编程开发之--java多线程学习总结(1)问题引入与概念叙述
1、经典问题,火车站售票,公共票源箱,多个窗口同时取箱中车票销售
package com.lfy.ThreadsSynchronize; /**
* 解决办法分析:即我们不能同时让超过两个以上的线程进入到 if(num>0)的代码块中
* 1、使用 同步代码块 2、使用 同步方法 3、使用 锁机制
*/
public class TicketSell1 extends Thread{ //定义一共有 50 张票,注意声明为 static,表示几个窗口共享
private static int num = 50; //调用父类构造方法,给线程命名
public TicketSell1(String string) {
super(string);
} @Override
public void run() {
//票分 50 次卖完
for(int i = 0 ; i < 50 ;i ++){
if(num > 0){
try {
Thread.sleep(10);//模拟卖票需要一定的时间
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// 由于父类的 run()方法没有抛出任何异常,根据继承的原则,子类抛出的异常不能大于父类, 故我们这里也不能抛出异常
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"卖出一张票,剩余"+(--num)+"张");
}
}
}
}
2、对于解决办法,java中专门提供了synchronized关键字处理多线程同步问题,有了synchronized关键字,多线程程序的运行结果将变得可以控制。synchronized关键字用于保护共享数据。synchronized实现同步的机制:synchronized依靠"锁"机制进行多线程同步,"锁"有2种,一种是对象锁,一种是类锁。synchronized关键字修饰普通方法时,获得的锁是对象锁,也就是this。而修饰静态方法时,锁是类锁,也就是类名.class。
阻塞:A、B线程同时运行,由于锁的控制,某时刻A线程还能继续执行,B线程被挂起等待了,就说B线程被阻塞了。
(1)对象锁,使用synchronized修饰多个普通方法,当不同线程调用同一个对象的不同被synchronized修饰过的方法时,第一个调用被synchronized修饰过的方法的线程会得到对象锁,其他线程处于阻塞状态,直至第一个得到锁的线程退出被synchronized修饰过的方法。举个例子:
package lfy;
public class TestSynchronized {
public synchronized void method1() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("method1 begin at:" + System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println("method1 begin to sleep 5s");
Thread.sleep(5000);
System.out.println("method1 end at:" + System.currentTimeMillis());
}
public synchronized void method2() throws InterruptedException {
for(int i=0;i<5;i++) {
System.out.println("method2 running");
Thread.sleep(200);
}
}
static TestSynchronized instance = new TestSynchronized();
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
instance.method1();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
for(int i=1; i<4; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Thread1 still alive");
}
System.out.println("Thread1 over");
}
});
Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
instance.method2();
System.out.println("Thread2 over");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
}
运行结果:
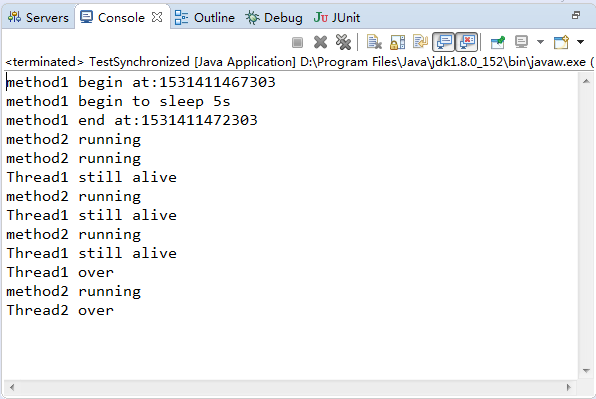
解释:创建了一个对象实例instance,创建两个线程Thread1、Thread2,它们分别调用instance的mothod1、mothod2方法,由于线程1先启动并先访问到被synchronized修饰的mothod1,此时instance对mothod2上锁,线程2此时只能等待mothod2的锁被释放,才能执行mothod2方法。这就是对象锁机制。
(2)类锁,对所有对象调用被synchronized修饰的static方法进行锁定,没有被synchronized修饰的static方法不会被上锁。
package lfy;
public class TestSynchronized {
public synchronized static void method1() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("method1 begin at:" + System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println("method1 begin to sleep 5s");
Thread.sleep(5000);
System.out.println("method1 end at:" + System.currentTimeMillis());
}
public synchronized static void method2() throws InterruptedException {
for(int i=0;i<5;i++) {
System.out.println("method2 running");
Thread.sleep(200);
}
}
/**
* 没有static、synchronized修饰的普通方法
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public void method3() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("method3 running");
Thread.sleep(200);
}
/**
* 只有synchronized修饰的普通方法
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public synchronized void method4() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("method4 running");
Thread.sleep(200);
}
static TestSynchronized instance1 = new TestSynchronized();
static TestSynchronized instance2 = new TestSynchronized();
static TestSynchronized instance3 = new TestSynchronized();
static TestSynchronized instance4 = new TestSynchronized();
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
instance1.method1();
//TestSynchronized.mothod1();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
for(int i=1; i<4; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Thread1 still alive");
}
System.out.println("Thread1 over");
}
});
Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
instance2.method2();
//TestSynchronized.mothod2();
System.out.println("Thread2 over");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
Thread thread3 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
instance3.method3();
System.out.println("method3 over");
Thread.sleep(10000);
System.out.println("Thread3 still alive");
System.out.println("Thread3 now to over");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
Thread thread4 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
instance4.method4();
System.out.println("method4 over");
Thread.sleep(10000);
System.out.println("Thread4 still alive");
System.out.println("Thread4 now to over");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread3.start();
thread4.start();
}
}
运行结果:
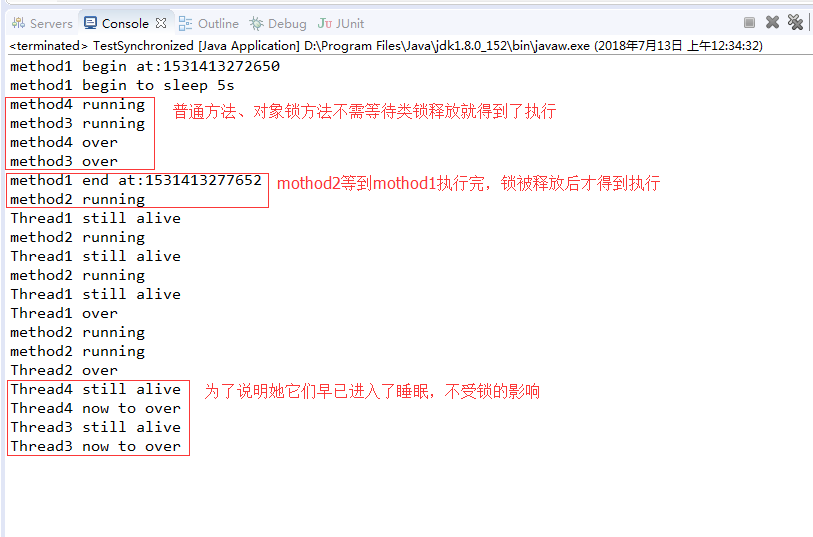
编程开发之--java多线程学习总结(1)问题引入与概念叙述的更多相关文章
- 编程开发之--java多线程学习总结(5)
4.对继承自Runnable的线程进行锁机制的使用 package com.lfy.ThreadsSynchronize; import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock ...
