Java浅拷贝与深拷贝(思维导图)
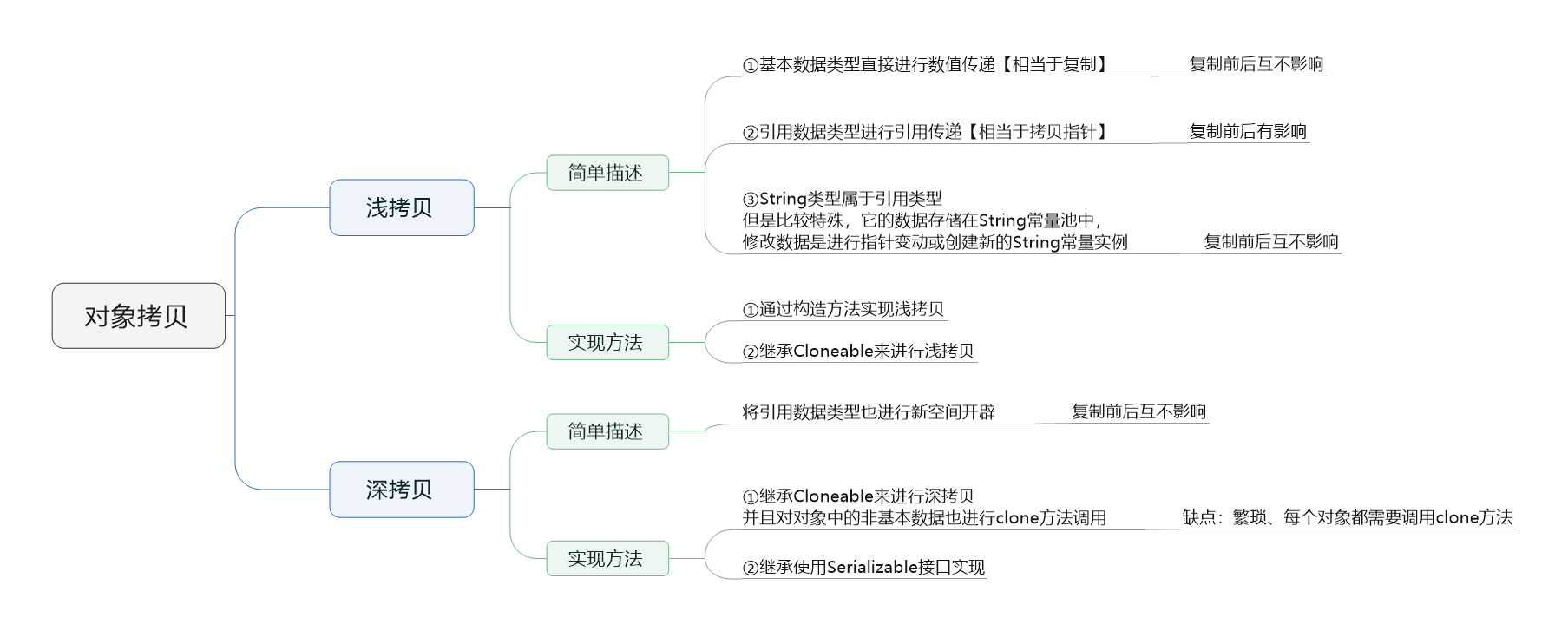
图1 拷贝思维导图(点击查看图片)
1,拷贝
有两个相同属性的对象A和B,A拥有初始化值,将其值拷贝到B中,使得B拥有与A“相同”数据的属性!注意这里的相同我有加双引号!
