JavaWeb_(Spring框架)xml配置文件
系列博文
JavaWeb_(Spring框架)xml配置文件 传送门
JavaWeb_(Spring框架)注解配置 传送门
Xml配置
a)Bean元素:交由Spring管理的对象都要配置在bean标签中;
i.Bean标签介绍和创建方式:空参构造、静态工厂、动态工厂;
ii.Scope属性介绍:singleton、protoptype、request、session;
iii.初始化方法Init-method和 销毁方法destroy-method介绍;
b)属性注入:
i.Set方法注入;
ii.构造函数注入;
iii.复杂类型注入:Array、List、Set、Map、Properties
1、xml配置-bean标签-配置及创建方式
ApplicationContext 配置的所有bean都会在容器创建的时候被创建出来,
如果配置的bean较多,那么在创建容的时候,会产生内存过大的问题;这种情况在机器硬件性能较为落后的时候体现的比较明显;
延迟加载(懒加载) true就是创建容器时不加载配置的bean对象,在获取的时候才创建;
<!-- name 是起一个名字,我们可以通过这个name来利用容器获取对象
name 可以使用特殊字符
name 可以重复
我们在实际开发中不推荐将多个对象名字命名为重复的-->
<!-- id与name作用基本相同,单不推荐使用 不支持特殊字符,不能重复 --> <!-- class:是被管理对象的全包名,spring会通过这个包名来创建对象 -->
<bean name="user" class="com.Gary.bean.User" lazy-init ="true">
<!-- 为u_id注入了一个id为2的值 -->
<property name="u_id" value="2"></property> </bean>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd "> <!-- name 是起一个名字,我们可以通过这个name来利用容器获取对象
name 可以使用特殊字符
name 可以重复
我们在实际开发中不推荐将多个对象名字命名为重复的-->
<!-- id与name作用基本相同,单不推荐使用 不支持特殊字符,不能重复 --> <!-- class:是被管理对象的全包名,spring会通过这个包名来创建对象 -->
<!-- request 在web环境下,如果scope属性为request 那么这个对象被创建出来 他的生命周期会与request请求一致-->
<!-- session 同理 ,生命周期与session一致 -->
<bean name="user" class="com.Gary.bean.User" lazy-init ="true">
<!-- 为u_id注入了一个id为2的值 -->
<property name="u_id" value="2"></property> </bean> </beans>
applicationContext.xml
2、xml配置-bean标签-scope属性
scope="singleton" 表示<bean>是单例的
<bean name="user" class="com.Gary.bean.User" lazy-init ="true" scope="singleton">
<!-- 为u_id注入了一个id为2的值 -->
<property name="u_id" value="2"></property>
</bean>
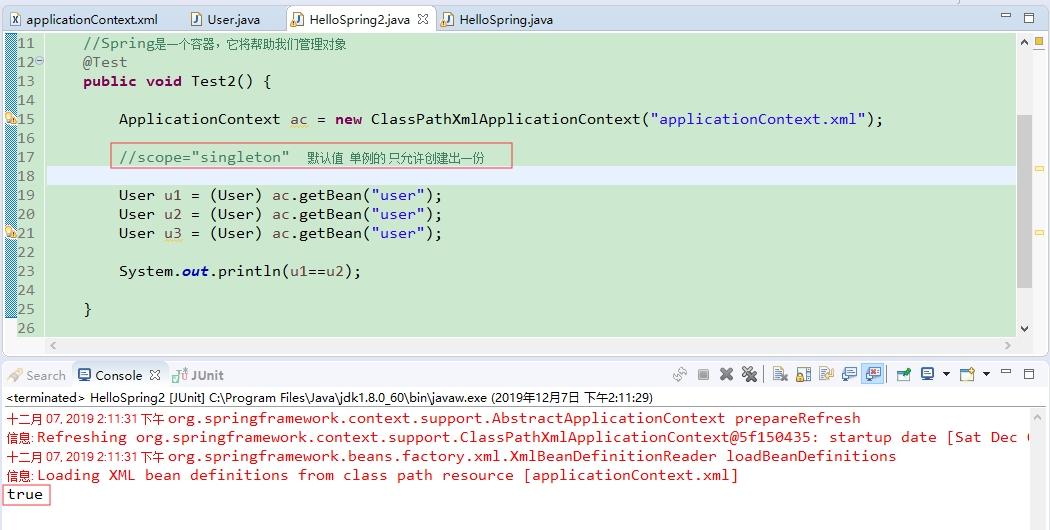
package com.Gary.test; import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.Gary.bean.User; public class HelloSpring2 { //Spring是一个容器,它将帮助我们管理对象
@Test
public void Test2() { ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); //scope="singleton" 默认值 单例的 只允许创建出一份 User u1 = (User) ac.getBean("user");
User u2 = (User) ac.getBean("user");
User u3 = (User) ac.getBean("user"); System.out.println(u1==u2); } }
HelloSpring2.java
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd "> <!-- name 是起一个名字,我们可以通过这个name来利用容器获取对象
name 可以使用特殊字符
name 可以重复
我们在实际开发中不推荐将多个对象名字命名为重复的-->
<!-- id与name作用基本相同,单不推荐使用 不支持特殊字符,不能重复 --> <!-- class:是被管理对象的全包名,spring会通过这个包名来创建对象 -->
<!-- request 在web环境下,如果scope属性为request 那么这个对象被创建出来 他的生命周期会与request请求一致-->
<!-- session 同理 ,生命周期与session一致 -->
<bean name="user" class="com.Gary.bean.User" lazy-init ="true" scope="singleton">
<!-- 为u_id注入了一个id为2的值 -->
<property name="u_id" value="2"></property> </bean> </beans>
applicationContext.xml
scope="prototype" 表示<bean>是多例的
<bean name="user" class="com.Gary.bean.User" lazy-init ="true" scope="prototype">
<!-- 为u_id注入了一个id为2的值 -->
<property name="u_id" value="2"></property>
</bean>
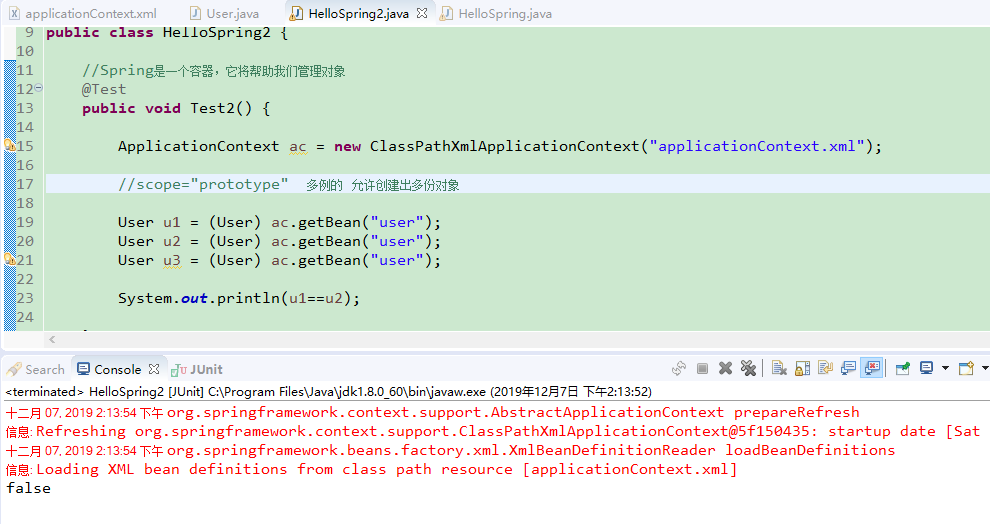
package com.Gary.test; import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.Gary.bean.User; public class HelloSpring2 { //Spring是一个容器,它将帮助我们管理对象
@Test
