沉淀再出发:java中的equals()辨析
沉淀再出发:java中的equals()辨析
一、前言
关于java中的equals,我们可能非常奇怪,在Object中定义了这个函数,其他的很多类中都重载了它,导致了我们对于辨析其中的内涵有了混淆,再加上和“==”的比较,就显得更加的复杂了。
二、java中的equals()
2.1、Object.java中的equals()
让我们来看一下Object.java中的equals()。
首先是Object的定义:
- /*
- * Copyright (c) 1994, 2012, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
- * ORACLE PROPRIETARY/CONFIDENTIAL. Use is subject to license terms.
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- */
- package java.lang;
- /**
- * Class {@code Object} is the root of the class hierarchy.
- * Every class has {@code Object} as a superclass. All objects,
- * including arrays, implement the methods of this class.
- *
- * @author unascribed
- * @see java.lang.Class
- * @since JDK1.0
- */
- public class Object {
- private static native void registerNatives();
- static {
- registerNatives();
- }
- /**
- * Returns the runtime class of this {@code Object}. The returned
- * {@code Class} object is the object that is locked by {@code
- * static synchronized} methods of the represented class.
- *
- * <p><b>The actual result type is {@code Class<? extends |X|>}
- * where {@code |X|} is the erasure of the static type of the
- * expression on which {@code getClass} is called.</b> For
- * example, no cast is required in this code fragment:</p>
- *
- * <p>
- * {@code Number n = 0; }<br>
- * {@code Class<? extends Number> c = n.getClass(); }
- * </p>
- *
- * @return The {@code Class} object that represents the runtime
- * class of this object.
- * @jls 15.8.2 Class Literals
- */
- public final native Class<?> getClass();
- /**
- * Returns a hash code value for the object. This method is
- * supported for the benefit of hash tables such as those provided by
- * {@link java.util.HashMap}.
- * <p>
- * The general contract of {@code hashCode} is:
- * <ul>
- * <li>Whenever it is invoked on the same object more than once during
- * an execution of a Java application, the {@code hashCode} method
- * must consistently return the same integer, provided no information
- * used in {@code equals} comparisons on the object is modified.
- * This integer need not remain consistent from one execution of an
- * application to another execution of the same application.
- * <li>If two objects are equal according to the {@code equals(Object)}
- * method, then calling the {@code hashCode} method on each of
- * the two objects must produce the same integer result.
- * <li>It is <em>not</em> required that if two objects are unequal
- * according to the {@link java.lang.Object#equals(java.lang.Object)}
- * method, then calling the {@code hashCode} method on each of the
- * two objects must produce distinct integer results. However, the
- * programmer should be aware that producing distinct integer results
- * for unequal objects may improve the performance of hash tables.
- * </ul>
- * <p>
- * As much as is reasonably practical, the hashCode method defined by
- * class {@code Object} does return distinct integers for distinct
- * objects. (This is typically implemented by converting the internal
- * address of the object into an integer, but this implementation
- * technique is not required by the
- * Java™ programming language.)
- *
- * @return a hash code value for this object.
- * @see java.lang.Object#equals(java.lang.Object)
- * @see java.lang.System#identityHashCode
- */
- public native int hashCode();
- /**
- * Indicates whether some other object is "equal to" this one.
- * <p>
- * The {@code equals} method implements an equivalence relation
- * on non-null object references:
- * <ul>
- * <li>It is <i>reflexive</i>: for any non-null reference value
- * {@code x}, {@code x.equals(x)} should return
- * {@code true}.
- * <li>It is <i>symmetric</i>: for any non-null reference values
- * {@code x} and {@code y}, {@code x.equals(y)}
- * should return {@code true} if and only if
- * {@code y.equals(x)} returns {@code true}.
- * <li>It is <i>transitive</i>: for any non-null reference values
- * {@code x}, {@code y}, and {@code z}, if
- * {@code x.equals(y)} returns {@code true} and
- * {@code y.equals(z)} returns {@code true}, then
- * {@code x.equals(z)} should return {@code true}.
- * <li>It is <i>consistent</i>: for any non-null reference values
- * {@code x} and {@code y}, multiple invocations of
- * {@code x.equals(y)} consistently return {@code true}
- * or consistently return {@code false}, provided no
- * information used in {@code equals} comparisons on the
- * objects is modified.
- * <li>For any non-null reference value {@code x},
- * {@code x.equals(null)} should return {@code false}.
- * </ul>
- * <p>
- * The {@code equals} method for class {@code Object} implements
- * the most discriminating possible equivalence relation on objects;
- * that is, for any non-null reference values {@code x} and
- * {@code y}, this method returns {@code true} if and only
- * if {@code x} and {@code y} refer to the same object
- * ({@code x == y} has the value {@code true}).
- * <p>
- * Note that it is generally necessary to override the {@code hashCode}
- * method whenever this method is overridden, so as to maintain the
- * general contract for the {@code hashCode} method, which states
- * that equal objects must have equal hash codes.
- *
- * @param obj the reference object with which to compare.
- * @return {@code true} if this object is the same as the obj
- * argument; {@code false} otherwise.
- * @see #hashCode()
- * @see java.util.HashMap
- */
- public boolean equals(Object obj) {
- return (this == obj);
- }
- /**
- * Creates and returns a copy of this object. The precise meaning
- * of "copy" may depend on the class of the object. The general
- * intent is that, for any object {@code x}, the expression:
- * <blockquote>
- * <pre>
- * x.clone() != x</pre></blockquote>
- * will be true, and that the expression:
- * <blockquote>
- * <pre>
- * x.clone().getClass() == x.getClass()</pre></blockquote>
- * will be {@code true}, but these are not absolute requirements.
- * While it is typically the case that:
- * <blockquote>
- * <pre>
- * x.clone().equals(x)</pre></blockquote>
- * will be {@code true}, this is not an absolute requirement.
- * <p>
- * By convention, the returned object should be obtained by calling
- * {@code super.clone}. If a class and all of its superclasses (except
- * {@code Object}) obey this convention, it will be the case that
- * {@code x.clone().getClass() == x.getClass()}.
- * <p>
- * By convention, the object returned by this method should be independent
- * of this object (which is being cloned). To achieve this independence,
- * it may be necessary to modify one or more fields of the object returned
- * by {@code super.clone} before returning it. Typically, this means
- * copying any mutable objects that comprise the internal "deep structure"
- * of the object being cloned and replacing the references to these
- * objects with references to the copies. If a class contains only
- * primitive fields or references to immutable objects, then it is usually
- * the case that no fields in the object returned by {@code super.clone}
- * need to be modified.
- * <p>
- * The method {@code clone} for class {@code Object} performs a
- * specific cloning operation. First, if the class of this object does
- * not implement the interface {@code Cloneable}, then a
- * {@code CloneNotSupportedException} is thrown. Note that all arrays
- * are considered to implement the interface {@code Cloneable} and that
- * the return type of the {@code clone} method of an array type {@code T[]}
- * is {@code T[]} where T is any reference or primitive type.
- * Otherwise, this method creates a new instance of the class of this
- * object and initializes all its fields with exactly the contents of
- * the corresponding fields of this object, as if by assignment; the
- * contents of the fields are not themselves cloned. Thus, this method
- * performs a "shallow copy" of this object, not a "deep copy" operation.
- * <p>
- * The class {@code Object} does not itself implement the interface
- * {@code Cloneable}, so calling the {@code clone} method on an object
- * whose class is {@code Object} will result in throwing an
- * exception at run time.
- *
- * @return a clone of this instance.
- * @throws CloneNotSupportedException if the object's class does not
- * support the {@code Cloneable} interface. Subclasses
- * that override the {@code clone} method can also
- * throw this exception to indicate that an instance cannot
- * be cloned.
- * @see java.lang.Cloneable
- */
- protected native Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException;
- /**
- * Returns a string representation of the object. In general, the
- * {@code toString} method returns a string that
- * "textually represents" this object. The result should
- * be a concise but informative representation that is easy for a
- * person to read.
- * It is recommended that all subclasses override this method.
- * <p>
- * The {@code toString} method for class {@code Object}
- * returns a string consisting of the name of the class of which the
- * object is an instance, the at-sign character `{@code @}', and
- * the unsigned hexadecimal representation of the hash code of the
- * object. In other words, this method returns a string equal to the
- * value of:
- * <blockquote>
- * <pre>
- * getClass().getName() + '@' + Integer.toHexString(hashCode())
- * </pre></blockquote>
- *
- * @return a string representation of the object.
- */
- public String toString() {
- return getClass().getName() + "@" + Integer.toHexString(hashCode());
- }
- /**
- * Wakes up a single thread that is waiting on this object's
- * monitor. If any threads are waiting on this object, one of them
- * is chosen to be awakened. The choice is arbitrary and occurs at
- * the discretion of the implementation. A thread waits on an object's
- * monitor by calling one of the {@code wait} methods.
- * <p>
- * The awakened thread will not be able to proceed until the current
- * thread relinquishes the lock on this object. The awakened thread will
- * compete in the usual manner with any other threads that might be
- * actively competing to synchronize on this object; for example, the
- * awakened thread enjoys no reliable privilege or disadvantage in being
- * the next thread to lock this object.
- * <p>
- * This method should only be called by a thread that is the owner
- * of this object's monitor. A thread becomes the owner of the
- * object's monitor in one of three ways:
- * <ul>
- * <li>By executing a synchronized instance method of that object.
- * <li>By executing the body of a {@code synchronized} statement
- * that synchronizes on the object.
- * <li>For objects of type {@code Class,} by executing a
- * synchronized static method of that class.
- * </ul>
- * <p>
- * Only one thread at a time can own an object's monitor.
- *
- * @throws IllegalMonitorStateException if the current thread is not
- * the owner of this object's monitor.
- * @see java.lang.Object#notifyAll()
- * @see java.lang.Object#wait()
- */
- public final native void notify();
- /**
- * Wakes up all threads that are waiting on this object's monitor. A
- * thread waits on an object's monitor by calling one of the
- * {@code wait} methods.
- * <p>
- * The awakened threads will not be able to proceed until the current
- * thread relinquishes the lock on this object. The awakened threads
- * will compete in the usual manner with any other threads that might
- * be actively competing to synchronize on this object; for example,
- * the awakened threads enjoy no reliable privilege or disadvantage in
- * being the next thread to lock this object.
- * <p>
- * This method should only be called by a thread that is the owner
- * of this object's monitor. See the {@code notify} method for a
- * description of the ways in which a thread can become the owner of
- * a monitor.
- *
- * @throws IllegalMonitorStateException if the current thread is not
- * the owner of this object's monitor.
- * @see java.lang.Object#notify()
- * @see java.lang.Object#wait()
- */
- public final native void notifyAll();
- /**
- * Causes the current thread to wait until either another thread invokes the
- * {@link java.lang.Object#notify()} method or the
- * {@link java.lang.Object#notifyAll()} method for this object, or a
- * specified amount of time has elapsed.
- * <p>
- * The current thread must own this object's monitor.
- * <p>
- * This method causes the current thread (call it <var>T</var>) to
- * place itself in the wait set for this object and then to relinquish
- * any and all synchronization claims on this object. Thread <var>T</var>
- * becomes disabled for thread scheduling purposes and lies dormant
- * until one of four things happens:
- * <ul>
- * <li>Some other thread invokes the {@code notify} method for this
- * object and thread <var>T</var> happens to be arbitrarily chosen as
- * the thread to be awakened.
- * <li>Some other thread invokes the {@code notifyAll} method for this
- * object.
- * <li>Some other thread {@linkplain Thread#interrupt() interrupts}
- * thread <var>T</var>.
- * <li>The specified amount of real time has elapsed, more or less. If
- * {@code timeout} is zero, however, then real time is not taken into
- * consideration and the thread simply waits until notified.
- * </ul>
- * The thread <var>T</var> is then removed from the wait set for this
- * object and re-enabled for thread scheduling. It then competes in the
- * usual manner with other threads for the right to synchronize on the
- * object; once it has gained control of the object, all its
- * synchronization claims on the object are restored to the status quo
- * ante - that is, to the situation as of the time that the {@code wait}
- * method was invoked. Thread <var>T</var> then returns from the
- * invocation of the {@code wait} method. Thus, on return from the
- * {@code wait} method, the synchronization state of the object and of
- * thread {@code T} is exactly as it was when the {@code wait} method
- * was invoked.
- * <p>
- * A thread can also wake up without being notified, interrupted, or
- * timing out, a so-called <i>spurious wakeup</i>. While this will rarely
- * occur in practice, applications must guard against it by testing for
- * the condition that should have caused the thread to be awakened, and
- * continuing to wait if the condition is not satisfied. In other words,
- * waits should always occur in loops, like this one:
- * <pre>
- * synchronized (obj) {
- * while (<condition does not hold>)
- * obj.wait(timeout);
- * ... // Perform action appropriate to condition
- * }
- * </pre>
- * (For more information on this topic, see Section 3.2.3 in Doug Lea's
- * "Concurrent Programming in Java (Second Edition)" (Addison-Wesley,
- * 2000), or Item 50 in Joshua Bloch's "Effective Java Programming
- * Language Guide" (Addison-Wesley, 2001).
- *
- * <p>If the current thread is {@linkplain java.lang.Thread#interrupt()
- * interrupted} by any thread before or while it is waiting, then an
- * {@code InterruptedException} is thrown. This exception is not
- * thrown until the lock status of this object has been restored as
- * described above.
- *
- * <p>
- * Note that the {@code wait} method, as it places the current thread
- * into the wait set for this object, unlocks only this object; any
- * other objects on which the current thread may be synchronized remain
- * locked while the thread waits.
- * <p>
- * This method should only be called by a thread that is the owner
- * of this object's monitor. See the {@code notify} method for a
- * description of the ways in which a thread can become the owner of
- * a monitor.
- *
- * @param timeout the maximum time to wait in milliseconds.
- * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the value of timeout is
- * negative.
- * @throws IllegalMonitorStateException if the current thread is not
- * the owner of the object's monitor.
- * @throws InterruptedException if any thread interrupted the
- * current thread before or while the current thread
- * was waiting for a notification. The <i>interrupted
- * status</i> of the current thread is cleared when
- * this exception is thrown.
- * @see java.lang.Object#notify()
- * @see java.lang.Object#notifyAll()
- */
- public final native void wait(long timeout) throws InterruptedException;
- /**
- * Causes the current thread to wait until another thread invokes the
- * {@link java.lang.Object#notify()} method or the
- * {@link java.lang.Object#notifyAll()} method for this object, or
- * some other thread interrupts the current thread, or a certain
- * amount of real time has elapsed.
- * <p>
- * This method is similar to the {@code wait} method of one
- * argument, but it allows finer control over the amount of time to
- * wait for a notification before giving up. The amount of real time,
- * measured in nanoseconds, is given by:
- * <blockquote>
- * <pre>
- * 1000000*timeout+nanos</pre></blockquote>
- * <p>
- * In all other respects, this method does the same thing as the
- * method {@link #wait(long)} of one argument. In particular,
- * {@code wait(0, 0)} means the same thing as {@code wait(0)}.
- * <p>
- * The current thread must own this object's monitor. The thread
- * releases ownership of this monitor and waits until either of the
- * following two conditions has occurred:
- * <ul>
- * <li>Another thread notifies threads waiting on this object's monitor
- * to wake up either through a call to the {@code notify} method
- * or the {@code notifyAll} method.
- * <li>The timeout period, specified by {@code timeout}
- * milliseconds plus {@code nanos} nanoseconds arguments, has
- * elapsed.
- * </ul>
- * <p>
- * The thread then waits until it can re-obtain ownership of the
- * monitor and resumes execution.
- * <p>
- * As in the one argument version, interrupts and spurious wakeups are
- * possible, and this method should always be used in a loop:
- * <pre>
- * synchronized (obj) {
- * while (<condition does not hold>)
- * obj.wait(timeout, nanos);
- * ... // Perform action appropriate to condition
- * }
- * </pre>
- * This method should only be called by a thread that is the owner
- * of this object's monitor. See the {@code notify} method for a
- * description of the ways in which a thread can become the owner of
- * a monitor.
- *
- * @param timeout the maximum time to wait in milliseconds.
- * @param nanos additional time, in nanoseconds range
- * 0-999999.
- * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the value of timeout is
- * negative or the value of nanos is
- * not in the range 0-999999.
- * @throws IllegalMonitorStateException if the current thread is not
- * the owner of this object's monitor.
- * @throws InterruptedException if any thread interrupted the
- * current thread before or while the current thread
- * was waiting for a notification. The <i>interrupted
- * status</i> of the current thread is cleared when
- * this exception is thrown.
- */
- public final void wait(long timeout, int nanos) throws InterruptedException {
- if (timeout < 0) {
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("timeout value is negative");
- }
- if (nanos < 0 || nanos > 999999) {
- throw new IllegalArgumentException(
- "nanosecond timeout value out of range");
- }
- if (nanos > 0) {
- timeout++;
- }
- wait(timeout);
- }
- /**
- * Causes the current thread to wait until another thread invokes the
- * {@link java.lang.Object#notify()} method or the
- * {@link java.lang.Object#notifyAll()} method for this object.
- * In other words, this method behaves exactly as if it simply
- * performs the call {@code wait(0)}.
- * <p>
- * The current thread must own this object's monitor. The thread
- * releases ownership of this monitor and waits until another thread
- * notifies threads waiting on this object's monitor to wake up
- * either through a call to the {@code notify} method or the
- * {@code notifyAll} method. The thread then waits until it can
- * re-obtain ownership of the monitor and resumes execution.
- * <p>
- * As in the one argument version, interrupts and spurious wakeups are
- * possible, and this method should always be used in a loop:
- * <pre>
- * synchronized (obj) {
- * while (<condition does not hold>)
- * obj.wait();
- * ... // Perform action appropriate to condition
- * }
- * </pre>
- * This method should only be called by a thread that is the owner
- * of this object's monitor. See the {@code notify} method for a
- * description of the ways in which a thread can become the owner of
- * a monitor.
- *
- * @throws IllegalMonitorStateException if the current thread is not
- * the owner of the object's monitor.
- * @throws InterruptedException if any thread interrupted the
- * current thread before or while the current thread
- * was waiting for a notification. The <i>interrupted
- * status</i> of the current thread is cleared when
- * this exception is thrown.
- * @see java.lang.Object#notify()
- * @see java.lang.Object#notifyAll()
- */
- public final void wait() throws InterruptedException {
- wait(0);
- }
- /**
- * Called by the garbage collector on an object when garbage collection
- * determines that there are no more references to the object.
- * A subclass overrides the {@code finalize} method to dispose of
- * system resources or to perform other cleanup.
- * <p>
- * The general contract of {@code finalize} is that it is invoked
- * if and when the Java™ virtual
- * machine has determined that there is no longer any
- * means by which this object can be accessed by any thread that has
- * not yet died, except as a result of an action taken by the
- * finalization of some other object or class which is ready to be
- * finalized. The {@code finalize} method may take any action, including
- * making this object available again to other threads; the usual purpose
- * of {@code finalize}, however, is to perform cleanup actions before
- * the object is irrevocably discarded. For example, the finalize method
- * for an object that represents an input/output connection might perform
- * explicit I/O transactions to break the connection before the object is
- * permanently discarded.
- * <p>
- * The {@code finalize} method of class {@code Object} performs no
- * special action; it simply returns normally. Subclasses of
- * {@code Object} may override this definition.
- * <p>
- * The Java programming language does not guarantee which thread will
- * invoke the {@code finalize} method for any given object. It is
- * guaranteed, however, that the thread that invokes finalize will not
- * be holding any user-visible synchronization locks when finalize is
- * invoked. If an uncaught exception is thrown by the finalize method,
- * the exception is ignored and finalization of that object terminates.
- * <p>
- * After the {@code finalize} method has been invoked for an object, no
- * further action is taken until the Java virtual machine has again
- * determined that there is no longer any means by which this object can
- * be accessed by any thread that has not yet died, including possible
- * actions by other objects or classes which are ready to be finalized,
- * at which point the object may be discarded.
- * <p>
- * The {@code finalize} method is never invoked more than once by a Java
- * virtual machine for any given object.
- * <p>
- * Any exception thrown by the {@code finalize} method causes
- * the finalization of this object to be halted, but is otherwise
- * ignored.
- *
- * @throws Throwable the {@code Exception} raised by this method
- * @see java.lang.ref.WeakReference
- * @see java.lang.ref.PhantomReference
- * @jls 12.6 Finalization of Class Instances
- */
- protected void finalize() throws Throwable { }
- }
Object的定义
其次我们看看其中的函数:


这就是Object中的equals,非常的简单,完全就是比较两个对象的引用是不是同一个内存空间。因此如果直接使用这个equals来比较,使用new创建的对象就不相等了。
- public boolean equals(Object obj) {
- return (this == obj);
- }
比如我们测试:
- package com.consumer.test;
- public class EqualTest {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- MyTest m1=new MyTest();
- MyTest m2=new MyTest();
- System.out.println(m1==m2);
- System.out.println(m1.equals(m2));
- }
- }
- class MyTest{
- public MyTest(){
- output();
- }
- private void output(){
- System.out.println("创建对象成功!");
- }
- }

2.2、String中的equals()
String的定义:
- /*
- * Copyright (c) 1994, 2013, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
- * ORACLE PROPRIETARY/CONFIDENTIAL. Use is subject to license terms.
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- */
- package java.lang;
- import java.io.ObjectStreamField;
- import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
- import java.nio.charset.Charset;
- import java.util.ArrayList;
- import java.util.Arrays;
- import java.util.Comparator;
- import java.util.Formatter;
- import java.util.Locale;
- import java.util.Objects;
- import java.util.StringJoiner;
- import java.util.regex.Matcher;
- import java.util.regex.Pattern;
- import java.util.regex.PatternSyntaxException;
- /**
- * The {@code String} class represents character strings. All
- * string literals in Java programs, such as {@code "abc"}, are
- * implemented as instances of this class.
- * <p>
- * Strings are constant; their values cannot be changed after they
- * are created. String buffers support mutable strings.
- * Because String objects are immutable they can be shared. For example:
- * <blockquote><pre>
- * String str = "abc";
- * </pre></blockquote><p>
- * is equivalent to:
- * <blockquote><pre>
- * char data[] = {'a', 'b', 'c'};
- * String str = new String(data);
- * </pre></blockquote><p>
- * Here are some more examples of how strings can be used:
- * <blockquote><pre>
- * System.out.println("abc");
- * String cde = "cde";
- * System.out.println("abc" + cde);
- * String c = "abc".substring(2,3);
- * String d = cde.substring(1, 2);
- * </pre></blockquote>
- * <p>
- * The class {@code String} includes methods for examining
- * individual characters of the sequence, for comparing strings, for
- * searching strings, for extracting substrings, and for creating a
- * copy of a string with all characters translated to uppercase or to
- * lowercase. Case mapping is based on the Unicode Standard version
- * specified by the {@link java.lang.Character Character} class.
