tensorflow 笔记8:RNN、Lstm源码,训练代码输入输出,维度分析
tensorflow 官网信息:https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/contrib/rnn/BasicLSTMCell
tensorflow 版本:1.10
如有错误还望指正,一起探讨;
当前层各个参数含义:

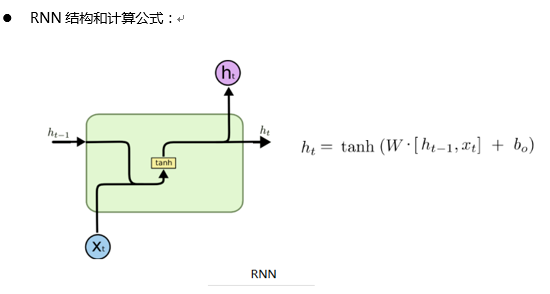
Tensorflow 中RNN单个时刻计算流程:

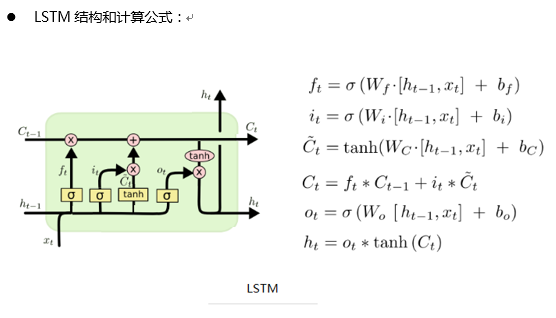
Tensorflow 中 lstm 单个时刻计算流程:

注:上面计算[H,X] * W后和B维度不同, 如何相加,解释如下;
- tensorflow代码中,用的这个 nn_ops.bias_add(gate_inputs, self._bias),这个函数的计算方法是,让每个 batch 的输出值,都加上这个 B;
- 所以维度不同可以相加:【batch_size,Hidden_size】,【Hidden_size】,见函数演示:nn_ops.bias_add
tensorflow 代码分析:见如下
tensorflow version:1.9
注:以下是一个batch,一个时刻的计算,若计算所有时刻,则循环执行以下代码,num_step(句长)次; tensorflow 已经封装好了,不需要我们写;
RNN 关键代码:
@tf_export("nn.rnn_cell.BasicRNNCell")
class BasicRNNCell(LayerRNNCell):
"""The most basic RNN cell.
Args:
num_units: int, The number of units in the RNN cell.
activation: Nonlinearity to use. Default: `tanh`.
reuse: (optional) Python boolean describing whether to reuse variables
in an existing scope. If not `True`, and the existing scope already has
the given variables, an error is raised.
name: String, the name of the layer. Layers with the same name will
share weights, but to avoid mistakes we require reuse=True in such
cases.
dtype: Default dtype of the layer (default of `None` means use the type
of the first input). Required when `build` is called before `call`.
""" def __init__(self,
num_units,
activation=None,
reuse=None,
name=None,
dtype=None):
super(BasicRNNCell, self).__init__(_reuse=reuse, name=name, dtype=dtype) # Inputs must be 2-dimensional.
self.input_spec = base_layer.InputSpec(ndim=2) self._num_units = num_units
self._activation = activation or math_ops.tanh @property
def state_size(self):
return self._num_units @property
def output_size(self):
return self._num_units def build(self, inputs_shape):
if inputs_shape[1].value is None:
raise ValueError("Expected inputs.shape[-1] to be known, saw shape: %s"
% inputs_shape) input_depth = inputs_shape[1].value # 初始化生成 W 和 B,shape 大小为
# W: [input_size + Hidden_size, Hidden_size)
# B: [Hidden_size]
self._kernel = self.add_variable(
_WEIGHTS_VARIABLE_NAME,
shape=[input_depth + self._num_units, self._num_units])
self._bias = self.add_variable(
_BIAS_VARIABLE_NAME,
shape=[self._num_units],
initializer=init_ops.zeros_initializer(dtype=self.dtype)) self.built = True
# 循环该函数 num_step(句子长度) 次,则该层计算完;
def call(self, inputs, state):
"""Most basic RNN: output = new_state = act(W * input + U * state + B)."""