public void Test2() { ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); //scope="prototype" 多例的 允许创建出多份对象 User u1 = (User) ac.getBean("user");
User u2 = (User) ac.getBean("user");
User u3 = (User) ac.getBean("user"); System.out.println(u1==u2); } }
HelloSpring2.java
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd "> <!-- name 是起一个名字,我们可以通过这个name来利用容器获取对象
name 可以使用特殊字符
name 可以重复
我们在实际开发中不推荐将多个对象名字命名为重复的-->
<!-- id与name作用基本相同,单不推荐使用 不支持特殊字符,不能重复 --> <!-- class:是被管理对象的全包名,spring会通过这个包名来创建对象 -->
<!-- request 在web环境下,如果scope属性为request 那么这个对象被创建出来 他的生命周期会与request请求一致-->
<!-- session 同理 ,生命周期与session一致 -->
<bean name="user" class="com.Gary.bean.User" lazy-init ="true" scope="prototype">
<!-- 为u_id注入了一个id为2的值 -->
<property name="u_id" value="2"></property> </bean> </beans>
applicationContext.xml
scrope的其它两个属性request、session(基本用不到这两个属性)
一般情况下使用singleton单例的,特殊情况下使用prototype多例的(使用struts时,它创建的action是多例的)
<!-- request 在web环境下,如果scope属性为request 那么这个对象被创建出来 他的生命周期会与request请求一致-->
<!-- session 同理 ,生命周期与session一致 -->
<bean name="user" class="com.Gary.bean.User" lazy-init ="true" scope="prototype">
<!-- 为u_id注入了一个id为2的值 -->
<property name="u_id" value="2"></property> </bean>
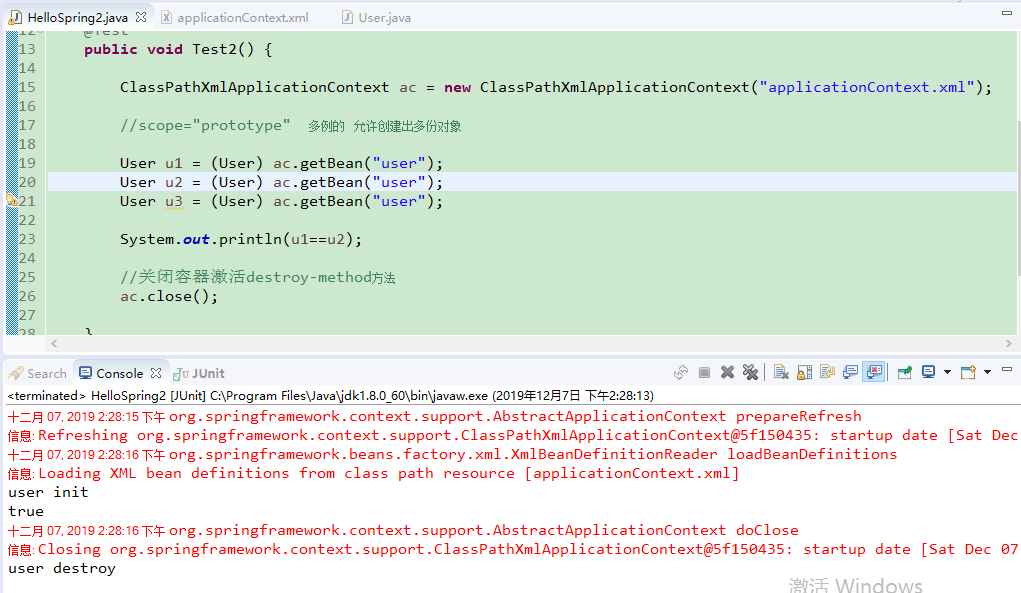
3、xml配置-bean标签-init-method与destroy-method的使用
在User.java中添加一个userInit()初始化方法与userDestroy()销毁容器时的方法
public void userInit() {
System.out.println("user init");
}
public void userDestroy() {
System.out.println("user destroy");
}
<bean name="user" class="com.Gary.bean.User" lazy-init ="true" init-method="userInit" destroy-method="userDestroy">
<!-- 为u_id注入了一个id为2的值 -->
<property name="u_id" value="2"></property> </bean>
package com.Gary.bean;
public class User {
private Integer u_id;
private String u_username;
private String u_password;
/*public User() {
System.out.println("默认使用 User 对象空参构造方法");
}*/
public Integer getU_id() {
return u_id;
}
public void setU_id(Integer u_id) {
this.u_id = u_id;
}
public String getU_username() {
return u_username;
}
public void setU_username(String u_username) {
this.u_username = u_username;
}
public String getU_password() {
return u_password;
}
public void setU_password(String u_password) {
this.u_password = u_password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [u_id=" + u_id + ", u_username=" + u_username + ", u_password=" + u_password + "]";
}
public void userInit() {
System.out.println("user init");
}
public void userDestroy() {
System.out.println("user destroy");
}
}
User.java
package com.Gary.test; import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.Gary.bean.User; public class HelloSpring2 { //Spring是一个容器,它将帮助我们管理对象
@Test
public void Test2() { ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); //scope="prototype" 多例的 允许创建出多份对象 User u1 = (User) ac.getBean("user");
User u2 = (User) ac.getBean("user");
User u3 = (User) ac.getBean("user"); System.out.println(u1==u2); //关闭容器激活destroy-method方法
ac.close(); } }
HelloSpring2.java
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd "> <!-- name 是起一个名字,我们可以通过这个name来利用容器获取对象