相同可能表示这么几个意思:①数值相同【指向不同的内存空间】;②地址相同【指向相同的内存空间】;
下面是直接使用"="进行复制的操作
package com.cnblogs.mufasa.Demo1;
import java.util.Date;
class Person{//
private int age=0;
private Birth birth=new Birth();
private String name="";
public Person(int age, Birth birth, String name) {
this.age = age;
this.birth = birth;
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Birth getBirth() {
return birth;
}
public void setBirth(Birth birth) {
this.birth = birth;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String toString(){
return "姓名:"+name+",年龄:"+age+",出生日期:"+birth.toString();
}
}
class Birth{//生日
private String date="";
public Birth(){}
public Birth(String date){
this.date=date;
}
public String getDate() {
return date;
}
public void setDate(String date) {
this.date = date;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.date;
}
}
public class Demo1 {//浅拷贝
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1=new Person(18,new Birth("19950729"),"万雨");
Person p2=p1;
System.out.println(p1.toString());
System.out.println(p2.toString());
p1.setAge(17);
p1.setBirth(new Birth("2018"));
p1.setName("Mufasa");
System.out.println(p1.toString());
System.out.println(p2.toString());
}
}
姓名:万雨,年龄:18,出生日期:19950729
姓名:万雨,年龄:18,出生日期:19950729
姓名:Mufasa,年龄:17,出生日期:2018
姓名:Mufasa,年龄:17,出生日期:2018
其实就相当于对原始对象进行操作
2,浅拷贝
Perosn类型对象有两个属性Age、name,将p1浅复制给p2
基本类型直接进行数值复制,引用类型进行地址拷贝(String类型比较特殊,属于引用类型,但是它存在一个常量池需要进行特殊对待)

图2 浅拷贝
使用构造方法进行浅拷贝:
package com.cnblogs.mufasa.Demo;
import java.util.Date;
class Person{//
private Age age;
private String name;
private int birth;
public Person(Age age, String name,int birth) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
this.birth = birth;
}
public Person(Person p1){
this.age=p1.age;
this.name=p1.name;
this.birth=p1.birth;
}
public int getAge() {
return this.age.getAge();
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age.setAge(age); ;
}
public void setAge(Age age) {
this.age = age;
}
public int getBirth() {
return birth;
}
public void setBirth(int birth) {
this.birth = birth;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String toString(){
return "姓名:"+this.name+",年龄:"+this.age+",出生日期:"+this.birth;
}
}
class Age{
private int age;
public Age(){}
public Age(int age){
this.age=age;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String toString(){
return this.age+"";
}
}
public class Demo {//浅拷贝-构造方法实现
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1=new Person(new Age(18),"万雨",1995);
Person p2=new Person(p1);
System.out.println(p1.toString());
System.out.println(p2.toString());
p1.setAge(17);
p1.setBirth(2019);
p1.setName("Mufasa");
System.out.println(p1.toString());
System.out.println(p2.toString());
}
}
使用继承Cloneable接口调用clone方法进行浅拷贝
package com.cnblogs.mufasa.Demo2;
import java.util.Date;
class Person implements Cloneable{//
private Age age;
private String name;
private int birth;
public Person(Age age, String name,int birth) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
this.birth = birth;
}
public Person clone(){
Person obj=null;
try {
obj=(Person) super.clone();
}catch (CloneNotSupportedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
// obj.age=(Age) this.getAge().clone();
return obj;
}
public Age getAge() {
return this.age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age.setAge(age); ;
}
public void setAge(Age age) {
this.age = age;
}
public int getBirth() {
return birth;
}
public void setBirth(int birth) {
this.birth = birth;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String toString(){
return "姓名:"+this.name+",年龄:"+this.age+",出生日期:"+this.birth;
}
}
class Age implements Cloneable{
private int age;
public Age(){}
public Age(int age){
this.age=age;
}
// public Age clone(){
// Age obj=null;
// try {
// obj=(Age) super.clone();
// }catch (CloneNotSupportedException e){
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
// return obj;
// }
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String toString(){
