spring中BeanPostProcessor之四:AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor(01)
在《spring中BeanPostProcessor之二:CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor(01)》中分析了CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类中的postProcessMergedBeanDefinition方法的作用,即是对类中的@Resources、@WebServiceRef、@EJB三个注解进行解析并缓存起来,以便后续执行postProcessProperties方法的时候用到缓存的信息。在spring启动过程中还有一个和CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类相似的bean后置处理器,该类就是AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor,该bean后置处理器的作用是处理@Autowired、@Value、@Inject注解。
一、概述
前面说到AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类是解析@Autowired注解的,那么该注解的作用是什么那,是怎么定义的那
- @Target({ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE})
- @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
- @Documented
- public @interface Autowired {
- /**
- * Declares whether the annotated dependency is required.
- * <p>Defaults to {@code true}.
- */
- boolean required() default true;
- }
上面是该注解的定义,该注解的作用是自动注入,该注解是Spring提供的注解(@Resource、@WebServiceRef、@EJB均是java提供的)。
AutowriedAnnotationBeanPostProcessor要解析@Autowired注解那么按照前面分析的CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor和InitDestroyBeanPostProcessor两个类,必须要先有要解析的类型,也就是初始化解析的类型,看AutoworedAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的构造方法,
- @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
- public AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor() {
- this.autowiredAnnotationTypes.add(Autowired.class);
- this.autowiredAnnotationTypes.add(Value.class);
- try {
- this.autowiredAnnotationTypes.add((Class<? extends Annotation>)
- ClassUtils.forName("javax.inject.Inject", AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class.getClassLoader()));
- logger.trace("JSR-330 'javax.inject.Inject' annotation found and supported for autowiring");
- }
- catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
- // JSR-330 API not available - simply skip.
- }
- }
上面是其默认的构造方法,可以看到向autowiredAnnotationTypes中加了三个注解:@Autowired、@Value、@Inject,其中@Inject是java中的注解,其余两个均是Spring提供的注解。那么这里其实是说明AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类是解析这三个注解的,我们继续往下分析。
二、详述
1、方法概述
下面看AutoWiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类中的方法,

上面给出了AutoWiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类中的主要的方法,重点看postProcessMergedBeanDefinition和postProcessProperties方法,postProcessPropertyValue方法在前边已经说过该方法已经废弃了,调用的是postProcessProperties方法。
2、postProcessMergedBeanDefinition
该方法的作用是解析类中标记了@AutoWired、@Value、@Inject注解的属性和方法,下面看具体的方法定义,
- @Override
- public void postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition, Class<?> beanType, String beanName) {
- InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, beanType, null);
- metadata.checkConfigMembers(beanDefinition);
- }
2.1、findAutowiringMetadata
下面看findAutowiringMetadata方法
- private InjectionMetadata findAutowiringMetadata(String beanName, Class<?> clazz, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) {
- // Fall back to class name as cache key, for backwards compatibility with custom callers.
- String cacheKey = (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) ? beanName : clazz.getName());
- // Quick check on the concurrent map first, with minimal locking.
//从缓存中获得该类的信息- InjectionMetadata metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
//判断是否需要刷新缓存- if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
- synchronized (this.injectionMetadataCache) {
- metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
- if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
- if (metadata != null) {
- metadata.clear(pvs);
- }
//查找目标类clazz中的标识了@AutoWired、@Value、@Inejct注解- metadata = buildAutowiringMetadata(clazz);
- this.injectionMetadataCache.put(cacheKey, metadata);
- }
- }
- }
- return metadata;
- }
从上面的代码中可以看出最终是把标识了@AutoWired、@Value、@Inject注解的方法或字段信息封装为Metadata然后放在了injectionMetadataCache中,重点看buildAutowiringMetadata方法,
- private InjectionMetadata buildAutowiringMetadata(final Class<?> clazz) {
- /**autowiredAnnotationTypes中得值为
- * @AutoWired org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired
- * @Value org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value
- * @Inject javax.inject.Inject
- *
- */
- if (!AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(clazz, this.autowiredAnnotationTypes)) {
- return InjectionMetadata.EMPTY;
- }
- List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> elements = new ArrayList<>();
- Class<?> targetClass = clazz;
- do {
- final List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> currElements = new ArrayList<>();
- //判断字段上是否存在autowiredAnnotationTypes中的注解
- ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalFields(targetClass, field -> {
- MergedAnnotation<?> ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(field);
- if (ann != null) {
- if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {
- if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
- logger.info("Autowired annotation is not supported on static fields: " + field);