name 可以使用特殊字符
name 可以重复
我们在实际开发中不推荐将多个对象名字命名为重复的-->
<!-- id与name作用基本相同,单不推荐使用 不支持特殊字符,不能重复 --> <!-- class:是被管理对象的全包名,spring会通过这个包名来创建对象 -->
<!-- request 在web环境下,如果scope属性为request 那么这个对象被创建出来 他的生命周期会与request请求一致-->
<!-- session 同理 ,生命周期与session一致 -->
<bean name="user" class="com.Gary.bean.User" lazy-init ="true" init-method="userInit" destroy-method="userDestroy">
<!-- 为u_id注入了一个id为2的值 -->
<property name="u_id" value="2"></property> </bean> </beans>
applicationContext.xml
4、xml配置-属性注入-Set方式注入
注入一个基本类型
创建一个applicationContext_Injection.xml和Test_Injection.java
<!-- 将user对象交给Spring管理,并注入类型 -->
<bean name="user" class="com.Gary.bean.User">
<property name="u_id" value="1"/>
<property name="u_username" value="Gary"/>
<property name="u_password" value="123"/>
</bean>
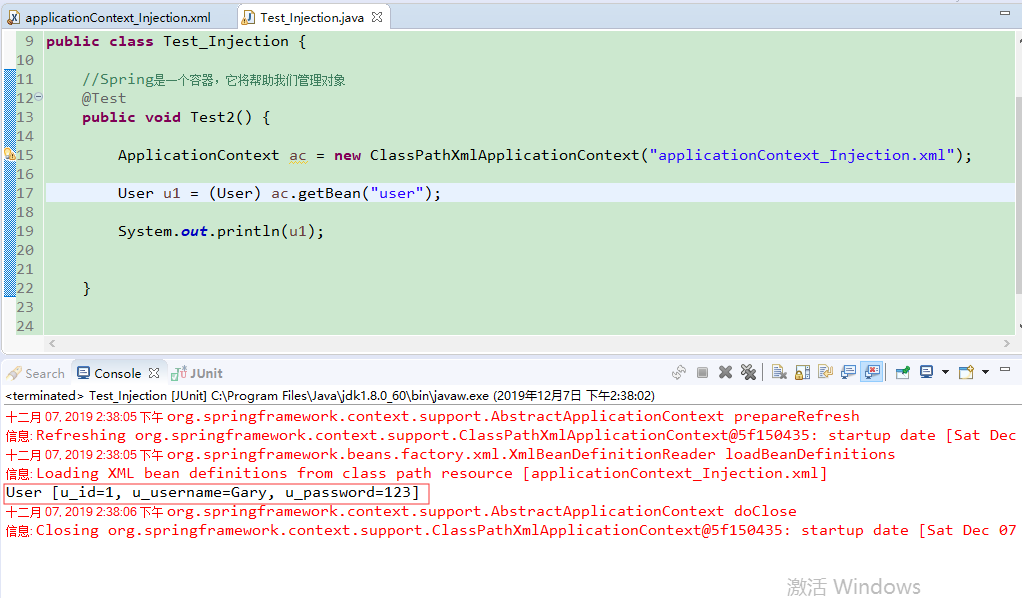
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd "> <!-- 将user对象交给Spring管理,并注入类型 -->
<bean name="user" class="com.Gary.bean.User">
<property name="u_id" value="1"/>
<property name="u_username" value="Gary"/>
<property name="u_password" value="123"/>
</bean> </beans>
applicationContext_Injection.xml
package com.Gary.test; import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.Gary.bean.User; public class Test_Injection { //Spring是一个容器,它将帮助我们管理对象
@Test
public void Test2() { ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext_Injection.xml"); User u1 = (User) ac.getBean("user"); System.out.println(u1); } }
Test_Injection.java
package com.Gary.bean;
public class User {
private Integer u_id;
private String u_username;
private String u_password;
/*public User() {
System.out.println("默认使用 User 对象空参构造方法");
}*/
public Integer getU_id() {
return u_id;
}
public void setU_id(Integer u_id) {
this.u_id = u_id;
}
public String getU_username() {
return u_username;
}
public void setU_username(String u_username) {
this.u_username = u_username;
}
public String getU_password() {
return u_password;
}
public void setU_password(String u_password) {
this.u_password = u_password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [u_id=" + u_id + ", u_username=" + u_username + ", u_password=" + u_password + "]";
}
public void userInit() {
System.out.println("user init");
}
public void userDestroy() {
System.out.println("user destroy");
}
}
User.java
注入引用类型
创建一个Pet.java宠物类
package com.Gary.bean;
public class Pet {
//宠物类型 猫 狗
private String petType;
//宠物颜色
private String color;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Pet [petType=" + petType + ", color=" + color + "]";
}
public String getPetType() {
return petType;
}
public void setPetType(String petType) {
this.petType = petType;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
}
Pet.java
在User.java中加入宠物字段
private Integer u_id;
private String u_username;
private String u_password; //加入宠物字段
private Pet u_pet;
package com.Gary.bean;
public class User {
private Integer u_id;
private String u_username;
private String u_password;
//加入宠物字段