- * <p>
- * The Java language provides special support for the string
- * concatenation operator ( + ), and for conversion of
- * other objects to strings. String concatenation is implemented
- * through the {@code StringBuilder}(or {@code StringBuffer})
- * class and its {@code append} method.
- * String conversions are implemented through the method
- * {@code toString}, defined by {@code Object} and
- * inherited by all classes in Java. For additional information on
- * string concatenation and conversion, see Gosling, Joy, and Steele,
- * <i>The Java Language Specification</i>.
- *
- * <p> Unless otherwise noted, passing a <tt>null</tt> argument to a constructor
- * or method in this class will cause a {@link NullPointerException} to be
- * thrown.
- *
- * <p>A {@code String} represents a string in the UTF-16 format
- * in which <em>supplementary characters</em> are represented by <em>surrogate
- * pairs</em> (see the section <a href="Character.html#unicode">Unicode
- * Character Representations</a> in the {@code Character} class for
- * more information).
- * Index values refer to {@code char} code units, so a supplementary
- * character uses two positions in a {@code String}.
- * <p>The {@code String} class provides methods for dealing with
- * Unicode code points (i.e., characters), in addition to those for
- * dealing with Unicode code units (i.e., {@code char} values).
- *
- * @author Lee Boynton
- * @author Arthur van Hoff
- * @author Martin Buchholz
- * @author Ulf Zibis
- * @see java.lang.Object#toString()
- * @see java.lang.StringBuffer
- * @see java.lang.StringBuilder
- * @see java.nio.charset.Charset
- * @since JDK1.0
- */
- public final class String
- implements java.io.Serializable, Comparable<String>, CharSequence {
- /** The value is used for character storage. */
- private final char value[];
- /** Cache the hash code for the string */
- private int hash; // Default to 0
- /** use serialVersionUID from JDK 1.0.2 for interoperability */
- private static final long serialVersionUID = -6849794470754667710L;
- /**
- * Class String is special cased within the Serialization Stream Protocol.
- *
- * A String instance is written into an ObjectOutputStream according to
- * <a href="{@docRoot}/../platform/serialization/spec/output.html">
- * Object Serialization Specification, Section 6.2, "Stream Elements"</a>
- */
- private static final ObjectStreamField[] serialPersistentFields =
- new ObjectStreamField[0];
- /**
- * Initializes a newly created {@code String} object so that it represents
- * an empty character sequence. Note that use of this constructor is
- * unnecessary since Strings are immutable.
- */
- public String() {
- this.value = "".value;
- }
- /**
- * Initializes a newly created {@code String} object so that it represents
- * the same sequence of characters as the argument; in other words, the
- * newly created string is a copy of the argument string. Unless an
- * explicit copy of {@code original} is needed, use of this constructor is
- * unnecessary since Strings are immutable.
- *
- * @param original
- * A {@code String}
- */
- public String(String original) {
- this.value = original.value;
- this.hash = original.hash;
- }
- /**
- * Allocates a new {@code String} so that it represents the sequence of
- * characters currently contained in the character array argument. The
- * contents of the character array are copied; subsequent modification of
- * the character array does not affect the newly created string.
- *
- * @param value
- * The initial value of the string
- */
- public String(char value[]) {
- this.value = Arrays.copyOf(value, value.length);
- }
- /**
- * Allocates a new {@code String} that contains characters from a subarray
- * of the character array argument. The {@code offset} argument is the
- * index of the first character of the subarray and the {@code count}
- * argument specifies the length of the subarray. The contents of the
- * subarray are copied; subsequent modification of the character array does
- * not affect the newly created string.
- *
- * @param value
- * Array that is the source of characters
- *
- * @param offset
- * The initial offset
- *
- * @param count
- * The length
- *
- * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException
- * If the {@code offset} and {@code count} arguments index
- * characters outside the bounds of the {@code value} array
- */
- public String(char value[], int offset, int count) {
- if (offset < 0) {
- throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset);
- }
- if (count <= 0) {
- if (count < 0) {
- throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(count);
- }
- if (offset <= value.length) {
- this.value = "".value;
- return;
- }
- }
- // Note: offset or count might be near -1>>>1.
- if (offset > value.length - count) {
- throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset + count);
- }
- this.value = Arrays.copyOfRange(value, offset, offset+count);
- }
- /**
- * Allocates a new {@code String} that contains characters from a subarray
- * of the <a href="Character.html#unicode">Unicode code point</a> array
- * argument. The {@code offset} argument is the index of the first code
- * point of the subarray and the {@code count} argument specifies the
- * length of the subarray. The contents of the subarray are converted to
- * {@code char}s; subsequent modification of the {@code int} array does not
- * affect the newly created string.
- *
- * @param codePoints
- * Array that is the source of Unicode code points
- *
- * @param offset
- * The initial offset
- *
- * @param count
- * The length
- *
- * @throws IllegalArgumentException
- * If any invalid Unicode code point is found in {@code
- * codePoints}
- *
- * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException
- * If the {@code offset} and {@code count} arguments index
- * characters outside the bounds of the {@code codePoints} array
- *
- * @since 1.5
- */
- public String(int[] codePoints, int offset, int count) {
- if (offset < 0) {
- throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset);
- }
- if (count <= 0) {
- if (count < 0) {
- throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(count);
- }
- if (offset <= codePoints.length) {
- this.value = "".value;
- return;
- }
- }
- // Note: offset or count might be near -1>>>1.
- if (offset > codePoints.length - count) {
- throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset + count);
- }
- final int end = offset + count;
- // Pass 1: Compute precise size of char[]
- int n = count;
- for (int i = offset; i < end; i++) {
- int c = codePoints[i];
- if (Character.isBmpCodePoint(c))
- continue;
- else if (Character.isValidCodePoint(c))
- n++;
- else throw new IllegalArgumentException(Integer.toString(c));
- }
- // Pass 2: Allocate and fill in char[]
- final char[] v = new char[n];
- for (int i = offset, j = 0; i < end; i++, j++) {
- int c = codePoints[i];
- if (Character.isBmpCodePoint(c))
- v[j] = (char)c;
- else
- Character.toSurrogates(c, v, j++);
- }
- this.value = v;
- }
- /**
- * Allocates a new {@code String} constructed from a subarray of an array
- * of 8-bit integer values.
- *
- * <p> The {@code offset} argument is the index of the first byte of the
- * subarray, and the {@code count} argument specifies the length of the
- * subarray.
- *
- * <p> Each {@code byte} in the subarray is converted to a {@code char} as
- * specified in the method above.
- *
- * @deprecated This method does not properly convert bytes into characters.
- * As of JDK 1.1, the preferred way to do this is via the
- * {@code String} constructors that take a {@link
- * java.nio.charset.Charset}, charset name, or that use the platform's
- * default charset.
- *
- * @param ascii
- * The bytes to be converted to characters
- *
- * @param hibyte
- * The top 8 bits of each 16-bit Unicode code unit
- *
- * @param offset
- * The initial offset
- * @param count
- * The length
- *
- * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException
- * If the {@code offset} or {@code count} argument is invalid
- *
- * @see #String(byte[], int)
- * @see #String(byte[], int, int, java.lang.String)
- * @see #String(byte[], int, int, java.nio.charset.Charset)
- * @see #String(byte[], int, int)
- * @see #String(byte[], java.lang.String)
- * @see #String(byte[], java.nio.charset.Charset)
- * @see #String(byte[])
- */
- @Deprecated
- public String(byte ascii[], int hibyte, int offset, int count) {
- checkBounds(ascii, offset, count);
- char value[] = new char[count];
- if (hibyte == 0) {
- for (int i = count; i-- > 0;) {
- value[i] = (char)(ascii[i + offset] & 0xff);
- }
- } else {
- hibyte <<= 8;
- for (int i = count; i-- > 0;) {
- value[i] = (char)(hibyte | (ascii[i + offset] & 0xff));
- }
- }
- this.value = value;
- }
- /**
- * Allocates a new {@code String} containing characters constructed from
- * an array of 8-bit integer values. Each character <i>c</i>in the
- * resulting string is constructed from the corresponding component
- * <i>b</i> in the byte array such that:
- *
- * <blockquote><pre>
- * <b><i>c</i></b> == (char)(((hibyte & 0xff) << 8)
- * | (<b><i>b</i></b> & 0xff))
- * </pre></blockquote>
- *
- * @deprecated This method does not properly convert bytes into
- * characters. As of JDK 1.1, the preferred way to do this is via the
- * {@code String} constructors that take a {@link
- * java.nio.charset.Charset}, charset name, or that use the platform's
- * default charset.
- *
- * @param ascii
- * The bytes to be converted to characters
- *
- * @param hibyte
- * The top 8 bits of each 16-bit Unicode code unit
- *
- * @see #String(byte[], int, int, java.lang.String)
- * @see #String(byte[], int, int, java.nio.charset.Charset)
- * @see #String(byte[], int, int)
- * @see #String(byte[], java.lang.String)
- * @see #String(byte[], java.nio.charset.Charset)
- * @see #String(byte[])
- */
- @Deprecated
- public String(byte ascii[], int hibyte) {
- this(ascii, hibyte, 0, ascii.length);
- }
- /* Common private utility method used to bounds check the byte array
- * and requested offset & length values used by the String(byte[],..)
- * constructors.
- */
- private static void checkBounds(byte[] bytes, int offset, int length) {
- if (length < 0)
- throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(length);
- if (offset < 0)
- throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset);
- if (offset > bytes.length - length)
- throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset + length);
- }
- /**
- * Constructs a new {@code String} by decoding the specified subarray of
- * bytes using the specified charset. The length of the new {@code String}
- * is a function of the charset, and hence may not be equal to the length
- * of the subarray.
- *
- * <p> The behavior of this constructor when the given bytes are not valid
- * in the given charset is unspecified. The {@link
- * java.nio.charset.CharsetDecoder} class should be used when more control
- * over the decoding process is required.
- *
- * @param bytes
- * The bytes to be decoded into characters
- *
- * @param offset
- * The index of the first byte to decode
- *
- * @param length
- * The number of bytes to decode
- * @param charsetName
- * The name of a supported {@linkplain java.nio.charset.Charset
- * charset}
- *
- * @throws UnsupportedEncodingException
- * If the named charset is not supported
- *
- * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException
- * If the {@code offset} and {@code length} arguments index
- * characters outside the bounds of the {@code bytes} array
- *
- * @since JDK1.1
- */
- public String(byte bytes[], int offset, int length, String charsetName)
- throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
- if (charsetName == null)
- throw new NullPointerException("charsetName");
- checkBounds(bytes, offset, length);
- this.value = StringCoding.decode(charsetName, bytes, offset, length);
- }
- /**
- * Constructs a new {@code String} by decoding the specified subarray of
- * bytes using the specified {@linkplain java.nio.charset.Charset charset}.
- * The length of the new {@code String} is a function of the charset, and
- * hence may not be equal to the length of the subarray.
- *
- * <p> This method always replaces malformed-input and unmappable-character
- * sequences with this charset's default replacement string. The {@link
- * java.nio.charset.CharsetDecoder} class should be used when more control
- * over the decoding process is required.
- *
- * @param bytes
- * The bytes to be decoded into characters
- *
- * @param offset
- * The index of the first byte to decode
- *
- * @param length
- * The number of bytes to decode
- *
- * @param charset
- * The {@linkplain java.nio.charset.Charset charset} to be used to
- * decode the {@code bytes}
- *
- * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException
- * If the {@code offset} and {@code length} arguments index
- * characters outside the bounds of the {@code bytes} array
- *
- * @since 1.6
- */
- public String(byte bytes[], int offset, int length, Charset charset) {
- if (charset == null)
- throw new NullPointerException("charset");
- checkBounds(bytes, offset, length);
- this.value = StringCoding.decode(charset, bytes, offset, length);
- }
- /**
- * Constructs a new {@code String} by decoding the specified array of bytes
- * using the specified {@linkplain java.nio.charset.Charset charset}. The
- * length of the new {@code String} is a function of the charset, and hence
- * may not be equal to the length of the byte array.
- *
- * <p> The behavior of this constructor when the given bytes are not valid
- * in the given charset is unspecified. The {@link
- * java.nio.charset.CharsetDecoder} class should be used when more control
- * over the decoding process is required.
- *
- * @param bytes
- * The bytes to be decoded into characters
- *
- * @param charsetName
- * The name of a supported {@linkplain java.nio.charset.Charset
- * charset}
- *
- * @throws UnsupportedEncodingException
- * If the named charset is not supported
- *
- * @since JDK1.1
- */
- public String(byte bytes[], String charsetName)
- throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
- this(bytes, 0, bytes.length, charsetName);
- }
- /**
- * Constructs a new {@code String} by decoding the specified array of
- * bytes using the specified {@linkplain java.nio.charset.Charset charset}.
- * The length of the new {@code String} is a function of the charset, and
- * hence may not be equal to the length of the byte array.
- *
- * <p> This method always replaces malformed-input and unmappable-character
- * sequences with this charset's default replacement string. The {@link
- * java.nio.charset.CharsetDecoder} class should be used when more control
- * over the decoding process is required.
- *
- * @param bytes
- * The bytes to be decoded into characters
- *
- * @param charset
- * The {@linkplain java.nio.charset.Charset charset} to be used to
- * decode the {@code bytes}
- *
- * @since 1.6
- */
- public String(byte bytes[], Charset charset) {
- this(bytes, 0, bytes.length, charset);
- }
- /**
- * Constructs a new {@code String} by decoding the specified subarray of
- * bytes using the platform's default charset. The length of the new
- * {@code String} is a function of the charset, and hence may not be equal
- * to the length of the subarray.
- *
- * <p> The behavior of this constructor when the given bytes are not valid
- * in the default charset is unspecified. The {@link
- * java.nio.charset.CharsetDecoder} class should be used when more control
- * over the decoding process is required.
- *
- * @param bytes
- * The bytes to be decoded into characters
- *
- * @param offset
- * The index of the first byte to decode
- *
- * @param length
- * The number of bytes to decode
- *
- * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException
- * If the {@code offset} and the {@code length} arguments index
- * characters outside the bounds of the {@code bytes} array
- *
- * @since JDK1.1
- */
- public String(byte bytes[], int offset, int length) {
- checkBounds(bytes, offset, length);
- this.value = StringCoding.decode(bytes, offset, length);
- }
- /**
- * Constructs a new {@code String} by decoding the specified array of bytes
- * using the platform's default charset. The length of the new {@code
- * String} is a function of the charset, and hence may not be equal to the
- * length of the byte array.
- *
- * <p> The behavior of this constructor when the given bytes are not valid
- * in the default charset is unspecified. The {@link
- * java.nio.charset.CharsetDecoder} class should be used when more control
- * over the decoding process is required.
- *
- * @param bytes
- * The bytes to be decoded into characters
- *
- * @since JDK1.1
- */
- public String(byte bytes[]) {
- this(bytes, 0, bytes.length);
- }
- /**
- * Allocates a new string that contains the sequence of characters
- * currently contained in the string buffer argument. The contents of the
- * string buffer are copied; subsequent modification of the string buffer
- * does not affect the newly created string.
- *
- * @param buffer
- * A {@code StringBuffer}
- */
- public String(StringBuffer buffer) {
- synchronized(buffer) {
- this.value = Arrays.copyOf(buffer.getValue(), buffer.length());
- }
- }
- /**
- * Allocates a new string that contains the sequence of characters
- * currently contained in the string builder argument. The contents of the
- * string builder are copied; subsequent modification of the string builder
- * does not affect the newly created string.
- *
- * <p> This constructor is provided to ease migration to {@code
- * StringBuilder}. Obtaining a string from a string builder via the {@code
- * toString} method is likely to run faster and is generally preferred.
- *
- * @param builder
- * A {@code StringBuilder}
- *
- * @since 1.5
- */
- public String(StringBuilder builder) {
- this.value = Arrays.copyOf(builder.getValue(), builder.length());
- }
- /*
- * Package private constructor which shares value array for speed.
- * this constructor is always expected to be called with share==true.
- * a separate constructor is needed because we already have a public
- * String(char[]) constructor that makes a copy of the given char[].
- */
- String(char[] value, boolean share) {
- // assert share : "unshared not supported";
- this.value = value;
- }
- /**
- * Returns the length of this string.
- * The length is equal to the number of <a href="Character.html#unicode">Unicode
- * code units</a> in the string.
- *
- * @return the length of the sequence of characters represented by this
- * object.
- */
- public int length() {
- return value.length;
- }
- /**
- * Returns {@code true} if, and only if, {@link #length()} is {@code 0}.
- *
- * @return {@code true} if {@link #length()} is {@code 0}, otherwise
- * {@code false}
- *
- * @since 1.6
- */
- public boolean isEmpty() {
- return value.length == 0;
- }
- /**
- * Returns the {@code char} value at the
- * specified index. An index ranges from {@code 0} to
- * {@code length() - 1}. The first {@code char} value of the sequence
- * is at index {@code 0}, the next at index {@code 1},
- * and so on, as for array indexing.
- *
- * <p>If the {@code char} value specified by the index is a
- * <a href="Character.html#unicode">surrogate</a>, the surrogate
- * value is returned.
- *
- * @param index the index of the {@code char} value.
- * @return the {@code char} value at the specified index of this string.
- * The first {@code char} value is at index {@code 0}.
- * @exception IndexOutOfBoundsException if the {@code index}
- * argument is negative or not less than the length of this
- * string.
- */
- public char charAt(int index) {
- if ((index < 0) || (index >= value.length)) {
- throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
- }
- return value[index];
- }
- /**
- * Returns the character (Unicode code point) at the specified
- * index. The index refers to {@code char} values
- * (Unicode code units) and ranges from {@code 0} to
- * {@link #length()}{@code - 1}.
- *
- * <p> If the {@code char} value specified at the given index
- * is in the high-surrogate range, the following index is less
- * than the length of this {@code String}, and the
- * {@code char} value at the following index is in the
- * low-surrogate range, then the supplementary code point
- * corresponding to this surrogate pair is returned. Otherwise,
- * the {@code char} value at the given index is returned.
- *
- * @param index the index to the {@code char} values
- * @return the code point value of the character at the
- * {@code index}
- * @exception IndexOutOfBoundsException if the {@code index}
- * argument is negative or not less than the length of this
- * string.
- * @since 1.5
- */
- public int codePointAt(int index) {
- if ((index < 0) || (index >= value.length)) {
- throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
- }
- return Character.codePointAtImpl(value, index, value.length);
- }
- /**
- * Returns the character (Unicode code point) before the specified
- * index. The index refers to {@code char} values
- * (Unicode code units) and ranges from {@code 1} to {@link
- * CharSequence#length() length}.
- *
- * <p> If the {@code char} value at {@code (index - 1)}
- * is in the low-surrogate range, {@code (index - 2)} is not
- * negative, and the {@code char} value at {@code (index -
- * 2)} is in the high-surrogate range, then the
- * supplementary code point value of the surrogate pair is
- * returned. If the {@code char} value at {@code index -
- * 1} is an unpaired low-surrogate or a high-surrogate, the
- * surrogate value is returned.
- *
- * @param index the index following the code point that should be returned
- * @return the Unicode code point value before the given index.
- * @exception IndexOutOfBoundsException if the {@code index}
- * argument is less than 1 or greater than the length
- * of this string.
- * @since 1.5
- */
- public int codePointBefore(int index) {
- int i = index - 1;
- if ((i < 0) || (i >= value.length)) {
- throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
- }
- return Character.codePointBeforeImpl(value, index, 0);
- }
- /**
- * Returns the number of Unicode code points in the specified text
- * range of this {@code String}. The text range begins at the
- * specified {@code beginIndex} and extends to the
- * {@code char} at index {@code endIndex - 1}. Thus the
- * length (in {@code char}s) of the text range is
- * {@code endIndex-beginIndex}. Unpaired surrogates within
- * the text range count as one code point each.
- *
- * @param beginIndex the index to the first {@code char} of
- * the text range.
- * @param endIndex the index after the last {@code char} of
- * the text range.
- * @return the number of Unicode code points in the specified text
- * range
- * @exception IndexOutOfBoundsException if the
- * {@code beginIndex} is negative, or {@code endIndex}
- * is larger than the length of this {@code String}, or
- * {@code beginIndex} is larger than {@code endIndex}.
- * @since 1.5
- */
- public int codePointCount(int beginIndex, int endIndex) {
- if (beginIndex < 0 || endIndex > value.length || beginIndex > endIndex) {
- throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
- }
- return Character.codePointCountImpl(value, beginIndex, endIndex - beginIndex);
- }
- /**
- * Returns the index within this {@code String} that is
- * offset from the given {@code index} by
- * {@code codePointOffset} code points. Unpaired surrogates
- * within the text range given by {@code index} and
- * {@code codePointOffset} count as one code point each.
- *
- * @param index the index to be offset
- * @param codePointOffset the offset in code points
- * @return the index within this {@code String}
- * @exception IndexOutOfBoundsException if {@code index}
- * is negative or larger then the length of this
- * {@code String}, or if {@code codePointOffset} is positive
- * and the substring starting with {@code index} has fewer
- * than {@code codePointOffset} code points,
- * or if {@code codePointOffset} is negative and the substring
- * before {@code index} has fewer than the absolute value
- * of {@code codePointOffset} code points.
- * @since 1.5
- */
- public int offsetByCodePoints(int index, int codePointOffset) {
- if (index < 0 || index > value.length) {
- throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
- }
- return Character.offsetByCodePointsImpl(value, 0, value.length,
- index, codePointOffset);
- }
- /**
- * Copy characters from this string into dst starting at dstBegin.
- * This method doesn't perform any range checking.
- */
- void getChars(char dst[], int dstBegin) {
- System.arraycopy(value, 0, dst, dstBegin, value.length);
- }
- /**
- * Copies characters from this string into the destination character
- * array.
- * <p>
- * The first character to be copied is at index {@code srcBegin};
- * the last character to be copied is at index {@code srcEnd-1}
- * (thus the total number of characters to be copied is
- * {@code srcEnd-srcBegin}). The characters are copied into the
- * subarray of {@code dst} starting at index {@code dstBegin}
- * and ending at index:
- * <blockquote><pre>
- * dstBegin + (srcEnd-srcBegin) - 1
- * </pre></blockquote>
- *
- * @param srcBegin index of the first character in the string
- * to copy.
- * @param srcEnd index after the last character in the string
- * to copy.
- * @param dst the destination array.
- * @param dstBegin the start offset in the destination array.
- * @exception IndexOutOfBoundsException If any of the following
- * is true:
- * <ul><li>{@code srcBegin} is negative.
