HT for Web 3D游戏设计设计--汉诺塔(Towers of Hanoi)
在这里我们将构造一个基于HT for Web的HTML5+JavaScript来实现汉诺塔游戏。
汉诺塔的游戏规则及递归算法分析请参考http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tower_of_Hanoi。
知道了汉诺塔的规则和算法,现在就开始创建元素。用HT for Web(http://www.hightopo.com)现有的3D模板创建底盘和3根柱子不是问题,问题是要创建若干个中空的圆盘。一开始的想法是:创建一个圆柱体,将圆柱体的上下两端隐藏,设置柱面的宽度来实现圆盘的效果,经过多次尝试并查阅相关api文档,发现柱面是没有厚度的,改方法不可行。
后来在HT for Web自定义3D模型的WebGL应用(http://www.hightopo.com/blog/381.html)受到启发,圆盘的形成就是在xy平面上的一个矩形,根据y轴旋转一周产生的,通过查阅相关文档,最总决定采用ht.Default.createRingModel方法来创建圆盘模型,然后在创建node的时候通过shape3d属性引用创建好的模型。
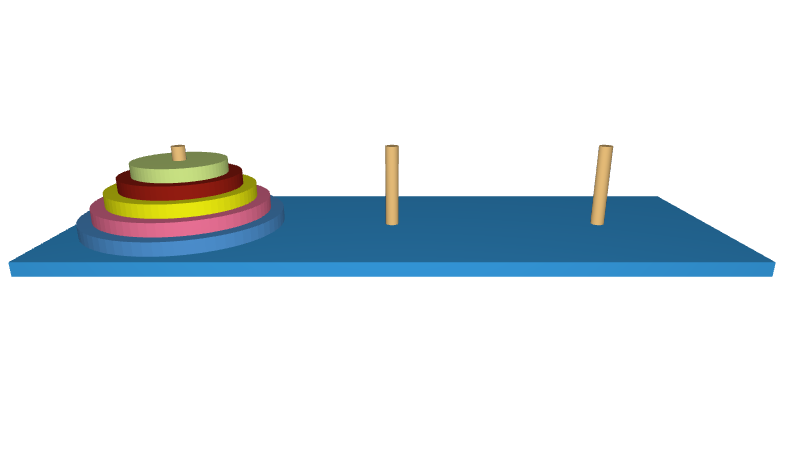
在逻辑实现上,采用了栈的先进后出的原理,对圆柱上的圆盘做顺序控制,确保每次移动的圆盘都是最小的圆盘。
在算法上,采用的是递归算法,通过递归算法,将搬迁过程一步一步记录下来,再采用堆的原理一步一步地执行搬迁过工作。
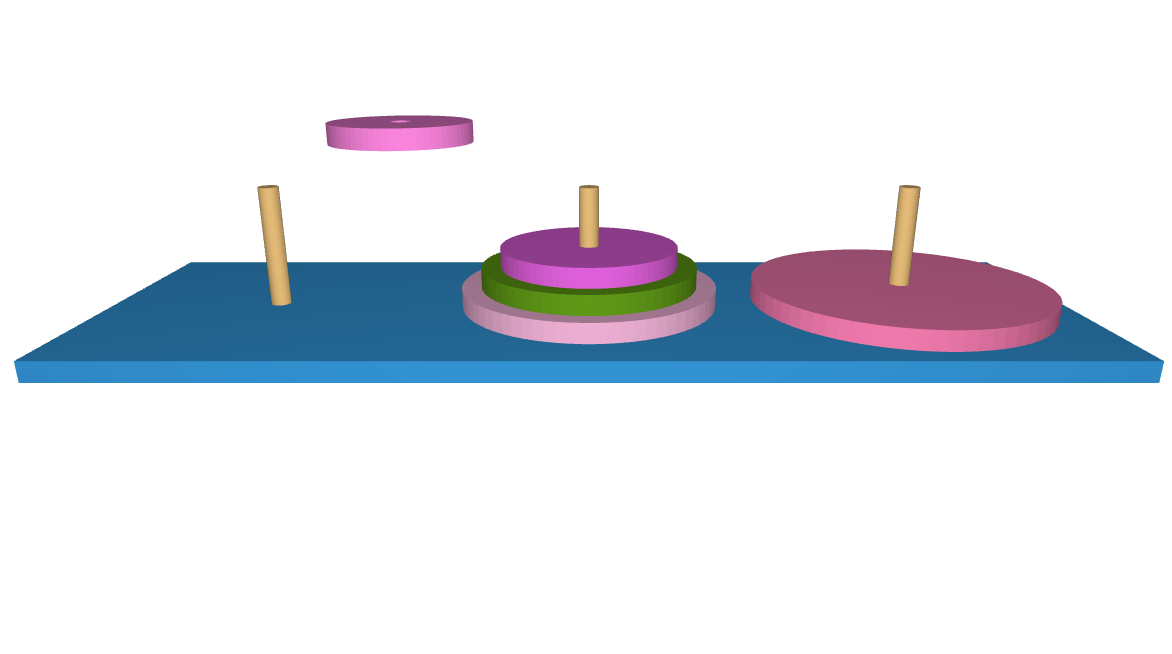
http://v.youku.com/v_show/id_XODcwMTk4MDI4.html
var barNum = 5, // 圆盘个数
cylinderHeight = barNum * 20 + 40, // 圆柱高度
barrelMinORadius = 50, // 圆盘最大外半径
barrelIRadius = 10, // 圆盘内半径
poorRadius = 20, // 圆盘外半径差值
barrelMaxORadius = barrelMinORadius + barNum * poorRadius,
barrelHeight = 20, // 圆盘高
barPadding = 20, // 柱体之间的间隙
floorX = barrelMaxORadius * 6 + barPadding * 4, // 底盘长
floorY = 20, // 底盘高
floorZ = 2 * barrelMaxORadius + barPadding * 2, // 底盘宽
// 柱体集
positions = [
{
barrels: [],
position: [-(2*barrelMaxORadius + barPadding), cylinderHeight / 2 + 1, 0]
},{
barrels: [],
position: [0, cylinderHeight / 2 + 1, 0]
},{
barrels: [],
position: [(2*barrelMaxORadius + barPadding), cylinderHeight / 2 + 1, 0]
}
],
runOrder = [], // 圆盘移动顺序集
// 动画参数
params = {
delay: 10,
duration: 500,
easing: Easing['easeBoth']
}; /**
* 初始化程序
* */
function init(){
dataModel = new ht.DataModel();
g3d = new ht.graph3d.Graph3dView(dataModel);
view = g3d.getView();
view.className = 'main';
document.body.appendChild(view);
window.addEventListener('resize', function (e) {
g3d.invalidate();
}, false); g3d.setEye([0, cylinderHeight * 2, floorX * sin(2*PI/360*60)]); // 初始化节点
initNodes(); moveAnimation();
} /**
* 构造游戏移动队列
* diskQuantity:圆盘个数
* positionA:起点
* positionB:中转点
* positionC:终点
* */
function buildRunOrder(diskQuantity, positionA, positionB, positionC){