- 编程开发之--java多线程学习总结(4)
3.使用锁机制lock,unlock package com.lfy.ThreadsSynchronize; import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock; impor ...
- 编程开发之--java多线程学习总结(2)同步代码块
1.第一种解决办法:同步代码块,关键字synchronized package com.lfy.ThreadsSynchronize; /** * 1.使用同步代码块 * 语法: synchroniz ...
- 编程开发之--java多线程学习总结(6)
5.测试 package com.lfy.ThreadsSynchronize; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) ...
- 编程开发之--java多线程学习总结(3)类锁
2.使用方法同步 package com.lfy.ThreadsSynchronize; /** * 1.使用同步方法 * 语法:即用 synchronized 关键字修饰方法(注意是在1个对象中用锁 ...
- Java多线程学习(转载)
Java多线程学习(转载) 时间:2015-03-14 13:53:14 阅读:137413 评论:4 收藏:3 [点我收藏+] 转载 :http://blog ...
- Java多线程学习(三)volatile关键字
转载请备注地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_34337272/article/details/79680693 系列文章传送门: Java多线程学习(一)Java多线程入门 Ja ...
- Java多线程学习(一)Java多线程入门
转载请备注地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_34337272/article/details/79640870 系列文章传送门: Java多线程学习(一)Java多线程入门 Ja ...
- 转:Java多线程学习(总结很详细!!!)
Java多线程学习(总结很详细!!!) 此文只能说是java多线程的一个入门,其实Java里头线程完全可以写一本书了,但是如果最基本的你都学掌握好,又怎么能更上一个台阶呢? 本文主要讲java中多线程 ...
随机推荐
- linux git server 简易搭建 (ssh访问)
git的服务器搭建,如果无需权限控制,仅团队内部使用,初始化一个服务器仓库,其他人通过ssh访问这个文件夹即可.如需复杂的管理,建议使用gitlab. yum install git -y id gi ...
- PHP 微信公众号开发 - 获取用户信息
项目微信公众号开发,记录获取用户微信号信息,和用户openid 1,登录微信公众平台 点击登录微信公众平台 2,获取公众号开发信息 登陆之后在 开发->基本配置 3,设置IP白名单 在这里添加服 ...
- FlexBox弹性盒布局
网页布局(layout)是 CSS 的一个重点应用. 布局的传统解决方案,基于盒状模型,依赖 display 属性 + position属性 + float属性.它对于那些特殊布局非常不方便,比如,垂 ...
- 修改TFS附件大小的限制
在TFS服务器使用浏览器上打开如下地址:http://localhost:8080/tfs/<CollectionName>/WorkItemTracking/v1.0/Configura ...
- 使用Array.prototype.indexOf()的几点注意
对应indexOf这个方法,在日常开发中比较常见的应该是String.prototype.indexOf()方法,Array.prototype.indexOf()方法和其有很大的相似性,本文不想去描 ...
- 网站图标ICO
效果图: 代码: 1 2 3 4 5 6 <head> ... <link rel="shortcut icon" href="/favicon.i ...
- Django博客项目思路整理
首先明确一点,我目前学习Django是为了做一个博客,那么以博客为目标进行实践的话,按照Django的MTV模型的顺序来思考的话,要考虑如下几个事情: (Models) 1.在博客里的各种数据模型: ...
- Sql语法高级应用之二:视图
SQL CREATE VIEW 语句 什么是视图? 在 SQL 中,视图是基于 SQL 语句的结果集的可视化的表. 视图包含行和列,就像一个真实的表.视图中的字段就是来自一个或多个数据库中的真实的表中 ...
- IIS服务器添加网站
1.添加IIS服务:对“我的电脑”右键,管理,点击服务和应用程序,如果下面没有”Internet Information Services(IIS)管理器“,打开控制面板,点击程序,启用或者关闭Win ...
- Asp.net Core过滤器
Asp.net Core五类过滤器:Authorization Filter.Resource Filter.Acton Filter.Exception Filter.Result Filter.优 ...