- * <li>{@code srcBegin} is greater than {@code srcEnd}
- * <li>{@code srcEnd} is greater than the length of this
- * string
- * <li>{@code dstBegin} is negative
- * <li>{@code dstBegin+(srcEnd-srcBegin)} is larger than
- * {@code dst.length}</ul>
- */
- public void getChars(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, char dst[], int dstBegin) {
- if (srcBegin < 0) {
- throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(srcBegin);
- }
- if (srcEnd > value.length) {
- throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(srcEnd);
- }
- if (srcBegin > srcEnd) {
- throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(srcEnd - srcBegin);
- }
- System.arraycopy(value, srcBegin, dst, dstBegin, srcEnd - srcBegin);
- }
- /**
- * Copies characters from this string into the destination byte array. Each
- * byte receives the 8 low-order bits of the corresponding character. The
- * eight high-order bits of each character are not copied and do not
- * participate in the transfer in any way.
- *
- * <p> The first character to be copied is at index {@code srcBegin}; the
- * last character to be copied is at index {@code srcEnd-1}. The total
- * number of characters to be copied is {@code srcEnd-srcBegin}. The
- * characters, converted to bytes, are copied into the subarray of {@code
- * dst} starting at index {@code dstBegin} and ending at index:
- *
- * <blockquote><pre>
- * dstBegin + (srcEnd-srcBegin) - 1
- * </pre></blockquote>
- *
- * @deprecated This method does not properly convert characters into
- * bytes. As of JDK 1.1, the preferred way to do this is via the
- * {@link #getBytes()} method, which uses the platform's default charset.
- *
- * @param srcBegin
- * Index of the first character in the string to copy
- *
- * @param srcEnd
- * Index after the last character in the string to copy
- *
- * @param dst
- * The destination array
- *
- * @param dstBegin
- * The start offset in the destination array
- *
- * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException
- * If any of the following is true:
- * <ul>
- * <li> {@code srcBegin} is negative
- * <li> {@code srcBegin} is greater than {@code srcEnd}
- * <li> {@code srcEnd} is greater than the length of this String
- * <li> {@code dstBegin} is negative
- * <li> {@code dstBegin+(srcEnd-srcBegin)} is larger than {@code
- * dst.length}
- * </ul>
- */
- @Deprecated
- public void getBytes(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, byte dst[], int dstBegin) {
- if (srcBegin < 0) {
- throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(srcBegin);
- }
- if (srcEnd > value.length) {
- throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(srcEnd);
- }
- if (srcBegin > srcEnd) {
- throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(srcEnd - srcBegin);
- }
- Objects.requireNonNull(dst);
- int j = dstBegin;
- int n = srcEnd;
- int i = srcBegin;
- char[] val = value; /* avoid getfield opcode */
- while (i < n) {
- dst[j++] = (byte)val[i++];
- }
- }
- /**
- * Encodes this {@code String} into a sequence of bytes using the named
- * charset, storing the result into a new byte array.
- *
- * <p> The behavior of this method when this string cannot be encoded in
- * the given charset is unspecified. The {@link
- * java.nio.charset.CharsetEncoder} class should be used when more control
- * over the encoding process is required.
- *
- * @param charsetName
- * The name of a supported {@linkplain java.nio.charset.Charset
- * charset}
- *
- * @return The resultant byte array
- *
- * @throws UnsupportedEncodingException
- * If the named charset is not supported
- *
- * @since JDK1.1
- */
- public byte[] getBytes(String charsetName)
- throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
- if (charsetName == null) throw new NullPointerException();
- return StringCoding.encode(charsetName, value, 0, value.length);
- }
- /**
- * Encodes this {@code String} into a sequence of bytes using the given
- * {@linkplain java.nio.charset.Charset charset}, storing the result into a
- * new byte array.
- *
- * <p> This method always replaces malformed-input and unmappable-character
- * sequences with this charset's default replacement byte array. The
- * {@link java.nio.charset.CharsetEncoder} class should be used when more
- * control over the encoding process is required.
- *
- * @param charset
- * The {@linkplain java.nio.charset.Charset} to be used to encode
- * the {@code String}
- *
- * @return The resultant byte array
- *
- * @since 1.6
- */
- public byte[] getBytes(Charset charset) {
- if (charset == null) throw new NullPointerException();
- return StringCoding.encode(charset, value, 0, value.length);
- }
- /**
- * Encodes this {@code String} into a sequence of bytes using the
- * platform's default charset, storing the result into a new byte array.
- *
- * <p> The behavior of this method when this string cannot be encoded in
- * the default charset is unspecified. The {@link
- * java.nio.charset.CharsetEncoder} class should be used when more control
- * over the encoding process is required.
- *
- * @return The resultant byte array
- *
- * @since JDK1.1
- */
- public byte[] getBytes() {
- return StringCoding.encode(value, 0, value.length);
- }
- /**
- * Compares this string to the specified object. The result is {@code
- * true} if and only if the argument is not {@code null} and is a {@code
- * String} object that represents the same sequence of characters as this
- * object.
- *
- * @param anObject
- * The object to compare this {@code String} against
- *
- * @return {@code true} if the given object represents a {@code String}
- * equivalent to this string, {@code false} otherwise
- *
- * @see #compareTo(String)
- * @see #equalsIgnoreCase(String)
- */
- public boolean equals(Object anObject) {
- if (this == anObject) {
- return true;
- }
- if (anObject instanceof String) {
- String anotherString = (String)anObject;
- int n = value.length;
- if (n == anotherString.value.length) {
- char v1[] = value;
- char v2[] = anotherString.value;
- int i = 0;
- while (n-- != 0) {
- if (v1[i] != v2[i])
- return false;
- i++;
- }
- return true;
- }
- }
- return false;
- }
- /**
- * Compares this string to the specified {@code StringBuffer}. The result
- * is {@code true} if and only if this {@code String} represents the same
- * sequence of characters as the specified {@code StringBuffer}. This method
- * synchronizes on the {@code StringBuffer}.
- *
- * @param sb
- * The {@code StringBuffer} to compare this {@code String} against
- *
- * @return {@code true} if this {@code String} represents the same
- * sequence of characters as the specified {@code StringBuffer},
- * {@code false} otherwise
- *
- * @since 1.4
- */
- public boolean contentEquals(StringBuffer sb) {
- return contentEquals((CharSequence)sb);
- }
- private boolean nonSyncContentEquals(AbstractStringBuilder sb) {
- char v1[] = value;
- char v2[] = sb.getValue();
- int n = v1.length;
- if (n != sb.length()) {
- return false;
- }
- for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
- if (v1[i] != v2[i]) {
- return false;
- }
- }
- return true;
- }
- /**
- * Compares this string to the specified {@code CharSequence}. The
- * result is {@code true} if and only if this {@code String} represents the
- * same sequence of char values as the specified sequence. Note that if the
- * {@code CharSequence} is a {@code StringBuffer} then the method
- * synchronizes on it.
- *
- * @param cs
- * The sequence to compare this {@code String} against
- *
- * @return {@code true} if this {@code String} represents the same
- * sequence of char values as the specified sequence, {@code
- * false} otherwise
- *
- * @since 1.5
- */
- public boolean contentEquals(CharSequence cs) {
- // Argument is a StringBuffer, StringBuilder
- if (cs instanceof AbstractStringBuilder) {
- if (cs instanceof StringBuffer) {
- synchronized(cs) {
- return nonSyncContentEquals((AbstractStringBuilder)cs);
- }
- } else {
- return nonSyncContentEquals((AbstractStringBuilder)cs);
- }
- }
- // Argument is a String
- if (cs instanceof String) {
- return equals(cs);
- }
- // Argument is a generic CharSequence
- char v1[] = value;
- int n = v1.length;
- if (n != cs.length()) {
- return false;
- }
- for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
- if (v1[i] != cs.charAt(i)) {
- return false;
- }
- }
- return true;
- }
- /**
- * Compares this {@code String} to another {@code String}, ignoring case
- * considerations. Two strings are considered equal ignoring case if they
- * are of the same length and corresponding characters in the two strings
- * are equal ignoring case.
- *
- * <p> Two characters {@code c1} and {@code c2} are considered the same
- * ignoring case if at least one of the following is true:
- * <ul>
- * <li> The two characters are the same (as compared by the
- * {@code ==} operator)
- * <li> Applying the method {@link
- * java.lang.Character#toUpperCase(char)} to each character
- * produces the same result
- * <li> Applying the method {@link
- * java.lang.Character#toLowerCase(char)} to each character
- * produces the same result
- * </ul>
- *
- * @param anotherString
- * The {@code String} to compare this {@code String} against
- *
- * @return {@code true} if the argument is not {@code null} and it
- * represents an equivalent {@code String} ignoring case; {@code
- * false} otherwise
- *
- * @see #equals(Object)
- */
- public boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString) {
- return (this == anotherString) ? true
- : (anotherString != null)
- && (anotherString.value.length == value.length)
- && regionMatches(true, 0, anotherString, 0, value.length);
- }
- /**
- * Compares two strings lexicographically.
- * The comparison is based on the Unicode value of each character in
- * the strings. The character sequence represented by this
- * {@code String} object is compared lexicographically to the
- * character sequence represented by the argument string. The result is
- * a negative integer if this {@code String} object
- * lexicographically precedes the argument string. The result is a
- * positive integer if this {@code String} object lexicographically
- * follows the argument string. The result is zero if the strings
- * are equal; {@code compareTo} returns {@code 0} exactly when
- * the {@link #equals(Object)} method would return {@code true}.
- * <p>
- * This is the definition of lexicographic ordering. If two strings are
- * different, then either they have different characters at some index
- * that is a valid index for both strings, or their lengths are different,
- * or both. If they have different characters at one or more index
- * positions, let <i>k</i> be the smallest such index; then the string
- * whose character at position <i>k</i> has the smaller value, as
- * determined by using the < operator, lexicographically precedes the
- * other string. In this case, {@code compareTo} returns the
- * difference of the two character values at position {@code k} in
- * the two string -- that is, the value:
- * <blockquote><pre>
- * this.charAt(k)-anotherString.charAt(k)
- * </pre></blockquote>
- * If there is no index position at which they differ, then the shorter
- * string lexicographically precedes the longer string. In this case,
- * {@code compareTo} returns the difference of the lengths of the
- * strings -- that is, the value:
- * <blockquote><pre>
- * this.length()-anotherString.length()
- * </pre></blockquote>
- *
- * @param anotherString the {@code String} to be compared.
- * @return the value {@code 0} if the argument string is equal to
- * this string; a value less than {@code 0} if this string
- * is lexicographically less than the string argument; and a
- * value greater than {@code 0} if this string is
- * lexicographically greater than the string argument.
- */
- public int compareTo(String anotherString) {
- int len1 = value.length;
- int len2 = anotherString.value.length;
- int lim = Math.min(len1, len2);
- char v1[] = value;
- char v2[] = anotherString.value;
- int k = 0;
- while (k < lim) {
- char c1 = v1[k];
- char c2 = v2[k];
- if (c1 != c2) {
- return c1 - c2;
- }
- k++;
- }
- return len1 - len2;
- }
- /**
- * A Comparator that orders {@code String} objects as by
- * {@code compareToIgnoreCase}. This comparator is serializable.
- * <p>
- * Note that this Comparator does <em>not</em> take locale into account,
- * and will result in an unsatisfactory ordering for certain locales.
- * The java.text package provides <em>Collators</em> to allow
- * locale-sensitive ordering.
- *
- * @see java.text.Collator#compare(String, String)
- * @since 1.2
- */
- public static final Comparator<String> CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER
- = new CaseInsensitiveComparator();
- private static class CaseInsensitiveComparator
- implements Comparator<String>, java.io.Serializable {
- // use serialVersionUID from JDK 1.2.2 for interoperability
- private static final long serialVersionUID = 8575799808933029326L;
- public int compare(String s1, String s2) {
- int n1 = s1.length();
- int n2 = s2.length();
- int min = Math.min(n1, n2);
- for (int i = 0; i < min; i++) {
- char c1 = s1.charAt(i);
- char c2 = s2.charAt(i);
- if (c1 != c2) {
- c1 = Character.toUpperCase(c1);
- c2 = Character.toUpperCase(c2);
- if (c1 != c2) {
- c1 = Character.toLowerCase(c1);
- c2 = Character.toLowerCase(c2);
- if (c1 != c2) {
- // No overflow because of numeric promotion
- return c1 - c2;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- return n1 - n2;
- }
- /** Replaces the de-serialized object. */
- private Object readResolve() { return CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER; }
- }
- /**
- * Compares two strings lexicographically, ignoring case
- * differences. This method returns an integer whose sign is that of
- * calling {@code compareTo} with normalized versions of the strings
- * where case differences have been eliminated by calling
- * {@code Character.toLowerCase(Character.toUpperCase(character))} on
- * each character.
- * <p>
- * Note that this method does <em>not</em> take locale into account,
- * and will result in an unsatisfactory ordering for certain locales.
- * The java.text package provides <em>collators</em> to allow
- * locale-sensitive ordering.
- *
- * @param str the {@code String} to be compared.
- * @return a negative integer, zero, or a positive integer as the
- * specified String is greater than, equal to, or less
- * than this String, ignoring case considerations.
- * @see java.text.Collator#compare(String, String)
- * @since 1.2
- */
- public int compareToIgnoreCase(String str) {
- return CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER.compare(this, str);
- }
- /**
- * Tests if two string regions are equal.
- * <p>
- * A substring of this {@code String} object is compared to a substring
- * of the argument other. The result is true if these substrings
- * represent identical character sequences. The substring of this
- * {@code String} object to be compared begins at index {@code toffset}
- * and has length {@code len}. The substring of other to be compared
- * begins at index {@code ooffset} and has length {@code len}. The
- * result is {@code false} if and only if at least one of the following
- * is true:
- * <ul><li>{@code toffset} is negative.
- * <li>{@code ooffset} is negative.
- * <li>{@code toffset+len} is greater than the length of this
- * {@code String} object.
- * <li>{@code ooffset+len} is greater than the length of the other
- * argument.
- * <li>There is some nonnegative integer <i>k</i> less than {@code len}
- * such that:
- * {@code this.charAt(toffset + }<i>k</i>{@code ) != other.charAt(ooffset + }
- * <i>k</i>{@code )}
- * </ul>
- *
- * @param toffset the starting offset of the subregion in this string.
- * @param other the string argument.
- * @param ooffset the starting offset of the subregion in the string
- * argument.
- * @param len the number of characters to compare.
- * @return {@code true} if the specified subregion of this string
- * exactly matches the specified subregion of the string argument;
- * {@code false} otherwise.
- */
- public boolean regionMatches(int toffset, String other, int ooffset,
- int len) {
- char ta[] = value;
- int to = toffset;
- char pa[] = other.value;
- int po = ooffset;
- // Note: toffset, ooffset, or len might be near -1>>>1.
- if ((ooffset < 0) || (toffset < 0)
- || (toffset > (long)value.length - len)
- || (ooffset > (long)other.value.length - len)) {
- return false;
- }
- while (len-- > 0) {
- if (ta[to++] != pa[po++]) {
- return false;
- }
- }
- return true;
- }
- /**
- * Tests if two string regions are equal.
- * <p>
- * A substring of this {@code String} object is compared to a substring
- * of the argument {@code other}. The result is {@code true} if these
- * substrings represent character sequences that are the same, ignoring
- * case if and only if {@code ignoreCase} is true. The substring of
- * this {@code String} object to be compared begins at index
- * {@code toffset} and has length {@code len}. The substring of
- * {@code other} to be compared begins at index {@code ooffset} and
- * has length {@code len}. The result is {@code false} if and only if
- * at least one of the following is true:
- * <ul><li>{@code toffset} is negative.
- * <li>{@code ooffset} is negative.
- * <li>{@code toffset+len} is greater than the length of this
- * {@code String} object.
- * <li>{@code ooffset+len} is greater than the length of the other
- * argument.
- * <li>{@code ignoreCase} is {@code false} and there is some nonnegative
- * integer <i>k</i> less than {@code len} such that:
- * <blockquote><pre>
- * this.charAt(toffset+k) != other.charAt(ooffset+k)
- * </pre></blockquote>
- * <li>{@code ignoreCase} is {@code true} and there is some nonnegative
- * integer <i>k</i> less than {@code len} such that:
- * <blockquote><pre>
- * Character.toLowerCase(this.charAt(toffset+k)) !=
- Character.toLowerCase(other.charAt(ooffset+k))
- * </pre></blockquote>
- * and:
- * <blockquote><pre>
- * Character.toUpperCase(this.charAt(toffset+k)) !=
- * Character.toUpperCase(other.charAt(ooffset+k))
- * </pre></blockquote>
- * </ul>
- *
- * @param ignoreCase if {@code true}, ignore case when comparing
- * characters.
- * @param toffset the starting offset of the subregion in this
- * string.
- * @param other the string argument.
- * @param ooffset the starting offset of the subregion in the string
- * argument.
- * @param len the number of characters to compare.
- * @return {@code true} if the specified subregion of this string
- * matches the specified subregion of the string argument;
- * {@code false} otherwise. Whether the matching is exact
- * or case insensitive depends on the {@code ignoreCase}
- * argument.
- */
- public boolean regionMatches(boolean ignoreCase, int toffset,
- String other, int ooffset, int len) {
- char ta[] = value;
- int to = toffset;
- char pa[] = other.value;
- int po = ooffset;
- // Note: toffset, ooffset, or len might be near -1>>>1.
- if ((ooffset < 0) || (toffset < 0)
- || (toffset > (long)value.length - len)
- || (ooffset > (long)other.value.length - len)) {
- return false;
- }
- while (len-- > 0) {
- char c1 = ta[to++];
- char c2 = pa[po++];
- if (c1 == c2) {
- continue;
- }
- if (ignoreCase) {
- // If characters don't match but case may be ignored,
- // try converting both characters to uppercase.
- // If the results match, then the comparison scan should
- // continue.
- char u1 = Character.toUpperCase(c1);
- char u2 = Character.toUpperCase(c2);
- if (u1 == u2) {
- continue;
- }
- // Unfortunately, conversion to uppercase does not work properly
- // for the Georgian alphabet, which has strange rules about case
- // conversion. So we need to make one last check before
- // exiting.
- if (Character.toLowerCase(u1) == Character.toLowerCase(u2)) {
- continue;
- }
- }
- return false;
- }
- return true;
- }
- /**
- * Tests if the substring of this string beginning at the
- * specified index starts with the specified prefix.
- *
- * @param prefix the prefix.
- * @param toffset where to begin looking in this string.
- * @return {@code true} if the character sequence represented by the
- * argument is a prefix of the substring of this object starting
- * at index {@code toffset}; {@code false} otherwise.
- * The result is {@code false} if {@code toffset} is
- * negative or greater than the length of this
- * {@code String} object; otherwise the result is the same
- * as the result of the expression
- * <pre>
- * this.substring(toffset).startsWith(prefix)
- * </pre>
- */
- public boolean startsWith(String prefix, int toffset) {
- char ta[] = value;
- int to = toffset;
- char pa[] = prefix.value;
- int po = 0;
- int pc = prefix.value.length;
- // Note: toffset might be near -1>>>1.
- if ((toffset < 0) || (toffset > value.length - pc)) {
- return false;
- }
- while (--pc >= 0) {
- if (ta[to++] != pa[po++]) {
- return false;
- }
- }
- return true;
- }
- /**
- * Tests if this string starts with the specified prefix.
- *
- * @param prefix the prefix.
- * @return {@code true} if the character sequence represented by the
- * argument is a prefix of the character sequence represented by
- * this string; {@code false} otherwise.
- * Note also that {@code true} will be returned if the
- * argument is an empty string or is equal to this
- * {@code String} object as determined by the
- * {@link #equals(Object)} method.
- * @since 1. 0
- */
- public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
- return startsWith(prefix, 0);
- }
- /**
- * Tests if this string ends with the specified suffix.
- *
- * @param suffix the suffix.
- * @return {@code true} if the character sequence represented by the
- * argument is a suffix of the character sequence represented by
- * this object; {@code false} otherwise. Note that the
- * result will be {@code true} if the argument is the
- * empty string or is equal to this {@code String} object
- * as determined by the {@link #equals(Object)} method.
- */
- public boolean endsWith(String suffix) {
- return startsWith(suffix, value.length - suffix.value.length);
- }
- /**
- * Returns a hash code for this string. The hash code for a
- * {@code String} object is computed as
- * <blockquote><pre>
- * s[0]*31^(n-1) + s[1]*31^(n-2) + ... + s[n-1]
- * </pre></blockquote>
- * using {@code int} arithmetic, where {@code s[i]} is the
- * <i>i</i>th character of the string, {@code n} is the length of
- * the string, and {@code ^} indicates exponentiation.
- * (The hash value of the empty string is zero.)
- *
- * @return a hash code value for this object.
- */
- public int hashCode() {
- int h = hash;
- if (h == 0 && value.length > 0) {
- char val[] = value;
- for (int i = 0; i < value.length; i++) {
- h = 31 * h + val[i];
- }
- hash = h;
- }
- return h;
- }
- /**
- * Returns the index within this string of the first occurrence of
- * the specified character. If a character with value
- * {@code ch} occurs in the character sequence represented by
- * this {@code String} object, then the index (in Unicode
- * code units) of the first such occurrence is returned. For
- * values of {@code ch} in the range from 0 to 0xFFFF
- * (inclusive), this is the smallest value <i>k</i> such that:
- * <blockquote><pre>
- * this.charAt(<i>k</i>) == ch
- * </pre></blockquote>
- * is true. For other values of {@code ch}, it is the
- * smallest value <i>k</i> such that:
- * <blockquote><pre>
- * this.codePointAt(<i>k</i>) == ch
- * </pre></blockquote>
- * is true. In either case, if no such character occurs in this
- * string, then {@code -1} is returned.
- *
- * @param ch a character (Unicode code point).
- * @return the index of the first occurrence of the character in the
- * character sequence represented by this object, or
- * {@code -1} if the character does not occur.
- */
- public int indexOf(int ch) {
- return indexOf(ch, 0);
- }
- /**
- * Returns the index within this string of the first occurrence of the
- * specified character, starting the search at the specified index.
- * <p>
- * If a character with value {@code ch} occurs in the
- * character sequence represented by this {@code String}
- * object at an index no smaller than {@code fromIndex}, then
- * the index of the first such occurrence is returned. For values
- * of {@code ch} in the range from 0 to 0xFFFF (inclusive),
- * this is the smallest value <i>k</i> such that:
- * <blockquote><pre>
- * (this.charAt(<i>k</i>) == ch) {@code &&} (<i>k</i> >= fromIndex)
- * </pre></blockquote>
- * is true. For other values of {@code ch}, it is the
- * smallest value <i>k</i> such that:
- * <blockquote><pre>
- * (this.codePointAt(<i>k</i>) == ch) {@code &&} (<i>k</i> >= fromIndex)
- * </pre></blockquote>
- * is true. In either case, if no such character occurs in this
- * string at or after position {@code fromIndex}, then
- * {@code -1} is returned.
- *
- * <p>
- * There is no restriction on the value of {@code fromIndex}. If it
- * is negative, it has the same effect as if it were zero: this entire
- * string may be searched. If it is greater than the length of this
- * string, it has the same effect as if it were equal to the length of
- * this string: {@code -1} is returned.
