nValuesSize < nThreads)
- {
- partial_accum.resize();
- BlockRange range;
- range.begin = begin;
- range.end = nValuesSize;
- range.id = ;
- body(range,&partial_accum);
- return accumulate(partial_accum.begin(),partial_accum.end(),retType());
- }
- // building blocks
- vector<BlockRange> blocks;
- int index = begin;
- int blockId = ;
- while(index <= nValuesSize)
- {
- BlockRange range;
- range.begin = index;
- range.end = index+ perBlockSize;
- range.id = blockId;
- blocks.push_back(range);
- index += (perBlockSize) ;
- blockId += ;
- }
- partial_accum.resize(blocks.size());
- // fix last block end size;
- blocks[blocks.size()-].end = nValuesSize;
- // thread pool to run
- typedef shared_ptr<thread> thread_ptr;
- vector<thread_ptr> pools;
- for(BlockRange&r:blocks)
- {
- pools.emplace_back(new thread(body,r,&partial_accum));
- }
- for(auto &t:pools)
- {
- t->join();
- }
- return accumulate(partial_accum.begin(),partial_accum.end(),retType());
- }
- void parallel()
- {
- vector<int> values();
- fill(values.begin(),values.end(),);
- double start,end,cost;
- start=clock();
- cout << "get the result :" <<parallel_add<int>(ApplyFoo(&values),values.size(),) <<endl;
- end= clock();
- cost = end -start;
- cout << "parallel for cost time:" << cost <<endl;
- }
- void serial()
- {
- vector<int> values();
- fill(values.begin(),values.end(),);
- double start,end,cost;
- start=clock();
- cout << "get the result :" <<accumulate(values.begin(),values.end(),) <<endl;
- end= clock();
- cost = end -start;
- cout << "parallel for cost time:" << cost <<endl;
- }
- int main()
- {
- parallel();
- //serial();
- return ;
- }
<n> boost bind
- #include <boost/bind.hpp>
- #include <boost/shared_ptr.hpp>
- #include <iostream>
- using namespace std;
- void dprint(int x,int y)
- {
- cout << x << " " <<y <<endl;
- }
- class Bind_test
- {
- public:
- void setData(int x,int y)
- {
- _x = x;
- _y = y;
- }
- void printData()
- {
- cout << _x << " " <<_y <<endl;
- }
- private:
- int _x;
- int _y;
- };
- void increnum(int &dg)
- {
- dg++;
- }
- int main()
- {
- boost::bind(&dprint,,)(); // 5,5
- boost::bind(&dprint,,_1)(); // 3, 5
- boost::bind(&dprint,_1,_1)(); // 2, 2
- boost::bind(&dprint,_1,_2)(,); // 1, 2
- boost::bind(&dprint,_2,_1)(,); // 2, 1 ->函数参数对掉
- cout << "\nbind the class function\n";
- boost::shared_ptr<Bind_test> bclass(new Bind_test);
- boost::bind(&Bind_test::setData,bclass,,)();
- bclass->printData();
- Bind_test *bclass_02 = new Bind_test;
- boost::bind(&Bind_test::setData,bclass_02,,)();
- bclass_02->printData(); // 2 ,3
- delete bclass_02;
- Bind_test bclass_03;
- boost::bind(&Bind_test::setData,&bclass_03,,)();
- bclass_03.printData(); // 4 ,5
- boost::bind(&Bind_test::setData,&bclass_03,_1,_1)();
- bclass_03.printData(); // 9 ,9
- boost::bind(&Bind_test::setData,&bclass_03,_1,_2)(,);
- bclass_03.printData(); // 9 ,10
- int dgNum = ;
- boost::bind(&increnum,boost::ref(dgNum))(); // 类似C++11 Thread 里要传递引用std::ref(x)
- cout << dgNum <<endl;
- cin.get();
- return ;
- }
额外的:
static_assert 编译时候assertions

下面将输出:hello \n no
- cout << R"(hello \n no)" <<endl;
。
1,Boost -> Bind的更多相关文章
- boost::bind
bind并不是一个单独的类或函数,而是非常庞大的家族,依据绑定的参数个数和要绑定的调用对象类型,总共有十个不同的形式,但它们的名字都叫bind. bind接受的第一个参数必须是一个可调用对象f,包括函 ...