- }
- return;
- }
- boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
- currElements.add(new AutowiredFieldElement(field, required));
- }
- });
- //判断方法上是否存在autowiredAnnotationTypes中的注解
- ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> {
- Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method);
- if (!BridgeMethodResolver.isVisibilityBridgeMethodPair(method, bridgedMethod)) {
- return;
- }
- MergedAnnotation<?> ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(bridgedMethod);
- if (ann != null && method.equals(ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, clazz))) {
- if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {
- if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
- logger.info("Autowired annotation is not supported on static methods: " + method);
- }
- return;
- }
- if (method.getParameterCount() == 0) {
- if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
- logger.info("Autowired annotation should only be used on methods with parameters: " +
- method);
- }
- }
- boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
- PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);
- currElements.add(new AutowiredMethodElement(method, required, pd));
- }
- });
- elements.addAll(0, currElements);
- targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();
- }
- while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);
- return InjectionMetadata.forElements(elements, clazz);
- }
该代码比较多,主要是对目标类中的方法和字段信息进行了检查,判断是否标注了@AutoWired、@Value、@Inject三个注解,最后返回InjectionMetadata.forElements该方法是做什么的那,由于前边生成的对象是elements的对象,看elements对象的类型,
- List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> elements = new ArrayList<>();
是一个ArrayList类型,泛型是InjectionMetadata.InejctedElement,下面看该方法,
- public static InjectionMetadata forElements(Collection<InjectedElement> elements, Class<?> clazz) {
- return (elements.isEmpty() ? InjectionMetadata.EMPTY : new InjectionMetadata(clazz, elements));
- }
从上面的代码可以看到,最终是new了一个InjectionMetadata的实例。最终buildAutowiringMetadata方法返回的是一个InjectionMetadata的实例。
buildAutowiringMetadata方法执行完以后,在findAutowiringMetadata方法中,把返回的InjectionMetadata实例放入了injectionMetadataCache中,最终返回一个InjectionMetadata实例。
2.2、checkConfigMembers
在postProcessMergedBeanDefinition方法中的第二行代码即调用了checkConfigMembers方法
- metadata.checkConfigMembers(beanDefinition);
该方法的定义如下,
- public void checkConfigMembers(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
- Set<InjectedElement> checkedElements = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.injectedElements.size());
- for (InjectedElement element : this.injectedElements) {
- Member member = element.getMember();
- if (!beanDefinition.isExternallyManagedConfigMember(member)) {
- beanDefinition.registerExternallyManagedConfigMember(member);
- checkedElements.add(element);
- if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
- logger.trace("Registered injected element on class [" + this.targetClass.getName() + "]: " + element);
- }
- }
- }
- this.checkedElements = checkedElements;
- }
从上面的代码中可以看出首先new了一个checkedElements,使用的是injectedElements的长度,injectedElements是什么那,怎么赋值的那。在buildAutowiringMetadata方法的最后调用了InectionMetadata.forElements方法,在该方法中最后生成了一个InjectionMetadata对象,传入了elements对象,便是该对象。
checkConfiMembers方法主要是调用了beanDefintion.isExternallyManagedConfigMemgber方法,该方法暂时不讨论。
3、postProcessProperties
上面分析了postProcessMergedBeanDefinition方法后,我们知道该方法的作用就是收集类中的标注了@AutoWired、@Value、@Inject注解的字段或方法,那么postProcessProperties方法便是在进行赋值的时候调用的,
- //完成@AutoWired属性的注入
- @Override
- public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) {
- //再次获取了类中标注了@AutoWired、@Value、@Inject属性的信息
- InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass(), pvs);
- try {
- //属性注入
- metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);
- }
- catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
- throw ex;
- }
- catch (Throwable ex) {
- throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Injection of autowired dependencies failed", ex);
- }
- return pvs;
- }
在该方法中又一次获取了类中标注了@AutoWired、@Value、@Inject属性的信息,重点是下面这行代码,
- //属性注入
- metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);
下面看inject方法,
- public void inject(Object target, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
- Collection<InjectedElement> checkedElements = this.checkedElements;
- //如果checkedElements为空,则取injectedElements
- Collection<InjectedElement> elementsToIterate =
- (checkedElements != null ? checkedElements : this.injectedElements);
- if (!elementsToIterate.isEmpty()) {
- for (InjectedElement element : elementsToIterate) {
- if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
- logger.trace("Processing injected element of bean '" + beanName + "': " + element);
- }
- //进行属性注入
- element.inject(target, beanName, pvs);
- }
- }
- }
上面在进行属性注入的时候调用了element.inject方法,该方法在InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement类中,进去该方法看到如下,
- /**
- * Either this or {@link #getResourceToInject} needs to be overridden.