- *
- * <p>All indices are specified in {@code char} values
- * (Unicode code units).
- *
- * @param ch a character (Unicode code point).
- * @param fromIndex the index to start the search from.
- * @return the index of the first occurrence of the character in the
- * character sequence represented by this object that is greater
- * than or equal to {@code fromIndex}, or {@code -1}
- * if the character does not occur.
- */
- public int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) {
- final int max = value.length;
- if (fromIndex < 0) {
- fromIndex = 0;
- } else if (fromIndex >= max) {
- // Note: fromIndex might be near -1>>>1.
- return -1;
- }
- if (ch < Character.MIN_SUPPLEMENTARY_CODE_POINT) {
- // handle most cases here (ch is a BMP code point or a
- // negative value (invalid code point))
- final char[] value = this.value;
- for (int i = fromIndex; i < max; i++) {
- if (value[i] == ch) {
- return i;
- }
- }
- return -1;
- } else {
- return indexOfSupplementary(ch, fromIndex);
- }
- }
- /**
- * Handles (rare) calls of indexOf with a supplementary character.
- */
- private int indexOfSupplementary(int ch, int fromIndex) {
- if (Character.isValidCodePoint(ch)) {
- final char[] value = this.value;
- final char hi = Character.highSurrogate(ch);
- final char lo = Character.lowSurrogate(ch);
- final int max = value.length - 1;
- for (int i = fromIndex; i < max; i++) {
- if (value[i] == hi && value[i + 1] == lo) {
- return i;
- }
- }
- }
- return -1;
- }
- /**
- * Returns the index within this string of the last occurrence of
- * the specified character. For values of {@code ch} in the
- * range from 0 to 0xFFFF (inclusive), the index (in Unicode code
- * units) returned is the largest value <i>k</i> such that:
- * <blockquote><pre>
- * this.charAt(<i>k</i>) == ch
- * </pre></blockquote>
- * is true. For other values of {@code ch}, it is the
- * largest value <i>k</i> such that:
- * <blockquote><pre>
- * this.codePointAt(<i>k</i>) == ch
- * </pre></blockquote>
- * is true. In either case, if no such character occurs in this
- * string, then {@code -1} is returned. The
- * {@code String} is searched backwards starting at the last
- * character.
- *
- * @param ch a character (Unicode code point).
- * @return the index of the last occurrence of the character in the
- * character sequence represented by this object, or
- * {@code -1} if the character does not occur.
- */
- public int lastIndexOf(int ch) {
- return lastIndexOf(ch, value.length - 1);
- }
- /**
- * Returns the index within this string of the last occurrence of
- * the specified character, searching backward starting at the
- * specified index. For values of {@code ch} in the range
- * from 0 to 0xFFFF (inclusive), the index returned is the largest
- * value <i>k</i> such that:
- * <blockquote><pre>
- * (this.charAt(<i>k</i>) == ch) {@code &&} (<i>k</i> <= fromIndex)
- * </pre></blockquote>
- * is true. For other values of {@code ch}, it is the
- * largest value <i>k</i> such that:
- * <blockquote><pre>
- * (this.codePointAt(<i>k</i>) == ch) {@code &&} (<i>k</i> <= fromIndex)
- * </pre></blockquote>
- * is true. In either case, if no such character occurs in this
- * string at or before position {@code fromIndex}, then
- * {@code -1} is returned.
- *
- * <p>All indices are specified in {@code char} values
- * (Unicode code units).
- *
- * @param ch a character (Unicode code point).
- * @param fromIndex the index to start the search from. There is no
- * restriction on the value of {@code fromIndex}. If it is
- * greater than or equal to the length of this string, it has
- * the same effect as if it were equal to one less than the
- * length of this string: this entire string may be searched.
- * If it is negative, it has the same effect as if it were -1:
- * -1 is returned.
- * @return the index of the last occurrence of the character in the
- * character sequence represented by this object that is less
- * than or equal to {@code fromIndex}, or {@code -1}
- * if the character does not occur before that point.
- */
- public int lastIndexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) {
- if (ch < Character.MIN_SUPPLEMENTARY_CODE_POINT) {
- // handle most cases here (ch is a BMP code point or a
- // negative value (invalid code point))
- final char[] value = this.value;
- int i = Math.min(fromIndex, value.length - 1);
- for (; i >= 0; i--) {
- if (value[i] == ch) {
- return i;
- }
- }
- return -1;
- } else {
- return lastIndexOfSupplementary(ch, fromIndex);
- }
- }
- /**
- * Handles (rare) calls of lastIndexOf with a supplementary character.
- */
- private int lastIndexOfSupplementary(int ch, int fromIndex) {
- if (Character.isValidCodePoint(ch)) {
- final char[] value = this.value;
- char hi = Character.highSurrogate(ch);
- char lo = Character.lowSurrogate(ch);
- int i = Math.min(fromIndex, value.length - 2);
- for (; i >= 0; i--) {
- if (value[i] == hi && value[i + 1] == lo) {
- return i;
- }
- }
- }
- return -1;
- }
- /**
- * Returns the index within this string of the first occurrence of the
- * specified substring.
- *
- * <p>The returned index is the smallest value <i>k</i> for which:
- * <blockquote><pre>
- * this.startsWith(str, <i>k</i>)
- * </pre></blockquote>
- * If no such value of <i>k</i> exists, then {@code -1} is returned.
- *
- * @param str the substring to search for.
- * @return the index of the first occurrence of the specified substring,
- * or {@code -1} if there is no such occurrence.
- */
- public int indexOf(String str) {
- return indexOf(str, 0);
- }
- /**
- * Returns the index within this string of the first occurrence of the
- * specified substring, starting at the specified index.
- *
- * <p>The returned index is the smallest value <i>k</i> for which:
- * <blockquote><pre>
- * <i>k</i> >= fromIndex {@code &&} this.startsWith(str, <i>k</i>)
- * </pre></blockquote>
- * If no such value of <i>k</i> exists, then {@code -1} is returned.
- *
- * @param str the substring to search for.
- * @param fromIndex the index from which to start the search.
- * @return the index of the first occurrence of the specified substring,
- * starting at the specified index,
- * or {@code -1} if there is no such occurrence.
- */
- public int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex) {
- return indexOf(value, 0, value.length,
- str.value, 0, str.value.length, fromIndex);
- }
- /**
- * Code shared by String and AbstractStringBuilder to do searches. The
- * source is the character array being searched, and the target
- * is the string being searched for.
- *
- * @param source the characters being searched.
- * @param sourceOffset offset of the source string.
- * @param sourceCount count of the source string.
- * @param target the characters being searched for.
- * @param fromIndex the index to begin searching from.
- */
- static int indexOf(char[] source, int sourceOffset, int sourceCount,
- String target, int fromIndex) {
- return indexOf(source, sourceOffset, sourceCount,
- target.value, 0, target.value.length,
- fromIndex);
- }
- /**
- * Code shared by String and StringBuffer to do searches. The
- * source is the character array being searched, and the target
- * is the string being searched for.
- *
- * @param source the characters being searched.
- * @param sourceOffset offset of the source string.
- * @param sourceCount count of the source string.
- * @param target the characters being searched for.
- * @param targetOffset offset of the target string.
- * @param targetCount count of the target string.
- * @param fromIndex the index to begin searching from.
- */
- static int indexOf(char[] source, int sourceOffset, int sourceCount,
- char[] target, int targetOffset, int targetCount,
- int fromIndex) {
- if (fromIndex >= sourceCount) {
- return (targetCount == 0 ? sourceCount : -1);
- }
- if (fromIndex < 0) {
- fromIndex = 0;
- }
- if (targetCount == 0) {
- return fromIndex;
- }
- char first = target[targetOffset];
- int max = sourceOffset + (sourceCount - targetCount);
- for (int i = sourceOffset + fromIndex; i <= max; i++) {
- /* Look for first character. */
- if (source[i] != first) {
- while (++i <= max && source[i] != first);
- }
- /* Found first character, now look at the rest of v2 */
- if (i <= max) {
- int j = i + 1;
- int end = j + targetCount - 1;
- for (int k = targetOffset + 1; j < end && source[j]
- == target[k]; j++, k++);
- if (j == end) {
- /* Found whole string. */
- return i - sourceOffset;
- }
- }
- }
- return -1;
- }
- /**
- * Returns the index within this string of the last occurrence of the
- * specified substring. The last occurrence of the empty string ""
- * is considered to occur at the index value {@code this.length()}.
- *
- * <p>The returned index is the largest value <i>k</i> for which:
- * <blockquote><pre>
- * this.startsWith(str, <i>k</i>)
- * </pre></blockquote>
- * If no such value of <i>k</i> exists, then {@code -1} is returned.
- *
- * @param str the substring to search for.
- * @return the index of the last occurrence of the specified substring,
- * or {@code -1} if there is no such occurrence.
- */
- public int lastIndexOf(String str) {
- return lastIndexOf(str, value.length);
- }
- /**
- * Returns the index within this string of the last occurrence of the
- * specified substring, searching backward starting at the specified index.
- *
- * <p>The returned index is the largest value <i>k</i> for which:
- * <blockquote><pre>
- * <i>k</i> {@code <=} fromIndex {@code &&} this.startsWith(str, <i>k</i>)
- * </pre></blockquote>
- * If no such value of <i>k</i> exists, then {@code -1} is returned.
- *
- * @param str the substring to search for.
- * @param fromIndex the index to start the search from.
- * @return the index of the last occurrence of the specified substring,
- * searching backward from the specified index,
- * or {@code -1} if there is no such occurrence.
- */
- public int lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex) {
- return lastIndexOf(value, 0, value.length,
- str.value, 0, str.value.length, fromIndex);
- }
- /**
- * Code shared by String and AbstractStringBuilder to do searches. The
- * source is the character array being searched, and the target
- * is the string being searched for.
- *
- * @param source the characters being searched.
- * @param sourceOffset offset of the source string.
- * @param sourceCount count of the source string.
- * @param target the characters being searched for.
- * @param fromIndex the index to begin searching from.
- */
- static int lastIndexOf(char[] source, int sourceOffset, int sourceCount,
- String target, int fromIndex) {
- return lastIndexOf(source, sourceOffset, sourceCount,
- target.value, 0, target.value.length,
- fromIndex);
- }
- /**
- * Code shared by String and StringBuffer to do searches. The
- * source is the character array being searched, and the target
- * is the string being searched for.
- *
- * @param source the characters being searched.
- * @param sourceOffset offset of the source string.
- * @param sourceCount count of the source string.
- * @param target the characters being searched for.
- * @param targetOffset offset of the target string.
- * @param targetCount count of the target string.
- * @param fromIndex the index to begin searching from.
- */
- static int lastIndexOf(char[] source, int sourceOffset, int sourceCount,
- char[] target, int targetOffset, int targetCount,
- int fromIndex) {
- /*
- * Check arguments; return immediately where possible. For
- * consistency, don't check for null str.
- */
- int rightIndex = sourceCount - targetCount;
- if (fromIndex < 0) {
- return -1;
- }
- if (fromIndex > rightIndex) {
- fromIndex = rightIndex;
- }
- /* Empty string always matches. */
- if (targetCount == 0) {
- return fromIndex;
- }
- int strLastIndex = targetOffset + targetCount - 1;
- char strLastChar = target[strLastIndex];
- int min = sourceOffset + targetCount - 1;
- int i = min + fromIndex;
- startSearchForLastChar:
- while (true) {
- while (i >= min && source[i] != strLastChar) {
- i--;
- }
- if (i < min) {
- return -1;
- }
- int j = i - 1;
- int start = j - (targetCount - 1);
- int k = strLastIndex - 1;
- while (j > start) {
- if (source[j--] != target[k--]) {
- i--;
- continue startSearchForLastChar;
- }
- }
- return start - sourceOffset + 1;
- }
- }
- /**
- * Returns a string that is a substring of this string. The
- * substring begins with the character at the specified index and
- * extends to the end of this string. <p>
- * Examples:
- * <blockquote><pre>
- * "unhappy".substring(2) returns "happy"
- * "Harbison".substring(3) returns "bison"
- * "emptiness".substring(9) returns "" (an empty string)
- * </pre></blockquote>
- *
- * @param beginIndex the beginning index, inclusive.
- * @return the specified substring.
- * @exception IndexOutOfBoundsException if
- * {@code beginIndex} is negative or larger than the
- * length of this {@code String} object.
- */
- public String substring(int beginIndex) {
- if (beginIndex < 0) {
- throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(beginIndex);
- }
- int subLen = value.length - beginIndex;
- if (subLen < 0) {
- throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(subLen);
- }
- return (beginIndex == 0) ? this : new String(value, beginIndex, subLen);
- }
- /**
- * Returns a string that is a substring of this string. The
- * substring begins at the specified {@code beginIndex} and
- * extends to the character at index {@code endIndex - 1}.
- * Thus the length of the substring is {@code endIndex-beginIndex}.
- * <p>
- * Examples:
- * <blockquote><pre>
- * "hamburger".substring(4, 8) returns "urge"
- * "smiles".substring(1, 5) returns "mile"
- * </pre></blockquote>
- *
- * @param beginIndex the beginning index, inclusive.
- * @param endIndex the ending index, exclusive.
- * @return the specified substring.
- * @exception IndexOutOfBoundsException if the
- * {@code beginIndex} is negative, or
- * {@code endIndex} is larger than the length of
- * this {@code String} object, or
- * {@code beginIndex} is larger than
- * {@code endIndex}.
- */
- public String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) {
- if (beginIndex < 0) {
- throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(beginIndex);
- }
- if (endIndex > value.length) {
- throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(endIndex);
- }
- int subLen = endIndex - beginIndex;
- if (subLen < 0) {
- throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(subLen);
- }
- return ((beginIndex == 0) && (endIndex == value.length)) ? this
- : new String(value, beginIndex, subLen);
- }
- /**
- * Returns a character sequence that is a subsequence of this sequence.
- *
- * <p> An invocation of this method of the form
- *
- * <blockquote><pre>
- * str.subSequence(begin, end)</pre></blockquote>
- *
- * behaves in exactly the same way as the invocation
- *
- * <blockquote><pre>
- * str.substring(begin, end)</pre></blockquote>
- *
- * @apiNote
- * This method is defined so that the {@code String} class can implement
- * the {@link CharSequence} interface.
- *
- * @param beginIndex the begin index, inclusive.
- * @param endIndex the end index, exclusive.
- * @return the specified subsequence.
- *
- * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException
- * if {@code beginIndex} or {@code endIndex} is negative,
- * if {@code endIndex} is greater than {@code length()},
- * or if {@code beginIndex} is greater than {@code endIndex}
- *
- * @since 1.4
- * @spec JSR-51
- */
- public CharSequence subSequence(int beginIndex, int endIndex) {
- return this.substring(beginIndex, endIndex);
- }
- /**
- * Concatenates the specified string to the end of this string.
- * <p>
- * If the length of the argument string is {@code 0}, then this
- * {@code String} object is returned. Otherwise, a
- * {@code String} object is returned that represents a character
- * sequence that is the concatenation of the character sequence
- * represented by this {@code String} object and the character
- * sequence represented by the argument string.<p>
- * Examples:
- * <blockquote><pre>
- * "cares".concat("s") returns "caress"
- * "to".concat("get").concat("her") returns "together"
- * </pre></blockquote>
- *
- * @param str the {@code String} that is concatenated to the end
- * of this {@code String}.
- * @return a string that represents the concatenation of this object's
- * characters followed by the string argument's characters.
- */
- public String concat(String str) {
- int otherLen = str.length();
- if (otherLen == 0) {
- return this;
- }
- int len = value.length;
- char buf[] = Arrays.copyOf(value, len + otherLen);
- str.getChars(buf, len);
- return new String(buf, true);
- }
- /**
- * Returns a string resulting from replacing all occurrences of
- * {@code oldChar} in this string with {@code newChar}.
- * <p>
- * If the character {@code oldChar} does not occur in the
- * character sequence represented by this {@code String} object,
- * then a reference to this {@code String} object is returned.
- * Otherwise, a {@code String} object is returned that
- * represents a character sequence identical to the character sequence
- * represented by this {@code String} object, except that every
- * occurrence of {@code oldChar} is replaced by an occurrence
- * of {@code newChar}.
- * <p>
- * Examples:
- * <blockquote><pre>
- * "mesquite in your cellar".replace('e', 'o')
- * returns "mosquito in your collar"
- * "the war of baronets".replace('r', 'y')
- * returns "the way of bayonets"
- * "sparring with a purple porpoise".replace('p', 't')
- * returns "starring with a turtle tortoise"
- * "JonL".replace('q', 'x') returns "JonL" (no change)
- * </pre></blockquote>
- *
- * @param oldChar the old character.
- * @param newChar the new character.
- * @return a string derived from this string by replacing every
- * occurrence of {@code oldChar} with {@code newChar}.
- */
- public String replace(char oldChar, char newChar) {
- if (oldChar != newChar) {
- int len = value.length;
- int i = -1;
- char[] val = value; /* avoid getfield opcode */
- while (++i < len) {
- if (val[i] == oldChar) {
- break;
- }
- }
- if (i < len) {
- char buf[] = new char[len];
- for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
- buf[j] = val[j];
- }
- while (i < len) {
- char c = val[i];
- buf[i] = (c == oldChar) ? newChar : c;
- i++;
- }
- return new String(buf, true);
- }
- }
- return this;
- }
- /**
- * Tells whether or not this string matches the given <a
- * href="../util/regex/Pattern.html#sum">regular expression</a>.
- *
- * <p> An invocation of this method of the form
- * <i>str</i>{@code .matches(}<i>regex</i>{@code )} yields exactly the
- * same result as the expression
- *
- * <blockquote>
- * {@link java.util.regex.Pattern}.{@link java.util.regex.Pattern#matches(String,CharSequence)
- * matches(<i>regex</i>, <i>str</i>)}
- * </blockquote>
- *
- * @param regex
- * the regular expression to which this string is to be matched
- *
- * @return {@code true} if, and only if, this string matches the
- * given regular expression
- *
- * @throws PatternSyntaxException
- * if the regular expression's syntax is invalid
- *
- * @see java.util.regex.Pattern
- *
- * @since 1.4
- * @spec JSR-51
- */
- public boolean matches(String regex) {
- return Pattern.matches(regex, this);
- }
- /**
- * Returns true if and only if this string contains the specified
- * sequence of char values.
- *
- * @param s the sequence to search for
- * @return true if this string contains {@code s}, false otherwise
- * @since 1.5
- */
- public boolean contains(CharSequence s) {
- return indexOf(s.toString()) > -1;
- }
- /**
- * Replaces the first substring of this string that matches the given <a
- * href="../util/regex/Pattern.html#sum">regular expression</a> with the
- * given replacement.
- *
- * <p> An invocation of this method of the form
- * <i>str</i>{@code .replaceFirst(}<i>regex</i>{@code ,} <i>repl</i>{@code )}
- * yields exactly the same result as the expression
- *
- * <blockquote>
- * <code>
- * {@link java.util.regex.Pattern}.{@link
- * java.util.regex.Pattern#compile compile}(<i>regex</i>).{@link
- * java.util.regex.Pattern#matcher(java.lang.CharSequence) matcher}(<i>str</i>).{@link
- * java.util.regex.Matcher#replaceFirst replaceFirst}(<i>repl</i>)
- * </code>
- * </blockquote>
- *
- *<p>
- * Note that backslashes ({@code \}) and dollar signs ({@code $}) in the
- * replacement string may cause the results to be different than if it were
- * being treated as a literal replacement string; see
- * {@link java.util.regex.Matcher#replaceFirst}.
- * Use {@link java.util.regex.Matcher#quoteReplacement} to suppress the special
- * meaning of these characters, if desired.
- *
- * @param regex
- * the regular expression to which this string is to be matched
- * @param replacement
- * the string to be substituted for the first match
- *
- * @return The resulting {@code String}
- *
- * @throws PatternSyntaxException
- * if the regular expression's syntax is invalid
- *
- * @see java.util.regex.Pattern
- *
- * @since 1.4
- * @spec JSR-51
- */
- public String replaceFirst(String regex, String replacement) {
- return Pattern.compile(regex).matcher(this).replaceFirst(replacement);
- }
- /**
- * Replaces each substring of this string that matches the given <a
- * href="../util/regex/Pattern.html#sum">regular expression</a> with the
- * given replacement.
- *
- * <p> An invocation of this method of the form
- * <i>str</i>{@code .replaceAll(}<i>regex</i>{@code ,} <i>repl</i>{@code )}
- * yields exactly the same result as the expression
- *
- * <blockquote>
- * <code>
- * {@link java.util.regex.Pattern}.{@link
- * java.util.regex.Pattern#compile compile}(<i>regex</i>).{@link
- * java.util.regex.Pattern#matcher(java.lang.CharSequence) matcher}(<i>str</i>).{@link
- * java.util.regex.Matcher#replaceAll replaceAll}(<i>repl</i>)
- * </code>
- * </blockquote>
- *
- *<p>
- * Note that backslashes ({@code \}) and dollar signs ({@code $}) in the
- * replacement string may cause the results to be different than if it were
- * being treated as a literal replacement string; see
- * {@link java.util.regex.Matcher#replaceAll Matcher.replaceAll}.
- * Use {@link java.util.regex.Matcher#quoteReplacement} to suppress the special
- * meaning of these characters, if desired.
- *
- * @param regex
- * the regular expression to which this string is to be matched
- * @param replacement
- * the string to be substituted for each match
- *
- * @return The resulting {@code String}
- *
- * @throws PatternSyntaxException
- * if the regular expression's syntax is invalid
- *
- * @see java.util.regex.Pattern
- *
- * @since 1.4
- * @spec JSR-51
- */
- public String replaceAll(String regex, String replacement) {
- return Pattern.compile(regex).matcher(this).replaceAll(replacement);
- }
- /**
- * Replaces each substring of this string that matches the literal target
- * sequence with the specified literal replacement sequence. The
- * replacement proceeds from the beginning of the string to the end, for
- * example, replacing "aa" with "b" in the string "aaa" will result in
- * "ba" rather than "ab".
- *
- * @param target The sequence of char values to be replaced
- * @param replacement The replacement sequence of char values
- * @return The resulting string
- * @since 1.5
- */
- public String replace(CharSequence target, CharSequence replacement) {
- return Pattern.compile(target.toString(), Pattern.LITERAL).matcher(
- this).replaceAll(Matcher.quoteReplacement(replacement.toString()));
- }
- /**
- * Splits this string around matches of the given
- * <a href="../util/regex/Pattern.html#sum">regular expression</a>.
- *
- * <p> The array returned by this method contains each substring of this
- * string that is terminated by another substring that matches the given
- * expression or is terminated by the end of the string. The substrings in
- * the array are in the order in which they occur in this string. If the
- * expression does not match any part of the input then the resulting array
- * has just one element, namely this string.
- *
- * <p> When there is a positive-width match at the beginning of this
- * string then an empty leading substring is included at the beginning
- * of the resulting array. A zero-width match at the beginning however
- * never produces such empty leading substring.