return this.age+"";
}
}
public class Demo2 {//浅拷贝-继承Cloneable接口实现
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1=new Person(new Age(18),"万雨",1995);
Person p2=(Person)p1.clone();
System.out.println(p1.toString());
System.out.println(p2.toString());
p1.setAge(17);
p1.setBirth(2019);
p1.setName("Mufasa");
System.out.println(p1.toString());
System.out.println(p2.toString());
}
}
姓名:万雨,年龄:18,出生日期:1995
姓名:万雨,年龄:18,出生日期:1995
姓名:Mufasa,年龄:17,出生日期:2019
姓名:万雨,年龄:17,出生日期:1995
3,深拷贝
引用类型数据也进行新内存开辟与幅值,
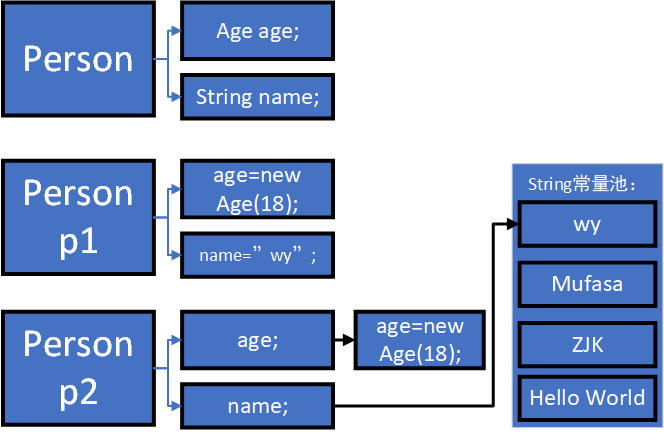
图3 深拷贝
使用继承Cloneable接口调用clone方法进行深拷贝【每个引用对象都需要使用clone方法进行拷贝】
package com.cnblogs.mufasa.Demo2;
import java.util.Date;
class Person implements Cloneable{//
private Age age;
private String name;
private int birth;
public Person(Age age, String name,int birth) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
this.birth = birth;
}
public Person clone(){
Person obj=null;
try {
obj=(Person) super.clone();
}catch (CloneNotSupportedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
obj.age=(Age) this.getAge().clone();
return obj;
}
public Age getAge() {
return this.age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age.setAge(age); ;
}
public void setAge(Age age) {
this.age = age;
}
public int getBirth() {
return birth;
}
public void setBirth(int birth) {
this.birth = birth;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String toString(){
return "姓名:"+this.name+",年龄:"+this.age+",出生日期:"+this.birth;
}
}
class Age implements Cloneable{
private int age;
public Age(){}
public Age(int age){
this.age=age;
}
public Age clone(){
Age obj=null;
try {
obj=(Age) super.clone();
}catch (CloneNotSupportedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return obj;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String toString(){
return this.age+"";
}
}
public class Demo2 {//浅拷贝-继承Cloneable接口实现
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1=new Person(new Age(18),"万雨",1995);
Person p2=(Person)p1.clone();
System.out.println(p1.toString());
System.out.println(p2.toString());
p1.setAge(17);
p1.setBirth(2019);
p1.setName("Mufasa");
System.out.println(p1.toString());
System.out.println(p2.toString());
}
}
使用继承Serializable接口进行序列化与反序列化进行深拷贝【注意对象不能使用transient进行修饰,原因:transient修饰的对象无法进行序列化!】
package com.cnblogs.mufasa.Demo3;
import java.io.*;
class Person implements Serializable{
private Age age;
private String name;
private int birth;
public Person(Age age, String name,int birth) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
this.birth = birth;
}
public Age getAge() {
return this.age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age.setAge(age); ;
}
public void setAge(Age age) {
this.age = age;
}
public int getBirth() {
return birth;
}
public void setBirth(int birth) {
this.birth = birth;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String toString(){
return "姓名:"+this.name+",年龄:"+this.age+",出生日期:"+this.birth;
}
}
class Age implements Serializable {
private int age;
public Age(){}
public Age(int age){
this.age=age;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String toString(){
return this.age+"";
}
}
public class Demo3 {//浅拷贝-继承Cloneable接口实现
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
Person p1=new Person(new Age(18),"万雨",1995);
ByteArrayOutputStream bos=new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
oos.writeObject(p1);//1,先进行序列化
oos.flush();
ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(bos.toByteArray()));
Person p2=(Person)ois.readObject();//2,进行反序列化
System.out.println(p1.toString());
System.out.println(p2.toString());
p1.setAge(17);
p1.setBirth(2019);
p1.setName("Mufasa");
System.out.println(p1.toString());
System.out.println(p2.toString());
}
}
姓名:万雨,年龄:18,出生日期:1995
姓名:万雨,年龄:18,出生日期:1995
姓名:Mufasa,年龄:17,出生日期:2019
姓名:万雨,年龄:18,出生日期:1995
Java浅拷贝与深拷贝(思维导图)的更多相关文章
- [Java 并发] Java并发编程实践 思维导图 - 第一章 简单介绍
阅读<Java并发编程实践>一书后整理的思维导图.