- */
- protected void inject(Object target, @Nullable String requestingBeanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs)
- throws Throwable {
- if (this.isField) {
- Field field = (Field) this.member;
- ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field);
- field.set(target, getResourceToInject(target, requestingBeanName));
- }
- else {
- if (checkPropertySkipping(pvs)) {
- return;
- }
- try {
- Method method = (Method) this.member;
- ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(method);
- method.invoke(target, getResourceToInject(target, requestingBeanName));
- }
- catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
- throw ex.getTargetException();
- }
- }
- }
看这方法的注释,意思是需要覆盖该方法,也就是说这里调用的不是上面的inject方法,在回到下面的代码
- public void inject(Object target, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
- Collection<InjectedElement> checkedElements = this.checkedElements;
- //如果checkedElements为空,则取injectedElements
- Collection<InjectedElement> elementsToIterate =
- (checkedElements != null ? checkedElements : this.injectedElements);
- if (!elementsToIterate.isEmpty()) {
- for (InjectedElement element : elementsToIterate) {
- if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
- logger.trace("Processing injected element of bean '" + beanName + "': " + element);
- }
- //进行属性注入
- element.inject(target, beanName, pvs);
- }
- }
- }
遍历elementsToIterate,通过调试我们看到这里的element是下面的类型
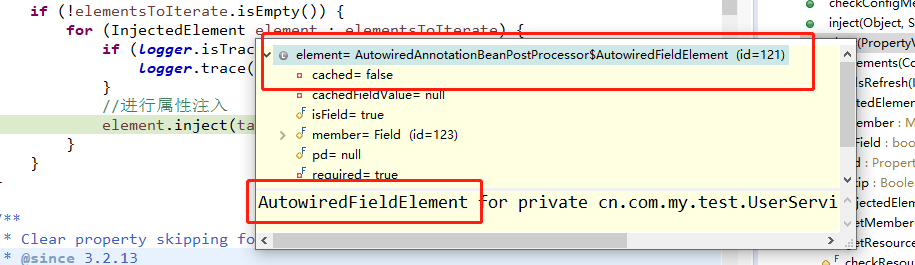
再来看AutowiredFieldElement是什么,
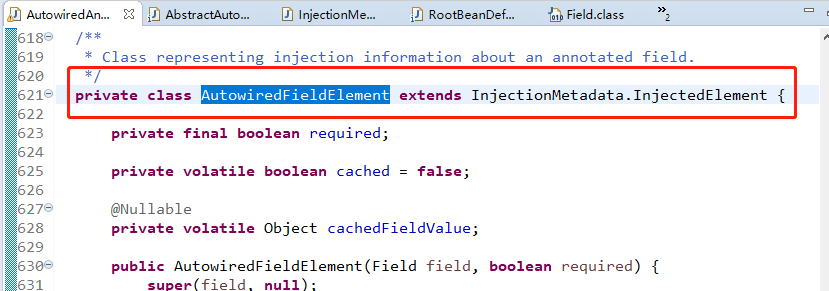
AutowiredFieldElement是AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor中的内部类,继承了InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement类,上面提到了该方法,那么该类中肯定覆盖了inject方法
- @Override
- protected void inject(Object bean, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
- Field field = (Field) this.member;
- Object value;
- if (this.cached) {
- value = resolvedCachedArgument(beanName, this.cachedFieldValue);
- }
- else {
- DependencyDescriptor desc = new DependencyDescriptor(field, this.required);
- desc.setContainingClass(bean.getClass());
- Set<String> autowiredBeanNames = new LinkedHashSet<>(1);
- Assert.state(beanFactory != null, "No BeanFactory available");
- TypeConverter typeConverter = beanFactory.getTypeConverter();
- try {
- value = beanFactory.resolveDependency(desc, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);
- }
- catch (BeansException ex) {
- throw new UnsatisfiedDependencyException(null, beanName, new InjectionPoint(field), ex);
- }
- synchronized (this) {
- if (!this.cached) {
- if (value != null || this.required) {
- this.cachedFieldValue = desc;
- registerDependentBeans(beanName, autowiredBeanNames);
- if (autowiredBeanNames.size() == 1) {
- String autowiredBeanName = autowiredBeanNames.iterator().next();
- if (beanFactory.containsBean(autowiredBeanName) &&
- beanFactory.isTypeMatch(autowiredBeanName, field.getType())) {
- this.cachedFieldValue = new ShortcutDependencyDescriptor(
- desc, autowiredBeanName, field.getType());
- }
- }
- }
- else {
- this.cachedFieldValue = null;
- }
- this.cached = true;
- }
- }
- }
- if (value != null) {
- ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field);
- field.set(bean, value);
- }
- }
- }
此方法的具体执行逻辑暂时不说。
三、使用场景
上面大体分析了AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类中的postProcessMergedBeanDefinition和postProcessProperties两个方法,了解了其作用及执行时机,文中遗留的问题后面会继续分析。

有不当之处,欢迎指正,感谢!
spring中BeanPostProcessor之四:AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor(01)的更多相关文章
- spring中BeanPostProcessor之三:InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor(01)
在<spring中BeanPostProcessor之二:CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor(01)>一文中,分析到在调用CommonAnnotationB ...