- *
- * <p> The {@code limit} parameter controls the number of times the
- * pattern is applied and therefore affects the length of the resulting
- * array. If the limit <i>n</i> is greater than zero then the pattern
- * will be applied at most <i>n</i> - 1 times, the array's
- * length will be no greater than <i>n</i>, and the array's last entry
- * will contain all input beyond the last matched delimiter. If <i>n</i>
- * is non-positive then the pattern will be applied as many times as
- * possible and the array can have any length. If <i>n</i> is zero then
- * the pattern will be applied as many times as possible, the array can
- * have any length, and trailing empty strings will be discarded.
- *
- * <p> The string {@code "boo:and:foo"}, for example, yields the
- * following results with these parameters:
- *
- * <blockquote><table cellpadding=1 cellspacing=0 summary="Split example showing regex, limit, and result">
- * <tr>
- * <th>Regex</th>
- * <th>Limit</th>
- * <th>Result</th>
- * </tr>
- * <tr><td align=center>:</td>
- * <td align=center>2</td>
- * <td>{@code { "boo", "and:foo" }}</td></tr>
- * <tr><td align=center>:</td>
- * <td align=center>5</td>
- * <td>{@code { "boo", "and", "foo" }}</td></tr>
- * <tr><td align=center>:</td>
- * <td align=center>-2</td>
- * <td>{@code { "boo", "and", "foo" }}</td></tr>
- * <tr><td align=center>o</td>
- * <td align=center>5</td>
- * <td>{@code { "b", "", ":and:f", "", "" }}</td></tr>
- * <tr><td align=center>o</td>
- * <td align=center>-2</td>
- * <td>{@code { "b", "", ":and:f", "", "" }}</td></tr>
- * <tr><td align=center>o</td>
- * <td align=center>0</td>
- * <td>{@code { "b", "", ":and:f" }}</td></tr>
- * </table></blockquote>
- *
- * <p> An invocation of this method of the form
- * <i>str.</i>{@code split(}<i>regex</i>{@code ,} <i>n</i>{@code )}
- * yields the same result as the expression
- *
- * <blockquote>
- * <code>
- * {@link java.util.regex.Pattern}.{@link
- * java.util.regex.Pattern#compile compile}(<i>regex</i>).{@link
- * java.util.regex.Pattern#split(java.lang.CharSequence,int) split}(<i>str</i>, <i>n</i>)
- * </code>
- * </blockquote>
- *
- *
- * @param regex
- * the delimiting regular expression
- *
- * @param limit
- * the result threshold, as described above
- *
- * @return the array of strings computed by splitting this string
- * around matches of the given regular expression
- *
- * @throws PatternSyntaxException
- * if the regular expression's syntax is invalid
- *
- * @see java.util.regex.Pattern
- *
- * @since 1.4
- * @spec JSR-51
- */
- public String[] split(String regex, int limit) {
- /* fastpath if the regex is a
- (1)one-char String and this character is not one of the
- RegEx's meta characters ".$|()[{^?*+\\", or
- (2)two-char String and the first char is the backslash and
- the second is not the ascii digit or ascii letter.
- */
- char ch = 0;
- if (((regex.value.length == 1 &&
- ".$|()[{^?*+\\".indexOf(ch = regex.charAt(0)) == -1) ||
- (regex.length() == 2 &&
- regex.charAt(0) == '\\' &&
- (((ch = regex.charAt(1))-'0')|('9'-ch)) < 0 &&
- ((ch-'a')|('z'-ch)) < 0 &&
- ((ch-'A')|('Z'-ch)) < 0)) &&
- (ch < Character.MIN_HIGH_SURROGATE ||
- ch > Character.MAX_LOW_SURROGATE))
- {
- int off = 0;
- int next = 0;
- boolean limited = limit > 0;
- ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
- while ((next = indexOf(ch, off)) != -1) {
- if (!limited || list.size() < limit - 1) {
- list.add(substring(off, next));
- off = next + 1;
- } else { // last one
- //assert (list.size() == limit - 1);
- list.add(substring(off, value.length));
- off = value.length;
- break;
- }
- }
- // If no match was found, return this
- if (off == 0)
- return new String[]{this};
- // Add remaining segment
- if (!limited || list.size() < limit)
- list.add(substring(off, value.length));
- // Construct result
- int resultSize = list.size();
- if (limit == 0) {
- while (resultSize > 0 && list.get(resultSize - 1).length() == 0) {
- resultSize--;
- }
- }
- String[] result = new String[resultSize];
- return list.subList(0, resultSize).toArray(result);
- }
- return Pattern.compile(regex).split(this, limit);
- }
- /**
- * Splits this string around matches of the given <a
- * href="../util/regex/Pattern.html#sum">regular expression</a>.
- *
- * <p> This method works as if by invoking the two-argument {@link
- * #split(String, int) split} method with the given expression and a limit
- * argument of zero. Trailing empty strings are therefore not included in
- * the resulting array.
- *
- * <p> The string {@code "boo:and:foo"}, for example, yields the following
- * results with these expressions:
- *
- * <blockquote><table cellpadding=1 cellspacing=0 summary="Split examples showing regex and result">
- * <tr>
- * <th>Regex</th>
- * <th>Result</th>
- * </tr>
- * <tr><td align=center>:</td>
- * <td>{@code { "boo", "and", "foo" }}</td></tr>
- * <tr><td align=center>o</td>
- * <td>{@code { "b", "", ":and:f" }}</td></tr>
- * </table></blockquote>
- *
- *
- * @param regex
- * the delimiting regular expression
- *
- * @return the array of strings computed by splitting this string
- * around matches of the given regular expression
- *
- * @throws PatternSyntaxException
- * if the regular expression's syntax is invalid
- *
- * @see java.util.regex.Pattern
- *
- * @since 1.4
- * @spec JSR-51
- */
- public String[] split(String regex) {
- return split(regex, 0);
- }
- /**
- * Returns a new String composed of copies of the
- * {@code CharSequence elements} joined together with a copy of
- * the specified {@code delimiter}.
- *
- * <blockquote>For example,
- * <pre>{@code
- * String message = String.join("-", "Java", "is", "cool");
- * // message returned is: "Java-is-cool"
- * }</pre></blockquote>
- *
- * Note that if an element is null, then {@code "null"} is added.
- *
- * @param delimiter the delimiter that separates each element
- * @param elements the elements to join together.
- *
- * @return a new {@code String} that is composed of the {@code elements}
- * separated by the {@code delimiter}
- *
- * @throws NullPointerException If {@code delimiter} or {@code elements}
- * is {@code null}
- *
- * @see java.util.StringJoiner
- * @since 1.8
- */
- public static String join(CharSequence delimiter, CharSequence... elements) {
- Objects.requireNonNull(delimiter);
- Objects.requireNonNull(elements);
- // Number of elements not likely worth Arrays.stream overhead.
- StringJoiner joiner = new StringJoiner(delimiter);
- for (CharSequence cs: elements) {
- joiner.add(cs);
- }
- return joiner.toString();
- }
- /**
- * Returns a new {@code String} composed of copies of the
- * {@code CharSequence elements} joined together with a copy of the
- * specified {@code delimiter}.
- *
- * <blockquote>For example,
- * <pre>{@code
- * List<String> strings = new LinkedList<>();
- * strings.add("Java");strings.add("is");
- * strings.add("cool");
- * String message = String.join(" ", strings);
- * //message returned is: "Java is cool"
- *
- * Set<String> strings = new LinkedHashSet<>();
- * strings.add("Java"); strings.add("is");
- * strings.add("very"); strings.add("cool");
- * String message = String.join("-", strings);
- * //message returned is: "Java-is-very-cool"
- * }</pre></blockquote>
- *
- * Note that if an individual element is {@code null}, then {@code "null"} is added.
- *
- * @param delimiter a sequence of characters that is used to separate each
- * of the {@code elements} in the resulting {@code String}
- * @param elements an {@code Iterable} that will have its {@code elements}
- * joined together.
- *
- * @return a new {@code String} that is composed from the {@code elements}
- * argument
- *
- * @throws NullPointerException If {@code delimiter} or {@code elements}
- * is {@code null}
- *
- * @see #join(CharSequence,CharSequence...)
- * @see java.util.StringJoiner
- * @since 1.8
- */
- public static String join(CharSequence delimiter,
- Iterable<? extends CharSequence> elements) {
- Objects.requireNonNull(delimiter);
- Objects.requireNonNull(elements);
- StringJoiner joiner = new StringJoiner(delimiter);
- for (CharSequence cs: elements) {
- joiner.add(cs);
- }
- return joiner.toString();
- }
- /**
- * Converts all of the characters in this {@code String} to lower
- * case using the rules of the given {@code Locale}. Case mapping is based
- * on the Unicode Standard version specified by the {@link java.lang.Character Character}
- * class. Since case mappings are not always 1:1 char mappings, the resulting
- * {@code String} may be a different length than the original {@code String}.
- * <p>
- * Examples of lowercase mappings are in the following table:
- * <table border="1" summary="Lowercase mapping examples showing language code of locale, upper case, lower case, and description">
- * <tr>
- * <th>Language Code of Locale</th>
- * <th>Upper Case</th>
- * <th>Lower Case</th>
- * <th>Description</th>
- * </tr>
- * <tr>
- * <td>tr (Turkish)</td>
- * <td>\u0130</td>
- * <td>\u0069</td>
- * <td>capital letter I with dot above -> small letter i</td>
- * </tr>
- * <tr>
- * <td>tr (Turkish)</td>
- * <td>\u0049</td>
- * <td>\u0131</td>
- * <td>capital letter I -> small letter dotless i </td>
- * </tr>
- * <tr>
- * <td>(all)</td>
- * <td>French Fries</td>
- * <td>french fries</td>
- * <td>lowercased all chars in String</td>
- * </tr>
- * <tr>
- * <td>(all)</td>
- * <td><img src="doc-files/capiota.gif" alt="capiota"><img src="doc-files/capchi.gif" alt="capchi">
- * <img src="doc-files/captheta.gif" alt="captheta"><img src="doc-files/capupsil.gif" alt="capupsil">
- * <img src="doc-files/capsigma.gif" alt="capsigma"></td>
- * <td><img src="doc-files/iota.gif" alt="iota"><img src="doc-files/chi.gif" alt="chi">
- * <img src="doc-files/theta.gif" alt="theta"><img src="doc-files/upsilon.gif" alt="upsilon">
- * <img src="doc-files/sigma1.gif" alt="sigma"></td>
- * <td>lowercased all chars in String</td>
- * </tr>
- * </table>
- *
- * @param locale use the case transformation rules for this locale
- * @return the {@code String}, converted to lowercase.
- * @see java.lang.String#toLowerCase()
- * @see java.lang.String#toUpperCase()
- * @see java.lang.String#toUpperCase(Locale)
- * @since 1.1
- */
- public String toLowerCase(Locale locale) {
- if (locale == null) {
- throw new NullPointerException();
- }
- int firstUpper;
- final int len = value.length;
- /* Now check if there are any characters that need to be changed. */
- scan: {
- for (firstUpper = 0 ; firstUpper < len; ) {
- char c = value[firstUpper];
- if ((c >= Character.MIN_HIGH_SURROGATE)
- && (c <= Character.MAX_HIGH_SURROGATE)) {
- int supplChar = codePointAt(firstUpper);
- if (supplChar != Character.toLowerCase(supplChar)) {
- break scan;
- }
- firstUpper += Character.charCount(supplChar);
- } else {
- if (c != Character.toLowerCase(c)) {
- break scan;
- }
- firstUpper++;
- }
- }
- return this;
- }
- char[] result = new char[len];
- int resultOffset = 0; /* result may grow, so i+resultOffset
- * is the write location in result */
- /* Just copy the first few lowerCase characters. */
- System.arraycopy(value, 0, result, 0, firstUpper);
- String lang = locale.getLanguage();
- boolean localeDependent =
- (lang == "tr" || lang == "az" || lang == "lt");
- char[] lowerCharArray;
- int lowerChar;
- int srcChar;
- int srcCount;
- for (int i = firstUpper; i < len; i += srcCount) {
- srcChar = (int)value[i];
- if ((char)srcChar >= Character.MIN_HIGH_SURROGATE
- && (char)srcChar <= Character.MAX_HIGH_SURROGATE) {
- srcChar = codePointAt(i);
- srcCount = Character.charCount(srcChar);
- } else {
- srcCount = 1;
- }
- if (localeDependent ||
- srcChar == '\u03A3' || // GREEK CAPITAL LETTER SIGMA
- srcChar == '\u0130') { // LATIN CAPITAL LETTER I WITH DOT ABOVE
- lowerChar = ConditionalSpecialCasing.toLowerCaseEx(this, i, locale);
- } else {
- lowerChar = Character.toLowerCase(srcChar);
- }
- if ((lowerChar == Character.ERROR)
- || (lowerChar >= Character.MIN_SUPPLEMENTARY_CODE_POINT)) {
- if (lowerChar == Character.ERROR) {
- lowerCharArray =
- ConditionalSpecialCasing.toLowerCaseCharArray(this, i, locale);
- } else if (srcCount == 2) {
- resultOffset += Character.toChars(lowerChar, result, i + resultOffset) - srcCount;
- continue;
- } else {
- lowerCharArray = Character.toChars(lowerChar);
- }
- /* Grow result if needed */
- int mapLen = lowerCharArray.length;
- if (mapLen > srcCount) {
- char[] result2 = new char[result.length + mapLen - srcCount];
- System.arraycopy(result, 0, result2, 0, i + resultOffset);
- result = result2;
- }
- for (int x = 0; x < mapLen; ++x) {
- result[i + resultOffset + x] = lowerCharArray[x];
- }
- resultOffset += (mapLen - srcCount);
- } else {
- result[i + resultOffset] = (char)lowerChar;
- }
- }
- return new String(result, 0, len + resultOffset);
- }
- /**
- * Converts all of the characters in this {@code String} to lower
- * case using the rules of the default locale. This is equivalent to calling
- * {@code toLowerCase(Locale.getDefault())}.
- * <p>
- * <b>Note:</b> This method is locale sensitive, and may produce unexpected
- * results if used for strings that are intended to be interpreted locale
- * independently.
- * Examples are programming language identifiers, protocol keys, and HTML
- * tags.
- * For instance, {@code "TITLE".toLowerCase()} in a Turkish locale
- * returns {@code "t\u005Cu0131tle"}, where '\u005Cu0131' is the
- * LATIN SMALL LETTER DOTLESS I character.
- * To obtain correct results for locale insensitive strings, use
- * {@code toLowerCase(Locale.ROOT)}.
- * <p>
- * @return the {@code String}, converted to lowercase.
- * @see java.lang.String#toLowerCase(Locale)
- */
- public String toLowerCase() {
- return toLowerCase(Locale.getDefault());
- }
- /**
- * Converts all of the characters in this {@code String} to upper
- * case using the rules of the given {@code Locale}. Case mapping is based
- * on the Unicode Standard version specified by the {@link java.lang.Character Character}
- * class. Since case mappings are not always 1:1 char mappings, the resulting
- * {@code String} may be a different length than the original {@code String}.
- * <p>
- * Examples of locale-sensitive and 1:M case mappings are in the following table.
- *
- * <table border="1" summary="Examples of locale-sensitive and 1:M case mappings. Shows Language code of locale, lower case, upper case, and description.">
- * <tr>
- * <th>Language Code of Locale</th>
- * <th>Lower Case</th>
- * <th>Upper Case</th>
- * <th>Description</th>
- * </tr>
- * <tr>
- * <td>tr (Turkish)</td>
- * <td>\u0069</td>
- * <td>\u0130</td>
- * <td>small letter i -> capital letter I with dot above</td>
- * </tr>
- * <tr>
- * <td>tr (Turkish)</td>
- * <td>\u0131</td>
- * <td>\u0049</td>
- * <td>small letter dotless i -> capital letter I</td>
- * </tr>
- * <tr>
- * <td>(all)</td>
- * <td>\u00df</td>
- * <td>\u0053 \u0053</td>
- * <td>small letter sharp s -> two letters: SS</td>
- * </tr>
- * <tr>
- * <td>(all)</td>
- * <td>Fahrvergnügen</td>
- * <td>FAHRVERGNÜGEN</td>
- * <td></td>
- * </tr>
- * </table>
- * @param locale use the case transformation rules for this locale
- * @return the {@code String}, converted to uppercase.
- * @see java.lang.String#toUpperCase()
- * @see java.lang.String#toLowerCase()
- * @see java.lang.String#toLowerCase(Locale)
- * @since 1.1
- */
- public String toUpperCase(Locale locale) {
- if (locale == null) {
- throw new NullPointerException();
- }
- int firstLower;
- final int len = value.length;
- /* Now check if there are any characters that need to be changed. */
- scan: {
- for (firstLower = 0 ; firstLower < len; ) {
- int c = (int)value[firstLower];
- int srcCount;
- if ((c >= Character.MIN_HIGH_SURROGATE)
- && (c <= Character.MAX_HIGH_SURROGATE)) {
- c = codePointAt(firstLower);
- srcCount = Character.charCount(c);
- } else {
- srcCount = 1;
- }
- int upperCaseChar = Character.toUpperCaseEx(c);
- if ((upperCaseChar == Character.ERROR)
- || (c != upperCaseChar)) {
- break scan;
- }
- firstLower += srcCount;
- }
- return this;
- }
- /* result may grow, so i+resultOffset is the write location in result */
- int resultOffset = 0;
- char[] result = new char[len]; /* may grow */
- /* Just copy the first few upperCase characters. */
- System.arraycopy(value, 0, result, 0, firstLower);
- String lang = locale.getLanguage();
- boolean localeDependent =
- (lang == "tr" || lang == "az" || lang == "lt");
- char[] upperCharArray;
- int upperChar;
- int srcChar;
- int srcCount;
- for (int i = firstLower; i < len; i += srcCount) {
- srcChar = (int)value[i];
- if ((char)srcChar >= Character.MIN_HIGH_SURROGATE &&
- (char)srcChar <= Character.MAX_HIGH_SURROGATE) {
- srcChar = codePointAt(i);
- srcCount = Character.charCount(srcChar);
- } else {
- srcCount = 1;
- }
- if (localeDependent) {
- upperChar = ConditionalSpecialCasing.toUpperCaseEx(this, i, locale);
- } else {
- upperChar = Character.toUpperCaseEx(srcChar);
- }
- if ((upperChar == Character.ERROR)
- || (upperChar >= Character.MIN_SUPPLEMENTARY_CODE_POINT)) {
- if (upperChar == Character.ERROR) {
- if (localeDependent) {
- upperCharArray =
- ConditionalSpecialCasing.toUpperCaseCharArray(this, i, locale);
- } else {
- upperCharArray = Character.toUpperCaseCharArray(srcChar);
- }
- } else if (srcCount == 2) {
- resultOffset += Character.toChars(upperChar, result, i + resultOffset) - srcCount;
- continue;
- } else {
- upperCharArray = Character.toChars(upperChar);
- }
- /* Grow result if needed */
- int mapLen = upperCharArray.length;
- if (mapLen > srcCount) {
- char[] result2 = new char[result.length + mapLen - srcCount];
- System.arraycopy(result, 0, result2, 0, i + resultOffset);
- result = result2;
- }
- for (int x = 0; x < mapLen; ++x) {
- result[i + resultOffset + x] = upperCharArray[x];
- }
- resultOffset += (mapLen - srcCount);
- } else {
- result[i + resultOffset] = (char)upperChar;
- }
- }
- return new String(result, 0, len + resultOffset);
- }
- /**
- * Converts all of the characters in this {@code String} to upper
- * case using the rules of the default locale. This method is equivalent to
- * {@code toUpperCase(Locale.getDefault())}.
- * <p>
- * <b>Note:</b> This method is locale sensitive, and may produce unexpected
- * results if used for strings that are intended to be interpreted locale
- * independently.
- * Examples are programming language identifiers, protocol keys, and HTML
- * tags.
- * For instance, {@code "title".toUpperCase()} in a Turkish locale
- * returns {@code "T\u005Cu0130TLE"}, where '\u005Cu0130' is the
- * LATIN CAPITAL LETTER I WITH DOT ABOVE character.
- * To obtain correct results for locale insensitive strings, use
- * {@code toUpperCase(Locale.ROOT)}.
- * <p>
- * @return the {@code String}, converted to uppercase.
- * @see java.lang.String#toUpperCase(Locale)
- */
- public String toUpperCase() {
- return toUpperCase(Locale.getDefault());
- }
- /**
- * Returns a string whose value is this string, with any leading and trailing
- * whitespace removed.
- * <p>
- * If this {@code String} object represents an empty character
- * sequence, or the first and last characters of character sequence
- * represented by this {@code String} object both have codes
- * greater than {@code '\u005Cu0020'} (the space character), then a
- * reference to this {@code String} object is returned.
- * <p>
- * Otherwise, if there is no character with a code greater than
- * {@code '\u005Cu0020'} in the string, then a
- * {@code String} object representing an empty string is
- * returned.
- * <p>
- * Otherwise, let <i>k</i> be the index of the first character in the
- * string whose code is greater than {@code '\u005Cu0020'}, and let
- * <i>m</i> be the index of the last character in the string whose code
- * is greater than {@code '\u005Cu0020'}. A {@code String}
- * object is returned, representing the substring of this string that
- * begins with the character at index <i>k</i> and ends with the
- * character at index <i>m</i>-that is, the result of
- * {@code this.substring(k, m + 1)}.
- * <p>
- * This method may be used to trim whitespace (as defined above) from
- * the beginning and end of a string.
- *
- * @return A string whose value is this string, with any leading and trailing white
- * space removed, or this string if it has no leading or
- * trailing white space.
- */
- public String trim() {
- int len = value.length;
- int st = 0;
- char[] val = value; /* avoid getfield opcode */
- while ((st < len) && (val[st] <= ' ')) {
- st++;
- }
- while ((st < len) && (val[len - 1] <= ' ')) {
- len--;
- }
- return ((st > 0) || (len < value.length)) ? substring(st, len) : this;
- }
- /**
- * This object (which is already a string!) is itself returned.
- *
- * @return the string itself.
- */
- public String toString() {
- return this;
- }
- /**
- * Converts this string to a new character array.
- *
- * @return a newly allocated character array whose length is the length
- * of this string and whose contents are initialized to contain
- * the character sequence represented by this string.
- */
- public char[] toCharArray() {
- // Cannot use Arrays.copyOf because of class initialization order issues
- char result[] = new char[value.length];
- System.arraycopy(value, 0, result, 0, value.length);
- return result;
- }
- /**
- * Returns a formatted string using the specified format string and
- * arguments.
- *
- * <p> The locale always used is the one returned by {@link
- * java.util.Locale#getDefault() Locale.getDefault()}.