private Pet u_pet;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [u_id=" + u_id + ", u_username=" + u_username + ", u_password=" + u_password + ", u_pet=" + u_pet
+ "]";
}
public Pet getU_pet() {
return u_pet;
}
public void setU_pet(Pet u_pet) {
this.u_pet = u_pet;
}
/*public User() {
System.out.println("默认使用 User 对象空参构造方法");
}*/
public Integer getU_id() {
return u_id;
}
public void setU_id(Integer u_id) {
this.u_id = u_id;
}
public String getU_username() {
return u_username;
}
public void setU_username(String u_username) {
this.u_username = u_username;
}
public String getU_password() {
return u_password;
}
public void setU_password(String u_password) {
this.u_password = u_password;
}
public void userInit() {
System.out.println("user init");
}
public void userDestroy() {
System.out.println("user destroy");
}
}
User.java
<!-- 将user对象交给Spring管理,并注入类型 -->
<bean name="user" class="com.Gary.bean.User">
<property name="u_id" value="1"/>
<property name="u_username" value="Gary"/>
<property name="u_password" value="123"/>
<!-- 引用类型的注入 -->
<property name="u_pet" ref="dog"/>
</bean> <!-- 注入引用类型 -->
<bean name="dog" class="com.Gary.bean.Pet">
<property name="petType" value="二哈"/>
<property name="color" value="灰白"/>
</bean>
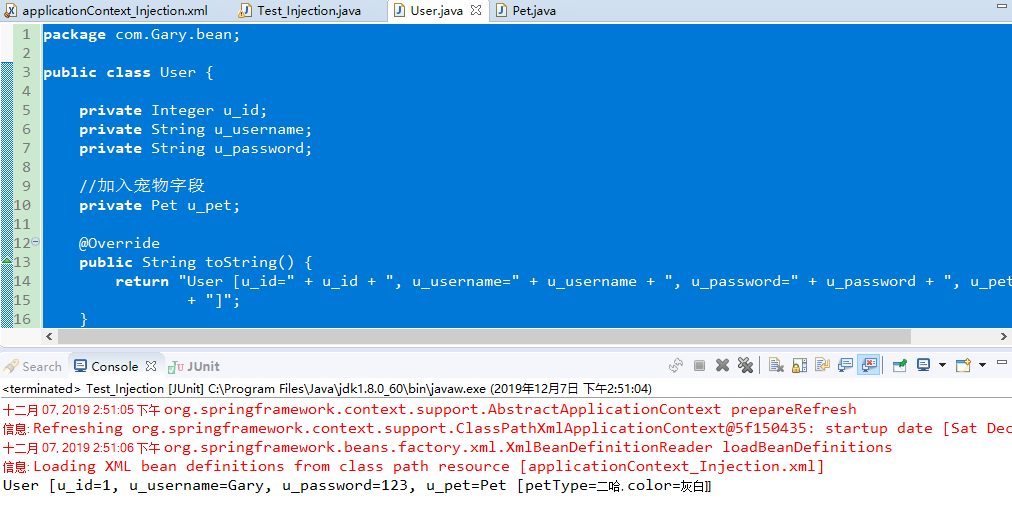
package com.Gary.bean;
public class User {
private Integer u_id;
private String u_username;
private String u_password;
//加入宠物字段
private Pet u_pet;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [u_id=" + u_id + ", u_username=" + u_username + ", u_password=" + u_password + ", u_pet=" + u_pet
+ "]";
}
public Pet getU_pet() {
return u_pet;
}
public void setU_pet(Pet u_pet) {
this.u_pet = u_pet;
}
/*public User() {
System.out.println("默认使用 User 对象空参构造方法");
}*/
public Integer getU_id() {
return u_id;
}
public void setU_id(Integer u_id) {
this.u_id = u_id;
}
public String getU_username() {
return u_username;
}
public void setU_username(String u_username) {
this.u_username = u_username;
}
public String getU_password() {
return u_password;
}
public void setU_password(String u_password) {
this.u_password = u_password;
}
public void userInit() {
System.out.println("user init");
}
public void userDestroy() {
System.out.println("user destroy");
}
}
User.java
package com.Gary.bean;
public class Pet {
//宠物类型 猫 狗
private String petType;
//宠物颜色
private String color;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Pet [petType=" + petType + ", color=" + color + "]";
}
public String getPetType() {
return petType;
}
public void setPetType(String petType) {
this.petType = petType;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
}
Pet.java
package com.Gary.test; import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.Gary.bean.User; public class Test_Injection { //Spring是一个容器,它将帮助我们管理对象
@Test
public void Test2() { ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext_Injection.xml"); User u1 = (User) ac.getBean("user"); System.out.println(u1); } }
Test_Injection.java
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd "> <!-- 将user对象交给Spring管理,并注入类型 -->