- spring中BeanPostProcessor之一:InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor(01)
在spring中beanPostProcessor绝对是开天辟地的产物,给了程序员很多自主权,beanPostProcessor即常说的bean后置处理器. 一.概览 先来说下Instantiatio ...
- Spring中BeanPostProcessor
Spring中BeanPostProcessor 前言: 本文旨在介绍Spring动态配置数据源的方式,即对一个DataSource的配置诸如jdbcUrl,user,password,driverC ...
- spring中BeanPostProcessor之二:CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor(01)
在上篇博客中分享了InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口中的四个方法,分别对其进行了详细的介绍,在文末留下了一个问题,那就是postProcessPropertie ...
- spring(三):spring中BeanPostProcessor的使用
spring中实现BeanPostProcessor的后置处理器 ApplicationContextAwareProcessor 进入该实现类内部 可以看到:该类帮我们组建IOC容器,判断我们的be ...
- spring中BeanPostProcessor之一:InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor(03)
前面介绍了InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor后置处理器的postProcessBeforeInstantiation和postProcessAfterInstant ...
- spring中BeanPostProcessor之一:InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor(02)
在上篇博客中写道了bean后置处理器InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor,只介绍了其中一个方法的作用及用法,现在来看postProcessBeforeInstanti ...
- Spring中的BeanPostProcessor
一.何谓BeanProcessor BeanPostProcessor是SpringFramework里非常重要的核心接口之一,我先贴出一段源代码: /* * Copyright 2002-2015 ...
- 通过BeanPostProcessor理解Spring中Bean的生命周期
通过BeanPostProcessor理解Spring中Bean的生命周期及AOP原理 Spring源码解析(十一)Spring扩展接口InstantiationAwareBeanPostProces ...
随机推荐
- golang:net/http理解总结
Go语言标准库内建提供了net/http包,涵盖了HTTP客户端和服务端的具体实现.使用net/http包,我们可以很方便地编写HTTP客户端或服务端的程序. http服务端的创建流程 在使用http ...
- SSH实现免密登陆
SSH实现免密登陆配置 ssh实现免密码登录的配置过程,主要分为以下几个步骤: serverA生成密钥,包括私钥和公钥 serverA将公钥传到serverB上 serverA上配置serverB登陆 ...
- Linux软件安装管理之——dpkg与apt-*详解
Linux软件安装管理之--dpkg与apt-*详解 [Linux软件安装管理系列]- - 传送门: - -<Linux软件安装管理之--源码安装详解> - -<Linux软件安装管 ...
- Linux_WEB访问控制示例(使用IPADDR类型)
前言: WEB服务使用访问控制,可以控制IP.主机名.以及某个网段的IP去访问我们的WEB服务,从而加减少流量的访问 一.使用IP控制访问 1.在/var/www/html下创建一个可访问的测试页面 ...
- 1.1Ubuntu安装
在虚拟机中安装 Ubuntu 步骤 安装前的准备和基本安装 设置语言环境 安装常用软件 1. 安装前的准备和基本安装 1.1 安装前的准备 访问 http://cn.ubuntu.com/downlo ...
- MyBatis 缓存机制(十三)
什么是缓存 缓存就是内存中的一个对象,用于对数据库查询结果的保存,用于减少与数据库的交互次数从而降低数据库的压力,进而提高响应速度. MyBatis 缓存机制原理 Mybatis 缓存机制原理是将第一 ...
- 8.8-9 fsck、dd
8.8 fsck:检查并修复Linux文件系统 fsck命令用于检查并修复文件系统中的错误,即针对有问题的系统或磁盘进行修复,类似的命令还有e2fsck命令.有关fsck的使用需要特别注意的是: ...
- STM32电路设计注意
以后画STM32的电路板 VDDA一定要接 张JF说 VDDA是给内部的时钟电路供电的 还有一定要留 串口或者 下载调试口(串口) 或者显示器接口 输入输出设备最好都留着 这样才能方便调试
- 安全漏洞扫描工具 burpsuite V1.7.32 资料
安装包下载地址:http://www.downxia.com/downinfo/229728.html 实战教程:https://t0data.gitbooks.io/burpsuite/conten ...
- Python数模笔记-PuLP库(1)线性规划入门
1.什么是线性规划 线性规划(Linear programming),在线性等式或不等式约束条件下求解线性目标函数的极值问题,常用于解决资源分配.生产调度和混合问题.例如: max fx = 2*x1 ...