- *
- * @param format
- * A <a href="../util/Formatter.html#syntax">format string</a>
- *
- * @param args
- * Arguments referenced by the format specifiers in the format
- * string. If there are more arguments than format specifiers, the
- * extra arguments are ignored. The number of arguments is
- * variable and may be zero. The maximum number of arguments is
- * limited by the maximum dimension of a Java array as defined by
- * <cite>The Java™ Virtual Machine Specification</cite>.
- * The behaviour on a
- * {@code null} argument depends on the <a
- * href="../util/Formatter.html#syntax">conversion</a>.
- *
- * @throws java.util.IllegalFormatException
- * If a format string contains an illegal syntax, a format
- * specifier that is incompatible with the given arguments,
- * insufficient arguments given the format string, or other
- * illegal conditions. For specification of all possible
- * formatting errors, see the <a
- * href="../util/Formatter.html#detail">Details</a> section of the
- * formatter class specification.
- *
- * @return A formatted string
- *
- * @see java.util.Formatter
- * @since 1.5
- */
- public static String format(String format, Object... args) {
- return new Formatter().format(format, args).toString();
- }
- /**
- * Returns a formatted string using the specified locale, format string,
- * and arguments.
- *
- * @param l
- * The {@linkplain java.util.Locale locale} to apply during
- * formatting. If {@code l} is {@code null} then no localization
- * is applied.
- *
- * @param format
- * A <a href="../util/Formatter.html#syntax">format string</a>
- *
- * @param args
- * Arguments referenced by the format specifiers in the format
- * string. If there are more arguments than format specifiers, the
- * extra arguments are ignored. The number of arguments is
- * variable and may be zero. The maximum number of arguments is
- * limited by the maximum dimension of a Java array as defined by
- * <cite>The Java™ Virtual Machine Specification</cite>.
- * The behaviour on a
- * {@code null} argument depends on the
- * <a href="../util/Formatter.html#syntax">conversion</a>.
- *
- * @throws java.util.IllegalFormatException
- * If a format string contains an illegal syntax, a format
- * specifier that is incompatible with the given arguments,
- * insufficient arguments given the format string, or other
- * illegal conditions. For specification of all possible
- * formatting errors, see the <a
- * href="../util/Formatter.html#detail">Details</a> section of the
- * formatter class specification
- *
- * @return A formatted string
- *
- * @see java.util.Formatter
- * @since 1.5
- */
- public static String format(Locale l, String format, Object... args) {
- return new Formatter(l).format(format, args).toString();
- }
- /**
- * Returns the string representation of the {@code Object} argument.
- *
- * @param obj an {@code Object}.
- * @return if the argument is {@code null}, then a string equal to
- * {@code "null"}; otherwise, the value of
- * {@code obj.toString()} is returned.
- * @see java.lang.Object#toString()
- */
- public static String valueOf(Object obj) {
- return (obj == null) ? "null" : obj.toString();
- }
- /**
- * Returns the string representation of the {@code char} array
- * argument. The contents of the character array are copied; subsequent
- * modification of the character array does not affect the returned
- * string.
- *
- * @param data the character array.
- * @return a {@code String} that contains the characters of the
- * character array.
- */
- public static String valueOf(char data[]) {
- return new String(data);
- }
- /**
- * Returns the string representation of a specific subarray of the
- * {@code char} array argument.
- * <p>
- * The {@code offset} argument is the index of the first
- * character of the subarray. The {@code count} argument
- * specifies the length of the subarray. The contents of the subarray
- * are copied; subsequent modification of the character array does not
- * affect the returned string.
- *
- * @param data the character array.
- * @param offset initial offset of the subarray.
- * @param count length of the subarray.
- * @return a {@code String} that contains the characters of the
- * specified subarray of the character array.
- * @exception IndexOutOfBoundsException if {@code offset} is
- * negative, or {@code count} is negative, or
- * {@code offset+count} is larger than
- * {@code data.length}.
- */
- public static String valueOf(char data[], int offset, int count) {
- return new String(data, offset, count);
- }
- /**
- * Equivalent to {@link #valueOf(char[], int, int)}.
- *
- * @param data the character array.
- * @param offset initial offset of the subarray.
- * @param count length of the subarray.
- * @return a {@code String} that contains the characters of the
- * specified subarray of the character array.
- * @exception IndexOutOfBoundsException if {@code offset} is
- * negative, or {@code count} is negative, or
- * {@code offset+count} is larger than
- * {@code data.length}.
- */
- public static String copyValueOf(char data[], int offset, int count) {
- return new String(data, offset, count);
- }
- /**
- * Equivalent to {@link #valueOf(char[])}.
- *
- * @param data the character array.
- * @return a {@code String} that contains the characters of the
- * character array.
- */
- public static String copyValueOf(char data[]) {
- return new String(data);
- }
- /**
- * Returns the string representation of the {@code boolean} argument.
- *
- * @param b a {@code boolean}.
- * @return if the argument is {@code true}, a string equal to
- * {@code "true"} is returned; otherwise, a string equal to
- * {@code "false"} is returned.
- */
- public static String valueOf(boolean b) {
- return b ? "true" : "false";
- }
- /**
- * Returns the string representation of the {@code char}
- * argument.
- *
- * @param c a {@code char}.
- * @return a string of length {@code 1} containing
- * as its single character the argument {@code c}.
- */
- public static String valueOf(char c) {
- char data[] = {c};
- return new String(data, true);
- }
- /**
- * Returns the string representation of the {@code int} argument.
- * <p>
- * The representation is exactly the one returned by the
- * {@code Integer.toString} method of one argument.
- *
- * @param i an {@code int}.
- * @return a string representation of the {@code int} argument.
- * @see java.lang.Integer#toString(int, int)
- */
- public static String valueOf(int i) {
- return Integer.toString(i);
- }
- /**
- * Returns the string representation of the {@code long} argument.
- * <p>
- * The representation is exactly the one returned by the
- * {@code Long.toString} method of one argument.
- *
- * @param l a {@code long}.
- * @return a string representation of the {@code long} argument.
- * @see java.lang.Long#toString(long)
- */
- public static String valueOf(long l) {
- return Long.toString(l);
- }
- /**
- * Returns the string representation of the {@code float} argument.
- * <p>
- * The representation is exactly the one returned by the
- * {@code Float.toString} method of one argument.
- *
- * @param f a {@code float}.
- * @return a string representation of the {@code float} argument.
- * @see java.lang.Float#toString(float)
- */
- public static String valueOf(float f) {
- return Float.toString(f);
- }
- /**
- * Returns the string representation of the {@code double} argument.
- * <p>
- * The representation is exactly the one returned by the
- * {@code Double.toString} method of one argument.
- *
- * @param d a {@code double}.
- * @return a string representation of the {@code double} argument.
- * @see java.lang.Double#toString(double)
- */
- public static String valueOf(double d) {
- return Double.toString(d);
- }
- /**
- * Returns a canonical representation for the string object.
- * <p>
- * A pool of strings, initially empty, is maintained privately by the
- * class {@code String}.
- * <p>
- * When the intern method is invoked, if the pool already contains a
- * string equal to this {@code String} object as determined by
- * the {@link #equals(Object)} method, then the string from the pool is
- * returned. Otherwise, this {@code String} object is added to the
- * pool and a reference to this {@code String} object is returned.
- * <p>
- * It follows that for any two strings {@code s} and {@code t},
- * {@code s.intern() == t.intern()} is {@code true}
- * if and only if {@code s.equals(t)} is {@code true}.
- * <p>
- * All literal strings and string-valued constant expressions are
- * interned. String literals are defined in section 3.10.5 of the
- * <cite>The Java™ Language Specification</cite>.
- *
- * @return a string that has the same contents as this string, but is
- * guaranteed to be from a pool of unique strings.
- */
- public native String intern();
- }
String的代码


再看一下其中的equals(),我们发现首先是看看是不是同一个对象,这个是和Object中的equals()一样的,否则如果是String类型或者继承该类型(不可能,因为String是final修饰的)的我们就比较,看看这两个字符串中的每一个字符是否相等,如果完全相等,则也返回true,这样就弥补了Object的缺点。
- public boolean equals(Object anObject) {
- if (this == anObject) {
- return true;
- }
- if (anObject instanceof String) {
- String anotherString = (String)anObject;
- int n = value.length;
- if (n == anotherString.value.length) {
- char v1[] = value;
- char v2[] = anotherString.value;
- int i = 0;
- while (n-- != 0) {
- if (v1[i] != v2[i])
- return false;
- i++;
- }
- return true;
- }
- }
- return false;
- }
下面是一个比较的例子,对于不使用new来产生的对象,其实存在方法区,作为静态常量处理,只有一个,因此比较起来就相等了;对于new创建出来的就直接放到了堆栈区了,创建了两个对象,因此引用不相等,但是值相等。
- package com.consumer.test;
- public class StringTest {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String i1="这是字符串";
- String i2="这是字符串";
- String i3=new String("这是字符串");
- String i4=new String("这是字符串");
- System.out.println("测试:"+(i1==i2));
- System.out.println("测试:"+(i3==i4));
- System.out.println("测试"+ (i1.equals(i2)));
- System.out.println("测试"+ (i3.equals(i4)));
- }
- }
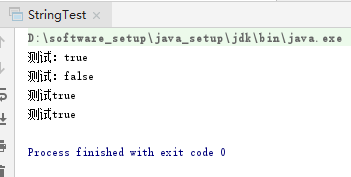
String的valueOf():
- public static String valueOf(Object obj) {
- return (obj == null) ? "null" : obj.toString();
- }
- public String toString() {
- return getClass().getName() + "@" + Integer.toHexString(hashCode());
- }
2.3、Integer中的equals()
最后让我们看看Integer中的equals方法,这里就更加的特殊了。
- /*
- * Copyright (c) 1994, 2013, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
- * ORACLE PROPRIETARY/CONFIDENTIAL. Use is subject to license terms.
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- *
- */
- package java.lang;
- import java.lang.annotation.Native;
- /**
- * The {@code Integer} class wraps a value of the primitive type
- * {@code int} in an object. An object of type {@code Integer}
- * contains a single field whose type is {@code int}.
- *
- * <p>In addition, this class provides several methods for converting
- * an {@code int} to a {@code String} and a {@code String} to an
- * {@code int}, as well as other constants and methods useful when
- * dealing with an {@code int}.
- *
- * <p>Implementation note: The implementations of the "bit twiddling"
- * methods (such as {@link #highestOneBit(int) highestOneBit} and
- * {@link #numberOfTrailingZeros(int) numberOfTrailingZeros}) are
- * based on material from Henry S. Warren, Jr.'s <i>Hacker's
- * Delight</i>, (Addison Wesley, 2002).
- *
- * @author Lee Boynton
- * @author Arthur van Hoff
- * @author Josh Bloch
- * @author Joseph D. Darcy
- * @since JDK1.0
- */
- public final class Integer extends Number implements Comparable<Integer> {
- /**
- * A constant holding the minimum value an {@code int} can
- * have, -2<sup>31</sup>.
- */
- @Native public static final int MIN_VALUE = 0x80000000;
- /**
- * A constant holding the maximum value an {@code int} can
- * have, 2<sup>31</sup>-1.
- */
- @Native public static final int MAX_VALUE = 0x7fffffff;
- /**
- * The {@code Class} instance representing the primitive type
- * {@code int}.
- *
- * @since JDK1.1
- */
- @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
- public static final Class<Integer> TYPE = (Class<Integer>) Class.getPrimitiveClass("int");
- /**
- * All possible chars for representing a number as a String
- */
- final static char[] digits = {
- '0' , '1' , '2' , '3' , '4' , '5' ,
- '6' , '7' , '8' , '9' , 'a' , 'b' ,
- 'c' , 'd' , 'e' , 'f' , 'g' , 'h' ,
- 'i' , 'j' , 'k' , 'l' , 'm' , 'n' ,
- 'o' , 'p' , 'q' , 'r' , 's' , 't' ,
- 'u' , 'v' , 'w' , 'x' , 'y' , 'z'
- };
- /**
- * Returns a string representation of the first argument in the
- * radix specified by the second argument.
- *
- * <p>If the radix is smaller than {@code Character.MIN_RADIX}
- * or larger than {@code Character.MAX_RADIX}, then the radix
- * {@code 10} is used instead.
- *
- * <p>If the first argument is negative, the first element of the
- * result is the ASCII minus character {@code '-'}
- * ({@code '\u005Cu002D'}). If the first argument is not
- * negative, no sign character appears in the result.
- *
- * <p>The remaining characters of the result represent the magnitude
- * of the first argument. If the magnitude is zero, it is
- * represented by a single zero character {@code '0'}
- * ({@code '\u005Cu0030'}); otherwise, the first character of
- * the representation of the magnitude will not be the zero
- * character. The following ASCII characters are used as digits:
- *
- * <blockquote>
- * {@code 0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz}
- * </blockquote>
- *
- * These are {@code '\u005Cu0030'} through
- * {@code '\u005Cu0039'} and {@code '\u005Cu0061'} through
- * {@code '\u005Cu007A'}. If {@code radix} is
- * <var>N</var>, then the first <var>N</var> of these characters
- * are used as radix-<var>N</var> digits in the order shown. Thus,
- * the digits for hexadecimal (radix 16) are
- * {@code 0123456789abcdef}. If uppercase letters are
- * desired, the {@link java.lang.String#toUpperCase()} method may
- * be called on the result:
- *
- * <blockquote>
- * {@code Integer.toString(n, 16).toUpperCase()}
- * </blockquote>
- *
- * @param i an integer to be converted to a string.
- * @param radix the radix to use in the string representation.
- * @return a string representation of the argument in the specified radix.
- * @see java.lang.Character#MAX_RADIX
- * @see java.lang.Character#MIN_RADIX
- */
- public static String toString(int i, int radix) {
- if (radix < Character.MIN_RADIX || radix > Character.MAX_RADIX)
- radix = 10;
- /* Use the faster version */
- if (radix == 10) {
- return toString(i);
- }
- char buf[] = new char[33];
- boolean negative = (i < 0);
- int charPos = 32;
- if (!negative) {
- i = -i;
- }
- while (i <= -radix) {
- buf[charPos--] = digits[-(i % radix)];
- i = i / radix;
- }
- buf[charPos] = digits[-i];
- if (negative) {
- buf[--charPos] = '-';
- }
- return new String(buf, charPos, (33 - charPos));
- }
- /**
- * Returns a string representation of the first argument as an
- * unsigned integer value in the radix specified by the second
- * argument.
- *
- * <p>If the radix is smaller than {@code Character.MIN_RADIX}
- * or larger than {@code Character.MAX_RADIX}, then the radix
- * {@code 10} is used instead.
- *
- * <p>Note that since the first argument is treated as an unsigned
- * value, no leading sign character is printed.
- *
- * <p>If the magnitude is zero, it is represented by a single zero
- * character {@code '0'} ({@code '\u005Cu0030'}); otherwise,
- * the first character of the representation of the magnitude will
- * not be the zero character.
- *
- * <p>The behavior of radixes and the characters used as digits
- * are the same as {@link #toString(int, int) toString}.
- *
- * @param i an integer to be converted to an unsigned string.
- * @param radix the radix to use in the string representation.
- * @return an unsigned string representation of the argument in the specified radix.
- * @see #toString(int, int)
- * @since 1.8
- */
- public static String toUnsignedString(int i, int radix) {
- return Long.toUnsignedString(toUnsignedLong(i), radix);
- }
- /**
- * Returns a string representation of the integer argument as an
- * unsigned integer in base 16.
- *
- * <p>The unsigned integer value is the argument plus 2<sup>32</sup>
- * if the argument is negative; otherwise, it is equal to the
- * argument. This value is converted to a string of ASCII digits
- * in hexadecimal (base 16) with no extra leading
- * {@code 0}s.
- *
- * <p>The value of the argument can be recovered from the returned
- * string {@code s} by calling {@link
- * Integer#parseUnsignedInt(String, int)
- * Integer.parseUnsignedInt(s, 16)}.
- *
- * <p>If the unsigned magnitude is zero, it is represented by a
- * single zero character {@code '0'} ({@code '\u005Cu0030'});
- * otherwise, the first character of the representation of the
- * unsigned magnitude will not be the zero character. The
- * following characters are used as hexadecimal digits:
- *
- * <blockquote>
- * {@code 0123456789abcdef}
- * </blockquote>
- *
- * These are the characters {@code '\u005Cu0030'} through
- * {@code '\u005Cu0039'} and {@code '\u005Cu0061'} through
- * {@code '\u005Cu0066'}. If uppercase letters are
- * desired, the {@link java.lang.String#toUpperCase()} method may
- * be called on the result:
- *
- * <blockquote>
- * {@code Integer.toHexString(n).toUpperCase()}
- * </blockquote>
- *
- * @param i an integer to be converted to a string.
- * @return the string representation of the unsigned integer value
- * represented by the argument in hexadecimal (base 16).
- * @see #parseUnsignedInt(String, int)
- * @see #toUnsignedString(int, int)
- * @since JDK1.0.2
- */
- public static String toHexString(int i) {
- return toUnsignedString0(i, 4);
- }
- /**
- * Returns a string representation of the integer argument as an
- * unsigned integer in base 8.
- *
- * <p>The unsigned integer value is the argument plus 2<sup>32</sup>
- * if the argument is negative; otherwise, it is equal to the
- * argument. This value is converted to a string of ASCII digits
- * in octal (base 8) with no extra leading {@code 0}s.
- *
- * <p>The value of the argument can be recovered from the returned
- * string {@code s} by calling {@link
- * Integer#parseUnsignedInt(String, int)
- * Integer.parseUnsignedInt(s, 8)}.
- *
- * <p>If the unsigned magnitude is zero, it is represented by a
- * single zero character {@code '0'} ({@code '\u005Cu0030'});
- * otherwise, the first character of the representation of the
- * unsigned magnitude will not be the zero character. The
- * following characters are used as octal digits:
- *
- * <blockquote>
- * {@code 01234567}
- * </blockquote>
- *
- * These are the characters {@code '\u005Cu0030'} through
- * {@code '\u005Cu0037'}.
- *
- * @param i an integer to be converted to a string.
- * @return the string representation of the unsigned integer value
- * represented by the argument in octal (base 8).
- * @see #parseUnsignedInt(String, int)
- * @see #toUnsignedString(int, int)
- * @since JDK1.0.2
- */
- public static String toOctalString(int i) {
- return toUnsignedString0(i, 3);
- }
- /**
- * Returns a string representation of the integer argument as an
- * unsigned integer in base 2.
- *
- * <p>The unsigned integer value is the argument plus 2<sup>32</sup>
- * if the argument is negative; otherwise it is equal to the
- * argument. This value is converted to a string of ASCII digits
- * in binary (base 2) with no extra leading {@code 0}s.
- *
- * <p>The value of the argument can be recovered from the returned
- * string {@code s} by calling {@link
- * Integer#parseUnsignedInt(String, int)
- * Integer.parseUnsignedInt(s, 2)}.
- *
- * <p>If the unsigned magnitude is zero, it is represented by a
- * single zero character {@code '0'} ({@code '\u005Cu0030'});
- * otherwise, the first character of the representation of the
- * unsigned magnitude will not be the zero character. The
- * characters {@code '0'} ({@code '\u005Cu0030'}) and {@code
- * '1'} ({@code '\u005Cu0031'}) are used as binary digits.
- *
- * @param i an integer to be converted to a string.
- * @return the string representation of the unsigned integer value
- * represented by the argument in binary (base 2).
- * @see #parseUnsignedInt(String, int)
- * @see #toUnsignedString(int, int)
- * @since JDK1.0.2
- */
- public static String toBinaryString(int i) {
- return toUnsignedString0(i, 1);
- }
- /**
- * Convert the integer to an unsigned number.
- */
- private static String toUnsignedString0(int val, int shift) {
- // assert shift > 0 && shift <=5 : "Illegal shift value";
- int mag = Integer.SIZE - Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(val);
- int chars = Math.max(((mag + (shift - 1)) / shift), 1);
- char[] buf = new char[chars];
- formatUnsignedInt(val, shift, buf, 0, chars);
- // Use special constructor which takes over "buf".
- return new String(buf, true);
- }
- /**
- * Format a long (treated as unsigned) into a character buffer.
- * @param val the unsigned int to format
- * @param shift the log2 of the base to format in (4 for hex, 3 for octal, 1 for binary)
- * @param buf the character buffer to write to
- * @param offset the offset in the destination buffer to start at
- * @param len the number of characters to write
- * @return the lowest character location used
- */
- static int formatUnsignedInt(int val, int shift, char[] buf, int offset, int len) {
- int charPos = len;
- int radix = 1 << shift;
- int mask = radix - 1;
- do {
- buf[offset + --charPos] = Integer.digits[val & mask];
- val >>>= shift;
- } while (val != 0 && charPos > 0);
- return charPos;
- }
- final static char [] DigitTens = {
- '0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0',
- '1', '1', '1', '1', '1', '1', '1', '1', '1', '1',
- '2', '2', '2', '2', '2', '2', '2', '2', '2', '2',
- '3', '3', '3', '3', '3', '3', '3', '3', '3', '3',
- '4', '4', '4', '4', '4', '4', '4', '4', '4', '4',
- '5', '5', '5', '5', '5', '5', '5', '5', '5', '5',
- '6', '6', '6', '6', '6', '6', '6', '6', '6', '6',
- '7', '7', '7', '7', '7', '7', '7', '7', '7', '7',
- '8', '8', '8', '8', '8', '8', '8', '8', '8', '8',
- '9', '9', '9', '9', '9', '9', '9', '9', '9', '9',
- } ;
- final static char [] DigitOnes = {
- '0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',
- '0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',
- '0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',
- '0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',
- '0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',
- '0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',
- '0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',
- '0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',
- '0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',
- '0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',
- } ;
- // I use the "invariant division by multiplication" trick to
- // accelerate Integer.toString. In particular we want to
- // avoid division by 10.
- //
- // The "trick" has roughly the same performance characteristics
- // as the "classic" Integer.toString code on a non-JIT VM.
- // The trick avoids .rem and .div calls but has a longer code
- // path and is thus dominated by dispatch overhead. In the
- // JIT case the dispatch overhead doesn't exist and the
- // "trick" is considerably faster than the classic code.
- //
- // TODO-FIXME: convert (x * 52429) into the equiv shift-add
- // sequence.
- //
- // RE: Division by Invariant Integers using Multiplication
- // T Gralund, P Montgomery
- // ACM PLDI 1994
- //
- /**
- * Returns a {@code String} object representing the
- * specified integer. The argument is converted to signed decimal
- * representation and returned as a string, exactly as if the
- * argument and radix 10 were given as arguments to the {@link
- * #toString(int, int)} method.
- *
- * @param i an integer to be converted.
- * @return a string representation of the argument in base 10.
- */
- public static String toString(int i) {
- if (i == Integer.MIN_VALUE)
- return "-2147483648";
- int size = (i < 0) ? stringSize(-i) + 1 : stringSize(i);
- char[] buf = new char[size];
- getChars(i, size, buf);
- return new String(buf, true);
- }
- /**
- * Returns a string representation of the argument as an unsigned
- * decimal value.