<bean name="user" class="com.Gary.bean.User">
<property name="u_id" value="1"/>
<property name="u_username" value="Gary"/>
<property name="u_password" value="123"/>
<!-- 引用类型的注入 -->
<property name="u_pet" ref="dog"/>
</bean> <!-- 注入引用类型 -->
<bean name="dog" class="com.Gary.bean.Pet">
<property name="petType" value="二哈"/>
<property name="color" value="灰白"/>
</bean> </beans>
applicationContext.xml
5、xml配置-属性注入-构造函数注入
在User.java中创建构造函数(一定要带空参构造方法)
public User(String u_username, Pet u_pet) {
System.out.println("方法1 String,Pet");
this.u_username = u_username;
this.u_pet = u_pet;
}
package com.Gary.bean;
public class User {
private Integer u_id;
private String u_username;
private String u_password;
public User(String u_username, Pet u_pet) {
System.out.println("方法1 String,Pet");
this.u_username = u_username;
this.u_pet = u_pet;
}
//加入宠物字段
private Pet u_pet;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [u_id=" + u_id + ", u_username=" + u_username + ", u_password=" + u_password + ", u_pet=" + u_pet
+ "]";
}
public Pet getU_pet() {
return u_pet;
}
public void setU_pet(Pet u_pet) {
this.u_pet = u_pet;
}
/*public User() {
System.out.println("默认使用 User 对象空参构造方法");
}*/
public Integer getU_id() {
return u_id;
}
public void setU_id(Integer u_id) {
this.u_id = u_id;
}
public String getU_username() {
return u_username;
}
public void setU_username(String u_username) {
this.u_username = u_username;
}
public String getU_password() {
return u_password;
}
public void setU_password(String u_password) {
this.u_password = u_password;
}
public void userInit() {
System.out.println("user init");
}
public void userDestroy() {
System.out.println("user destroy");
}
}
User.java
在applicationContext_Injection.xml中使用构造方法注入配置<bean>元素
<!-- 构造方法注入 -->
<bean name="user1" class="com.Gary.bean.User">
<constructor-arg name="u_username" value="Gary2"/>
<constructor-arg name="u_pet" ref="dog"/>
</bean>

package com.Gary.bean;
public class User {
private Integer u_id;
private String u_username;
private String u_password;
public User(String u_username, Pet u_pet) {
System.out.println("方法1 String,Pet");
this.u_username = u_username;
this.u_pet = u_pet;
}
//加入宠物字段
private Pet u_pet;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [u_id=" + u_id + ", u_username=" + u_username + ", u_password=" + u_password + ", u_pet=" + u_pet
+ "]";
}
public Pet getU_pet() {
return u_pet;
}
public void setU_pet(Pet u_pet) {
this.u_pet = u_pet;
}
public User() {
System.out.println("默认使用 User 对象空参构造方法");
}
public Integer getU_id() {
return u_id;
}
public void setU_id(Integer u_id) {
this.u_id = u_id;
}
public String getU_username() {
return u_username;
}
public void setU_username(String u_username) {
this.u_username = u_username;
}
public String getU_password() {
return u_password;
}
public void setU_password(String u_password) {
this.u_password = u_password;
}
}
User.java
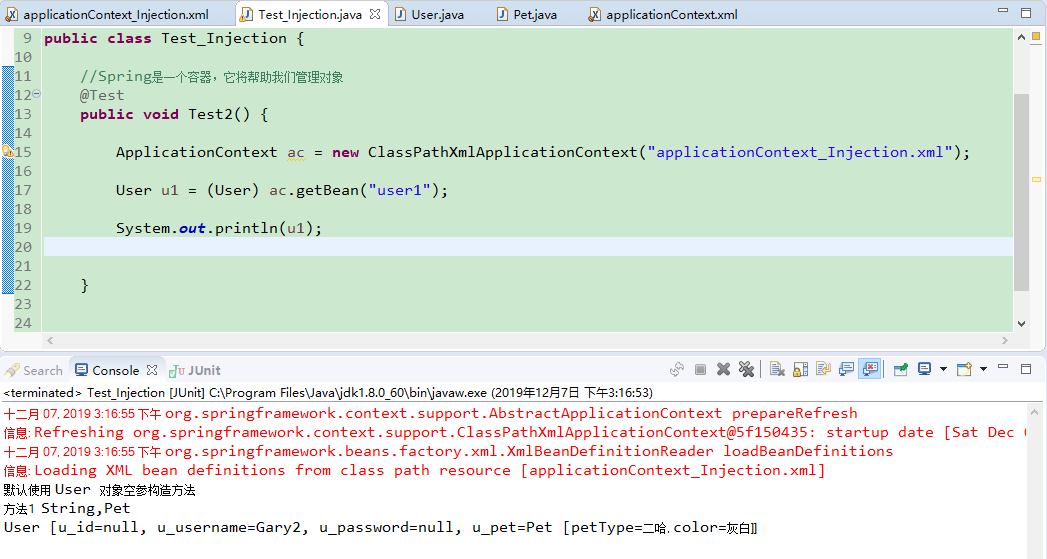
package com.Gary.test; import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.Gary.bean.User; public class Test_Injection { //Spring是一个容器,它将帮助我们管理对象