- boost::bind 和 boost::function 基本用法
这是一篇介绍bind和function用法的文章,起因是近来读陈硕的文章,提到用bind和function替代继承,于是就熟悉了下bind和function的用法,都是一些网上都有的知识,记录一下,期 ...
- 以boost::function和boost:bind取代虚函数
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/Solstice/archive/2008/10/13/3066268.aspx 这是一篇比较情绪化的blog,中心思想是“继承就像一条贼船,上去就下不 ...
- (转)boost::bind介绍
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/sld666666/archive/2010/12/14/1905980.html 这篇文章介绍boost::bind()的用法, 文章的主要内容是 ...
- boost::bind实践2——来自《Beyond the C++ Standard Library ( An Introduction to Boost )》
直接代码: 代码段1: #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <boost/bind/bind.hpp> c ...
- boost::bind实践
第一部分源码为基础实践: /*Beyond the C++ Standard Library ( An Introduction to Boost )[CN].chm*/ /*bind的用法*/ #i ...
- 关于boost::function与boost::bind函数的使用心得
最近开始写一个线程池,期间想用一个通用的函数模板来使得各个线程执行不同的任务,找到了Boost库中的function函数. Boost::function是一个函数包装器,也即一个函数模板,可以用来代 ...
- [转] [翻译]图解boost::bind
http://kelvinh.github.io/blog/2013/12/03/boost-bind-illustrated/ 其实这是很久之前留的一个坑了,一直没有填.. 记得在刚开始看到 boo ...
- 使用BOOST BIND库提高C++程序性能
Boost.Bind为函数和函数对象,值语义和指针提供语义了一致的语法.我们首先通过一些简单的例子来看看它的基本用法,之后我们会延伸到嵌套绑定以实现功能组合.理解bind用法的一个关键是理解占位符(p ...
随机推荐
- 关于iis8.5中发布的网站无法连接数据库的解决方案。
发布的网站在浏览时出现如下提示: “/”应用程序中的服务器错误. 在与 SQL Server 建立连接时出现与网络相关的或特定于实例的错误.未找到或无法访问服务器.请验证实例名称是否正确并且 SQL ...
- Apache增加Basic Auth
在.htaccess文件中增加 AuthUserFile /var/www/htpasswd/test.htpasswd AuthName EnterPassword AuthType Basic r ...
- hadoop2.7下载mirror
http://mirror.bit.edu.cn/apache/hadoop/common/
- shell 条件判断
一.数值判断 INT1 -eq INT2 INT1和INT2两数相等为真 INT1 -ne INT2 INT1和INT2两数不等为真 INT1 -gt INT2 ...
- python jenkins-api,jira crowd. email-servers
jenkins user authentication: http://stackoverflow.com/questions/15411208/authenticate-jenkins-users ...
- Linux基本操作命令
Linux基本操作命令 首先介绍一个名词“控制台(console)”,它就是我们通常见到的使用字符操作界面的人机接口,例如dos.我们说控制台命令,就是指通过字符界面输入的可以操作系统的命令,例如do ...
- CSS之伪元素
1. :first-line 向元素的首行文本添加样式,不必关心首行是元素节点还是文本节点 <style> body,htm,div,p{ margin:0; padding:0; } d ...
- 各种同步方法性能比较(synchronized,ReentrantLock,Atomic)
synchronized: 在资源竞争不是很激烈的情况下,偶尔会有同步的情形下,synchronized是很合适的.原因在于,编译程序通常会尽可能的进行优化synchronize,另外可读性非常好,不 ...
- Windows RabbitMQ 命令
启动: 后台运行:rabbitmq-server -detached D:\Program Files\RabbitMQ Server\rabbitmq_server-3.6.6\sbin>ra ...
- C++学习笔记 四种新式类型转换
static_cast ,dynamic_cast,const_cast,reinterpret_cast static_cast 定义:通俗的说就是静态显式转换,用于基本的数据类型转换,及指针之间的 ...