- *
- * The argument is converted to unsigned decimal representation
- * and returned as a string exactly as if the argument and radix
- * 10 were given as arguments to the {@link #toUnsignedString(int,
- * int)} method.
- *
- * @param i an integer to be converted to an unsigned string.
- * @return an unsigned string representation of the argument.
- * @see #toUnsignedString(int, int)
- * @since 1.8
- */
- public static String toUnsignedString(int i) {
- return Long.toString(toUnsignedLong(i));
- }
- /**
- * Places characters representing the integer i into the
- * character array buf. The characters are placed into
- * the buffer backwards starting with the least significant
- * digit at the specified index (exclusive), and working
- * backwards from there.
- *
- * Will fail if i == Integer.MIN_VALUE
- */
- static void getChars(int i, int index, char[] buf) {
- int q, r;
- int charPos = index;
- char sign = 0;
- if (i < 0) {
- sign = '-';
- i = -i;
- }
- // Generate two digits per iteration
- while (i >= 65536) {
- q = i / 100;
- // really: r = i - (q * 100);
- r = i - ((q << 6) + (q << 5) + (q << 2));
- i = q;
- buf [--charPos] = DigitOnes[r];
- buf [--charPos] = DigitTens[r];
- }
- // Fall thru to fast mode for smaller numbers
- // assert(i <= 65536, i);
- for (;;) {
- q = (i * 52429) >>> (16+3);
- r = i - ((q << 3) + (q << 1)); // r = i-(q*10) ...
- buf [--charPos] = digits [r];
- i = q;
- if (i == 0) break;
- }
- if (sign != 0) {
- buf [--charPos] = sign;
- }
- }
- final static int [] sizeTable = { 9, 99, 999, 9999, 99999, 999999, 9999999,
- 99999999, 999999999, Integer.MAX_VALUE };
- // Requires positive x
- static int stringSize(int x) {
- for (int i=0; ; i++)
- if (x <= sizeTable[i])
- return i+1;
- }
- /**
- * Parses the string argument as a signed integer in the radix
- * specified by the second argument. The characters in the string
- * must all be digits of the specified radix (as determined by
- * whether {@link java.lang.Character#digit(char, int)} returns a
- * nonnegative value), except that the first character may be an
- * ASCII minus sign {@code '-'} ({@code '\u005Cu002D'}) to
- * indicate a negative value or an ASCII plus sign {@code '+'}
- * ({@code '\u005Cu002B'}) to indicate a positive value. The
- * resulting integer value is returned.
- *
- * <p>An exception of type {@code NumberFormatException} is
- * thrown if any of the following situations occurs:
- * <ul>
- * <li>The first argument is {@code null} or is a string of
- * length zero.
- *
- * <li>The radix is either smaller than
- * {@link java.lang.Character#MIN_RADIX} or
- * larger than {@link java.lang.Character#MAX_RADIX}.
- *
- * <li>Any character of the string is not a digit of the specified
- * radix, except that the first character may be a minus sign
- * {@code '-'} ({@code '\u005Cu002D'}) or plus sign
- * {@code '+'} ({@code '\u005Cu002B'}) provided that the
- * string is longer than length 1.
- *
- * <li>The value represented by the string is not a value of type
- * {@code int}.
- * </ul>
- *
- * <p>Examples:
- * <blockquote><pre>
- * parseInt("0", 10) returns 0
- * parseInt("473", 10) returns 473
- * parseInt("+42", 10) returns 42
- * parseInt("-0", 10) returns 0
- * parseInt("-FF", 16) returns -255
- * parseInt("1100110", 2) returns 102
- * parseInt("2147483647", 10) returns 2147483647
- * parseInt("-2147483648", 10) returns -2147483648
- * parseInt("2147483648", 10) throws a NumberFormatException
- * parseInt("99", 8) throws a NumberFormatException
- * parseInt("Kona", 10) throws a NumberFormatException
- * parseInt("Kona", 27) returns 411787
- * </pre></blockquote>
- *
- * @param s the {@code String} containing the integer
- * representation to be parsed
- * @param radix the radix to be used while parsing {@code s}.
- * @return the integer represented by the string argument in the
- * specified radix.
- * @exception NumberFormatException if the {@code String}
- * does not contain a parsable {@code int}.
- */
- public static int parseInt(String s, int radix)
- throws NumberFormatException
- {
- /*
- * WARNING: This method may be invoked early during VM initialization
- * before IntegerCache is initialized. Care must be taken to not use
- * the valueOf method.
- */
- if (s == null) {
- throw new NumberFormatException("null");
- }
- if (radix < Character.MIN_RADIX) {
- throw new NumberFormatException("radix " + radix +
- " less than Character.MIN_RADIX");
- }
- if (radix > Character.MAX_RADIX) {
- throw new NumberFormatException("radix " + radix +
- " greater than Character.MAX_RADIX");
- }
- int result = 0;
- boolean negative = false;
- int i = 0, len = s.length();
- int limit = -Integer.MAX_VALUE;
- int multmin;
- int digit;
- if (len > 0) {
- char firstChar = s.charAt(0);
- if (firstChar < '0') { // Possible leading "+" or "-"
- if (firstChar == '-') {
- negative = true;
- limit = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
- } else if (firstChar != '+')
- throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
- if (len == 1) // Cannot have lone "+" or "-"
- throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
- i++;
- }
- multmin = limit / radix;
- while (i < len) {
- // Accumulating negatively avoids surprises near MAX_VALUE
- digit = Character.digit(s.charAt(i++),radix);
- if (digit < 0) {
- throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
- }
- if (result < multmin) {
- throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
- }
- result *= radix;
- if (result < limit + digit) {
- throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
- }
- result -= digit;
- }
- } else {
- throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
- }
- return negative ? result : -result;
- }
- /**
- * Parses the string argument as a signed decimal integer. The
- * characters in the string must all be decimal digits, except
- * that the first character may be an ASCII minus sign {@code '-'}
- * ({@code '\u005Cu002D'}) to indicate a negative value or an
- * ASCII plus sign {@code '+'} ({@code '\u005Cu002B'}) to
- * indicate a positive value. The resulting integer value is
- * returned, exactly as if the argument and the radix 10 were
- * given as arguments to the {@link #parseInt(java.lang.String,
- * int)} method.
- *
- * @param s a {@code String} containing the {@code int}
- * representation to be parsed
- * @return the integer value represented by the argument in decimal.
- * @exception NumberFormatException if the string does not contain a
- * parsable integer.
- */
- public static int parseInt(String s) throws NumberFormatException {
- return parseInt(s,10);
- }
- /**
- * Parses the string argument as an unsigned integer in the radix
- * specified by the second argument. An unsigned integer maps the
- * values usually associated with negative numbers to positive
- * numbers larger than {@code MAX_VALUE}.
- *
- * The characters in the string must all be digits of the
- * specified radix (as determined by whether {@link
- * java.lang.Character#digit(char, int)} returns a nonnegative
- * value), except that the first character may be an ASCII plus
- * sign {@code '+'} ({@code '\u005Cu002B'}). The resulting
- * integer value is returned.
- *
- * <p>An exception of type {@code NumberFormatException} is
- * thrown if any of the following situations occurs:
- * <ul>
- * <li>The first argument is {@code null} or is a string of
- * length zero.
- *
- * <li>The radix is either smaller than
- * {@link java.lang.Character#MIN_RADIX} or
- * larger than {@link java.lang.Character#MAX_RADIX}.
- *
- * <li>Any character of the string is not a digit of the specified
- * radix, except that the first character may be a plus sign
- * {@code '+'} ({@code '\u005Cu002B'}) provided that the
- * string is longer than length 1.
- *
- * <li>The value represented by the string is larger than the
- * largest unsigned {@code int}, 2<sup>32</sup>-1.
- *
- * </ul>
- *
- *
- * @param s the {@code String} containing the unsigned integer
- * representation to be parsed
- * @param radix the radix to be used while parsing {@code s}.
- * @return the integer represented by the string argument in the
- * specified radix.
- * @throws NumberFormatException if the {@code String}
- * does not contain a parsable {@code int}.
- * @since 1.8
- */
- public static int parseUnsignedInt(String s, int radix)
- throws NumberFormatException {
- if (s == null) {
- throw new NumberFormatException("null");
- }
- int len = s.length();
- if (len > 0) {
- char firstChar = s.charAt(0);
- if (firstChar == '-') {
- throw new
- NumberFormatException(String.format("Illegal leading minus sign " +
- "on unsigned string %s.", s));
- } else {
- if (len <= 5 || // Integer.MAX_VALUE in Character.MAX_RADIX is 6 digits
- (radix == 10 && len <= 9) ) { // Integer.MAX_VALUE in base 10 is 10 digits
- return parseInt(s, radix);
- } else {
- long ell = Long.parseLong(s, radix);
- if ((ell & 0xffff_ffff_0000_0000L) == 0) {
- return (int) ell;
- } else {
- throw new
- NumberFormatException(String.format("String value %s exceeds " +
- "range of unsigned int.", s));
- }
- }
- }
- } else {
- throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
- }
- }
- /**
- * Parses the string argument as an unsigned decimal integer. The
- * characters in the string must all be decimal digits, except
- * that the first character may be an an ASCII plus sign {@code
- * '+'} ({@code '\u005Cu002B'}). The resulting integer value
- * is returned, exactly as if the argument and the radix 10 were
- * given as arguments to the {@link
- * #parseUnsignedInt(java.lang.String, int)} method.
- *
- * @param s a {@code String} containing the unsigned {@code int}
- * representation to be parsed
- * @return the unsigned integer value represented by the argument in decimal.
- * @throws NumberFormatException if the string does not contain a
- * parsable unsigned integer.
- * @since 1.8
- */
- public static int parseUnsignedInt(String s) throws NumberFormatException {
- return parseUnsignedInt(s, 10);
- }
- /**
- * Returns an {@code Integer} object holding the value
- * extracted from the specified {@code String} when parsed
- * with the radix given by the second argument. The first argument
- * is interpreted as representing a signed integer in the radix
- * specified by the second argument, exactly as if the arguments
- * were given to the {@link #parseInt(java.lang.String, int)}
- * method. The result is an {@code Integer} object that
- * represents the integer value specified by the string.
- *
- * <p>In other words, this method returns an {@code Integer}
- * object equal to the value of:
- *
- * <blockquote>
- * {@code new Integer(Integer.parseInt(s, radix))}
- * </blockquote>
- *
- * @param s the string to be parsed.
- * @param radix the radix to be used in interpreting {@code s}
- * @return an {@code Integer} object holding the value
- * represented by the string argument in the specified
- * radix.
- * @exception NumberFormatException if the {@code String}
- * does not contain a parsable {@code int}.
- */
- public static Integer valueOf(String s, int radix) throws NumberFormatException {
- return Integer.valueOf(parseInt(s,radix));
- }
- /**
- * Returns an {@code Integer} object holding the
- * value of the specified {@code String}. The argument is
- * interpreted as representing a signed decimal integer, exactly
- * as if the argument were given to the {@link
- * #parseInt(java.lang.String)} method. The result is an
- * {@code Integer} object that represents the integer value
- * specified by the string.
- *
- * <p>In other words, this method returns an {@code Integer}
- * object equal to the value of:
- *
- * <blockquote>
- * {@code new Integer(Integer.parseInt(s))}
- * </blockquote>
- *
- * @param s the string to be parsed.
- * @return an {@code Integer} object holding the value
- * represented by the string argument.
- * @exception NumberFormatException if the string cannot be parsed
- * as an integer.
- */
- public static Integer valueOf(String s) throws NumberFormatException {
- return Integer.valueOf(parseInt(s, 10));
- }
- /**
- * Cache to support the object identity semantics of autoboxing for values between
- * -128 and 127 (inclusive) as required by JLS.
- *
- * The cache is initialized on first usage. The size of the cache
- * may be controlled by the {@code -XX:AutoBoxCacheMax=<size>} option.
- * During VM initialization, java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high property
- * may be set and saved in the private system properties in the
- * sun.misc.VM class.
- */
- private static class IntegerCache {
- static final int low = -128;
- static final int high;
- static final Integer cache[];
- static {
- // high value may be configured by property
- int h = 127;
- String integerCacheHighPropValue =
- sun.misc.VM.getSavedProperty("java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high");
- if (integerCacheHighPropValue != null) {
- try {
- int i = parseInt(integerCacheHighPropValue);
- i = Math.max(i, 127);
- // Maximum array size is Integer.MAX_VALUE
- h = Math.min(i, Integer.MAX_VALUE - (-low) -1);
- } catch( NumberFormatException nfe) {
- // If the property cannot be parsed into an int, ignore it.
- }
- }
- high = h;
- cache = new Integer[(high - low) + 1];
- int j = low;
- for(int k = 0; k < cache.length; k++)
- cache[k] = new Integer(j++);
- // range [-128, 127] must be interned (JLS7 5.1.7)
- assert IntegerCache.high >= 127;
- }
- private IntegerCache() {}
- }
- /**
- * Returns an {@code Integer} instance representing the specified
- * {@code int} value. If a new {@code Integer} instance is not
- * required, this method should generally be used in preference to
- * the constructor {@link #Integer(int)}, as this method is likely
- * to yield significantly better space and time performance by
- * caching frequently requested values.
- *
- * This method will always cache values in the range -128 to 127,
- * inclusive, and may cache other values outside of this range.
- *
- * @param i an {@code int} value.
- * @return an {@code Integer} instance representing {@code i}.
- * @since 1.5
- */
- public static Integer valueOf(int i) {
- if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high)
- return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)];
- return new Integer(i);
- }
- /**
- * The value of the {@code Integer}.
- *
- * @serial
- */
- private final int value;
- /**
- * Constructs a newly allocated {@code Integer} object that
- * represents the specified {@code int} value.
- *
- * @param value the value to be represented by the
- * {@code Integer} object.
- */
- public Integer(int value) {
- this.value = value;
- }
- /**
- * Constructs a newly allocated {@code Integer} object that
- * represents the {@code int} value indicated by the
- * {@code String} parameter. The string is converted to an
- * {@code int} value in exactly the manner used by the
- * {@code parseInt} method for radix 10.
- *
- * @param s the {@code String} to be converted to an
- * {@code Integer}.
- * @exception NumberFormatException if the {@code String} does not
- * contain a parsable integer.
- * @see java.lang.Integer#parseInt(java.lang.String, int)
- */
- public Integer(String s) throws NumberFormatException {
- this.value = parseInt(s, 10);
- }
- /**
- * Returns the value of this {@code Integer} as a {@code byte}
- * after a narrowing primitive conversion.
- * @jls 5.1.3 Narrowing Primitive Conversions
- */
- public byte byteValue() {
- return (byte)value;
- }
- /**
- * Returns the value of this {@code Integer} as a {@code short}
- * after a narrowing primitive conversion.
- * @jls 5.1.3 Narrowing Primitive Conversions
- */
- public short shortValue() {
- return (short)value;
- }
- /**
- * Returns the value of this {@code Integer} as an
- * {@code int}.
- */
- public int intValue() {
- return value;
- }
- /**
- * Returns the value of this {@code Integer} as a {@code long}
- * after a widening primitive conversion.
- * @jls 5.1.2 Widening Primitive Conversions
- * @see Integer#toUnsignedLong(int)
- */
- public long longValue() {
- return (long)value;
- }
- /**
- * Returns the value of this {@code Integer} as a {@code float}
- * after a widening primitive conversion.
- * @jls 5.1.2 Widening Primitive Conversions
- */
- public float floatValue() {
- return (float)value;
- }
- /**
- * Returns the value of this {@code Integer} as a {@code double}
- * after a widening primitive conversion.
- * @jls 5.1.2 Widening Primitive Conversions
- */
- public double doubleValue() {
- return (double)value;
- }
- /**
- * Returns a {@code String} object representing this
- * {@code Integer}'s value. The value is converted to signed
- * decimal representation and returned as a string, exactly as if
- * the integer value were given as an argument to the {@link
- * java.lang.Integer#toString(int)} method.
- *
- * @return a string representation of the value of this object in
- * base 10.
- */
- public String toString() {
- return toString(value);
- }
- /**
- * Returns a hash code for this {@code Integer}.
- *
- * @return a hash code value for this object, equal to the
- * primitive {@code int} value represented by this
- * {@code Integer} object.
- */
- @Override
- public int hashCode() {
- return Integer.hashCode(value);
- }
- /**
- * Returns a hash code for a {@code int} value; compatible with
- * {@code Integer.hashCode()}.
- *
- * @param value the value to hash
- * @since 1.8
- *
- * @return a hash code value for a {@code int} value.
- */
- public static int hashCode(int value) {
- return value;
- }
- /**
- * Compares this object to the specified object. The result is
- * {@code true} if and only if the argument is not
- * {@code null} and is an {@code Integer} object that
- * contains the same {@code int} value as this object.
- *
- * @param obj the object to compare with.
- * @return {@code true} if the objects are the same;
- * {@code false} otherwise.
- */
- public boolean equals(Object obj) {
- if (obj instanceof Integer) {
- return value == ((Integer)obj).intValue();
- }
- return false;
- }
- /**
- * Determines the integer value of the system property with the
- * specified name.
- *
- * <p>The first argument is treated as the name of a system
- * property. System properties are accessible through the {@link
- * java.lang.System#getProperty(java.lang.String)} method. The
- * string value of this property is then interpreted as an integer
- * value using the grammar supported by {@link Integer#decode decode} and
- * an {@code Integer} object representing this value is returned.
- *
- * <p>If there is no property with the specified name, if the
- * specified name is empty or {@code null}, or if the property
- * does not have the correct numeric format, then {@code null} is
- * returned.
- *
- * <p>In other words, this method returns an {@code Integer}
- * object equal to the value of:
- *
- * <blockquote>
- * {@code getInteger(nm, null)}
- * </blockquote>
- *
- * @param nm property name.
- * @return the {@code Integer} value of the property.
- * @throws SecurityException for the same reasons as
- * {@link System#getProperty(String) System.getProperty}
- * @see java.lang.System#getProperty(java.lang.String)
- * @see java.lang.System#getProperty(java.lang.String, java.lang.String)
- */
- public static Integer getInteger(String nm) {
- return getInteger(nm, null);
- }
- /**
- * Determines the integer value of the system property with the
- * specified name.
- *
- * <p>The first argument is treated as the name of a system
- * property. System properties are accessible through the {@link
- * java.lang.System#getProperty(java.lang.String)} method. The
- * string value of this property is then interpreted as an integer
- * value using the grammar supported by {@link Integer#decode decode} and
- * an {@code Integer} object representing this value is returned.
- *
- * <p>The second argument is the default value. An {@code Integer} object
- * that represents the value of the second argument is returned if there
- * is no property of the specified name, if the property does not have
- * the correct numeric format, or if the specified name is empty or
- * {@code null}.
- *
- * <p>In other words, this method returns an {@code Integer} object
- * equal to the value of:
- *
- * <blockquote>
- * {@code getInteger(nm, new Integer(val))}
- * </blockquote>
- *
- * but in practice it may be implemented in a manner such as:
- *
- * <blockquote><pre>
- * Integer result = getInteger(nm, null);
- * return (result == null) ? new Integer(val) : result;
- * </pre></blockquote>
- *
- * to avoid the unnecessary allocation of an {@code Integer}
- * object when the default value is not needed.
- *
- * @param nm property name.
- * @param val default value.
- * @return the {@code Integer} value of the property.
- * @throws SecurityException for the same reasons as
- * {@link System#getProperty(String) System.getProperty}
- * @see java.lang.System#getProperty(java.lang.String)
- * @see java.lang.System#getProperty(java.lang.String, java.lang.String)
- */
- public static Integer getInteger(String nm, int val) {
- Integer result = getInteger(nm, null);
- return (result == null) ? Integer.valueOf(val) : result;
- }
- /**
- * Returns the integer value of the system property with the
- * specified name. The first argument is treated as the name of a
- * system property. System properties are accessible through the
- * {@link java.lang.System#getProperty(java.lang.String)} method.
- * The string value of this property is then interpreted as an
- * integer value, as per the {@link Integer#decode decode} method,
- * and an {@code Integer} object representing this value is
- * returned; in summary:
- *
- * <ul><li>If the property value begins with the two ASCII characters
- * {@code 0x} or the ASCII character {@code #}, not
- * followed by a minus sign, then the rest of it is parsed as a
- * hexadecimal integer exactly as by the method
- * {@link #valueOf(java.lang.String, int)} with radix 16.
- * <li>If the property value begins with the ASCII character
- * {@code 0} followed by another character, it is parsed as an
- * octal integer exactly as by the method
- * {@link #valueOf(java.lang.String, int)} with radix 8.
- * <li>Otherwise, the property value is parsed as a decimal integer
- * exactly as by the method {@link #valueOf(java.lang.String, int)}
- * with radix 10.
- * </ul>
- *
- * <p>The second argument is the default value. The default value is
- * returned if there is no property of the specified name, if the
- * property does not have the correct numeric format, or if the
- * specified name is empty or {@code null}.
- *
- * @param nm property name.
- * @param val default value.
- * @return the {@code Integer} value of the property.
- * @throws SecurityException for the same reasons as
- * {@link System#getProperty(String) System.getProperty}
- * @see System#getProperty(java.lang.String)
- * @see System#getProperty(java.lang.String, java.lang.String)
- */
- public static Integer getInteger(String nm, Integer val) {
- String v = null;
- try {
- v = System.getProperty(nm);
- } catch (IllegalArgumentException | NullPointerException e) {
- }
- if (v != null) {
- try {
- return Integer.decode(v);
- } catch (NumberFormatException e) {
- }
- }
- return val;
- }
- /**
- * Decodes a {@code String} into an {@code Integer}.
- * Accepts decimal, hexadecimal, and octal numbers given
- * by the following grammar:
- *
- * <blockquote>
- * <dl>
- * <dt><i>DecodableString:</i>
- * <dd><i>Sign<sub>opt</sub> DecimalNumeral</i>
- * <dd><i>Sign<sub>opt</sub></i> {@code 0x} <i>HexDigits</i>
- * <dd><i>Sign<sub>opt</sub></i> {@code 0X} <i>HexDigits</i>
- * <dd><i>Sign<sub>opt</sub></i> {@code #} <i>HexDigits</i>
- * <dd><i>Sign<sub>opt</sub></i> {@code 0} <i>OctalDigits</i>
- *
- * <dt><i>Sign:</i>
- * <dd>{@code -}
- * <dd>{@code +}
- * </dl>
- * </blockquote>
- *
- * <i>DecimalNumeral</i>, <i>HexDigits</i>, and <i>OctalDigits</i>
- * are as defined in section 3.10.1 of
- * <cite>The Java™ Language Specification</cite>,
- * except that underscores are not accepted between digits.
- *
- * <p>The sequence of characters following an optional
- * sign and/or radix specifier ("{@code 0x}", "{@code 0X}",
- * "{@code #}", or leading zero) is parsed as by the {@code
- * Integer.parseInt} method with the indicated radix (10, 16, or
- * 8). This sequence of characters must represent a positive
- * value or a {@link NumberFormatException} will be thrown. The
- * result is negated if first character of the specified {@code
- * String} is the minus sign. No whitespace characters are
- * permitted in the {@code String}.