@Test
public void Test2() { ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext_Injection.xml"); User u1 = (User) ac.getBean("user1"); System.out.println(u1); } }
Test_Injection.java
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd "> <!-- 将user对象交给Spring管理,并注入类型 -->
<bean name="user" class="com.Gary.bean.User">
<property name="u_id" value="1"/>
<property name="u_username" value="Gary"/>
<property name="u_password" value="123"/>
<!-- 引用类型的注入 -->
<property name="u_pet" ref="dog"/>
</bean> <!-- 注入引用类型 -->
<bean name="dog" class="com.Gary.bean.Pet">
<property name="petType" value="二哈"/>
<property name="color" value="灰白"/>
</bean> <!-- 构造方法注入 -->
<bean name="user1" class="com.Gary.bean.User">
<constructor-arg name="u_username" value="Gary2"/>
<constructor-arg name="u_pet" ref="dog"/>
</bean> </beans>
applicationContext_Injection.xml
如果有多个构造方法,可以使用type:指定参数的类型,index :指定参数
6、xml配置-属性注入-复杂类型注入Array、List、Set、Map、Properties
在MyCollection.java中定义几个复杂类型变量
//数组
private Object[] array; //list
private List list; //set
private Set set; //map
private Map map; //properties
private Properties properties;
<!-- 复杂类型注入 -->
<bean name="collection" class="com.Gary.bean.MyCollection">
<!-- array -->
<property name="array">
<array>
<value>123</value>
<value>abc</value>
</array>
</property>
</bean>
package com.Gary.bean; import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Set; public class MyCollection {
//数组
private Object[] array; //list
private List list; //set
private Set set; //map
private Map map; //properties
private Properties properties; public Object[] getArray() {
return array;
} public void setArray(Object[] array) {
this.array = array;
} public List getList() {
return list;
} public void setList(List list) {
this.list = list;
} public Set getSet() {
return set;
} public void setSet(Set set) {
this.set = set;
} public Map getMap() {
return map;
} public void setMap(Map map) {
this.map = map;
} public Properties getProperties() {
return properties;
} public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
} @Override
public String toString() {
return "MyCollection [array=" + Arrays.toString(array) + ", list=" + list + ", set=" + set + "]";
} }
MyCollection.java
package com.Gary.test; import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.Gary.bean.MyCollection;
import com.Gary.bean.User; public class Test_Injection { //Spring是一个容器,它将帮助我们管理对象
@Test
public void Test2() { ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext_Injection.xml"); MyCollection mc = (MyCollection) ac.getBean("collection"); System.out.println(mc); } }
Test_Injection.java
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd "> <!-- 将user对象交给Spring管理,并注入类型 -->
<bean name="user" class="com.Gary.bean.User">
<property name="u_id" value="1"/>
<property name="u_username" value="Gary" />
<property name="u_password" value="123"/>
<!-- 引用类型的注入 -->
<property name="u_pet" ref="dog"/>