# output = Ht = tanh([x,Ht-1]*W + B)
# 如果是第 0 时刻,那么当前的 state(即上一时刻的输出H0)的值全部为0;
# input 的 shape为: [batch_size,emb_size]
# state 的 shape为:[batch_zize,Hidden_size]
# matmul : 矩阵相乘
# array_ops.concat: 两个矩阵连接,连接后的 shape 为 [batch_size,input_size + Hidden_size],实际就是[Xt,Ht-1] # 此时计算: [input,state] * [W,U] == [Xt,Ht-1] * W,得到的shape为:[batch_size,Hidden_size]
gate_inputs = math_ops.matmul(
array_ops.concat([inputs, state], 1), self._kernel)
# B 的shape 为:【Hidden_size】,[Xt,Ht-1] * W 计算后的shape为:[batch_size,Hidden_size]
# nn_ops.bias_add,这个函数的计算方法是,让每个 batch 得到的值,都加上这个 B;
# 这一步,加上B后:Ht = tanh([Xt,Ht-1] * W + B),得到的 shape 还是: [batch_size,Hidden_size]
# 那么这个 Ht 将作为下一时刻的输入和下一层的输入;
gate_inputs = nn_ops.bias_add(gate_inputs, self._bias)
output = self._activation(gate_inputs)
#此时return的维度为:[batch_size,Hidden_size]
# 一个output作为下一时刻的输入Ht,另一个作为下一层的输入 Ht
return output, output LSTM 关键代码: @tf_export("nn.rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell")
class BasicLSTMCell(LayerRNNCell):
"""Basic LSTM recurrent network cell.
The implementation is based on: http://arxiv.org/abs/1409.2329.
We add forget_bias (default: 1) to the biases of the forget gate in order to
reduce the scale of forgetting in the beginning of the training.
It does not allow cell clipping, a projection layer, and does not
use peep-hole connections: it is the basic baseline.
For advanced models, please use the full @{tf.nn.rnn_cell.LSTMCell}
that follows.
""" def __init__(self,
num_units,
forget_bias=1.0,
state_is_tuple=True,
activation=None,
reuse=None,
name=None,
dtype=None):
"""Initialize the basic LSTM cell.
Args:
num_units: int, The number of units in the LSTM cell.
forget_bias: float, The bias added to forget gates (see above).
Must set to `0.0` manually when restoring from CudnnLSTM-trained
checkpoints.
state_is_tuple: If True, accepted and returned states are 2-tuples of
the `c_state` and `m_state`. If False, they are concatenated
along the column axis. The latter behavior will soon be deprecated.
activation: Activation function of the inner states. Default: `tanh`.
reuse: (optional) Python boolean describing whether to reuse variables
in an existing scope. If not `True`, and the existing scope already has
the given variables, an error is raised.
name: String, the name of the layer. Layers with the same name will
share weights, but to avoid mistakes we require reuse=True in such
cases.
dtype: Default dtype of the layer (default of `None` means use the type
of the first input). Required when `build` is called before `call`.
When restoring from CudnnLSTM-trained checkpoints, must use
`CudnnCompatibleLSTMCell` instead.
"""
super(BasicLSTMCell, self).__init__(_reuse=reuse, name=name, dtype=dtype)
if not state_is_tuple:
logging.warn("%s: Using a concatenated state is slower and will soon be "
"deprecated. Use state_is_tuple=True.", self) # Inputs must be 2-dimensional.
self.input_spec = base_layer.InputSpec(ndim=2) self._num_units = num_units
self._forget_bias = forget_bias
self._state_is_tuple = state_is_tuple
self._activation = activation or math_ops.tanh @property
def state_size(self):
# 隐藏层的 size:
return (LSTMStateTuple(self._num_units, self._num_units)
if self._state_is_tuple else 2 * self._num_units) @property
def output_size(self):
# 输出层的size:Hidden_size
return self._num_units def build(self, inputs_shape):
if inputs_shape[1].value is None:
raise ValueError("Expected inputs.shape[-1] to be known, saw shape: %s"
% inputs_shape) #inputs的维度为:[batch_size,input_size]
#如果是第一层每个时刻词语的输入,则这个input_size 就是 embedding_size,就等于词向量的维度;
# 所以 此时 input_depth,就是input_size
input_depth = inputs_shape[1].value
# h_depth 就是 Hidden_size,隐藏层的维度
h_depth = self._num_units # self._kernel == W;则此时 W的维度 为【input_size + Hidden_size,4* Hidden_size】
# 此处定义四个 W 和 B,是为了,一次就把 i,j,f,o 计算出来;相当于图中的 ft,it,ct‘,ot
self._kernel = self.add_variable(
_WEIGHTS_VARIABLE_NAME,
shape=[input_depth + h_depth, 4 * self._num_units])
# 此时的B的维度为【4 * Hidden_size】
self._bias = self.add_variable(
_BIAS_VARIABLE_NAME,
shape=[4 * self._num_units],
initializer=init_ops.zeros_initializer(dtype=self.dtype)) self.built = True def call(self, inputs, state):
"""Long short-term memory cell (LSTM).
Args:
inputs: `2-D` tensor with shape `[batch_size, input_size]`.
state: An `LSTMStateTuple` of state tensors, each shaped
`[batch_size, num_units]`, if `state_is_tuple` has been set to
`True`. Otherwise, a `Tensor` shaped
`[batch_size, 2 * num_units]`.