- *
- * @param nm the {@code String} to decode.
- * @return an {@code Integer} object holding the {@code int}
- * value represented by {@code nm}
- * @exception NumberFormatException if the {@code String} does not
- * contain a parsable integer.
- * @see java.lang.Integer#parseInt(java.lang.String, int)
- */
- public static Integer decode(String nm) throws NumberFormatException {
- int radix = 10;
- int index = 0;
- boolean negative = false;
- Integer result;
- if (nm.length() == 0)
- throw new NumberFormatException("Zero length string");
- char firstChar = nm.charAt(0);
- // Handle sign, if present
- if (firstChar == '-') {
- negative = true;
- index++;
- } else if (firstChar == '+')
- index++;
- // Handle radix specifier, if present
- if (nm.startsWith("0x", index) || nm.startsWith("0X", index)) {
- index += 2;
- radix = 16;
- }
- else if (nm.startsWith("#", index)) {
- index ++;
- radix = 16;
- }
- else if (nm.startsWith("0", index) && nm.length() > 1 + index) {
- index ++;
- radix = 8;
- }
- if (nm.startsWith("-", index) || nm.startsWith("+", index))
- throw new NumberFormatException("Sign character in wrong position");
- try {
- result = Integer.valueOf(nm.substring(index), radix);
- result = negative ? Integer.valueOf(-result.intValue()) : result;
- } catch (NumberFormatException e) {
- // If number is Integer.MIN_VALUE, we'll end up here. The next line
- // handles this case, and causes any genuine format error to be
- // rethrown.
- String constant = negative ? ("-" + nm.substring(index))
- : nm.substring(index);
- result = Integer.valueOf(constant, radix);
- }
- return result;
- }
- /**
- * Compares two {@code Integer} objects numerically.
- *
- * @param anotherInteger the {@code Integer} to be compared.
- * @return the value {@code 0} if this {@code Integer} is
- * equal to the argument {@code Integer}; a value less than
- * {@code 0} if this {@code Integer} is numerically less
- * than the argument {@code Integer}; and a value greater
- * than {@code 0} if this {@code Integer} is numerically
- * greater than the argument {@code Integer} (signed
- * comparison).
- * @since 1.2
- */
- public int compareTo(Integer anotherInteger) {
- return compare(this.value, anotherInteger.value);
- }
- /**
- * Compares two {@code int} values numerically.
- * The value returned is identical to what would be returned by:
- * <pre>
- * Integer.valueOf(x).compareTo(Integer.valueOf(y))
- * </pre>
- *
- * @param x the first {@code int} to compare
- * @param y the second {@code int} to compare
- * @return the value {@code 0} if {@code x == y};
- * a value less than {@code 0} if {@code x < y}; and
- * a value greater than {@code 0} if {@code x > y}
- * @since 1.7
- */
- public static int compare(int x, int y) {
- return (x < y) ? -1 : ((x == y) ? 0 : 1);
- }
- /**
- * Compares two {@code int} values numerically treating the values
- * as unsigned.
- *
- * @param x the first {@code int} to compare
- * @param y the second {@code int} to compare
- * @return the value {@code 0} if {@code x == y}; a value less
- * than {@code 0} if {@code x < y} as unsigned values; and
- * a value greater than {@code 0} if {@code x > y} as
- * unsigned values
- * @since 1.8
- */
- public static int compareUnsigned(int x, int y) {
- return compare(x + MIN_VALUE, y + MIN_VALUE);
- }
- /**
- * Converts the argument to a {@code long} by an unsigned
- * conversion. In an unsigned conversion to a {@code long}, the
- * high-order 32 bits of the {@code long} are zero and the
- * low-order 32 bits are equal to the bits of the integer
- * argument.
- *
- * Consequently, zero and positive {@code int} values are mapped
- * to a numerically equal {@code long} value and negative {@code
- * int} values are mapped to a {@code long} value equal to the
- * input plus 2<sup>32</sup>.
- *
- * @param x the value to convert to an unsigned {@code long}
- * @return the argument converted to {@code long} by an unsigned
- * conversion
- * @since 1.8
- */
- public static long toUnsignedLong(int x) {
- return ((long) x) & 0xffffffffL;
- }
- /**
- * Returns the unsigned quotient of dividing the first argument by
- * the second where each argument and the result is interpreted as
- * an unsigned value.
- *
- * <p>Note that in two's complement arithmetic, the three other
- * basic arithmetic operations of add, subtract, and multiply are
- * bit-wise identical if the two operands are regarded as both
- * being signed or both being unsigned. Therefore separate {@code
- * addUnsigned}, etc. methods are not provided.
- *
- * @param dividend the value to be divided
- * @param divisor the value doing the dividing
- * @return the unsigned quotient of the first argument divided by
- * the second argument
- * @see #remainderUnsigned
- * @since 1.8
- */
- public static int divideUnsigned(int dividend, int divisor) {
- // In lieu of tricky code, for now just use long arithmetic.
- return (int)(toUnsignedLong(dividend) / toUnsignedLong(divisor));
- }
- /**
- * Returns the unsigned remainder from dividing the first argument
- * by the second where each argument and the result is interpreted
- * as an unsigned value.
- *
- * @param dividend the value to be divided
- * @param divisor the value doing the dividing
- * @return the unsigned remainder of the first argument divided by
- * the second argument
- * @see #divideUnsigned
- * @since 1.8
- */
- public static int remainderUnsigned(int dividend, int divisor) {
- // In lieu of tricky code, for now just use long arithmetic.
- return (int)(toUnsignedLong(dividend) % toUnsignedLong(divisor));
- }
- // Bit twiddling
- /**
- * The number of bits used to represent an {@code int} value in two's
- * complement binary form.
- *
- * @since 1.5
- */
- @Native public static final int SIZE = 32;
- /**
- * The number of bytes used to represent a {@code int} value in two's
- * complement binary form.
- *
- * @since 1.8
- */
- public static final int BYTES = SIZE / Byte.SIZE;
- /**
- * Returns an {@code int} value with at most a single one-bit, in the
- * position of the highest-order ("leftmost") one-bit in the specified
- * {@code int} value. Returns zero if the specified value has no
- * one-bits in its two's complement binary representation, that is, if it
- * is equal to zero.
- *
- * @param i the value whose highest one bit is to be computed
- * @return an {@code int} value with a single one-bit, in the position
- * of the highest-order one-bit in the specified value, or zero if
- * the specified value is itself equal to zero.
- * @since 1.5
- */
- public static int highestOneBit(int i) {
- // HD, Figure 3-1
- i |= (i >> 1);
- i |= (i >> 2);
- i |= (i >> 4);
- i |= (i >> 8);
- i |= (i >> 16);
- return i - (i >>> 1);
- }
- /**
- * Returns an {@code int} value with at most a single one-bit, in the
- * position of the lowest-order ("rightmost") one-bit in the specified
- * {@code int} value. Returns zero if the specified value has no
- * one-bits in its two's complement binary representation, that is, if it
- * is equal to zero.
- *
- * @param i the value whose lowest one bit is to be computed
- * @return an {@code int} value with a single one-bit, in the position
- * of the lowest-order one-bit in the specified value, or zero if
- * the specified value is itself equal to zero.
- * @since 1.5
- */
- public static int lowestOneBit(int i) {
- // HD, Section 2-1
- return i & -i;
- }
- /**
- * Returns the number of zero bits preceding the highest-order
- * ("leftmost") one-bit in the two's complement binary representation
- * of the specified {@code int} value. Returns 32 if the
- * specified value has no one-bits in its two's complement representation,
- * in other words if it is equal to zero.
- *
- * <p>Note that this method is closely related to the logarithm base 2.
- * For all positive {@code int} values x:
- * <ul>
- * <li>floor(log<sub>2</sub>(x)) = {@code 31 - numberOfLeadingZeros(x)}
- * <li>ceil(log<sub>2</sub>(x)) = {@code 32 - numberOfLeadingZeros(x - 1)}
- * </ul>
- *
- * @param i the value whose number of leading zeros is to be computed
- * @return the number of zero bits preceding the highest-order
- * ("leftmost") one-bit in the two's complement binary representation
- * of the specified {@code int} value, or 32 if the value
- * is equal to zero.
- * @since 1.5
- */
- public static int numberOfLeadingZeros(int i) {
- // HD, Figure 5-6
- if (i == 0)
- return 32;
- int n = 1;
- if (i >>> 16 == 0) { n += 16; i <<= 16; }
- if (i >>> 24 == 0) { n += 8; i <<= 8; }
- if (i >>> 28 == 0) { n += 4; i <<= 4; }
- if (i >>> 30 == 0) { n += 2; i <<= 2; }
- n -= i >>> 31;
- return n;
- }
- /**
- * Returns the number of zero bits following the lowest-order ("rightmost")
- * one-bit in the two's complement binary representation of the specified
- * {@code int} value. Returns 32 if the specified value has no
- * one-bits in its two's complement representation, in other words if it is
- * equal to zero.
- *
- * @param i the value whose number of trailing zeros is to be computed
- * @return the number of zero bits following the lowest-order ("rightmost")
- * one-bit in the two's complement binary representation of the
- * specified {@code int} value, or 32 if the value is equal
- * to zero.
- * @since 1.5
- */
- public static int numberOfTrailingZeros(int i) {
- // HD, Figure 5-14
- int y;
- if (i == 0) return 32;
- int n = 31;
- y = i <<16; if (y != 0) { n = n -16; i = y; }
- y = i << 8; if (y != 0) { n = n - 8; i = y; }
- y = i << 4; if (y != 0) { n = n - 4; i = y; }
- y = i << 2; if (y != 0) { n = n - 2; i = y; }
- return n - ((i << 1) >>> 31);
- }
- /**
- * Returns the number of one-bits in the two's complement binary
- * representation of the specified {@code int} value. This function is
- * sometimes referred to as the <i>population count</i>.
- *
- * @param i the value whose bits are to be counted
- * @return the number of one-bits in the two's complement binary
- * representation of the specified {@code int} value.
- * @since 1.5
- */
- public static int bitCount(int i) {
- // HD, Figure 5-2
- i = i - ((i >>> 1) & 0x55555555);
- i = (i & 0x33333333) + ((i >>> 2) & 0x33333333);
- i = (i + (i >>> 4)) & 0x0f0f0f0f;
- i = i + (i >>> 8);
- i = i + (i >>> 16);
- return i & 0x3f;
- }
- /**
- * Returns the value obtained by rotating the two's complement binary
- * representation of the specified {@code int} value left by the
- * specified number of bits. (Bits shifted out of the left hand, or
- * high-order, side reenter on the right, or low-order.)
- *
- * <p>Note that left rotation with a negative distance is equivalent to
- * right rotation: {@code rotateLeft(val, -distance) == rotateRight(val,
- * distance)}. Note also that rotation by any multiple of 32 is a
- * no-op, so all but the last five bits of the rotation distance can be
- * ignored, even if the distance is negative: {@code rotateLeft(val,
- * distance) == rotateLeft(val, distance & 0x1F)}.
- *
- * @param i the value whose bits are to be rotated left
- * @param distance the number of bit positions to rotate left
- * @return the value obtained by rotating the two's complement binary
- * representation of the specified {@code int} value left by the
- * specified number of bits.
- * @since 1.5
- */
- public static int rotateLeft(int i, int distance) {
- return (i << distance) | (i >>> -distance);
- }
- /**
- * Returns the value obtained by rotating the two's complement binary
- * representation of the specified {@code int} value right by the
- * specified number of bits. (Bits shifted out of the right hand, or
- * low-order, side reenter on the left, or high-order.)
- *
- * <p>Note that right rotation with a negative distance is equivalent to
- * left rotation: {@code rotateRight(val, -distance) == rotateLeft(val,
- * distance)}. Note also that rotation by any multiple of 32 is a
- * no-op, so all but the last five bits of the rotation distance can be
- * ignored, even if the distance is negative: {@code rotateRight(val,
- * distance) == rotateRight(val, distance & 0x1F)}.
- *
- * @param i the value whose bits are to be rotated right
- * @param distance the number of bit positions to rotate right
- * @return the value obtained by rotating the two's complement binary
- * representation of the specified {@code int} value right by the
- * specified number of bits.
- * @since 1.5
- */
- public static int rotateRight(int i, int distance) {
- return (i >>> distance) | (i << -distance);
- }
- /**
- * Returns the value obtained by reversing the order of the bits in the
- * two's complement binary representation of the specified {@code int}
- * value.
- *
- * @param i the value to be reversed
- * @return the value obtained by reversing order of the bits in the
- * specified {@code int} value.
- * @since 1.5
- */
- public static int reverse(int i) {
- // HD, Figure 7-1
- i = (i & 0x55555555) << 1 | (i >>> 1) & 0x55555555;
- i = (i & 0x33333333) << 2 | (i >>> 2) & 0x33333333;
- i = (i & 0x0f0f0f0f) << 4 | (i >>> 4) & 0x0f0f0f0f;
- i = (i << 24) | ((i & 0xff00) << 8) |
- ((i >>> 8) & 0xff00) | (i >>> 24);
- return i;
- }
- /**
- * Returns the signum function of the specified {@code int} value. (The
- * return value is -1 if the specified value is negative; 0 if the
- * specified value is zero; and 1 if the specified value is positive.)
- *
- * @param i the value whose signum is to be computed
- * @return the signum function of the specified {@code int} value.
- * @since 1.5
- */
- public static int signum(int i) {
- // HD, Section 2-7
- return (i >> 31) | (-i >>> 31);
- }
- /**
- * Returns the value obtained by reversing the order of the bytes in the
- * two's complement representation of the specified {@code int} value.
- *
- * @param i the value whose bytes are to be reversed
- * @return the value obtained by reversing the bytes in the specified
- * {@code int} value.
- * @since 1.5
- */
- public static int reverseBytes(int i) {
- return ((i >>> 24) ) |
- ((i >> 8) & 0xFF00) |
- ((i << 8) & 0xFF0000) |
- ((i << 24));
- }
- /**
- * Adds two integers together as per the + operator.
- *
- * @param a the first operand
- * @param b the second operand
- * @return the sum of {@code a} and {@code b}
- * @see java.util.function.BinaryOperator
- * @since 1.8
- */
- public static int sum(int a, int b) {
- return a + b;
- }
- /**
- * Returns the greater of two {@code int} values
- * as if by calling {@link Math#max(int, int) Math.max}.
- *
- * @param a the first operand
- * @param b the second operand
- * @return the greater of {@code a} and {@code b}
- * @see java.util.function.BinaryOperator
- * @since 1.8
- */
- public static int max(int a, int b) {
- return Math.max(a, b);
- }
- /**
- * Returns the smaller of two {@code int} values
- * as if by calling {@link Math#min(int, int) Math.min}.
- *
- * @param a the first operand
- * @param b the second operand
- * @return the smaller of {@code a} and {@code b}
- * @see java.util.function.BinaryOperator
- * @since 1.8
- */
- public static int min(int a, int b) {
- return Math.min(a, b);
- }
- /** use serialVersionUID from JDK 1.0.2 for interoperability */
- @Native private static final long serialVersionUID = 1360826667806852920L;
- }
Integer的代码

public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (obj instanceof Integer) {
return value == ((Integer)obj).intValue();
}
return false;
}

首先看看这个对象是不是Integer的类型的,如果是的话,我们比较一下两个对象的int类型的value是否相等。这样似乎和String的比较方法差不多了,但是如果是使用“==”来比较的时候就差得多了,因为这里的Integer使用了缓存,将[-128,127]的数字都缓存了一下,导致了两者相同,否则就创建出一个新的对象。
package com.consumer.test;
public class IntegerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer i1=1;
Integer i2=1;
Integer i3=128;
Integer i4=128;
Integer i5=-128;
Integer i6=-128;
Integer i7=1000;
Integer i8=1000;
System.out.println("测试:"+(i1==i2));
System.out.println("测试:"+(i3==i4));
System.out.println("测试:"+(i5==i6));
System.out.println("测试:"+(i7==i8));
System.out.println("====================");
System.out.println("测试"+ (i1.equals(i2)));
System.out.println("测试"+ (i3.equals(i4)));
System.out.println("测试"+ (i5.equals(i6)));
System.out.println("测试"+ (i7.equals(i8)));
}
}
让我们来看看这个缓存的定义,我们可以看到自动为我们创建了[-128,127]这么大的缓存空间。
private static class IntegerCache {
static final int low = -128;
static final int high;
static final Integer cache[];
static {
// high value may be configured by property
int h = 127;
String integerCacheHighPropValue =
sun.misc.VM.getSavedProperty("java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high");
if (integerCacheHighPropValue != null) {
try {
int i = parseInt(integerCacheHighPropValue);
i = Math.max(i, 127);
// Maximum array size is Integer.MAX_VALUE
h = Math.min(i, Integer.MAX_VALUE - (-low) -1);
} catch( NumberFormatException nfe) {
// If the property cannot be parsed into an int, ignore it.
}
}
high = h;
cache = new Integer[(high - low) + 1];
int j = low;
for(int k = 0; k < cache.length; k++)
cache[k] = new Integer(j++);
// range [-128, 127] must be interned (JLS7 5.1.7)
assert IntegerCache.high >= 127;
}
private IntegerCache() {}
}
再看一下valueOf方法,可以看到当我们传递的数字如果在这个期间的话直接就发挥缓存的值,这样空间得到了节省,否则我们在新建一个Integer对象返回,这就是其中的奥秘。

由此可以看到String和Integer都采用了优化方法,对于String,如果是str="..."这样定义的对象,就会将这些东西放到一个String池之中,只保留一份备份,因此,无论String的字符串是什么都可以这样来做==是true的;但是对于Integer就采用了另一种缓存的方式,只缓存了[-128,127]这些数值,超出了就直接创建新的对象,这样的设计和两者的应用场合是相关的,我们应该有清晰的了解。
三、总结
通过源码和一些例子,我们更加清晰地了解了equals和“==”的作用,以及在不同地方的区别,对我们编写程序有着深刻的意义。
沉淀再出发:java中的equals()辨析的更多相关文章
- 沉淀再出发:java中注解的本质和使用
沉淀再出发:java中注解的本质和使用 一.前言 以前XML是各大框架的青睐者,它以松耦合的方式完成了框架中几乎所有的配置,但是随着项目越来越庞大,XML的内容也越来越复杂,维护成本变高.于是就有人提 ...
- 沉淀再出发:java中的HashMap、ConcurrentHashMap和Hashtable的认识
沉淀再出发:java中的HashMap.ConcurrentHashMap和Hashtable的认识 一.前言 很多知识在学习或者使用了之后总是会忘记的,但是如果把这些只是背后的原理理解了,并且记忆下 ...
- 沉淀再出发:java中的CAS和ABA问题整理
沉淀再出发:java中的CAS和ABA问题整理 一.前言 在多并发程序设计之中,我们不得不面对并发.互斥.竞争.死锁.资源抢占等等问题,归根到底就是读写的问题,有了读写才有了增删改查,才有了所有的一切 ...
- 沉淀再出发:java中线程池解析
沉淀再出发:java中线程池解析 一.前言 在多线程执行的环境之中,如果线程执行的时间短但是启动的线程又非常多,线程运转的时间基本上浪费在了创建和销毁上面,因此有没有一种方式能够让一个线程执行完自己的 ...
- 沉淀再出发:如何在eclipse中查看java的核心代码
沉淀再出发:如何在eclipse中查看java的核心代码 一.前言 很多时候我们在eclipse中按F3键打算查看某一个系统类的定义的时候,总是弹出找不到类这样的界面,这里我们把核心对应的代码加进 ...
- 沉淀再出发:关于java中的AQS理解
沉淀再出发:关于java中的AQS理解 一.前言 在java中有很多锁结构都继承自AQS(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer)这个抽象类如果我们仔细了解可以发现AQS的作用是非常大的 ...
- 沉淀再出发:java的文件读写
沉淀再出发:java的文件读写 一.前言 对于java的文件读写是我们必须使用的一项基本技能,因此了解其中的原理,字节流和字符流的本质有着重要的意义. 二.java中的I/O操作 2.1.文件读写的本 ...
- 沉淀再出发:再谈java的多线程机制
沉淀再出发:再谈java的多线程机制 一.前言 自从我们学习了操作系统之后,对于其中的线程和进程就有了非常深刻的理解,但是,我们可能在C,C++语言之中尝试过这些机制,并且做过相应的实验,但是对于ja ...
- 沉淀再出发:在python3中导入自定义的包
沉淀再出发:在python3中导入自定义的包 一.前言 在python中如果要使用自己的定义的包,还是有一些需要注意的事项的,这里简单记录一下. 二.在python3中导入自定义的包 2.1.什么是模 ...
随机推荐
- Go语言学习笔记三: 常量
Go语言学习笔记三: 常量 定义常量 常量就是在声明后不能再修改的量. const x int = 100 const y string = "abc" const z = &qu ...
- Oracle 汉字转拼音触发器
--函数GetHzFullPY(string)用于获取汉字字符串的拼音 --select GetHzFullPY('中华人民共和国') from dual; --返回:ZhongHuaRenMinGo ...
- R语言变量赋值
变量可以使用向左,向右且等于操作符来分配值.可以使用 print() 或 cat() 函数打印变量的值.cat() 函数将多个项目并成连续并打印输出. # Assignment using equal ...
- 企业如何选择最佳的SSL
如果你的企业有意采购SSL,那么本文可以给一个很好的方向.在本文中,我们将先简要介绍SSL定义及其工作原理,并探讨目前各种可用的SSL证书类型以及企业如何选择最佳的SSL. SSL定义 SSL及传输层 ...
- Objekt Orientierte Programmierung C++
1.Funtion Overloading C++ erlaubt,dass einige Funktion gleiches Names deklariert wird.Der Formale Pa ...
- [shell进阶]——shell多线程
关于shell的多线程 1. 多线程并发执行任务,而不用一台台的串行执行,能更快更高效 2. Shell并没有多线程的概念,所以: * 一般使用wait.read等命令技巧性地模拟多线程实 * 使用命 ...
- 移动端的touchstart,touchmove,touchend事件中的获取当前touch位置
前提:touchstart,touchmove,touchend这三个事件可以通过原生和jq绑定. 原生:document.querySelector("#aa").addEven ...
- 删除弹出提示框_MVC
<td> @Ajax.ActionLink(@shared.Delete, "DeleteServicetag", new { id = item.ID }, new ...
- 述一个程序员的技能:系统安装(win7版)idea配置
idea配置:http://www.phperz.com/article/15/0923/159043.html 作为一名计算机专业出身的程序员,组装电脑和安装系统是基本技能.打造一个安全稳定高效的开 ...
- No Mapping For GET "xxx.do"
今天写的一个form表单提交时总是报错找不到mapping,form如下: <form action="toUpdate.do" method="post" ...