</bean> <!-- 注入引用类型 -->
<bean name="dog" class="com.Gary.bean.Pet">
<property name="petType" value="二哈"/>
<property name="color" value="灰白"/>
</bean> <!-- 构造方法注入 -->
<bean name="user1" class="com.Gary.bean.User">
<constructor-arg name="u_username" value="Gary2" type=""/>
<constructor-arg name="u_pet" ref="dog"/>
</bean> <!-- 复杂类型注入 -->
<bean name="collection" class="com.Gary.bean.MyCollection">
<!-- array -->
<property name="array">
<array>
<value>123</value>
<value>abc</value>
</array>
</property>
</bean> </beans>
applicationContext_Injection.xml
同理剩下几个复杂类型配置
<!-- 复杂类型注入 -->
<bean name="collection" class="com.Gary.bean.MyCollection">
<!-- array -->
<property name="array">
<array>
<value>123</value>
<value>abc</value>
<ref bean="dog"/>
</array>
</property> <!-- list -->
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>456</value>
<value>cba</value>
<ref bean="user1"/>
</list>
</property> <!--set -->
<property name="set">
<set>
<value>111</value>
<value>aaa</value>
<ref bean="user1"/>
</set>
</property> <!-- map -->
<property name="map">
<map>
<entry key="username" value="root"/>
<entry key="password" value="123"/>
<entry key-ref="user1" value-ref="dog"/>
</map>
</property> <!-- properties -->
<property name="prop">
<props>
<prop key="name">老李</prop>
<prop key="age">25</prop>
</props>
</property> </bean>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd "> <!-- 将user对象交给Spring管理,并注入类型 -->
<bean name="user" class="com.Gary.bean.User">
<property name="u_id" value="1"/>
<property name="u_username" value="Gary" />
<property name="u_password" value="123"/>
<!-- 引用类型的注入 -->
<property name="u_pet" ref="dog"/>
</bean> <!-- 注入引用类型 -->
<bean name="dog" class="com.Gary.bean.Pet">
<property name="petType" value="二哈"/>
<property name="color" value="灰白"/>
</bean> <!-- 构造方法注入 -->
<bean name="user1" class="com.Gary.bean.User">
<constructor-arg name="u_username" value="Gary2" type=""/>
<constructor-arg name="u_pet" ref="dog"/>
</bean> <!-- 复杂类型注入 -->
<bean name="collection" class="com.Gary.bean.MyCollection">
<!-- array -->
<property name="array">
<array>
<value>123</value>
<value>abc</value>
<ref bean="dog"/>
</array>
</property> <!-- list -->
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>456</value>
<value>cba</value>
<ref bean="user1"/>
</list>
</property> <!--set -->
<property name="set">
<set>
<value>111</value>
<value>aaa</value>
<ref bean="user1"/>
</set>
</property> <!-- map -->
<property name="map">
<map>
<entry key="username" value="root"/>
<entry key="password" value="123"/>
<entry key-ref="user1" value-ref="dog"/>
</map>
</property> <!-- properties -->
<property name="prop">
<props>
<prop key="name">老李</prop>
<prop key="age">25</prop>
</props>
</property> </bean> </beans>
applicationContext_Injection.xml
JavaWeb_(Spring框架)xml配置文件的更多相关文章
- Spring框架xml配置文件 复杂类型属性注入——数组 list map properties DI dependency injection 依赖注入——属性值的注入依赖于建立的对象(堆空间)
Person类中的各种属性写法如下: package com.swift.person; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; import ...