Returns:
A pair containing the new hidden state, and the new state (either a
`LSTMStateTuple` or a concatenated state, depending on
`state_is_tuple`).
"""
sigmoid = math_ops.sigmoid
one = constant_op.constant(1, dtype=dtypes.int32)
# Parameters of gates are concatenated into one multiply for efficiency.
# 每一层的第0时刻的 c 和 h,元素全部初始化为0;
if self._state_is_tuple:
c, h = state
else:
c, h = array_ops.split(value=state, num_or_size_splits=2, axis=one) # 此时刻的 input:Xt 和 上一时刻的输出:Ht-1,进行结合;
# inputs shape : [batch_size,input_size],第一层的时候,input_size,就相当于 embedding_size
# 结合后的维度为【batch_size,input_size + Hidden_size】,W的维度为【input_size + Hidden_size,4*hidden_size】
# 两者进行矩阵相乘后的维度为:【batch_size,4*hidden_size】
gate_inputs = math_ops.matmul(
array_ops.concat([inputs, h], 1), self._kernel)
# B 的shape 为:【4 * Hidden_size】,[Xt,Ht-1] * W 计算后的shape为:[batch_size, 4 * Hidden_size]
# nn_ops.bias_add,这个函数的计算方法是,让每个 batch 得到的值,都加上这个 B;
# 这一步,加上B后,得到的是,i,j,f,o 的结合, [Xt,Ht-1] * W + B,得到的 shape 还是: [batch_size, 4 * Hidden_size]
# 加上偏置B后的维度为:【batch_size,4 * Hidden_size】
gate_inputs = nn_ops.bias_add(gate_inputs, self._bias) # i = input_gate, j = new_input, f = forget_gate, o = output_gate
# 从以上的矩阵相乘后,分割出来四部分,就是 i,j,f,o的值;
# 每个的维度为【batch_size,Hidden_size】
i, j, f, o = array_ops.split(
value=gate_inputs, num_or_size_splits=4, axis=one) forget_bias_tensor = constant_op.constant(self._forget_bias, dtype=f.dtype) # Note that using `add` and `multiply` instead of `+` and `*` gives a
# performance improvement. So using those at the cost of readability.
add = math_ops.add
# 此处加上遗忘的 bias,选择遗忘元素;
# 以下计算是:对应元素相乘:因为四个参数的维度都是【batch_size,hidden_size】,计算后维度不变;
# new_c = c*sigmoid(f+bias) + sigmoid(i)*tanh(o) # 计算后的维度为【batch_size,hidden_size】
multiply = math_ops.multiply
new_c = add(multiply(c, sigmoid(add(f, forget_bias_tensor))),
multiply(sigmoid(i), self._activation(j)))
# 以下计算是:对应元素相乘:因为2个参数的维度都是【batch_size,hidden_size】,计算后维度不变;
#new_h = sigmoid(o) * tanh(new_c) new_h = multiply(self._activation(new_c), sigmoid(o)) # 计算后的维度是(值不相等):new_c == new_h == 【batch_size,hidden_size】 if self._state_is_tuple:
new_state = LSTMStateTuple(new_c, new_h)
else:
new_state = array_ops.concat([new_c, new_h], 1)
# new_h:最后一个时刻的H,new_state:最后一个时刻的 H和C;循环执行该函数,执行 num_step次(即 最大的步长),则该层计算完全;
# 此时的 new_c 和 new_h,作为下一时刻的输入,new_h 和下一时刻的,Xt+1 进行连接,连接后的维度为,【batch_size,input_size + Hidden_size】
# 如果还有下一层的话,那么此刻的 new_h,变身为下一时刻的 Xt
return new_h, new_state
tensorflow 笔记8:RNN、Lstm源码,训练代码输入输出,维度分析的更多相关文章
- tensorflow笔记:多层LSTM代码分析
tensorflow笔记:多层LSTM代码分析 标签(空格分隔): tensorflow笔记 tensorflow笔记系列: (一) tensorflow笔记:流程,概念和简单代码注释 (二) ten ...
- tensorflow笔记:模型的保存与训练过程可视化
tensorflow笔记系列: (一) tensorflow笔记:流程,概念和简单代码注释 (二) tensorflow笔记:多层CNN代码分析 (三) tensorflow笔记:多层LSTM代码分析 ...
- [笔记] Ubuntu 18.04源码安装caffe流程
虽然Ubuntu 18.04可以通过apt安装caffe,但是为了使用最新的代码,还是值得从源码安装一遍的. 安装环境 OS: Ubuntu 18.04 64 bit 显卡: NVidia GTX 1 ...
- tensorflow笔记:流程,概念和简单代码注释
tensorflow是google在2015年开源的深度学习框架,可以很方便的检验算法效果.这两天看了看官方的tutorial,极客学院的文档,以及综合tensorflow的源码,把自己的心得整理了一 ...