if (diskQuantity == 1) {
runOrder.push([positionA, positionC]);
} else {
buildRunOrder(diskQuantity - 1, positionA, positionC, positionB);
buildRunOrder(1, positionA, positionB, positionC);
buildRunOrder(diskQuantity - 1, positionB, positionA, positionC);
}
} /**
* 移动动画
* positionA:起点
* positionC:终点
* */
function moveAnimation(positionA, positionC){
if(!positionA){
var poses = runOrder.shift();
if(!poses){
setTimeout(reset, 500);
}else{
moveAnimation(positions[poses[0]], positions[poses[1]]);
}
}else {
var barrel = positionA.barrels.pop();
var position = positionC.cylinder.p3(),
barPos = barrel.getPosition3d();
position[1] = position[1] + floorY + barrelHeight * positionC.barrels.length - cylinderHeight / 2;
setPolylinePoints(polyline, barPos, position);
params.action = function (v, t) {
var length = g3d.getLineLength(polyline),
offset = g3d.getLineOffset(polyline, length * v),
point = offset.point,
px = point.x,
py = point.y,
pz = point.z;
barrel.p3(px, py, pz);
};
params.finishFunc = function () {
positionC.barrels.push(barrel);
var poses = runOrder.shift();
if (!poses) {
moveAnimation();
} else {
moveAnimation(positions[poses[0]], positions[poses[1]]);
}
};
anim = ht.Default.startAnim(params);
}
} /**
* 重置游戏
* */
function reset(){
if(positions[0].barrels.length == 0){
positions[0].barrels = positions[2].barrels;
}
positions[2].barrels = [];
for(var i = 0, len = positions[0].barrels.length; i < len; i++){
var pos = positions[0].cylinder.p3();
pos[1] = pos[1] + floorY + i * barrelHeight - cylinderHeight / 2;
positions[0].barrels[i].p3(pos);
}
buildRunOrder(barNum, 0, 1, 2);
setTimeout(moveAnimation, 500);
} /**
* 初始化节点
* */
function initNodes(){
// 底盘
floor = createNode([0, floorY / 2, 0], [floorX, floorY, floorZ]).s({
'shape3d': 'box',
'3d.movable': false
}); // 创建柱子
for(var i = 0, len = 3; i < len; i++){
positions[i].cylinder = createNode(positions[i].position, [20, cylinderHeight, 20], floor).s({
'shape3d': 'cylinder',
'shape3d.color': '#E5BB77',
'3d.movable': false
});
} // 创建圆盘
createBarrels(barNum, positions[0].cylinder); // 创建圆盘运行轨迹