- JavaWeb_(Spring框架)注解配置
系列博文 JavaWeb_(Spring框架)xml配置文件 传送门 JavaWeb_(Spring框架)注解配置 传送门 Spring注解配置 a)导包和约束:基本包.aop包+context约束 ...
- JavaWeb_(Mybatis框架)主配置文件介绍_四
系列博文: JavaWeb_(Mybatis框架)JDBC操作数据库和Mybatis框架操作数据库区别_一 传送门 JavaWeb_(Mybatis框架)使用Mybatis对表进行增.删.改.查操作_ ...
- JavaWeb_(Spring框架)Spring整合Hibernate
Dao层类要继承HibernateDaoSupport.java父类 原先使用Hibernate框架hibernate.cfg.xml配置数据库 <hibernate-configuration ...
- Spring 通过XML配置文件以及通过注解形式来AOP 来实现前置,环绕,异常通知,返回后通知,后通知
本节主要内容: 一.Spring 通过XML配置文件形式来AOP 来实现前置,环绕,异常通知 1. Spring AOP 前置通知 XML配置使用案例 2. Spring AOP ...
- (转)在编写Spring框架的配置文件时,标签无提示符的解决办法
http://blog.csdn.net/yerenyuan_pku/article/details/52831618 问题描述 初学者在学习Spring框架的过程中,大概会碰到这样一个问题:在编写S ...
- Spring框架的配置文件
Spring框架的配置文件 (2014-12-18 20:43:42) 转载▼ 标签: 配置文件 例子 构造函数 成员 spring 分类: 专业知识 (注:文中的"<"均需 ...
- [error] eclipse编写spring等xml配置文件时只有部分提示,tx无提示
eclipse编写spring等xml配置文件时只有<bean>.<context>等有提示,其他标签都没有提示 这时就需要做以下两步操作(下面以事务管理标签为例) 1,添加命 ...
- Spring根据XML配置文件注入对象类型属性
这里有dao.service和Servlet三个地方 通过配过文件xml生成对象,并注入对象类型的属性,降低耦合 dao文件代码: package com.swift; public class Da ...
随机推荐
- (三十一)web 开发基础项目
1. 编写index.jsp <%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" ...
- (五)lucene之特定项搜索和查询表达式
需求:模糊搜索. 前提: 本例中使用lucene 5.3.0 package com.shyroke.lucene; import java.io.File; import java.io.File ...
- (三)Redis之数据结构概念以及数据结构之字符串
一.数据结构 五种数据类型: 字符串(String) 字符串列表(list) 有序字符串集合(sorted set) 哈希(hash) 字符串集合(set) 二.数据结构之字符串 二进制安全的,存入和 ...
- 前端开发 Vue -3axios
Axios是什么? 应该念“阿克希奥斯”……但是太长太拗口,我一般念“阿笑斯”…… Axios 是一个基于 promise 的 HTTP 库,简单的讲就是可以发送get.post请求.说到get.po ...
- regarding-hsts-in-netscaler
regarding-hsts-in-netscaler 参考: Strict Transport Security (STS or HSTS) with Citrix NetScaler and Ac ...
- springload热更新的优缺点
java开发web应用没有.net的方便快捷, 原因是传统开发模式下新增修改代码后要查看效果, 一般要重启应用, 导致浪费了许多无谓的时间,没有.net的高效, 任意更新文件实时生效. 但是有个叫sp ...
- 【Hibernate】Hibernate关联关系的映射
一.实体之间的关系 二.一对多的配置 2.1 第一步创建两个实体 2.2 第二步:配置映射文件 2.3 第三步:将映射放到核心配置文件中 三.级联 3.1 Hibernate中级联保存的效果 3.2 ...
- IDEA部署项目到远程服务器
一.idea安装阿里插件Alibaba Cloud Toolkit 二.添加Host 三.应用部署 四.修改源程序重新部署 五.查看实时日志 欲买桂花同载酒,终不似,少年游
- win10关闭防火墙和其通知
Win10电脑在关闭防火墙后,防火墙的通知会不定期提醒,如果误点后,防火墙就悄悄的开启了,导致好多功能就用不了了,所以比较有效的方法是:关闭防火墙,并关闭防火墙通知 1.关闭防火墙 在控制面板中,选择 ...
- idou老师教你学istio 21:基于角色的访问控制
istio的授权功能,也称为基于角色的访问控制(RBAC),它为istio服务网格中的服务提供命名空间级别.服务级别和方法级别的访问控制.基于角色的访问控制具有简单易用.灵活和高性能等特性.本文介绍如 ...