- 老李推荐:第6章8节《MonkeyRunner源码剖析》Monkey原理分析-事件源-事件源概览-小结
老李推荐:第6章8节<MonkeyRunner源码剖析>Monkey原理分析-事件源-事件源概览-小结 本章我们重点围绕处理网络过来的命令的MonkeySourceNetwork这个事 ...
- 老李推荐:第6章7节《MonkeyRunner源码剖析》Monkey原理分析-事件源-事件源概览-注入按键事件实例
老李推荐:第6章7节<MonkeyRunner源码剖析>Monkey原理分析-事件源-事件源概览-注入按键事件实例 poptest是国内唯一一家培养测试开发工程师的培训机构,以学员能胜 ...
- 老李推荐:第6章6节《MonkeyRunner源码剖析》Monkey原理分析-事件源-事件源概览-命令队列
老李推荐:第6章6节<MonkeyRunner源码剖析>Monkey原理分析-事件源-事件源概览-命令队列 事件源在获得字串命令并把它翻译成对应的MonkeyEvent事件后,会把这些 ...
- 老李推荐:第6章4节《MonkeyRunner源码剖析》Monkey原理分析-事件源-事件源概览-翻译命令字串
老李推荐:第6章4节<MonkeyRunner源码剖析>Monkey原理分析-事件源-事件源概览-翻译命令字串 poptest是国内唯一一家培养测试开发工程师的培训机构,以学员能胜任自 ...
- 老李推荐:第6章5节《MonkeyRunner源码剖析》Monkey原理分析-事件源-事件源概览-事件
老李推荐:第6章5节<MonkeyRunner源码剖析>Monkey原理分析-事件源-事件源概览-事件 从网络过来的命令字串需要解析翻译出来,有些命令会在翻译好后直接执行然后返回,但有 ...
- 老李推荐:第6章3节《MonkeyRunner源码剖析》Monkey原理分析-事件源-事件源概览-命令翻译类
老李推荐:第6章3节<MonkeyRunner源码剖析>Monkey原理分析-事件源-事件源概览-命令翻译类 每个来自网络的字串命令都需要进行解析执行,只是有些是在解析的过程中直接执行 ...
随机推荐
- pandas.cut使用总结
用途 pandas.cut用来把一组数据分割成离散的区间.比如有一组年龄数据,可以使用pandas.cut将年龄数据分割成不同的年龄段并打上标签. 原型 pandas.cut(x, bins, rig ...
- Unity 之 中文乱码
更改 C#脚本的编码格式: 文件 -> 高级保存选项 -> Unicode
- 递归回溯groupSum
- 使用cxf两个声明导致ObjectFactory 类中发生冲突
在网上搜了答案都是一样的,没有解决这个问题. 后来发现原因在于 -p com.XXX.XXX这个命令. 解决方法: 只需要把命名包的这个命令去掉. 但要注意,在移动到项目中去时,必须Refactor包 ...
- Centos下基于Hadoop安装Spark(分布式)
前提 Hadoop可成功在分布式系统下启动 下载scala 链接是https://downloads.lightbend.com/scala/2.12.7/scala-2.12.7.tgz Mast ...
- git小白入门全攻略
git是什么(写在前边的叨叨,就是给一点不懂的小白打个比喻,大佬请自行跳过) git在平时的开发中用的太频繁了,以至于我都不知道如何去形容它.囧. 假设我们开发的工作类似于图书整理,写的代码就是很多人 ...
- {}+[]与console.log({}+[])结果不同?从JavaScript的大括号谈起
看到这样一个问题:为什么直接在控制台运行{} + []和用console.log({} + [])输出,两者结果不一样? 于是乎打开chrome的控制台运行了一下: 为什么结果会这样呢?不得已学习一下 ...
- 洛谷.3374.[模板]树状数组1(CDQ分治)
题目链接 简易CDQ分治教程 //每个操作分解为一个有序数对(t,p),即(时间,操作位置),时间默认有序,用CDQ分治处理第二维 //对于位置相同的操作 修改优先于查询 //时间是默认有序的 所以可 ...
- BZOJ.3920.Yuuna的礼物(莫队 分块套分块 分段离散化)
题目链接 详细题解:https://www.cnblogs.com/autsky-jadek/p/4376091.html 代码参考自:https://www.cnblogs.com/Sakits/p ...
- 潭州课堂25班:Ph201805201 第六课:散列类型,运算符优先级和逻辑运算 (课堂笔记)
# # 集合:# se1 = { 1,3,4,5,'a'} # 如果直接添加元素,不能直接添加可变元素# se2 = set() # 定义一个空集合# se3 = {'a'} # 定义个单元素的集合# ...