polyline = new ht.Polyline();
polyline.setSegments([1, 2, 4, 2]);
polyline.s({
'shape.background': null,
'shape.border.color': 'rgba(0,0,0,0)',
'shape.border.gradient.color': 'rgba(0,0,0,0)',
'shape.border.pattern': [20, 10],
'shape3d.resolution': 50
});
dataModel.add(polyline);
} /**
* 设置路线节点
* */
function setPolylinePoints(polyline, from, to){
polyline.setPoints([
{x: from[0], y: from[2], e: from[1]},
{x: from[0], y: from[2], e: cylinderHeight},
{x: from[0], y: from[2], e: cylinderHeight + 60},
{x: to[0], y: to[2], e: cylinderHeight + 60},
{x: to[0], y: to[2], e: cylinderHeight},
{x: to[0], y: to[2], e: to[1]}
]);
return polyline;
} /**
* 创建圆盘
* barNum:圆盘个数
* host:吸附节点
* */
function createBarrels(barNum, host){
// 圆盘初始x位置
var pos = host.p3(); for(var i = barNum, j = 0; i > 0; i--, j++){
pos[1] = barrelHeight * j + floorY;
positions[0].barrels.push(createBarrel(pos, [1, barrelHeight, 1], barrelMinORadius + i*poorRadius, barrelIRadius, host).s({
'shape3d.color': randomColor(),
'3d.movable': false
}));
}
} /**
* 创建节点
* p3:节点位置
* s3:节点大小
* host:吸附节点
* */
function createNode(p3, s3, host){
var node = new ht.Node();
node.p3(p3);
node.s3(s3);
node.setHost(host);
node.s({
'wf.visible': 'selected',
'wf.color': '#FF6B10',
'wf.width': 2,
'wf.short': true
});
dataModel.add(node);
return node;
} /**
* 创建空心圆柱
* p3:圆桶位置
* s3:圆桶大小
* oRadius:圆桶外径
* iRadius:圆桶内径
* host:吸附节点
* */
function createBarrel(p3, s3, oRadius, iRadius, host){
return createNode(p3, s3, host).s({
'shape3d': ht.Default.createRingModel([
oRadius, 1,
oRadius, 0,
iRadius, 0,
iRadius, 1,
oRadius, 1
], null, 20, false, false, 70)
});
}
HT for Web 3D游戏设计设计--汉诺塔(Towers of Hanoi)的更多相关文章
- 汉诺塔问题(Hanoi Tower)递归算法解析(Python实现)
汉诺塔问题 1.问题来源:汉诺塔来源于印度传说的一个故事,上帝创造世界时作了三根金刚石柱子,在一根柱子上从上往下从小到大顺序摞着64片黄金圆盘.上帝命令婆罗门把圆盘从下面开始按大小顺序重新摆放在另一根 ...
- 汉诺塔 Tower of Hanoi
假设柱子标为A,B.C.要由A搬至C,在仅仅有一个盘子时,就将它直接搬至C:当有两个盘子,就将B作为辅助柱.假设盘数超过2个.将第二个下面的盘子遮起来,就非常easy了.每次处理两个盘子,也就是:A- ...
- what' the python之递归函数、二分算法与汉诺塔游戏
what's the 递归? 递归函数的定义:在函数里可以再调用函数,如果这个调用的函数是函数本身,那么就形成了一个递归函数. 递归的最大深度为997,这个是程序强制定义的,997完全可以满足一般情况 ...