- [Java 并发] Java并发编程实践 思维导图 - 第二章 线程安全性
依据<Java并发编程实践>一书整理的思维导图.
- [Java 并发] Java并发编程实践 思维导图 - 第四章 对象的组合
依据<Java并发编程实践>一书整理的思维导图. 第一部分: 第二部分:
- 学习Java的9张思维导图
转自:https://blog.csdn.net/aitaozi11/article/details/79652943 网上搜集了java的学习思维导图,分享给大家. 01.Java程序设计(基础) ...
- Java建造者模式(思维导图)
图1 建造者模式[点击查看大图] 基本的知识点已在思维导图中,下面是demo 1,Builder 为创建一个产品对象的各个部件指定抽象接口 public interface PersonBuilder ...
- Java组合模式(思维导图)
图1 组合模式[点击查看图片] 1,以公司职员为例的结构 package com.cnblogs.mufasa.demo3; import java.util.ArrayList; import ja ...
- Java门面模式(思维导图)
图1 门面模式[点击查看图片] 1,实体对象类 package com.cnblogs.mufasa.demo1; //3个子系统,解决问题的实体 public class StoreA { //示意 ...
- Java Web学习过程的思维导图
今天找文件,无意中翻到老师前段时间总结的知识点.觉得应该有点用处,所以分享给大家. 第一次在博客园发表,如有错误,还请指正.
- java编程思想-泛型思维导图
- java编程思想-并发思维导图
随机推荐
- 笔记七(编写第一个UEFI程序)
搭建好uefi开发环境之后,在MyWorkspace文件夹中建立一个文件夹ExamplePkg; ,然后在ExamplePkg文件夹中创建HelloWorld文件夹,Include文件夹,Exampl ...
- H264基础简介
前言 H264是属于视频的编码层的标准格式,视频编码显然是为了压缩大小.我们看下一个完全没压缩的视频数据大小.假设视频是高清(1280 * 720),每秒30帧,也就是每秒的数据 1280 * 720 ...
- es搭建过程会存在的问题 针对6.x
常见的四个基本错误 错误1 can not run elasticsearch as root 解决方案: 因为安全问题elasticsearch 不让用root用户直接运行,所以要创建新用户 第一步 ...
- Understanding the ASP.NET MVC Execution Process
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/aspnet/mvc/overview/older-versions-1/overview/understanding-the-asp ...
- centos7.4出现yum command not found
购买的云服务器运行yum命令出现yum command not found. 通过将云主机自带的yum和python卸载掉,并且同时需要关注/usr/bin/yum文件的首行解释.我定义其为" ...
- 阶段5 3.微服务项目【学成在线】_day03 CMS页面管理开发_15-异常处理-异常处理流程
右侧是框架报的异常 不可预知的,例如数据库连不上这一类的.可以在map中制定某些类的异常,如果找不到就最右边的 99999的, 系统对异常的处理使用统一的异常处理流程: 1.自定义异常类型. 2.自定 ...
- 阶段5 3.微服务项目【学成在线】_day03 CMS页面管理开发_01-自定义查询页面-服务端-Dao
在页面输入查询条件,查询符合条件的页面信息. 查询条件如下: 站点Id:精确匹配 模板Id:精确匹配 页面别名:模糊匹配 spring mongoDB如何自定义条件 在Repository的findA ...
- BTE增强
转自https://www.cnblogs.com/Garfield/p/5313962.html Enhancement(1)--BTEs 最近一个同事碰到一个FI的增强,要用BTEs实现,我也是第 ...
- 安装完 MySQL 后必须调整的 10 项配置(转)
当我们被人雇来监测MySQL性能时,人们希望我们能够检视一下MySQL配置然后给出一些提高建议.许多人在事后都非常惊讶,因为我们建议他们仅仅改动几个设置,即使是这里有好几百个配置项.这篇文章的目的在于 ...
- lexicalized Parsing
$q$(S $\rightarrow$ NP VP) * $q$(NP $\rightarrow$ NNP) * $q$(VP $\rightarrow$ VB NP) * $q$(NP $\righ ...