- 汉诺塔 Hanoi Tower
电影<猩球崛起>刚开始的时候,年轻的Caesar在玩一种很有意思的游戏,就是汉诺塔...... 汉诺塔源自一个古老的印度传说:在世界的中心贝拿勒斯的圣庙里,一块黄铜板上插着三支宝石针.印度 ...
- 【Python实践-3】汉诺塔问题递归求解(打印移动步骤及计算移动步数)
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- #汉诺塔移动问题 # 定义move(n,a,b,c)函数,接受参数n,表示3个柱子A.B.C中第1个柱子A的盘子数量 # 然后打印出把所有盘子从A借助B ...
- 学C记录(理解递归问题之汉诺塔)
汉诺游戏规则如下: 1.有三根相邻的柱子,标号为A,B,C. 2.A柱子上从下到上按金字塔状叠放着n个不同大小的圆盘. 3.现在把所有盘子一个一个移动到柱子B上,并且每次移动同一根柱子上都不能出现大盘 ...
- 【学习】Python解决汉诺塔问题
参考文章:http://www.cnblogs.com/dmego/p/5965835.html 一句话:学程序不是目的,理解就好:写代码也不是必然,省事最好:拿也好,查也好,解决问题就好! ...
- c++汉诺塔相关知识总结1
困扰已久,难以攻克的汉诺塔总结来啦 Part One 汉诺塔到底是什么呢? 汉诺塔(Tower of Hanoi)源于印度传说中,大梵天创造世界时造了三根金钢石柱子,其中一根柱子自底向上叠着64片黄金 ...
- 基于HTML5的WebGL设计汉诺塔3D游戏
在这里我们将构造一个基于HT for Web的HTML5+JavaScript来实现汉诺塔游戏. http://hightopo.com/demo/hanoi_20151106/index.html ...
随机推荐
- VS2008 Pocket PC 2003 SE仿真程序上网设置
设置大体分为3个步骤:Microsoft ActiveSync安装配置.Pocket PC 2003 SE仿真程序配置.Pocket PC 2003连接到Microsoft ActiveSync. 1 ...
- Xamarin.IOS之多视图
欢迎大家加入以下开源社区 Xamarin-Cn:https://github.com/Xamarin-Cn Mvvmcross-Cn:https://github.com/Mvvmcross-Cn ...
- c# 动态执行脚本,相关的几个脚本引擎.
Jint 嵌入式的javascript脚本支持引擎,一直都在更新,对各种方法支持也比较好,可以 C# 交互. https://github.com/sebastienros/jint Jurass ...
- GitHub的多人协同开发配置
GitHub For Windows 下载地址:https://windows.github.com/ 基本的注册登录就不细讲了. 在源代码管理上,最重要的就是仓库了.仓库这一概念很容易理解,所谓仓库 ...
- 《C#图解教程》读书笔记之三:方法
本篇已收录至<C#图解教程>读书笔记目录贴,点击访问该目录可获取更多内容. 一.方法那些事儿 (1)方法的结构:方法头—指定方法的特征,方法体—可执行代码的语句序列: (2)方法的调用:参 ...
- (翻译)反射处理java泛型
当我们声明了一个泛型的接口或类,或需要一个子类继承至这个泛型类,而我们又希望利用反射获取这些泛型参数信息.这就是本文将要介绍的ReflectionUtil就是为了解决这类问题的辅助工具类,为java. ...
- python--批量下载豆瓣图片
溜达豆瓣的时候,发现一些图片,懒得一个一个扒,之前写过c#和python版本的图片下载,因此拿之前的Python代码来改了改,折腾出一个豆瓣版本,方便各位使用 # -*- coding:utf8 -* ...
- Linux cat命令
200 ? "200px" : this.width)!important;} --> 介绍 cat命令经常会用来查看一个文件的内容,并且结合它本身的一些参数经常可以用来做一 ...
- Android按需添加Google Play服务
以前无论使用何种Google Play服务,都是直接在gradle文件中引用一个库. compile 'com.google.android.gms:play-services:9.4.0' 这直接导 ...
- Homebrew简介及安装
Homebrew官网 http://brew.sh/index_zh-cn.html Homebrew是神马 linux系统有个让人蛋疼的通病,软件包依赖,好在当前主流的两大发行版本都自带了解决方案, ...
